
Design and Assessment of User Interface Optimized for Elderly
People. A Case Study of Actgo-Gate Platform
Artur Rot, Robert Kutera and Wieslawa Gryncewicz
Department of Information Systems, Wroclaw University of Economics,
Komandorska 118/120, 53-345 Wroclaw, Poland
Keywords: User Experience, Elderly People, Human-computer Interaction, GUI, Web-based Applications.
Abstract: In much of the world, particularly the developed world, there’s a growing aging population. Our work
focuses on user experience and its impact on user interface design of web-based applications for elderly
people. The paper presents the set of aging-centered user interface design guidelines. An initial collection of
guidelines was first developed through an extensive review of the human-computer interaction and aging-
oriented literature and through applying a series of classification methods. Then the Authors proposed an
assessment framework, which could be used as an universal tool to evaluate the web-based system
according the user interfaces dedicated for elderly people. The detailed guidelines were grouped into 7
categories which were granted with appropriate importance weights. In the next section ActGo-Gate
platform was presented as a web-based application dedicated for activating and supporting elderly people.
Finally, the user interface of the system was evaluated according the proposed criteria.
1 INTRODUCTION
The population in nowadays societies is older than
ever, and it is expected to get even older (Rocznik,
2015). Today’s seniors are living longer, are
healthier, wealthier, have a better education, and are
more experienced with technology (Leitãob et al.,
2014). This trend is accompanied by the
globalization and by the development of the
information and communication technologies (ICT).
Different studies also acknowledge the increasing
number of adults using ICT solutions. The two
aforementioned trends are highly connected and
dependent on each other. Subsequently there is an
increasing call for web-based applications to cater
more for elderly users. Designing the ICT systems
dedicated for older adults is more complex and
challenging than for typical user. The young
developers usually have limited experience and
understanding in age-related requirements,
especially in the context of designing graphical user
interfaces (GUI). They are in fact the most important
touchpoint where users really interact with the
system. That is why there is a strong need to put
emphasis on best practices in that area. The good
starting point could be to define an universal set of
principles for web-based applications. Thus the aim
of the paper is to propose GUI assesment framework
and evaluate our aging-centered ActGo-Gate web
application based on authors’ framework.
2 ELDERLY USERS AND THE
ICT IN THE CONTEXT OF
DEMOGRAPHICAL CHANGES
Globally, life expectancy for people born between
2010 and 2015 is 70 years (77 in Europe) and it is
expected to keep rising. Moreover, population aged
60 or over accounts in 2015 for 12% of the global
population (24% in Europe) and this age group is the
fastest growing (3.26% per year) (UN, 2015). What
is more, many of adult people have the basic skills
that allow them to use most interactive devices, and
thus, are more likely to already be familiar with
computers, mobile devices, and related technology.
Eurostat’s statistics on ICT show that in 2014 more
than one third (38%) of the elderly population (aged
65–74) in the EU used the internet on a regular
basis. Over one fifth (22%) of the analyzed
population made use of internet banking, this was
half the share recorded for the total population
Rot, A., Kutera, R. and Gryncewicz, W.
Design and Assessment of User Interface Optimized for Elderly People. A Case Study of Actgo-Gate Platform.
DOI: 10.5220/0006320001570163
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health (ICT4AWE 2017), pages 157-163
ISBN: 978-989-758-251-6
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
157
(44%). A similar share (23%) of the elderly
purchased products or services via the internet
(Eurostat, 2015). The increased participation of
senior citizens, demanded by the demographic
change, is in line with the observed transition to a
decentralized and skill-based service economy. The
experience and wisdom of elderly people are a huge
asset and underutilized enabler of Internet-facilitated
service economy of today (Maciaszek et al., 2016).
Along with an aging population and the
opportunities offered by ICT, solutions that reflect
on the needs of this particular user group are in
demand. Recent technology and software
engineering development produce a new generation
of applications (Rot, Sobinska 2013) that provide
their services in a more flexible and adaptive
manner, with easy to use interfaces dedicated for
elderly people.
3 ACTGO-GATE – THE PROJECT
SCOPE
The problems and opportunities mentioned in the
previous section are addressed by the project Active
Retiree and Golden Workers Gate (ActGo-Gate). Its
vision is to create an ICT based marketplace
supporting entrepreneurship, self-fulfillment and
social participation for golden workers and active
retirees. The project aims to create a transferable
model as gate for different occupation modules. The
model builds on local social marketplaces that serve
as a basis and starting point for developing three
occupational modules, starting with an established
user base and along existing structures: “Serve the
community”, “Flexible occupation”, and “Get
involved with organizations”, that will start off in
three different pilot regions.
In the long range, the vision is that the pilot
cases expand their offerings and converge into the
ActGo-Gate as central intermediate for occupation
and participation possibilities. The fully developed
ActGo-Gate will be the first of its kind to provide a
gate for a wide range of occupational possibilities
(voluntary, paid, task-based, project-based, etc.).
Thereby, market fragmentations as we see them
nowadays can be transcended. ActGo-Gate will
provide end users with easy access to this integrated
gate and enable them to offer their skills, abilities
and experiences to other community members.
To integrate the occupational modules with the
existing local social marketplaces, a modular
approach is targeted for the technical realization. It
will further offer tools for efficient transactional
occupational operations (appointments coordination,
quality assurance, payment handling, reporting etc.),
both for professional as well as informal activities.
4 GUI ASSESSMENT
FRAMEWORK FOR AGING-
CENTERED WEB
APPLICATIONS
The main goal of human-computer interaction (HCI)
is to improve the way that users interact with
computers and to improve user experience.
Interaction design for elderly users is more complex
than general user group since they might have
physical ability and mental declines. Moreover, most
software is made by the younger developers. With
their limited experience in age-related decline, they
may hardly understand limitation of elderly users
(Phiriyapokanon, 2011). GUI design should match
with user experience and expectations (Sommerville,
2004). A poor interface can lead to major errors by
user mistake. It is the reason that many software
application were never used.
In order to design good software, designers
should take into account user interface guidelines for
elderly users. Ambient Assisted Living is currently
one of the important research and development
areas, where accessibility, usability and learning
play a major role and where future interfaces are an
important concern for applied engineering
(Kleinberger et al., 2007).
Many researches recommended different user
interface guidelines for designing HCI. In different
approaches, the researchers argue that the user
interface design should be responded to the different
user needs, experiences and capabilities. A number
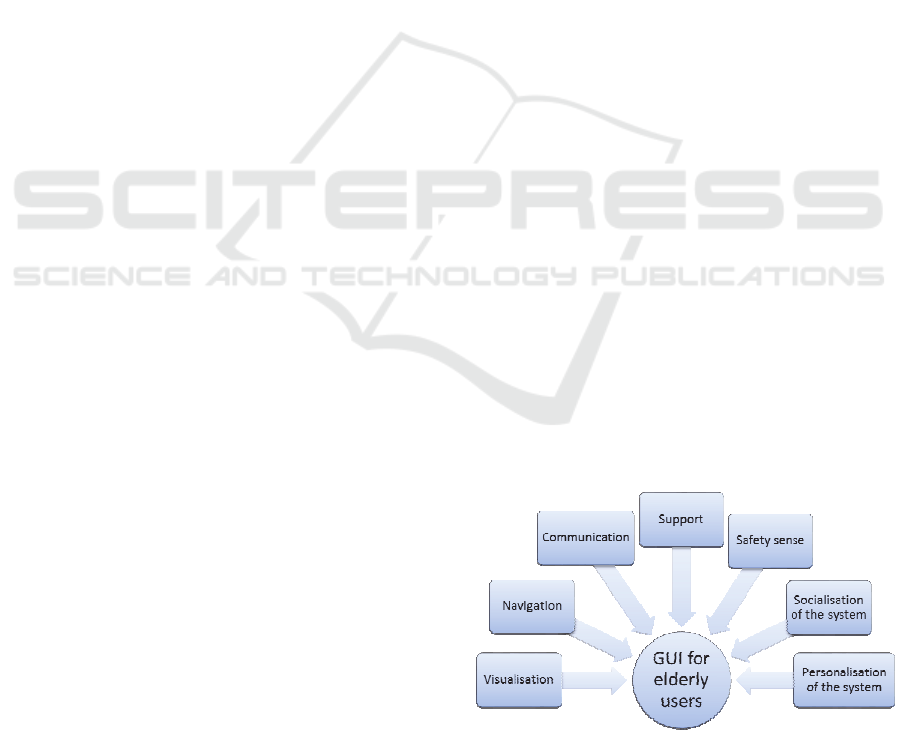
Figure 1: Main groups of GUI categories.
ICT4AWE 2017 - 3rd International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
158

of researches have suggested aging-centered design
guidelines (Kurniawan, 2005) (Loureiro and
Rodrigues, 2014) (Fisk et. Al, 2009) (Vines, 2015).
We proposed 7 main groups of categories of GUI
guidelines (see Fig. 1) with importance weights.
Within this set we proposed detailed guidelines, that
might improve the performance of the software
when used by the elderly users. They are gathered
on the basis of results of the literature research
(Boustani, 2010) (Kurniawan and Zaphiris, 2005),
our own experiences and focus interviews with
experts. The interviews were also used for
estimating importance weights for each group. The
weights were granted based upon their experience
and the observation of elderly people’s behaviors
using web applications. Experts granted their
weights, the average values were calculated and
obtained results were normalized. That is why the
Table 1: The proposition of assessment framework for web applications.
No.
Group of GUI
guidelines
Importance
weights
Proposition of detailed guidelines
1. Visualization 0,2 Provide generous spacing between items and lines of text
Main body of the text should be in sentence case and not all capital letters
Text should have clear large headings
Avoid fancy font types (suggested font: black font, sans-serif, size: 14+ points)
Make use of proper size interface components
Graphics should be relevant and not for decoration
Use simple and meaningful icons along with labels
No animation should be present
2. Navigation 0,25 Screen layout and navigation should be simple, clear and consistent
Provide a site map and show the current location clearly
Use the home screen menu and the back button as a safe point of return
Do not use a deep hierarchy, group information into meaningful categories
Avoid double click and minimize the use of the keyboard
Provide only one open window
Links should be clearly named and should be in a bulleted list
Rarely used functions should be removed
3. Communication 0,2 Design error messages (make it clear that the user isn’t the cause of the error)
Make it easy for user to correct input errors
Search engines should cater for spelling errors
Keep communication area in the center of working page
Use word-based interface than graphic-based interface (Bladder, 2008)
Language should be simple, use wordings suiting older adults’ semantic field
Avoid irrelevant information on the screen and highlight important ones
Give elderly people time to read
Avoid use of complex interactions and use wizard for complex tasks (one page-
one task and confirmations every possible time)
4. Support 0,1 Provide on screen help
Support user control and freedom
Error messages should be simple and easy to follow
Provide feedback continuously, distinct feedback from each action
Be prepared for older adults that refuse to learn
5. Safety sense 0,15 Provide and attach reviews, users’ opinions, certificates and usage statistics,
which would increase the sense of safety for the elderly users
6. Socialization of
the system
0,05 Allow discussion and comments on content (enquiries about the details, reviews,
comparisons, opportunity to be heard, to receive notifications)
Provide activity log, activity feed, timeline
Allow to establish a relationship between users: profiles and relationships
between them, the opportunity to follow the profile
Provide viral marketing content: direct recommendations between users
7. Personalization
of the system
0,05 Ensure the user can easily make interface elements larger
Provide ample time to read information
Accessibility issues should be taken into account
Enable older adults to adjust the volume at their will
Increase duration of sound signals if needed
Allow users to store shortcuts to their favorite functions
Design and Assessment of User Interface Optimized for Elderly People. A Case Study of Actgo-Gate Platform
159

most important ones are navigation, visualization,
and communication, while the personalization and
socialization seem to be less important for users.
The proposed model can be used as an universal
assessment framework for aging-centered web
applications, which could be used for evaluation of
the extent of fulfilling the UX-related requirements.
On the basis of it we perform an evaluation of the
ActGo-Gate platform.
5 IMPROVING ELDERLY USERS’
EXPERIENCE IN USING WEB
APPLICATIONS – THE ACTGO-
GATE CASE STUDY
The ActGo-Gate platform is a gate web application,
which main functional feature is to gather
occupational opportunities, coming from different
service e-marketplaces, and offer them to older
adults. In a result, it stimulates its end users to active
participation in occupational-oriented communities,
where people could help each other in the fields,
they are experienced in. Users can search for one-
time formal and informal services, search for long-
term, recurrent jobs or post a one-time demand of
something that has be to done for them.
Technically, the gate application is an offer
aggregator, that integrates some data flows (offer
feeds, notifications). The information on offers is
standardized and grouped into categories which can
be browsed in different views of catalog: the list, the
grid and the map. Each view is focused on alternate
information: the list – on name and short text
description of the offer, the grid – on its graphical
illustration, and the map – on its localization. The
catalog is built with the intent to browse offers
quickly and efficiently by using basic or advanced
sorting and filtering options. Also a location-
oriented full-text search engine is provided to users
for shortening the way of getting the right offer if
they exactly know what they are looking for. The
geo-location is an important part of the application
as it is able to adapt to current user location and
provide him/her with offers nearby him/her. It also
enables single sign on to all connected web services
(therefore with using an ActGo-Gate account users
can log into each connected service). On the other
hand in ActGo-Gate user profile section users can
edit their user data (which will be synchronized with
all connected services), browse and manage all
offers belonging to them and view all notifications
coming from connected services. The core logic of
the specific processes (like recruitment or
appointment coordination) remains the responsibility
of particular services. The web application is
designed with the principles of responsive web
design paradigm using technologies like HTML5,
AngularJS, Bootstrap and Sass. That is why it can
easily adapt its content to different screen sizes of
end devices.
Taking into account the proposed assessment
framework, we would like to check to what extent
the ActGo-Gate application is currently adapted to
the perceptual characteristics of its target group.
The visualization of the platform is intended to
be suitable for perception of elderly people. First of
all we use large sans-serif fonts – Source Sans Pro
with minimal size of 18 pts. Spacing between items
and text lines is intended to be kept as large as
possible. All components are large and clearly
separated from other parts (some are hidden and can
be displayed intentionally like advanced search
filters). The headings are highlighted so they can be
easily identified. Selected elements on the web
pages are equipped with adequate icons and labels
on the desktop view (on mobile views only icons are
displayed to ensure readability). The active elements
react on hover actions by highlighting the active
element. The color palette consists of white, blue
and black. Such a palette makes the interface clear
and light – most of texts are black. Graphics are used
for being the background of primary call to action
and to strengthen its message by presenting elderly
people that are actively spending their free time on
the retirement. Other graphics play the role of
illustrations supporting the text messages (e.g.
photos of people in testimonials) or give the real
information value. The animations are limited to the
extent possible. We can then assess that part of the
framework as passed with 100% accuracy.
Very important issue was to provide an intuitive
and simple navigation schema and consistent
vocabulary for supporting users at every stage of the
app usage. The user interface is designed to be
consistent in each part – there is a common header
and common footer section, that help to navigate
inside the platform. The similar convention of
building particular modules is used – highlighted
titles, rectangular buttons, the same hover actions on
active elements of the website (mostly the
background of the element is getting darker). Once
used element looks the same in each part of the
platform: search form is the same on landing page as
well as on the catalog page; although it is a separate
view, also uses the structure of the catalog list.
ICT4AWE 2017 - 3rd International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
160

For easier navigation a breadcrumbs module was
prepared, which aim is to show the current location
of the user within the structure of the website. It
enables to locate users themselves but also to skip to
any top level location from that point, including the
home page. The back button in the browser could
also be used in most cases as asynchronous
communication within the platform is limited to the
possible extent. There are also shortcuts to the
catalog, adding new offer feature and to the user
profile section. We don’t provide a site map.
Links are named clearly, mostly with using full
phrases. Double click is not used at all, while
keyboard usage is minimized to fill out the contact
form and search forms. Main content entity – the
offer – is categorized and the lists/grids of offers are
dynamically paginated. Both concepts are aimed at
minimizing the number of offers to be reviewed by
the user. The platform uses pull down menu for user
profile sub-menu in the header as well as in the
filters section of the catalog, what is inconsistent
with the defined GUI principles. The requirements
made us to use modal windows when presenting the
content from connected web applications. Such a
solution is a mode that temporarily disables the main
window, but still keeps it visible with the modal
window as an active child window in front of it. To
return to the parent application, users have to
interact with the modal window first. Users do some
actions there, like reading offer details, requesting it
etc. and finally close the modal window. Following
this line the registration and login path was based on
the same pattern with using modal windows.
Summarizing, the score of navigation part of the
framework could be estimated as completed in 85%.
The communication between the user and the
system is another priority. The application is
multilanguage-ready. Each page (except the landing
page) provides one main function so it doesn’t
distract users. The communicates are simple and
easy to understand by the users. Only important
information are presented to the user, most
important ones are specially highlighted like our
main Call to Action. The general communication is
usually conducted in central part of the application.
The designed user paths are shortened, not complex
and equipped with proper after-action messages –
confirmations or error reports. The errors of the
users are communicated clearly, supported by
special styling of the input with wrong content but
they are not handled by any autosuggestion
mechanisms and not corrected automatically. Search
engine isn’t able to handle input errors and display
correct results. System errors are reported
differently, so users know that they didn’t cause the
problematic situation. Because of lack of
mechanisms of errors autocorrection and inflexible
search engine the overall score can be only 70%.
Support of users at primary stage is also very
crucial issue. The platform provides a categorized
help system based on Question-Answer (QA) model.
User can also search for relevant content or use the
embedded video introduction, where most important
functions are explained. User is also supported by
contextual help. Each content element is tagged and
those tags are the basis for selecting proper help
notes on the top of the list. For feedback the
universal contact form could be used – there are no
plans to organize a special tool for feedbacks. The
support group can be estimated as compliant with
principles in 90% because of the lack of dedicated
tool of gathering feedback.
The platform considers a safety sense as an
concern and therefore does everything to convince
the user about the quality of offered services,
reliability of the providers or recruiters on the
platform as well as the platform itself. We present
success stories (testimonials) of former users of the
platform and the strong academic and socio-political
foundations of AAL Europe, National Funding
Agencies and leading Swiss and Polish universities.
The platform presents logotypes of all patrons and
supporters. The visualization and communication
also are aimed at maximizing the trust building. The
possibility of reviewing offers on the basis of
previous transactions has not been implemented yet.
Resultantly, this part can be assessed as 80%
compliant with the principles.
The platform doesn’t provide any social features
that allow building communities and widely named
socialization. Some functions can be provided by
client applications but there is a need of making an
additional effort to go directly to the client, find it
there and utilize data. The score for this part is 0%.
Personalization of the system is the last group of
principles to discuss. ActGo-Gate platform is
offering adjustment tool that allows for resizing text
content from 18 to 22 pts and change the original
layout on the simplified, high-contrast one. The
application will adapt properly to any screen size.
The application doesn’t handle voice communication
so people with serious sight disabilities can’t use it
currently but improvements in that area are planned.
The application gives the possibility of marking
offers and categories as favorites so the users can
have a quick access to them. The overall score for
that part is estimated as completing the requirements
of the framework to the extent of 90%.
Design and Assessment of User Interface Optimized for Elderly People. A Case Study of Actgo-Gate Platform
161

The overall calculation gives the following
result: (0,2 x 100%) + (0,25 x 85%)+ (0,2 x 70%) +
(0,1 x 90%) + (0,15 x 80%) + (0,05 x 0%) + (0,05 x
90%) =0,8075, what means that the gate application
is compliant with up-to-date GUI principles for
elderly people in 80%, which means that the
application is ready for being used by elderly people
– should support them in their operations on the
website, guide them to the target efficiently and
communicate easily, but only by text. Users should
feel safe on the website – the personalization
features should make the impression of “their” place
in the net. Two dimensions that definitely should be
improved, are socialization of the website and
making the voice communication available for
people with sight disabilities.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The study has demonstrated that the elderly people
experience a number of issues concerning the
access and use of the web-based applications. Their
growing health disabilities, as well as fact of rapidly
aging society especially in the developed countries,
make them the special group of interest for GUI
designers of web applications. Based on the
cognitive findings of the paper the utilitarian tool
for improving UX of modern GUIs – the assessment
framework with set of detailed guidelines – was
developed. With the use of that tool the
characteristics and evaluation of the platform was
made. All the details concerning the interaction
between the users and the system were explained in
the context of each framework category. In a result
a few missing important functions were identified,
which should be taken into account in future
releases of the application. Despite these minor
shortcomings the application still can be considered
as being adapted to the needs of elderly people and
providing positive user experiences. As a further
research it is planned to run a field trial with elderly
users, the system will be evaluated to identify
potential areas of improvement.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
ActGo-Gate is part of AAL Joint Programme Call
6, a funding activity that aims to create better
condition of life for the older adults and to
strengthen the industrial opportunities in Europe
through the use of ICT. The consortium consists of
7 partners from Switzerland, Germany and Poland.
In Poland, the project is funded by the National
Centre for Research and Development and realized
at Wroclaw University of Economics (AAL6/2015).
REFERENCES
Bladder, A., 2008. Intuitive Interaction with Complex
Artefacts: Empirically based research. SaarbrUcken:
VDM Verlag Dr. MUUer.
Boustani, S., 2010. Designing touch-based interfaces for
the elderly, University of Sydney, Oct. 2010, pp.93.
Eurostat, 2015. People in the EU – statistics on an ageing
society,http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained
/index.php/People_in_the_EU_statistics_on_an_agein
g_society#Economically_active_senior_citizens
Fisk, A. D., Rogers, W. A., Charness, N., Czaja, S. J. and
Sharit, J., 2009. Designing for Older Adults:
Principles and Creative Human Factors Approaches,
2. ed.
Kleinberger, T., Becker, M., Ras, E., Holzinger, A. and
Müller, P., 2007. Ambient Intelligence in Assisted
Living: Enable Elderly People to Handle Future
Interfaces, Lecture Notes in Computer Science Vol.
4555, pp 103-112
Kurniawan, S., Zaphiris, P., 2005. Research-Derived Web
Design Guidelines for Older People, Assets '05
Proceedings of the 7
th
international ACM
SIGACCESS conference on Computers and
accessibility, pp 129-135, Baltimore, MD, USA.
Leitãob, R., Correia de Barrosa, A., Ribeiroa, J., 2014.
Design and evaluation of a mobile user interface for
older adults: navigation, interaction and visual design
recommendations. 5th International Conference on
Software Development and Technologies for
Enhancing Accessibility and Fighting Info-exclusion,
Procedia Computer Science 27, pp. 369 – 378
Loureiro, B., Rodrigues, R., 2014. Design Guidelines and
Design Recommendations of Multi-Touch Interfaces
for Elders, ACHI 2014: 7
th
International Conference
on Advances in Computer-Human Interactions
Maciaszek, L., Gryncewicz, W., Kutera, R., 2016.
Integrated Service E-marketplace for Independent and
Assisted Living – Business and Software Engineering
Challenges. Springer LNBIP, in print
Phiriyapokanon, T., 2011. Is a big button interface enough
for elderly users? Towards user interface guidelines
for elderly users, Mälardalen University, Sweden.
Rocznik statystyki miedzynarodowej, 2015.
http://stat.gov.pl/files/gfx/portalinformacyjny/pl/defaul
taktualnosci/5515/10/3/1/rocznik_statystyki_miedzyna
rodowej_2015.pdf
Rot, A., Sobinska, M., 2013. IT security threats in cloud
computing sourcing model, Proceedings of the 2013
Federated Conference on Computer Science and
Information FedCSIS 2013, PTI, Krakow
Sommerville, I., 2004. Software engineering 7th ED.
University of Michigan: Pearson/Addison-Wesley.
UN, 2015. World Population Prospects. Key Findings &
Advanced Tables, United Nations, p.66
ICT4AWE 2017 - 3rd International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
162

Vines, J., Pritchard, G., Wright, P., Olivier, P., & Brittain,
K., 2015. An age-old problem: Examining the
discourses of ageing in HCI and strategies for future
research. ACM Trans. Comput.-Hum. Interact., 22(1),
2:1–2:27
Design and Assessment of User Interface Optimized for Elderly People. A Case Study of Actgo-Gate Platform
163
