
Adaptation of Learning Object Interface based on Learning Style
Zenaide Carvalho da Silva, Leandro Rodrigues Ferreira and Andrey Ricardo Pimentel
Department of Informatics, Federal University of Parana, Curitiba, Parana, Brazil
Keywords: Learning Style, Learning Object, Adaptation, Interface.
Abstract: Learning styles (LS) refer to the ways and forms that the student prefers to learn in the teaching and learning
process. Each student has their own way of receiving and processing information, and bearing in mind the
learning style is important to better understand their individual preferences and to understand why certain
teaching methods and techniques work better for some students, while for others they do not. We believe
that knowledge of these styles enables the possibility of making propositions for teaching, thus reorganizing
teaching methods and techniques in order to allow learning that is adapted to the individual needs of the
student. This would be possible through the creation of online educational resources adapted to the style of
the student. In this context, this article presents the structure of a learning object interface adaptation based
on the learning style. This should enable the creation of the adapted learning object according to the
student's learning style, contributing to the increase of student’s motivation in the use of a learning object as
an educational resource.
1 INTRODUCTION
The learning style (LS) refers to a person's
individual preferences, in relation to the ways and
forms that they prefer to learn in the teaching and
learning process. An investigation by Haider, Sinha
and Chaudharyal (2010) indicates that pedagogical
strategies related to the learner's learning style
contribute to making learning easier. It also presents
improvements in the learning process, if the
educational material used by the learner matches
their learning style.
Each LS contains specific characteristics that
need to be collected and mapped in order to enable
the adaptation of the educational material. This
research considered as educational material the
learning object (LO), so that the student benefits
more from this resource that has been widely
available in learning virtual environments.
The adaptation of the learning object interface
considering the student's LS is one of the
possibilities that allows the offering of digital
educational resources adapted to students’ individual
learning preferences. In this case it is expected to
obtain a greater motivation of the student with the
use of this type of educational resource because the
LO will be presented in a way that respects their
individual preferences of learning.
There are several models of learning styles
available in the literature that describe how to
classify the student in a learning style as in (Felder
and Silverman, 1988), (Kolb, 1984). These models
classify students as to the form or manner that they
prefer to perceive and process the information
received when they are learning, so their individual
learning preferences can be identified.
This research used the Felder-Silverman
Learning Styles Model (FSLSM) (Felder and
Silverman, 1988), because it is considered the most
suitable to be used in educational environments, and
a better match of their scales to the characteristics of
learning materials (Akbulut and Cardak, 2012),
(Truong, 2015).
In this perspective, this study proposes a
structure of learning object interface adaptation
based on the learning style to allow the creation of
the LO adapted according to the learning style of the
student, contributing to the increase of student
motivation in the use of LO as an educational
resource. This work makes the following
contributions:
● Defines an association of the characteristics of LS
with the most appropriate forms of presentation of
the LO content for each LS of the Felder-
Silverman model;
Silva, Z., Ferreira, L. and Pimentel, A.
Adaptation of Learning Object Interface based on Learning Style.
DOI: 10.5220/0006319001190126
In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2017) - Volume 3, pages 119-126
ISBN: 978-989-758-249-3
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
119

● Creates a structure of adaptation of the learning
object interface based on LS, from the in-depth
research and analysis of the characteristics of the
styles of the Felder-Silverman model to contribute
to the creation of adapted LO to the LS;
● Analyzes the proposed structure to demonstrate the
validity of the approaches used.
The text is structured as follows. Section 2
presents a theoretical basis. Section 3 presents
related works. Section 4 describes the structure of
the interface adaptation based on learning style.
Section 5 presents an analysis and discussion of the
work. In section 6, the final considerations and
suggested future work are made.
2 LEARNING OBJECT (LO) AND
LEARNING STYLES (LS)
LO can be understood as "[...] any digital resource
that can be reused to support learning" (Wiley,
2001). They are produced by different institutions
and researchers, and are usually cataloged in
repositories.
LO in an overview can be understood as
autonomous information segments that are intended
for use in remote or face-to-face learning situations.
It can also be considered as a resource that can assist
the teacher in his teaching activity. This type of
educational resource can contribute to the teaching
and learning process of the students, since it is
designed to meet a defined pedagogical objective. It
is expected that LO could be adapted according to
the student's different manners and ways of learning,
which may characterize different profiles of learners.
These different profiles can be identified through the
learning styles (LS) of the students.
LS are student preferences and trends that define
ways to receive, process, perceive, and organize the
information (Felder and Silverman, 1988). In this
work, we consider the cognitive dimension, that is, if
the learning process and educational resources are
appropriate to the style, the person will probably be
more successful as a learner, and may be more
motivated to use LO as an educational resource in
the learning process.
There are several LS models, which have been
developed by various authors and can be used by
educational systems to represent student styles
(Felder and Silverman 1988, Honey and Munford
2000, Kolb 1984). LS are defined by these authors
differently, influenced by different theories of
learning psychology.
This research used the Felder-Silverman model
(Felder and Silverman, 1988), because it is
considered the most suitable for use in educational
environments, and better adapting its scales to the
characteristics of learning materials. It is also widely
used in the international context in research on the
adaptation and customization of learning materials,
as well as providing a good degree of adaptability to
student profiles (Al-Azawei and Badii, 2014).
The Felder-Silverman model (1988) was
developed by Professor Richard M. Felder and by
psychologist Linda K. Silverman, and classifies
students in scale number according to how each
student perceives, retains, processes, and organizes
information. In this way the student can be classified
in four dimensions of the model: a) Perception
(Sensory x Intuitive); b) Retention (Visual vs.
Verbal); c) Processing (Active x Reflective) and d)
Organization (Sequential vs. Global). The
characteristics of students according to their LS for
each dimension are more detailed in (Felder and
Silverman, 1988).
This model uses the ILS (Index of Learning
Styles) as a mensuration instrument to identify the
LS based on FSLSM (Felder and Silverman
Learning Style Model), which comprises forty four
questions, eleven for each of the four dimensions
described above. More details in (Felder and
Soloman, 2006). In this research we consider that
the style of the student has already been identified
and the adaptation occurs from the knowledge of the
style.
3 RELATED WORKS
Graf (2007) in her PhD work carried out an
expansion of the Learning Management Systems
(LMS) to provide adaptability, incorporating
learning styles according to the Felder-Silverman
learning style model. She created an automated
approach to identify learning styles from students
behavior and actions. This approach was designed,
implemented and evaluated, demonstrating that it is
adequate to identify learning styles. Moodle was
used as a prototype to extend an LMS, making it
possible to automatically generate and present
courses according to students' learning styles. The
results showed that the concept proposed to offer
adapted courses was successful to support students
in learning.
Yang, Hwang and Yang (2013) developed an
adaptive learning system considering various
dimensions of personalized characteristics, proposed
ICEIS 2017 - 19th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
120

a customized presentation module for the
development of adaptive learning systems based on
the dependent/independent field cognitive style
model and the LS of the Felder-Silverman learning
style model. Their experimental results showed that
the proposed approach is capable of helping students
to improve their performance in the learning
process.
The work of Fasihuddin, Skinner and Athauda
(2014) presented a proposal for an adaptive model to
customize open learning environments based on the
Felder-Silverman learning style model. This model
consists of two main agents to execute its
functionalities; the identification agent is responsible
for identifying the student's learning styles,
monitoring certain patterns of behavior from student
with the learning objects, while the student interacts
with learning materials; and the recommendation
agent is responsible for providing adaptive
navigation support based on the identified learning
styles and preferences.
The works presented in this section used the
learning styles to adapt and/or customize the
learning environments, or to adapt the presentation
of the learning material. However, no further studies
were found that explore how to use the
characteristics of each style of the Felder-Silverman
model, mapped in relation to aspects of format and
order of LO contents to provide adaptation of the
interface of this educational resource.
4 ADAPTATION OF THE
INTERFACE OF THE
LEARNING OBJECT BASED
ON LEARNING STYLE
From the study and research on the "presentation
characteristics for LO" with regard to sequencing,
presentation and form/format of content and
resources that compose the learning object, raised
from an in-depth analysis of the properties of the
styles of the Felder-Silverman model (Felder and
Silverman, 1988). It was possible to establish the
required parameters and attributes to define the
structure so as to adapt the learning object's interface
based on the characteristics of the styles (Silva and
Pimentel, 2015).
This structure was designed and composed
respecting the principles of the Cognitive Theory of
Multimedia Learning (Mayer, 2005). The principles
of this theory help to avoid the inappropriate use of
resources in the most varied formats, which can lead
to the student's distraction and lack of motivation in
the use of this type of resource, which can cause
failure in the learning process.
In the definition of the structure we consider that
in the creation of the LO it will be formed by
"elements of content composition " that constitute
the stages: Summary (Sum): provides an overview of
the content that will be approached; Introduction
(Int): composed of a brief content for presentation of
the subject to be studied of a domain; Development
(Dev): composed of a more comprehensive content
that contemplates the subject of a domain in a more
complete way; Activity (Act): formed by content to
fix the subject; and, Assessment (Ass): assessment of
the content covered by a domain. These "elements of
content composition" are organized in relation to the
parameters and attributes defined from the
characteristics of the styles, and are described as
follows:
● Resource (R): defines the types of resources that
can be used in the elements of the content
composition to present the LO. The resources
assigned in the model can be: Video (Vid); or
Diagram (Dia); or Graph (Gra); or Picture (Pic);
or Narration (Nar); or Lecture (Lec); or Slide (Sli);
or Self-Assessment (Sas); or Table (Tab); or
Experiment (Exp); or Exercise (Exe); or
Simulation (Sim); or Questionnaire (Que); or
Scheme (Sch); or Animation (Ani); or Photo (Pho);
or Web Page (Wpa); or Map (Map); or
Demonstration (Dem); or Example (Exa
).
● Exploration Form (EF): defines how the content
can be structured in relation to the way it is
explored by the student. It can be in Network (Net)
- investigation more random, without following a
script; or Linear (Lin) - more directed research,
with a script to follow.
● Detailing Order (DO): establishes how the student
prefers to approach the contents presented in the
LO. It can be Specific-to-General (Spe-t-Gen): it
begins in the specific part and proceeds to the
general part for comprehension of a whole; or
General-to-Specific (Gen-t-Spe): begins in the
general part and proceeds to the specific part for
comprehension of a whole.
● Composition Order (CO): defines the organization
of the stages used in the composition of the
Adaptation of Learning Object Interface based on Learning Style
121

Figure 1: Overview of the LO structure.
contents of an LO, that is, the order in which these
stages will be presented to the student. There are
three composition orders defined: order 1 - 1st
Introduction, 2nd Development, 3rd Summary, 4th
Activity, 5th Assessment; Order 2 - 1st
Introduction, 2nd Development, 3rd Activity, 4th
Summary, 5th Assessment; and Order 3 - 1st
Summary, 2nd Introduction, 3rd Development, 4th
Activity, 5th Assessment.
The overview of the elements created from the
"presentation characteristics for LO" in relation to
the sequencing, presentation and form / format of
content and resources that compose the LO can be
visualized in figure 1. These elements were defined
to create the interface adaptation of the learning
object, based on the characteristics of the styles.
The simplified form of the composition of the
LO interface adaptation can be represented in the
formulation StyleInterface (S) = ∑(CO(x), DO(j),
EF(k), R(r
1
, r
2
, .. ., r
n
)), where, S indicates the styles
of the Felder-Silverman model, described in section
4; x can assume 1, 2 and 3, which indicates,
respectively, first, second and third composition
order ; j can assume 1 = "specific-for-general" and 2
= "general-for-specific"; k can assume 1 = "network"
and 2 = "linear"; r
i
are the resources that can be used
in LO composition; CO indicates the order of
composition that the stages used in the composition
of the contents will be presented in LO; DO
indicates the detailing order of each stage of LO; EF
indicates the exploration form that will be used in
the presentation of the LO; R indicates the resources
that can be used in the composition of the LO.
So as to adapt the interface according to the
styles of the Felder-Silverman model, it was
necessary to investigate the characteristics and
preferences of each style to define the most
appropriate ways to modify the presentation of the
LO to obtain an adapted interface to the style of the
student. This is so because we believe that adapting
the style-based LO interface can improve the
student's motivation for using OA as an educational
resource, and consequently can to enable
improvements in learning.
Table 1 presents the attributes and parameters of
the proposed interface adaptation structure, defined
with the values referring to the preference according
to the adaptation rules for each style.
The composition of the LO interface adaptation
structure according to the styles was defined
considering the following question "How and what
can be modified in the LO interface presentation for
students with different learning styles?”. Thus,
adaptation rules were created for the attributes and
parameters defined in the structure, in relation to:
sequence of the content composition elements of the
OA (composition order); number and type of
resources used to create LO (resources); the level of
detail of the composition elements of LO content
(detailing order); the way the student can explore
ICEIS 2017 - 19th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
122

Table 1. Analysis of the styles of the Felder-Silverman
model (1988) in relation to the attributes and parameters
of the proposed structure.
Style
Explora
tion Form
(EF)
Compo
sition
Order
(CO)
Detailing
Order
(DO)
Resource
(R)
Active network order 2
general-
to-
specífic
vid, dia,
gra, pic,
sas, exe,
sim, sch,
wpa,
map, exa
Reflecti
ve
linear order 1
specific-
to-
general
dia, gra,
lec, sli,
sas, tab,
exe, sim,
sch,ani,
wpa,
dem, exa
Visual network order 3
general-
to-
specífic
vid, dia,
gra, pic,
sli,sas,
tab, exp,
exe, sim,
ani, fot,
wpa,
map,
dem, exa
Verbal linear order 3
specific-
to-
general
dia, nar,
lec, sli,
sas, tab,
exe, que,
wpa,
dem, exa
Global network order 3
general-
to-
specífic
dia, gra,
pic, sli,
sas, exp,
exe, sch,
wpa,
map, exa
Sequen
tial
linear order 2
specific-
to-
general
dia, gra,
pic, nar,
lec,
sli,sas,
exe, sim,
que, sch,
ani, wpa,
dem, exa
Sensory network order 3
specific-
to-
general
vid, gra,
nar, sli,
sas, tab,
exp, exe,
que, wpa,
map,
dem, exa
Intuiti
ve
linear order 1
general-
to-
specífic
gra, pic,
nar, lec,
sli, sas,
exe, sim,
que, ani,
p
ho, exa
the LO contents (exploration form); besides the
arrangement of these elements in the LO
presentation. For each style, the LO interface is
modified following the attributes and parameters
presented in table 1. A prototype of the interface was
created following the defined adaptation structure, in
order to carry out an initial validation of the
proposal, and will be discussed in the next section.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
As mentioned earlier, in this research the
preferences and characteristics of each style of the
Felder-Silverman model were identified and mapped
to "LO presentation characteristics". These
characteristics were the basis for defining the LO
interface adaptation structure of the according to
each style. In the creation of the structure we
considered some aspects of modeling described in
the following components.
Assignment of Levels. The levels were created to
demonstrate how the student prefers to approach the
contents presented by the teacher in a learning object
respecting the detailing order (DO) established for
each style.
Quantity of Sub-stages. For each item of the
composition order (CO) that corresponds to an LO
stage, it is defined how many sub-stages will
comprise each stage. The uniform pattern was
adopted for all stages having the same quantity of
sub-stages.
Number of Levels. Related to the detailing order
(DO) of the content, which establishes how to
approach the contents presented. If in a "more
general to specific" or "more specific to general"
form. The lowest value was adopted for "more
specific" and the greater value for "more general".
Each level will be evenly distributed according to
the total amount of sub-stages of all stages,
following the composition order (CO) definition for
the selected style. The formula for find out how
many sub-stages will be allocated for each level is
represented by (stages * sub-stages / total levels),
adding the rest of the division to the last level.
Amount of Resources on the Screen. Maximum
quantity of resources allowed to appear on the
screen for each sub-stage.
Standard values were defined for the
components: 3 for the quantity of sub-stages; 5 for
the total levels of detailing; and 5 for the maximum
numbers of resources to display in the screen. In this
case, these values are assigned if these components
are not filled in or filled in incorrectly (informing
Adaptation of Learning Object Interface based on Learning Style
123

something that is not an integer). Also possible
inconsistencies are controlled, for example, if the
total levels are less than the number of sub-stages,
the same quantity of sub-stages is assigned to the
total levels.
After the assignment of these values, the
organization of the total levels for the sub-stages is
done through a staggering of the sub-stages. Firstly
it is indicated which detailing order (DO) the
selected style has. If it is the "specific to general"
order the lowest level receives the lowest value (in
this case, the value "1") and the highest level
receives the highest value (that is, the value of the
quantity of levels). If the order is "General to
Specific" the opposite happens. Then, each sub-stage
will receive a value, respecting the composition
order (OC) of the style. That is, if the total of levels
is equal to 6, the detailing order (DO) is "general to
specific" and each stage has 4 sub-stages, each level
has 3 sub-stages, being the last level with 5 sub-
stages. The current sub-stage on the screen will
display the level to which it belongs.
Content Index Display. It consists of displaying the
stages and their respective sub-stages in an
arrangement of a hierarchical tree, forming nodes for
the stages and sub-stages and following the
composition order (CO) belonging to the style. The
items in this content index will be released
according to the "Exploration Form" of the
identified style. That is, if the exploration form is
Linear (EF = "Linear"), the item subsequent to the
current sub-stage will be released only if the current
stage is completed, indicated by an "OK" button on
the screen, which when clicked / selected informs
the system to release next stage / sub-stage.
Clicking on the "OK" button indicates the
completion of the current stage / sub-stage in this
case enables navigation to the next stage / sub-stage
and / or returns to the completed stage / sub-stage,
and / or to go to the first completed stage. If the
exploration form is network (EF = "Network"), all
items that include the stages and / or sub-stages as
well as elements of the navigation control will be
enabled for exploration at any time during the use of
LO.
Navigation Control. Controls the display of the
content index and navigation buttons, depending on
the exploration form (EF) indicated by the identified
style and the navigation flow between the sub-
stages, following the composition order (CO)
defined for the style. The navigation control must
agree with the defined exploration form for the style.
In this case, if the exploration form is network (EF =
"Network"), all elements of the navigation control
are enabled allowing the student to navigate in a non
sequential or random way in the stages and sub-
stages composed for the learning object.
Resources Assignment. Defines which resources
will be displayed on the screen for each sub-stage in
the content composition of the learning object for
the identified style. For each sub-step, a maximum
number of resources to be displayed are randomly
selected. This random number will be between 2 and
5 (default number). However, in order to guarantee
the principles of the CTML (Cognitive Theory of
Multimedia Learning), such as: multimedia
(combination of resources in the image and text
format) and spatial proximity (when a resource in
the text format describes a resource in the visual
format, these should be close), there is guarantee
that at least 2 resources will be displayed in each
sub-stage. This component is also responsible for
ensuring that the principle of modality (for all
animation resource one must use the narration
resource rather than using a written text) is met.
In order to execute an initial validation of the
work proposal, a prototype of the interface was
defined and implemented to preliminarily analyze
the interface structure defined. In the interface
implementation, rules for basis of styles that has a
rule for each style defined in the interface adaptation
structure was created. The actions in each rule
consist of completing the information of each
parameter of the selected style. First, we will
allocate the CO, then allocate the
Rs, then the EF
and finally the DO.
These actions obey the proposed modeling for
this fill, according to appropriate adaptation rules to
each style, in the example below, we have the rule
for the active style:
Rule Name = “ActiveStyle”
Conditions:
Style = "Active"
Actions:
a) Create an CO in the following order:
"Introduction", "Development", "Activity",
"Summary", and "Assessment";
b) Provide the following Rs: “Video”,
“Diagram”, “Picture”, “Graph”, “Self-
Assessment”, “Exercise”, “Simulation”,
“Schema”, “Web page”, “Map” e “Example”;
c) Indicate the EF "Network";
d) And indicate the DO “General to specific”.
ICEIS 2017 - 19th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
124
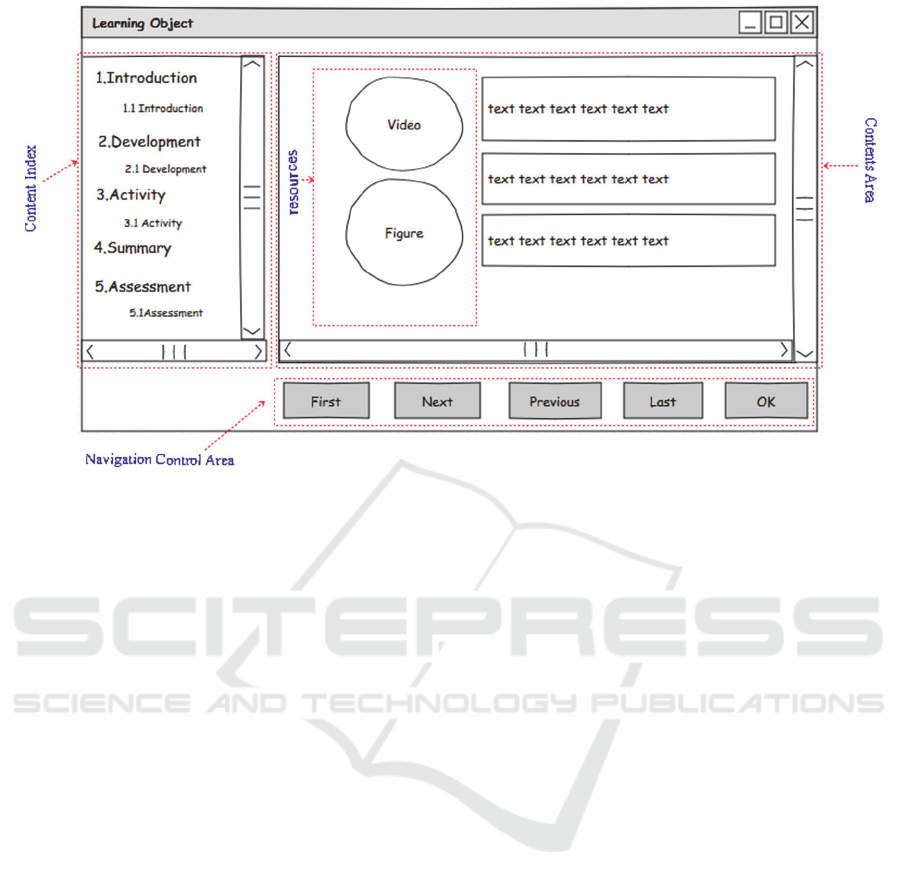
Figure 2: Example of interface screen for the "Active" style.
In this case, as observed in figure 2, the elements
that make up the interface are arranged following the
adaptation rules that were created to modify the
elements according to the characteristics of each
style. The "Content Index", which consists of
displaying the stages and their respective sub-stages
of the "content composition elements" in an
arrangement of a hierarchical tree, forming nodes for
the stages and sub-stages, and follows in accordance
with the style CO. Items in the "Content Index" are
released according to the EF of the selected style.
That is, if EF is linear (EF = "linear"), the
subsequent item to the current sub-stage will only
be released if the current stage is completed,
indicated by a button on the screen, which when
clicked / selected informs the system to releasing
next stage / sub-stage, that is, a more targeted
exploration in LO. If EF is network (FE =
"network"), all items that include the stages and / or
sub-stages, as well as elements of the "Navigation
Control Area" are enabled, so a more random
exploration can be performed in the LO.
In the "Content Area" the resources that make up
each sub-stage in the creation of OA content are
displayed. To ensure that the principles of CTML,
such as: multimedia (combination of resources in the
image and text format); spatial proximity (when a
resource in the text format describes a resource in
visual format, these should be close), and the
modality (for all the animation resource you must
use the narration resource instead of using a written
text) are met, it has been established that at least two
features are displayed in each sub-step in the
"Content Area".
The "Detailing Order Indication" is related to the
levels that were created to demonstrate how the
student prefers to approach the presented contents by
the teacher in an LO, respecting the DO of each
style. Thus if the DO is "specific-to-general" (DO =
"specific-to-general"), the lowest level receives the
smallest value (in this case the value "1") and the
highest level receives the highest value (in this case
the value of the quantity of defined levels), if the DO
is "general-to-specific" (DO = "general-to-specific")
the opposite happens. Therefore, the lowest value
was adopted for "more specific" and the greater
value for "more general".
The "Navigation Control Area" controls the
display of the "Content Index" and the navigation
buttons, according to the EF indicated by the
informed style and the navigation flow between the
sub-stages, following the CO defined for the style.
As previously mentioned the "Navigation Control
Area" must conform to the EF defined for the style.
In this case, if EF is "network" (EF = "network"), all
elements of the "Navigation Control Area" are
enabled allowing the student to navigate non
sequentially or randomly in the composite stages and
sub-stages for LO. If EF is "linear" (EF = "linear"),
navigation is sequential, i.e. step by step, the student
needs to complete the current stage / sub-stage to
proceed to the next stage / sub-stage.
Therefore for each style of the Felder-Silverman
model the interface has undergone changes to adapt
Adaptation of Learning Object Interface based on Learning Style
125

according to the attributes and parameters mapped
from the characteristics of each style, following the
adaptation rules created for the styles in relation to
sequencing, presentation and form / format of
content and resources that make up a learning object,
providing an adapted and adequate learning object to
the students' learning style.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The creation of new forms/formats to present the
LO contents taking into account the student's LS can
generate a greater motivation from the student in the
use of this type of educational resource, since the
students would receive this adapted resource
according to their individual learning preferences.
Thus, we developed an interface that considered the
characteristics and preferences of the LS, which
were mapped in relation to the forms, formats,
content sequencing, appropriate to each style that
established the definition of the LO interface
adaptation structure so that it is adapted to the
student style. This structure was designed and
composed respecting the principles of the Cognitive
Theory of Multimedia Learning (CTML), since the
principles of these theories help to avoid the
inadequate use of resources in the most varied
formats, that can lead to the student's distraction and
demotivation in the use of this resources type and
may cause failure in the learning process.
Therefore, this work brought contributions to the
teaching and learning process by defining a LO
interface adaption structure, according to the
student's LS. This is so because we believe that the
student who receives the adapted learning object to
his/her style can generate an increase in the
motivation to use the learning object as an
educational resource, since the learning object will
meet their individual learning preferences, and
consequently may bring improvements in your
learning process.
As future work we intend to conduct experiments
with students using adapted LO to their style to
measure the emotional response and motivation of
the student in relation to the use of LO, and
consequently to verify if there was an increase in
learning.
REFERENCES
Akbulut, Y. and Cardak, C. S. (2012) ‘Adaptive
educational hypermedia accommodating learning
styles: A content analysis of publications from 2000 to
2011’, Comput. Educ., vol. 58, no. 2, pp. 835–842.
Al-Azawei, A. and Badii, A. (2014) ‘State of The Art of
Learning Styles-Based Adaptive Educational
Hypermedia Systems (LS-BAEHSs)’, International
Journal of Computer Science and Information
Technology, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 1-19.
Fasihuddin, H., Skinner, G. and Athauda, R. (2014)
‘Towards an Adaptive Model to Personalise Open
Learning Environments Using Learning Styles’,
In Information, Communication Technology and
System (ICTS), IEEE, p. 183-188.
Felder, R. M and B. Soloman (2006) Index of Learning
Style Questionnaire, North Carolina State University,
[Online], Available
http://www4.ncsu.edu/unity/lockers/users/f/felder/publ
ic/ILSpage.html [ 20 set. 2016].
Felder, R. M. and Silverman, L. K. (1988) ‘Learning and
Teaching Styles in Engineering Education’, Journal of
Engineering Education, vol. 78(7), pp. 674–681.
Graf, S. (2007) ‘Adaptivity in Learning Management
Systems Focussing on Learning Styles’, Doctoral
Thesis, Vienna University of Technology.
Haider, M. T. U., Sinha, A. K., and Chaudhary, B. D.
(2010) ‘An investigation of relationship between
learning styles and performance of learners’, Intern.
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology, vol.
2(7), pp. 2813–2819.
Kolb, D. (1984) Experiential learning: Experience as the
Source of Learning and Development, Prentice-Hall
Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Mayer, R. E. (2005) ‘Principles for Managing Essential
Processing in Multimedia Learning: Segmenting,
Pretraining, and Modality Principles’, In: MAYER, R.
E., pp. 169-182.
Silva, Z., and Pimentel, A. R. (2015) ‘Metamodelo de
Categorização de Estilos de Aprendizagem’, In Anais
do Simpósio Brasileiro de Informática na Educação,
v. 26, no. 1, pp. 937-946.
Truong,
H. M. (2015) ‘Integrating learning styles and
adaptive e-learning system: current developments,
problems and opportunities’,
Computers in human
behavior,
55, pp. 1185-1193.
Wiley, D. A. (2001) Connecting learning objects to
instructional design theory: A definition, a metaphor,
and a taxonomy, Utah State University. [Online]
Available:
www.reusability.org/read/chapters/wiley.doc [15 Jan
2015].
Yang, T.C., Hwang, G.J. and Yang, S. J.H. (2013)
‘Development of an Adaptive Learning System with
Multiple Perspectives Based on Students' Learning
Styles and Cognitive Styles’, Educational Technology
& Society, 16 (4), pp. 185–200.
ICEIS 2017 - 19th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
126
