
Layer-by-layer Assembled Films for Ocular Drug Delivery
M
´
onica Ara
´
ujo
1
, Jorge Morgado
1,2
and Quirina Ferreira
1
1
Instituto de Telecomunicac¸
˜
oes, Av. Rovisco Pais, 1049-001, Lisbon, Portugal
2
Bioengineering Department, Instituto Superior T
´
ecnico, University of Lisbon,
Av. Rovisco Pais, 1049-001, Lisbon, Portugal
Keywords:
Drug Delivery, Layer-by-layer Films, Glaucoma.
Abstract:
In this paper we describe a simple and versatile method to prepare drug delivery films composed of an ocular
drug used in glaucoma treatment, brimonidine, which was encapsulated in a polymer-beta cyclodextrin. The
films were developed in order to allow a controlled sequential release during long periods of time. Here we
show that by introducing barrier layers of graphene oxide between the drug delivery ones it is possible to
delay the brimonidine release for a few days. The time interval between two dosages of drug release will be
controlled by adjusting the number and/or thickness of the graphene layers.
1 INTRODUCTION
The layer-by-layer method is a simple and versatile
tool for the controlled fabrication of thin films to a
wide range of purposes (Raposo and Oliveira, 2000;
Ferreira et al., 2014; Ferreira et al., 2012). This
method was primarily introduced by Decher in 1992
as an assembly technique based on complementary
chemical interaction (Decher et al., 1992). However,
in theory, hydrogen bonding, Van der Waals forces
and also biomolecular recognition (i.e. any comple-
mentary interaction) can be used (Seo et al., 2008;
Ferreira et al., 2012; Ferreira et al., 2014). This tech-
nique is independent of the substrate type and due to
its simplicity, versatility and robustness has been ap-
plied to biomolecules, biosensores, implantable mate-
rials and drug delivery systems. Several surfaces can
be used to adsorb multilayers films such as metals,
polymers, glasses and any kind of biomaterial (Tang
et al., 2006; Ferreira et al., 2007; Ferreira et al., 2014).
The LbL technique enables the formation of com-
plex multilayer films merely through the sequential
adsorption of oppositely charged polymers, ceram-
ics, nanoparticles and biological molecules. With this
kind of deposition, it is possible to obtain ultrathin
mono-, bi- or multilayers with precision at molecular
scale. Varying the process parameters, such as con-
centration of the components, pH, ionic strenght and
immersion time, it is possible to fine-tune the films
(Hal
´
asz et al., 2015; Oliveira, O.N.Jr.; He, J.-A.; Zu-
colotto, V.; Balasubramanian, S.; Li, L.; Nalwa, H.S.;
Kumar, J.; Tripathy, 2002). A wide range of technolo-
gies, with different standard tools and procedures, can
be applied for the production of LbL films depending
on the intended application.
In this article we present drug delivery (DD) films
fabricated by LbL method which can be used for glau-
coma treatment. Glaucoma is an ocular degenera-
tive disease caused by optical nerve inflammation and
leads to an intraocular pressure (IOP) increase which
can cause total loss of vision. Its treatment, at initial
stage, is based on the prescription of eye drops com-
posed of an α
2
adrenergic agonist such as brimoni-
dine. However the non-compliance of the patients
(Leit
˜
ao et al., 2010; Nordstrom et al., 2005) for the
auto-administration of the eye drops, as well as the
low ocular bioavailability leads to the progress of the
disease (European Glaucoma Society, 2014). The use
of novel controlled drug delivery systems have proved
to be particularly interesting since it increases the res-
idence time of drugs in the eye.
In order to develop an autonomously system able to
release brimonidine during long periods we develop
multilayers and biocompatible films with DD func-
tion. Brimonidine was encapsulated in a polymer-β-
cyclodextrin (PolyCD) (see Figure1) and the release
was controlled by the presence of barrier layers com-
posed of two materials: an hydrosoluble polymer -
poly beta aminoester (PBAE) and charged graphene
oxide(GO) layers (see Figure2). The PBAE was
used to control de brimonidine release. PBAE is a
cationic polymer, degradable by hydrolysis of the es-
AraÞjo M., Morgado J. and Ferreira Q.
Layer-by-layer Assembled Films for Ocular Drug Delivery.
DOI: 10.5220/0006320503950401
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
ter bonds of the backbone at physiological relevant
pH (Zugates et al., 2007; Macdonald et al., 2008).
It was designed by Langer and co-workers, produced
through Michael addition polymerization of acrylate
and amine monomers (Lynn and Langer, 2000; Smith,
2010). Studies in vivo showed that the hydrolysis
of the polyester backbone of the polymer persists for
several hours to a few days, but this property is largely
affected by the polymer structure as well as the sur-
rounding cellular condition (Deng et al., 2014). The
GO is a single layer of two-dimensional carbon lat-
tice tightly packed (Hong et al., 2012). GO is a
graphene sheet funcionalized with oxygen-rich func-
tional groups in the form of ether, hydroxyl, carboxyl,
and epoxy groups (Choi et al., 2013). Graphene and
GO layers have become an appelative field of study
due to the promising biomedical applications revealed
by these nanomaterials, such as in enzime adsorption,
cell imaging, biosensors and drug delivery. Due to the
fact that GO is highly hydrophilic, planar and chem-
ically stable, it is possible to use these nanosheets as
a temporary protective layer coating for the PBAE
and poly-CD, delaying hydrolysis (Choi et al., 2013;
Bosch-Navarro et al., 2012).
Results on the growth of films composed of brimoni-
dine encapsulated in PolyCD and intercalated with
layers of PBAE and GO are discussed in this article.
The brimonidine release was followed under physio-
logical conditions.
2 EXPERIMENTAL SECTION
2.1 Materials
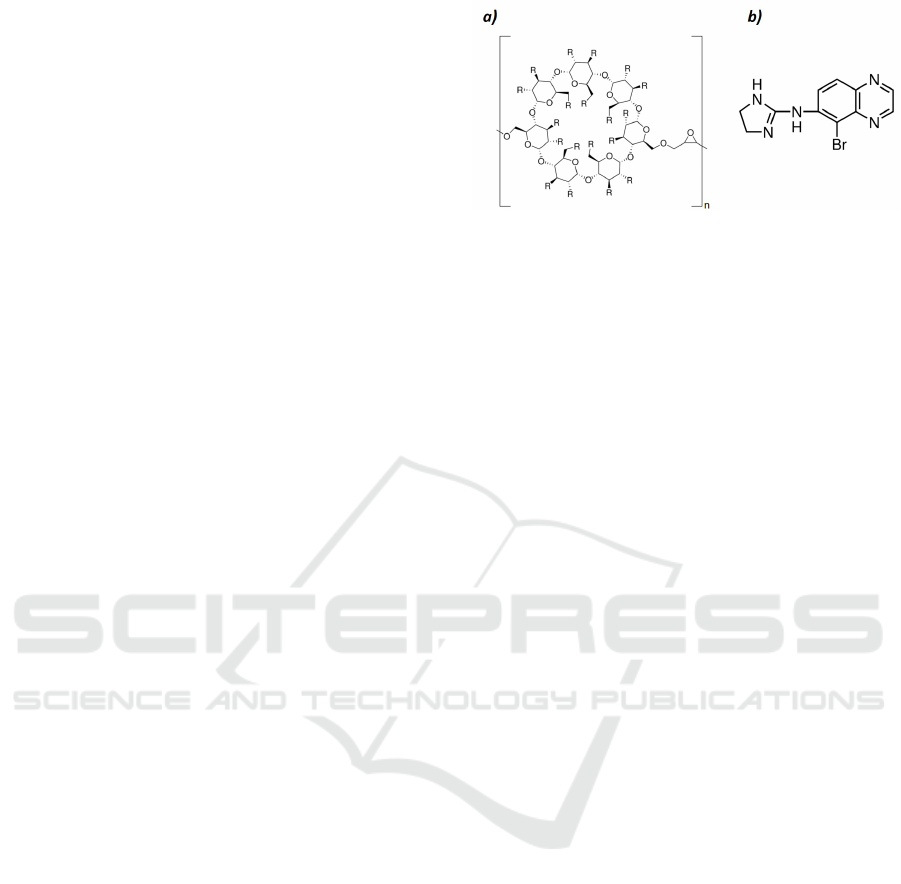
The poly-β-cyclodextrin (polyCD) and the brimoni-
dine (see figure 1) were purchase from Sigma Aldrich
and used as received.
The poly-β-aminoester (PBAE) (see figure 2)
was synthetized using the protocol described by
Lynn et al. (Lynn and Langer, 2000), adding 3.28
g of 4,4
0
-trimethylenedipiperidine (S1) (97% purity,
Sigma Aldrich, CAS number 16898-52-5) added
to 2.87 mL of 1,4-butanediol diacrylate (S2) (99%
purity, Alfa Aesar, CAS number 1070-70-8). The
copolymerization of these monomers was carried
out in THF (that was previously distilled) at a
temperature of 50
◦
C, during 48 h. The final polymer
PBAE, (Figure 2) was purified through repeated
precipitation into diethyl ether. The precipitated
polymer was vacuum filtrated with a Buchner funnel
and left to dry in vacuum over night. The structure of
the final product was confirmed by nuclear magnetic
Figure 1: Chemical structure of a) β-cyclodextrin polymer
and b) brimonidine. The polymer is composed of n rings of
cyclodextrin. R corresponds to the hydroxyl group present
in the molecule.
resonance spectroscopy. It was further characterized
by gel permeation chromatography.
The negatively charged graphene (GO-COO
−
)
was purchased from Graphenea, as an aqueous
dispersion with a concentration of 0.5 mg/mL (see
Figure 2). The negative charges are due to the
presence of carboxylic acids that deprotonate in low
pH.
The positive graphene (GO-NH
+
3
) was pre-
pared in laboratory reducing the negative GO
and linking amine groups to the carboxylic acids
(Hwang et al., 2012). A method developed
by Hwang, et al. was used to prepare posi-
tively charged GO. 50 mL of negative GO solu-
tion were mixed with 0.625 g of N-ethyl-N’-(3-
dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimede (EDC) (Sigma
Aldrich) and with 5 mL of ethylenediamine (Sigma
Aldrich). The solution was left stirring for 12 hours.
EDC reacted with carboxylic groups activating the
coupling of ethylenediamine. A dialysis of the final
solution was performed in order to separate the func-
tionalized graphene from the secondary products.
2.2 Methods
The films were prepared by layer-by-layer technique
(Ferreira et al., 2014). Quartz substrates were used
to adsorb the films that were previously submitted to
oxygen plasma and immersed in a piranha solution
in order to clean all organic residues and to nega-
tively charge the surfaces. A quartz crystal lamella
was immersed into a solution of PBAE. After re-
maining in this solution during 5 minutes, the sub-
strate was rinsed with sodium acetate (with pH ad-
justed to 5.0) in order to remove all the molecules
that are not adsorbed, or only physically adsorbed
and then dried with nitrogen gas. After this sequence
of steps a monolayer of PBAE formed. Then the
substrate was immersed, one more time, but now in
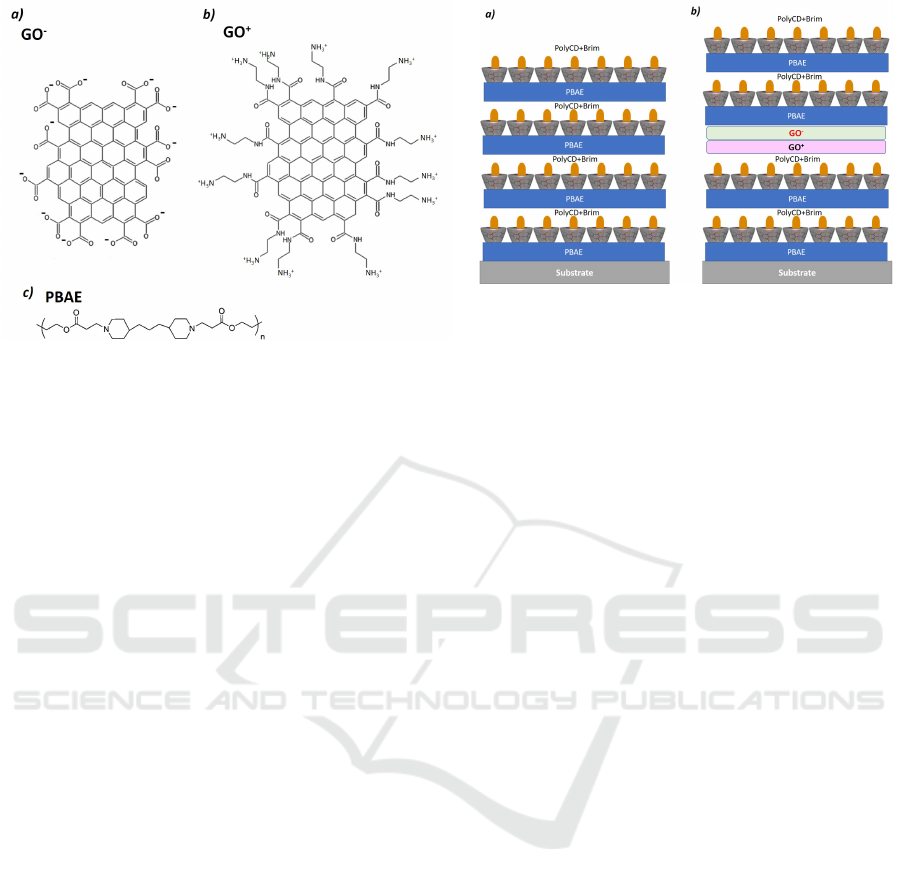
Figure 2: Schematic representation of chemically modified
graphene oxide a) GO-COO
−
and b) GO-NH
+
3
. c) Chemi-
cal structure of poly(β-amino ester) (PBAE).
the polymeric solution of polyCD. The quartz sub-
strate was left in the polyCD solution during 5 min-
utes and then was washed in sodium acetate (pH=5.0)
and dried with nitrogen. This process completes one
cycle of the LbL assembly, forming one bilayer of
(PBAE/polyCD). The deposition cycle was repeated
the number of times equivalent to the number of bi-
layers intended.
3 RESULTS
The DD LbL films were prepared using the LbL
technique, where each layer adsorption was followed
by UV-Vis spectroscopy. Two types of films were
performed: films with polymeric bilayers of PBAE
and PolyCD+Brim and films with charged GO lay-
ers intercalated between the polymeric ones, see the
schematic illustration of Figure 3.
Figure 4 shows the absorption spectra of each
(PBAE/PolyCD) bilayer of a film with 4 bilayers.
The film has an almost linear growth, established by
an increase in the absorbance of brimonidine, which
means that more molecules are being added to the
film. The brimonidine release was also followed
by UV-Vis spectroscopy. The LbL films were im-
mersed in a Phosphate Buffer Saline (PBS) solution
that has properties similar to those of biological flu-
ids, in terms of pH (pH=7.4, equal to the physiologic
pH) and concentration of salts. A phosphate buffered
saline solution consists on a phosphate buffer with a
concentration of 0.01M and a sodium chloride con-
centration of 0.154 M. The experiments were done at
37
◦
C in order to mimic the physiological conditions
where a glass beaker with PBS was maintained in-
Figure 3: Schematic representation of drug delivery layer-
by-layer (DD LBL) films. a)DD LBL film composed
of 4 bilayers of (PBAE/PolyCD + Brim)
4
. b)DD LBL
film composed of a graphene bilayer of charged graphene
between DD bilayers - ((PBAE/PolyCD + Brim)
2
/GO −
COO
−
/GO − NH
+
3
/(PBAE/PolyCD + Brim)
2
.
side an oven at this temperature. The PBS solution is
changed at the end of each immersion. After a spe-
cific period of time the substrate was removed, dried
with a nitrogen flux and its absorption spectrum was
recorded. The Figure 5 shows the absorption spec-
trum of (PBAE/polyCD + Brim)
4
and the absorption
spectra of the same film, after immersion into a PBS
solution at 37
◦
C, after determined periods of time up
to a maximum of 14 minutes and 30 seconds. It is pos-
sible to see that the absorbance of the film immersed
in to the PBS solution decreases in time demonstrat-
ing the brimonidine desorption. In particular, it is
possible to observe that after 30 seconds of immer-
sion, the film has lost one bilayer because its absorp-
tion spectrum is similar to that of the film with 3 bi-
layers. This means that it takes 30 seconds for the
4
th
bilayer to be released to the PBS solution. It was
also observed that after 1 minute and 30 seconds in
PBS solution the same film has the same spectrum as
that obtained for two bilayers revealing that the third
bilayer was released. The immersion of the film in
PBS solution continued up to 14 minutes and 30 sec-
onds. However, after the 10 minutes of immersion,
salt deposition was observed on the top of the film
that affected the absorption spectra. The kinetics of
brimonidine was only quantified up to 10 minutes of
film immersion.
Figure 6 represents the percentage of brimonidine
released to the PBS solution as function of time that
was calculated subtracting the absorbance at 220 nm
after the film immersion to the absorbance at the same
wavelength before film immersion. The brimonidine
kinetic shows that after 9 minutes of immersion time
in PBS, 30% of the drug was released. That could
correspond to the two outer (PBAE/polyCD+Brim)
bilayers. The kinetics of brimonidine released, repre-
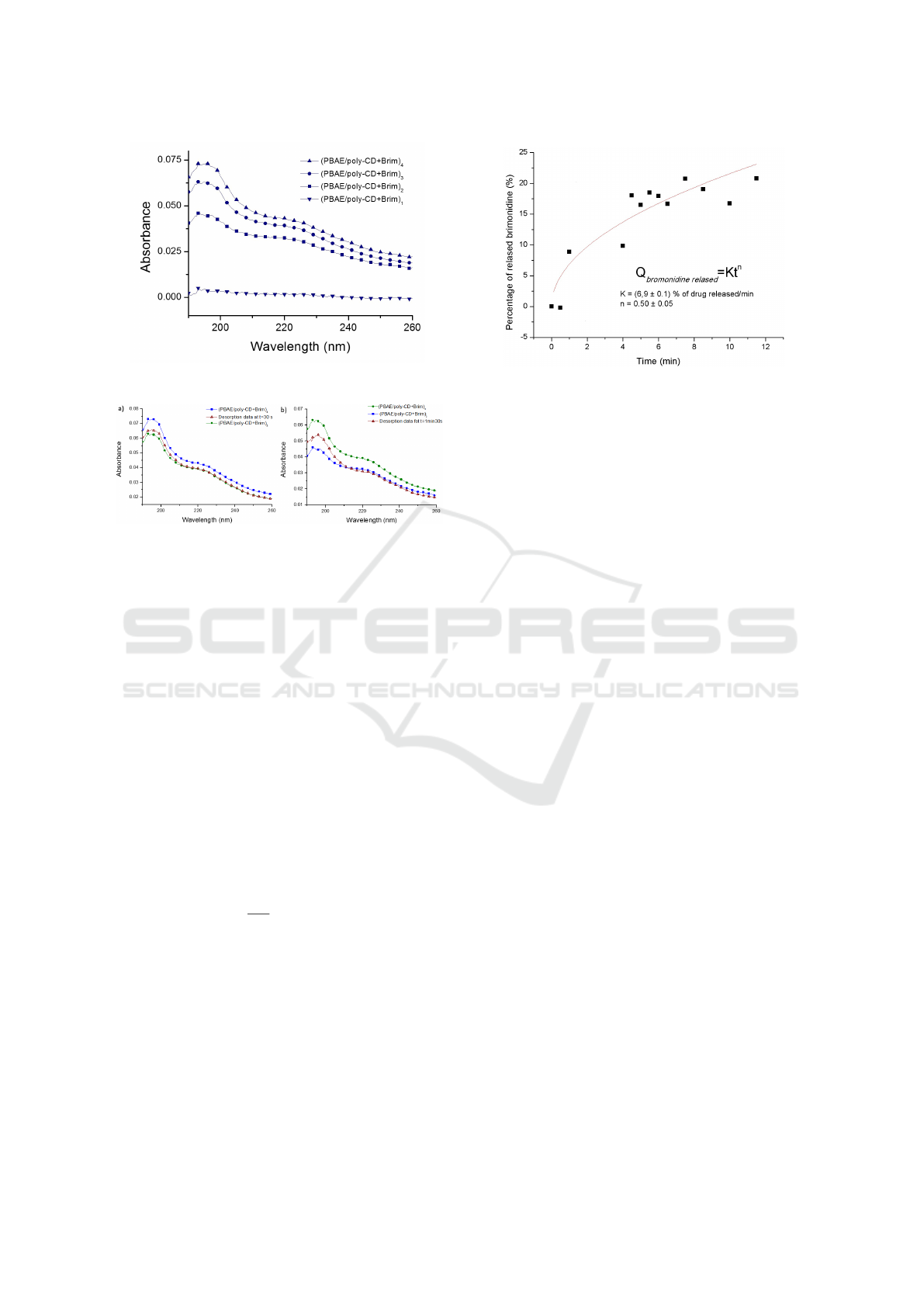
Figure 4: Absorption spectrum of each of the 4
(PBAE/PolyCD + Brim) bilayers.
Figure 5: Absorption spectra of a)(PBAE/polyCD +
Brim)
4
and (PBAE/polyCD + Brim)
3
layers and the spec-
trum obtained after immersion in PBS solution of the film
with 4 bilayers during 30 seconds. b)(PBAE/polyCD +
Brim)
3
and (PBAE/polyCD + Brim)
2
layers and the spec-
trum of the film obtained after immersion in PBS solution
during 1 minute and 30 seconds.
sented in Figure 6 was fitted with Korsemeyer-Peppas
model.
The majority of drugs reveal a first-order release
(or “burst release”) from the substrate followed by a
continuous decrease in drug concentration in the PBS
solution. The ideal pharmacokinetic system is rep-
resented by a zero-order kinetic response over time,
since it minimizes the variation of drug concentration,
allowing a constant release rate of drug. To analyse
the release, the Korsemeyer-Peppas equation (equa-
tion 1) (Holowka and Bhatia, 2014) was used, by
which the dissolution rate of the drug from the ma-
trix was determined:
M
t
M
∞
= Kt
n
(1)
where M
t
is the amount of drug released at time t,
M
∞
corresponds to the total amount of drug present,
K is the kinetic constant; and n is the diffusion value.
In this model, the kinetics is determined by the diffu-
sion expoent value (n). Values of n=0.5 imply clas-
sic Fickian diffusion, i.e. the main mechanism that
controls the release of the drug in the system is pure
diffusion. In diffusion-controlled systems, the drug
release process occurs due to aqueous stimuli through
polymer swelling, causing an uniform volume expan-
Figure 6: Percentage of released brimonidine for the
(PBAE/polyCD + Brim)
4
after 8 minutes of immersion
time in PBS solution. The fitting curve was calculated using
equation (1).
sion of the bulk material. Ultimately, this will lead to
pore opening of the matrix structure. Values of n in
the range of 0.5 <n <1, indicate that the drug release
occurs by Fickian diffusion and Case II transport,
i.e., in this regime the drug release is both diffusion-
controlled, and erosion-controlled, respectively. In
erosion-control systems the mechanism of drug re-
lease relies on the attack of the covalent bonds in the
polymer matrix by the components present in the re-
lease solution, allowing the drug to escape. It can
occur due to volume decrease of the matrix, where
its density remains constant; or due to decrease in
the matrix density, while the volume remains con-
stant. In these cases the diffusion obeys the Fick’s
law (Fick, 1995). If the diffusion exponent is n=1,
it suggests Case II transport (or zero-order release)
with constant release rate and controlled by polymer
relaxation. At last, cases with n >1, indicate Super
Case II transport (or release that is erosion-controlled)
(Holowka and Bhatia, 2014; Siegel and Rathbone,
2012). The value of diffusion exponent for this sys-
tem is n = 0.49 ± 0.04 with K = 12.0 ± 0.1, which
means that, in this case, the mechanism of drug re-
lease follows the Fickian diffusion (the driving force
behind the brimonidine release in this film is diffu-
sion).
Due to the fast brimonidine release to the biolog-
ical medium, layers of graphene oxide were intro-
duced between the polymeric (PBAE/PolyCD+Brim)
bilayers (see schema of Figure 3). The multilayer film
growth and subsequent release kinetics were monitor-
ized by UV-Vis absorption. The films were also pre-
pared by LbL method. Figure 7 shows the absorbance
spectra of all layers of a film composed of 4 bilayers
of (PBAE/PolyCD + Brim)
4
followed by one bilayer
of charged graphene (GO
+
/GO
−
) and with more four
outer polymeric bilayers of PBAE/PolyCD + Brim)
4
.
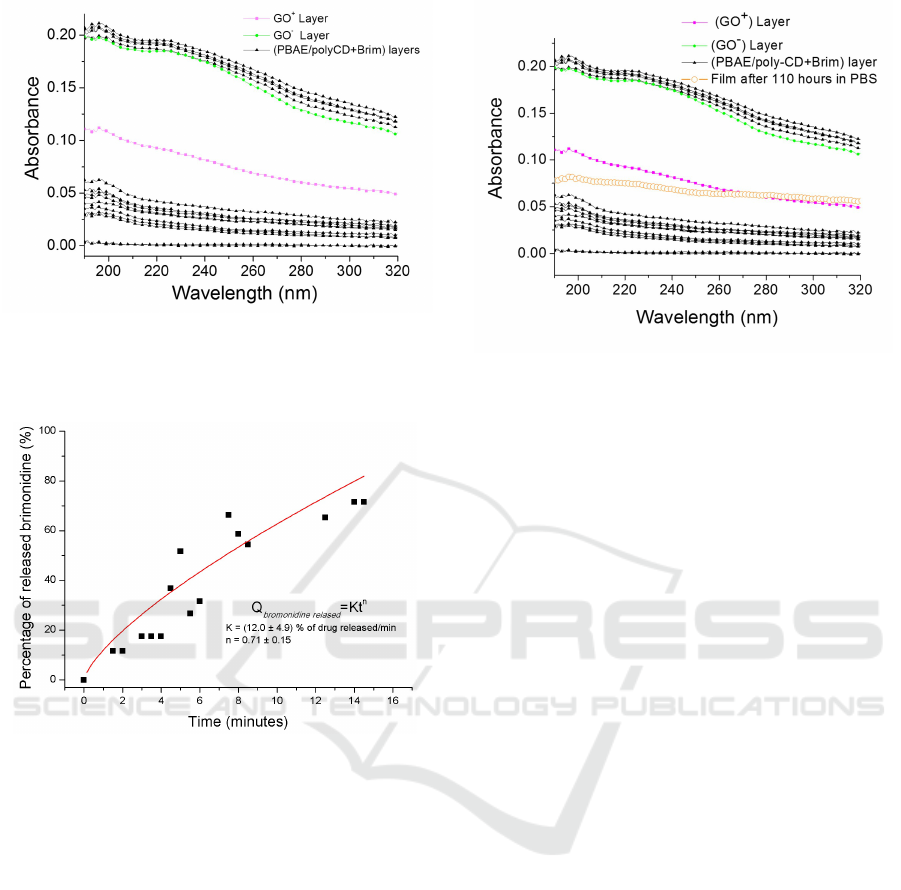
Figure 7: Absorption spectra of LbL film as
a function of the growth step, up to the fi-
nal structure composed by (PBAE/polyCD +
Brim)
10
/(GO
+
/GO
−
)/(PBAE/polyCD + Brim)
4
.
Figure 8: Percentage of released bri-
monidine for the (PBAE/polyCD +
Brim)
10
/(GO
+
/GO
−
)/(PBAE/polyCD + Brim)
4
after
15 minutes immersion film in PBS solution.
The drug release kinetics study was developed
with the immersion of the film with DD layers into a
PBS solution (diluted in milli-Q water 1/10, pH=7.4)
at 37
◦
C as described previously. During the first 15
minutes, spectra were recorded every 30 seconds of
immersion in PBS, and the PBS solution was changed
after each measurement. After that, the spectra were
obtained with 30 minutes interval up to a total of
3 hours and 15 minutes of immersion (changing the
PBS solution after each 15 minutes). Afterwards the
immersion time was extended to 1 hour, until the total
desorption time reached 6 hours and 15 minutes (with
fresh PBS solution after each half hour). Concluding
this period, the desorption time has been extended to
an average of 12 hours of continuous desorption, fol-
lowed by spectral analysis.
Between the beginning of the experiment until
the 15
th
minute the outer polymer bilayers were des-
Figure 9: Absorption spectra of a
film with all layers: (PBAE/polyCD +
Brim)
10
/(GO
+
/GO
−
)/(PBAE/polyCD + Brim)
4
. Af-
ter more than 4 and a half days, the outer polymeric layers
and the GO
+
layer were desorbed remaining only the layer
of GO
+
. The absorbance spectrum of this desorption data
is almost coincident to the GO
+
layer.
orbed from the substrate. The release of the brimoni-
dine from the outer bilayers was quantified using the
Korsemeyer-Peppas equation (described in equation
1). It is possible to observe that about 80% of bri-
monidine presented in the outer two bilayers is re-
lease during 14 minutes. The red line is the result
of the fitting, where it was obtained a n greater than
0.5 (n = 0.71 ± 0.15) and K = 12.0 ± 4.9, leading to
the conclusion that this system exhibits a drug re-
lease that is both diffusion-controlled and erosion-
controlled. By definition, in controlled released sys-
tems with 0.5 ≤ n ≤ 1.0, the drug release is a com-
bination of Fikian diffusion and Case II transport of
drug molecules through the polymeric film (Enscore
et al., 1977; Ritger and Peppas, 1987). The monitor-
ization of the kinetics continued during more than 5
days. At t=110 h (more than 4 and a half days after
the desorption began) the adsorption has undergone
an impressive decrease in its intensity. The spectrum
of the film was almost coincident with the spectrum of
the GO
+
layer as we can see in (figure 9). After this
immersion time, the absorbance spectrum indicated
that only the layers (PBAE/polyCD + Brim)
4
/(GO
+
)
remained in the film.
After 5 days in immersion (approximately
t=121 h) the last GO layer was desorbed. The ob-
tained absorbance spectrum is almost coincident with
the (PBAE/polyCD + Brim)
4
film, as it is possible to
conclude from the spectra of Figure 10.
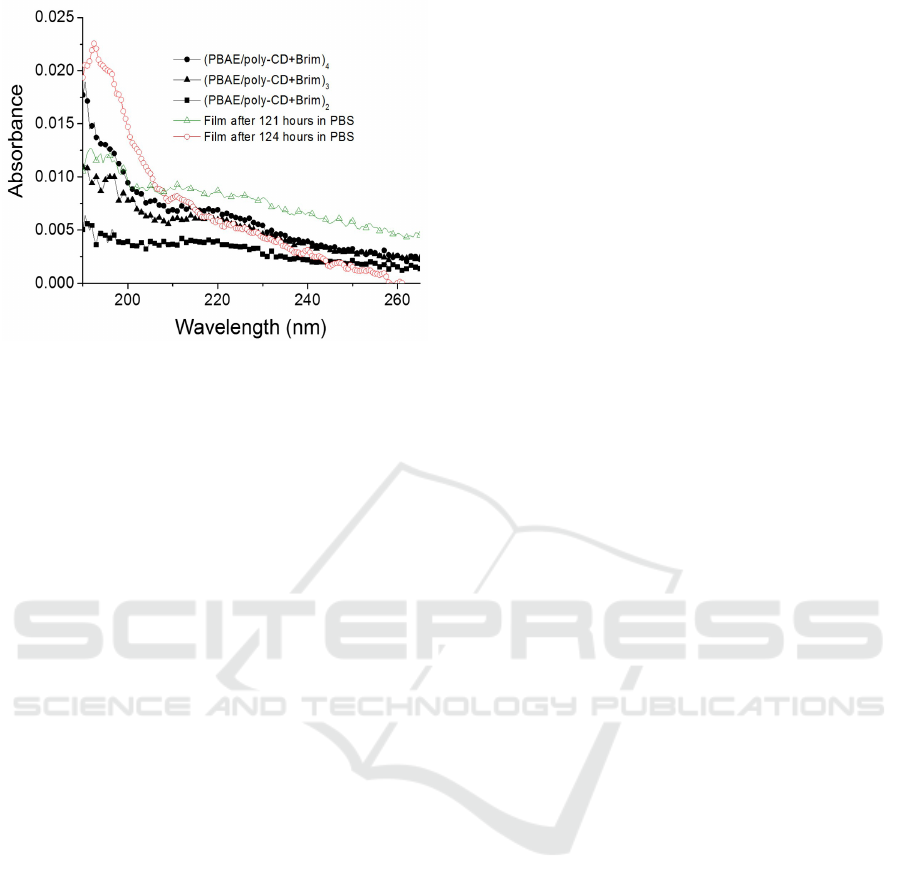
Figure 10: Absorption spectra of a
film with all layers: (PBAE/polyCD +
Brim)
4
/(GO
+
/GO
−
)/(PBAE/polyCD + Brim)
4
and
the spectrum obtained after more than 5 days immersion
time.
4 CONCLUSIONS
A new drug delivery system based on multilayer films
fabricated by the layer-by-layer technique was pre-
sented. This versatile method allowed the fabrication
of a time controlled system introducing in the com-
position of the film an hydrosoluble polymer - poly
(β-amino ester) - and charged graphene oxyde layers.
Both materials are able to control the release of the
studied drug (brimonidine) encapsulated in a poly β-
cyclodextrin but the presence of graphene oxide can
delay the brimonidine release up to 5 days. This is
an important result for the study of time-controlled
drug delivery systems since it allows adaptation of the
number of layers and the film architecture in order to
delay the film desorption, stopping the release of bri-
monidine in the eye, in the way that only the needed
dose will be administrated.
This work developed the first DD LbL films
for glaucoma treatment using biocompatible and
biodegradable materials for the release of precise
amounts of an anti-IOP drug, at determined periods
of time. The high non-compliance level in glau-
coma treatment leads to thousands of individuals to go
blind every year. However, the latest developments on
drug delivery of drugs, with the most varied carriers
have revolutionized the ophthalmic treatments offer-
ing new, improved systems that can control the glau-
coma condition but also substitute the current treat-
ments with daily eye drop application.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors thank Fundac¸ao para a Ci
ˆ
encia e
Tecnologia-Portugal for financial support under the
project UID/EEA/50008/2013 and Post-Doc grant
SFRH/BPD/75338/2010.
REFERENCES
Bosch-Navarro, C., Coronado, E., Mart
´
ı-Gastaldo, C.,
S
´
anchez-Royo, J. F., and G
´
omez, M. G. (2012). Influ-
ence of the ph on the synthesis of reduced graphene
oxide under hydrothermal conditions. Nanoscale,
4(13):3977.
Choi, W., Choi, J., Bang, J., and Lee, J. H. (2013). Layer-
by-layer assembly of graphene oxide nanosheets on
polyamide membranes for durable reverse-osmosis
applications. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces,
5(23):12510–12519.
Decher, G., Hong, J., and Schmitt, J. (1992). Buildup of
ultrathin multilayer films by a self-assembly process:
Iii. consecutively alternating adsorption of anionic and
cationic polyelectrolytes on charged surfaces. Thin
Solid Films, 210-211:831–835.
Deng, X., Zheng, N., Song, Z., Yin, L., and Cheng, J.
(2014). Trigger-responsive, fast-degradable poly(β-
amino ester)s for enhanced dna unpackaging and re-
duced toxicity. Biomaterials, 35(18):5006–5015.
Enscore, D., Hopfenberg, H., Stannett, V., and Berens, A.
(1977). Effect of prior sample history on n-hexane
sorption in glassy polystyrene microspheres. Polymer,
18(11):1105–1110.
European Glaucoma Society (2014). Terminolology and
guidelines for glaucoma. European Glaucoma Soci-
ety, 4th edition edition.
Ferreira, Q., Braganca, A. M., Alcacer, L., and Morgado, J.
(2014). Conductance of well-defined porphyrin self-
assembled molecular wires up to 14 nm in length.
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 118(13):7229–7234.
Ferreira, Q., Gomes, P., Maneira, M., Ribeiro, P., and Ra-
poso, M. (2007). Mechanisms of adsorption of an azo-
polyelectrolyte onto layer-by-layer films. Sensors and
Actuators B: Chemical, 126(1):311–317.
Ferreira, Q., Ribeiro, P. A., Oliveira, O. N., and Raposo, M.
(2012). Long-term stability at high temperatures for
birefringence in pazo/pah layer-by-layer films. ACS
Applied Materials & Interfaces, 4(3):1470–1477.
Fick, A. (1995). On liquid diffusion. Journal of Membrane
Science, 100(1):33–38.
Hal
´
asz, K., Hosakun, Y., and Cs
´
oka, L. (2015). Reduc-
ing water vapor permeability of poly(lactic acid) film
and bottle through layer-by-layer deposition of green-
processed cellulose nanocrystals and chitosan. Inter-
national Journal of Polymer Science, 2015:1–6.
Holowka, E. P. and Bhatia, S. K. (2014). Drug Delivery,
volume 197 of Handbook of Experimental Pharma-
cology. Springer New York.

Hong, J., Shah, N. J., Drake, A. C., DeMuth, P. C., Lee,
J. B., Chen, J., and Hammond, P. T. (2012). Graphene
multilayers as gates for multi-week sequential release
of proteins from surfaces. ACS Nano, 6(1):81–88.
Hwang, H., Joo, P., Kang, M. S., Ahn, G., Han, J. T., Kim,
B.-S., and Cho, J. H. (2012). Highly tunable charge
transport in layer-by-layer assembled graphene tran-
sistors. ACS Nano, 6(3):2432–2440.
Leit
˜
ao, P., Amaral, A., Pinto, L. A., Ferreira, J., Magric¸o,
A., Trinc
˜
ao, F., Silva, J. P., and M., R. (2010).
Avaliac¸
˜
ao do Conhecimento , Ades
˜
ao Terap
ˆ
eutica e
Repercuss
˜
ao de uma Sess
˜
ao Educativa sobre o Glau-
coma numa Populac¸
˜
ao de Doentes seguidos na Con-
sulta de Especialidade num Hospital Central. Oftal-
mologia, 34:295 – 300.
Lynn, D. M. and Langer, R. (2000). Degradable poly
(beta-amino esters ): Synthesis , characterization , and
self-assembly with plasmid dna. J Am Chem Soc,
122(10):10761–10768.
Macdonald, M., Rodriguez, N. M., Smith, R., and Ham-
mond, P. T. (2008). Release of a model protein from
biodegradable self assembled films for surface de-
livery applications. Journal of Controlled Release,
131(3):228–234.
Nordstrom, B. L., Friedman, D. S., Mozaffari, E., Quigley,
H. A., and Walker, A. M. (2005). Persistence and Ad-
herence With Topical Glaucoma Therapy. American
Journal of Ophthalmology, 140(4):598.e1–598.e11.
Oliveira, O.N.Jr.; He, J.-A.; Zucolotto, V.; Balasubrama-
nian, S.; Li, L.; Nalwa, H.S.; Kumar, J.; Tripathy,
S. (2002). Layer-by-layer polyelectrolyte-based thin
films for electronic and photonic applications. Hand-
book of Polyelectrolytes and Their Applications, 1:1–
38.
Raposo, M. and Oliveira, O. N. (2000). Energies of adsorp-
tion of poly( o -methoxyaniline) layer-by-layer films.
Langmuir, 16(6):2839–2844.
Ritger, P. L. and Peppas, N. A. (1987). A simple equa-
tion for description of solute release II. Fickian and
anomalous release from swellable devices. Journal of
Controlled Release, 5(1):37–42.
Seo, J., Lutkenhaus, J. L., Kim, J., Hammond, P. T., and
Char, K. (2008). Effect of the layer-by-layer (lbl) de-
position method on the surface morphology and wet-
ting behavior of hydrophobically modified peo and
paa lbl films. Langmuir, 24(15):7995–8000.
Siegel, R. A. and Rathbone, M. J. (2012). Fundamentals
and Applications of Controlled Release Drug Deliv-
ery. Springer US, Boston, MA.
Smith, R. C. (2010). Toward a Drug Delivery Coating for
Intraocular. PhD thesis, University of North Carolina
- Massachussets Institute of Technology.
Tang, Z., Wang, Y., Podsiadlo, P., and Kotov, N. A. (2006).
Biomedical applications of layer-by-layer assembly:
From biomimetics to tissue engineering. Advanced
Materials, 18(24):3203–3224.
Zugates, G. T., Tedford, N. C., Zumbuehl, A., Jhunjhun-
wala, S., Kang, C. S., Griffith, L. G., Lauffenburger,
D. a., Langer, R., and Anderson, D. G. (2007). Gene
delivery properties of end-modified poly(beta-amino
ester)s. Bioconjugate chemistry, 18(6):1887–1896.
