
Evaluation of a Gamified 3D Virtual Reality System to Enhance the
Understanding of Movement in Physics
Diego Alonso Iquira Becerra, José Alfredo Herrera Quispe, Roni Guillermo Apaza Aceituno, Gaby
Mary Poma Vargas, Flor Gabriela Fernandez Zamora, José Luis Huillca Mango, Guadalupe Paulina
Anccasi Figueroa, Aldo Alexis Perez Vizcarra and Jaison Willian Torres Chana
Computer Science, National University of San Agustín, Arequipa, Perú
Keywords:
Virtual Reality, Gamification, Mixed Reality, Interactive, Physics Learning.
Abstract:
The creation of new technological tools in education provides different learning opportunities to students.
The present research evaluates an application that we have developed for the use of virtual reality to enhance
the understanding of movement in physics, using gamification techniques on the application allowed us to
improve the motivation of the students to learn, the validation of this research was made using a methodology
to evaluate the didactic value of educational software, and this evaluation was carried out on a group of
teachers.
1 INTRODUCTION
Education is constantly improving in every country;
however this improvement is affected by different fac-
tors like economic, political and social capacities, of
which the economic aspect is the most critical in dif-
ferent countries, creating a tangible limitation.
The use of technology in education allows low-
cost alternatives to improve education; one of these
technologies is virtual reality.
For instance the term virtual reality has two virtu-
ally opposite concepts: real (which has real and effec-
tive existence) and virtual (which has not physically
existing).
Consequently virtual reality is the name given to
a set of computer-based techniques and technologies
that approximate the visualization of concepts, ob-
jects and actions in three dimensions in an interac-
tive way, that resembles or not reality (Gobbetti and
Scateni, 1998).
In addition, virtual reality gives the possibility of
rebuilding the real world, creating digital scenarios so
realistic that create the sensation of being transported
to fantastic worlds in seconds, this is a reason why vir-
tual reality is a technology than can be used in various
areas.
On the other hand, many of the principals devel-
opments in virtual reality are focused on entertain-
ment, from video games to video consumption, there
are other less publicized but interesting application,
such as in the area of medicine and art (Mazuryk and
Gervautz, 1996).
The characteristics mentioned before turns virtual
reality into a technological tool with potential for the
creation of educational software, although this tech-
nology is not suitable for teaching directly, a set of
processes and procedures are necessary to guarantee
the correct use in the classroom.
In fact, educational software is a technological
tool created to improve the learning process at dif-
ferent learning levels (Fredes et al., 2012) (Bus-
tos Sánchez and Coll Salvador, 2010), this technol-
ogy combined with Virtual Reality allows to place
students in scenarios, that could not be accessed in
reality.
In addition the use of gamification in education
helps to improve the student motivation to learn,
through the use of game elements in learning environ-
ments with the goal of maximizing entertaining and
engaging the student, which helps them to continue
learning. (Dicheva et al., 2015).
Summing up, the section 2 will show research re-
lated to virtual reality and the impact that generates in
the educational field. The proposal of the immersive
laboratory for enhance the understanding of move-
ment in physics, that we develop will be discussed
in section 3. Section 4 shows the system that we de-
velop, exploring the configuration, scenarios and ac-
Becerra, D., Quispe, J., Aceituno, R., Vargas, G., Zamora, F., Mango, J., Figueroa, G., Vizcarra, A. and Chana, J.
Evaluation of a Gamified 3D Virtual Reality System to Enhance the Understanding of Movement in Physics.
DOI: 10.5220/0006328003950401
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2017) - Volume 1, pages 395-401
ISBN: 978-989-758-239-4
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
395

tivities that the virtual laboratory contain. The exper-
iment and results are shown in section 5, where this
educational software was validated against teachers,
who have pedagogical experience. Finally, section 6
shows the conclusions.
2 RELATED RESEARCH
In recent years the investigations related to the use
of virtual reality in the educational field has begun to
increase.
In fact, education is currently one of the most
promising areas for the design and development of
virtual reality applications, mainly thanks to the abil-
ity to introduce the student to immersive and multi-
sensory environments (sight, touch, ears). In which
students can interact with an virtual environment that
stimulates their learning process.
2.1 Educational Software
Educational software is the technological tool to the
new learning society (Fredes et al., 2012) (Colegio
and Minnaard, 2016), because of this, strategies have
been adopted at different levels, from an institutional
level to a classroom level, searching for the appro-
priately use of educational software. Simulation in
virtual environments can be a powerful tool to place
students in "practical" scenarios that could not be ac-
cessed in reality (Saxena et al., 2016).
For example virtual environments are au-
tonomous, intercommunicated worlds that interact
with an user that is also located inside the computer;
there are two types of virtual environments applica-
tions that can be applied on education: simulators
and video games.
At all the different levels of education, virtual re-
ality has the potential to be involved on the learning
process, to lead students to new discoveries, to moti-
vate and stimulate the process of learning (Ott et al.,
2015). In fact, students can participate in the learning
environment with immersion, that is a sense of pres-
ence of being part of the environment.
2.2 Virtual Reality in the Education
In brief virtual reality is an alternative world filled
with computer generated images that respond to hu-
man movements. These simulated environments are
usually visited with the aid of head-mounted goggles
and fiber-optic data gloves (Steuer, 1992).
For instance, some of the main characteristics of
virtual reality are immersion and presence, whose are
focused on generating the sensation of being present
in a simulated place, this allows to give a focused
viewpoint in terms of human experience rather than
technology to virtual reality. However, the concept of
presence does not refer to what surrounds one, as in
the physical world, but to the perception of the envi-
ronment through an automatic and controlled mental
process (Gibson, 2014), on the other hand Immersion
can be defined as the feeling of being present in a cer-
tain environment.
In the past there have been certain difficulties in
the use of technologies focused on the use of vir-
tual reality, there were problems with the techno-
logical devices as they were expensive and not very
widespread, and on the other hand, their characteris-
tics were such that often cause a sense of aversion to
their users due to the mismatch between head move-
ments and the corresponding change in the scene
(Ohta and Tamura, 2014).
Now with the creation of commercial products
such as Google Cardboard which is a development
platform created by Google to use mobile devices as
virtual reality glasses. For example the glasses are
used by placing a mobile device in the back and mak-
ing the visualization through the lenses in the front
(MacIsaac et al., 2015) (Laffont et al., 2016).
Evidently, due to the versatility of virtual reality
technology, the uses of this technology is not lim-
ited in a specific area for such reason among the ar-
eas in which it can be used are: military training,
education, health, entertainment, fashion, museums,
business, engineering, sports, media, scientific visual-
ization, telecommunications and construction (Cum-
mings and Bailenson, 2016).
On the whole, education is an area in which vir-
tual reality is used through the creation of teaching
and learning situations, allowing large groups of stu-
dents to interact with each other in three-dimensional
environments (Helsel, 1992)
2.3 Gamification in the Education
The term gamification is the application of game el-
ements and principles of game designs in other non-
game contexts. In brief gamification uses game de-
sign elements to improve user motivation, participa-
tion, and productivity (Deterding et al., 2011).
A general definition of gamification is the use of
game design elements in contexts other than games
(Deterding et al., 2011).
In fact the use of gamification in education, helps
to improve the motivation on students to learn through
play elements in learning environments, with the goal
of maximizing entertaining and engaging the stu-
CSEDU 2017 - 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
396

dent and inspiring them to continue learning (Dicheva
et al., 2015).
The main advantages of using gamification in ed-
ucation are:
• Freedom for trial and error without negative reper-
cussions, increasing the fun in the classroom.
• Differentiated education according to the stu-
dent’s abilities.
• Visualization of the realized learning, providing a
set of tasks and subtasks
• Motivate students to continue their learning and
give the student the freedom to do their own learn-
ing.
2.4 Virtual Laboratories
Lessons made in classrooms are not always appreci-
ated by the students, in a classroom; both the learning
and the motivation of the student and the teacher can
be affected by external stimulus or by a lack of atten-
tion and interest.
Nevertheless, to be able to do the correct laborato-
ries practices of what is learned in a theoretical way,
it is necessary to manipulate instruments and objects,
the classes in these laboratories require a set time and
a suitable room.
Evidently, the large number of students enrolled
in the first years of higher education, material limita-
tions (number of rooms, facilities) and lack of human
resources make it difficult to learn only through prac-
tical exercises in the classroom.
Certainly taking into account the evolution of stu-
dents’ attention capacity, lack of time and resources
for acquiring knowledge through practice, an alterna-
tive that has been used is the application of virtual
labs in which classes can be held remotely; These lab-
oratories seek to consolidate the learning in class and
acquire additional knowledge (Ballu et al., 2016).
For example, the following are the main ad-
vantages of using virtual laboratories (Bonde et al.,
2014):
• Economic: Virtual systems turn out to be a more
profitable alternative in schools and universities,
since it allows taking classes in a laboratory of
high quality.
• Flexibility: You can easily create different virtual
experiments and these can involve different com-
ponents.
• Multiple Accesses: Multiple students can use the
same virtual laboratory at the same time.
• Configurable: It is possible to modify the param-
eters, allowing the creation of more adaptable ex-
ercises.
• Damage Resistance: Allows interaction with the
different components without running the risk of
damaging the equipment if an incorrect interac-
tion is made by the user.
• Visibility of Components: Because you work in a
virtual environment it is possible to see the inter-
nal structure of the different components.
3 PROPOSAL
3.1 System Proposal
In this research, students of the National University
of Saint Agustín of Arequipa (UNSA) are expected to
use virtual reality to learn physics concepts through
a virtual environment in which they interacted with a
Google Cardboard.
This immersive laboratory of physics is oriented
to university students who follow who follow the
physics curriculum of the UNSA. About the labora-
tory, three types of users have been identified:
1. The user who makes normal use of the laboratory
and learns.
2. The user who already knows the educational con-
tent, therefore will have little interest in learning.
3. The user who has problems using the laboratory.
In terms of the competencies and skills, students
have to achieve according to the national standards of
learning, progress maps are established where learn-
ing goals are defined, to identify what is expected to
be achieved with each competency.
One of the main problems identified when con-
ducting the different surveys and interviews with the
students is the great dependence that exists to a phys-
ical place when performing the laboratory practices,
due to this to realize the practices it is necessary to
request the laboratory classroom; which has time lim-
itations according to a pre-established schedule and
does not allow the repetition of such practices.
For this reason, experiments made on the labora-
tory are affected by a specific time interval and a lo-
cation with difficult access.
Evaluation of a Gamified 3D Virtual Reality System to Enhance the Understanding of Movement in Physics
397
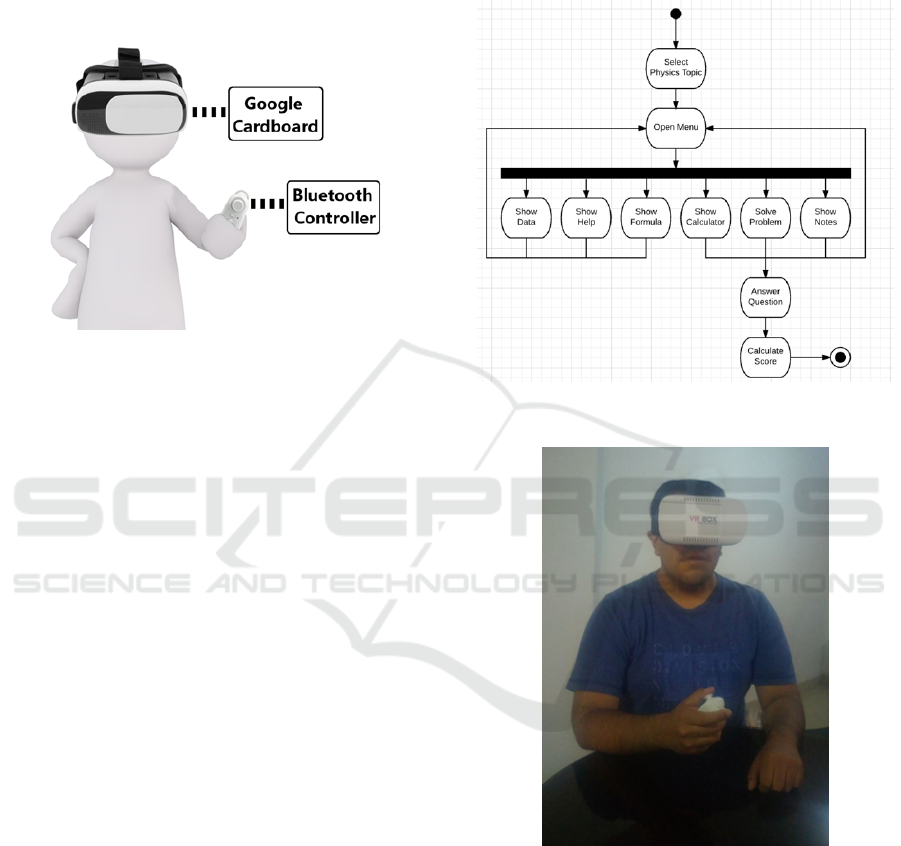
4 SYSTEM
4.1 Configuration
The system is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: System Configuration.
The software used for the development of the
system was the game engine Unity, the system was
created in conjunction with teachers of the area of
physics of the UNSA, the activities of the system
were based on the first year courses in the area of
physics, Which correspond to the displacement of ob-
jects, throwing of projectiles and the laws of newton,
in any case students using the application must belong
to the physics area.
The architecture of the system consists of a mobile
device with a resolution of 2560 x 1440 pixels with a
gyroscope sensor, an android version of 4.1 or higher;
Which will be used with a Google Cardboard that will
allow the virtual reality visualization and to achieve
the interaction with the system, a Bluetooth controller
will be connected to the mobile device.
We decided to use Google Cardboard to achieve
a greater accessibility using the app, because it is not
limited to a physical room. Before beginning to use
the application the user must place the mobile device
in his VR Box and start the application; when it starts,
show a splash screen; after this, user must select the
physics movement that they want to learn.
In order to make the selection, a hand-shaped icon
will be displayed in the center of the screen. To per-
form the interaction with the application, the Blue-
tooth controller must be used;
As for the visualization with the helmet, the
Google Cardboard gives the user freedom with re-
spect to the physical space to be able to realize a turn
of his head of 360 degrees and be able to observe the
whole scene.
4.2 Use Scenario
The system flowchart is shown in Figure 2. Scene of
using the system is in Figure 3.
Figure 2: Flowchart of the virtual physics laboratory.
Figure 3: Using the system.
Before beginning to use the application the user
must place the mobile device inside the VR Box and
start the application; when the application starts is dis-
played a splash screen, in which the user must select
the Movement in Physics that they want to study.
In order to make the selection, a hand-shaped icon
will be displayed in the center of the screen. To per-
form the interaction with the application, the Blue-
tooth controller must be used;
As for the visualization with the Google Card-
board, the user has freedom with respect to the physi-
CSEDU 2017 - 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
398

cal space to be able to realize a turn of his head of 360
degrees and be able to observe the whole scene.
Once selected the subject to study, a screen is pre-
sented in which a voice will guide the user with the
actions to be performed to solve the activity in the
virtual laboratory is shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4: System menu on the application.
At first the user must enter the data section to see
the different variables and their values, the formula
section must then be accessed in order to know the
formula needed to solve the problem, then you en-
ter the calculator section to make the corresponding
calculations, the calculations are saved in the notes
section, in the help section the user is allowed to use
coins obtained in the application to solve the problem,
where a step-by-step resolution of the problem is be-
ing carried out, and finally to write the correct answer
the user must write the answer in the resolution sec-
tion.
Once the correct answer is found the score is cal-
culated based on the time used to solve the exercise
and the numbers of attempts, to gain additional points
the user is asked a question about the subject of move-
ment in physics.
4.3 Educational Activities
In order to improve the user’s interest in carrying out
the educational activities, we chose to use gamifica-
tion techniques in conjunction with educational activ-
ities.
A score system is created to evaluate the perfor-
mance of each activity in which the user is rewarded
according to his performance, this rewards can be
used to purchase virtual objects within the application
or as an aid resolving the activities
5 PEDAGOGICAL EVALUATION
The next step after the development of the educational
software would be to do the pedagogical evaluation
with the help of teachers, who have pedagogical expe-
rience, following this sequence, it is necessary to use
a methodology for pedagogical validation of the edu-
cational software mentioned above, the methodology
chosen will be the one developed by Abreu (Abreu,
2010), which was applied in other work, where they
wanted to evaluate the didactic point of view of an
educational material (Aceituno and Bruschi, ).
This methodology consists of three groups of cri-
teria to be evaluated, which are: general usability,
didactic usability and usability of distance learning
websites (Abreu, 2010)
For purposes of this work we used only the group
of didactic usability. This group is composed of 10
criteria. The criteria to be evaluated in the didactic
usability are the following:
• Control of the student.
• Student activity.
• Collaborative / cooperative learning.
• Orientation to Objectives.
• Applicability.
• Value Added.
• Motivation.
• Evaluation of previous knowledge.
• Flexibility.
• Feedback.
5.1 Objective
The main objective is to recognize the pedagogical
value of the educational software developed, using a
methodology oriented to measure the didactic usabil-
ity.
5.2 Procedure
Once the methodology is chosen, it is necessary to
make a survey to apply this methodology. This sur-
vey is based on the methodology criteria for didactic
usability, which has 18 questions. The questions have
the alternatives of "Agree", "Partially agree", "Unde-
cided", "Partially disagree" and "Disagree". Ques-
tions are scored from 1 to 5 and mean the following
(5) Agree, (4) Partially agree, (3) Undecided, (2) Par-
tially disagree and (1) Disagree.
Evaluation of a Gamified 3D Virtual Reality System to Enhance the Understanding of Movement in Physics
399
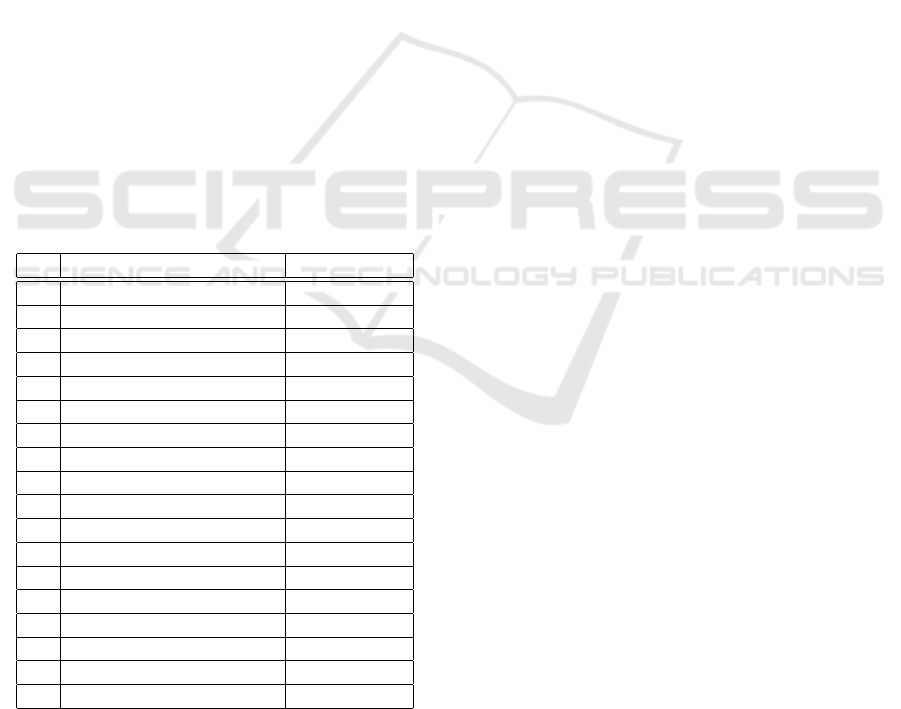
5.3 Result
The survey was applied to several teachers. The result
of the survey is shown in Table 1, Where the criteria
column represents the criteria evaluated, where some
criteria are represented with two questions in the sur-
vey, the second column represents the average score
obtained with each question.
Table 1: Results Obtained, Questions: 1. When I use the
application I felt that I had control over the tool and not the
other way around, 2. When I use the application, I have
different ways to get to the same action, 3. When I work
with the application, I can abstract myself so much that I
lose track of time, 4. The application allows me to interact
with other teachers, 5. You can define group jobs with the
application, 6. The application shows me through the prac-
tice how much progress I had in its use, 7. The application
itself shows why it is important to learn how to use it, 8.
The application is based on the idea "someone learns better
by practice", 9. The application fits into the student abili-
ties, 10. The images in the application help to learn, 11. It
is easier to learn topics with the application, than to learn
using conventional methods, 12. I want to learn as much as
I can from the application, 13. I would like to receive a high
rating on future evaluations of the application, 14. I can use
my previous knowledge when I use the application, 15. The
application helps by displaying previous information before
performing a complex task, 16. The application allows the
development of consecutive tasks, 17. When I make a mis-
take the application sends me a friendly warning, 18. The
application sends me a motivational feedback.
Criterion Average
1 Control of the student 4.714285714
2 Control of the student 4.857142857
3 Student activity 4.142857143
4 Cooperative learning 4.285714286
5 Cooperative learning 4.571428571
6 Orientation to Objectives 4.714285714
7 Orientation to Objectives 4.285714286
8 Applicability 4.142857143
9 Applicability 3.714285714
10 Value Added 5
11 Value Added 4.285714286
12 Motivation 4.857142857
13 Motivation 4.714285714
14 Evaluation knowledge 4.714285714
15 Evaluation knowledge 4.714285714
16 Flexibility 4.142857143
17 Feedback 4.285714286
18 Feedback 4.571428571
The results show a high value in score, all close to
5 or 4, meaning a general acceptance to the criteria of
didactic usability.
The didactic value of this software is validated ac-
cording to this methodology.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Through the tests carried out in the previous section
and according to the objectives we can conclude the
following:
• The results obtained from the point of view of
the teachers demonstrate that the educational soft-
ware developed has a high didactic utility.
• It is verified that when using virtual reality com-
bined with gamification the didactic value of the
educational software increases.
• It is shown that students of the UNSA can use vir-
tual reality to enhance the understanding of move-
ment in physics using Google Cardboard
• The educational software needs a feedback from
teachers with pedagogical experience.
The evaluation with more teachers and students to
measure the performance of the educational software
will be carried out as future work.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by CIENCIACTIVA,
CITEC, CONCYTEC and the UNSA. We thank our
colleagues from the area of education in the UNSA,
who provided insight and expertise that greatly as-
sisted the research.
REFERENCES
Abreu, A. d. (2010). Avaliação de usabilidade em soft-
wares educativos. Master’s thesis, Universidade Es-
tadual do Ceará, Fortaleza, Ceará, Brasil. Retrieved
July, 12:2012.
Aceituno, R. G. A. and Bruschi, S. M. Aplicaç ao da
metodologia aim-cid nos conceitos da disciplina sis-
temas operacionais, no domınio de gerenciamento de
processos.
Ballu, A., Yan, X., Blanchard, A., Clet, T., Mouton, S., and
Niandou, H. (2016). Virtual metrology laboratory for
e-learning. Procedia CIRP, 43:148–153.
Bonde, M. T., Makransky, G., Wandall, J., Larsen, M. V.,
Morsing, M., Jarmer, H., and Sommer, M. O. (2014).
Improving biotech education through gamified labo-
ratory simulations. Nature biotechnology, 32(7):694–
697.
CSEDU 2017 - 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
400

Bustos Sánchez, A. and Coll Salvador, C. (2010). Los en-
tornos virtuales como espacios de enseñanza y apren-
dizaje. una perspectiva psicoeducativa para su carac-
terización y análisis. Revista mexicana de investi-
gación educativa, 15(44):163–184.
Colegio, M. C. and Minnaard, V. (2016). Evaluación
por competencias en entornos virtuales de apren-
dizaje (eva). Revista Iberoamericana de Producción
Académica y Gestión Educativa.
Cummings, J. J. and Bailenson, J. N. (2016). How immer-
sive is enough? a meta-analysis of the effect of immer-
sive technology on user presence. Media Psychology,
19(2):272–309.
Deterding, S., Dixon, D., Khaled, R., and Nacke, L. (2011).
From game design elements to gamefulness: defin-
ing gamification. In Proceedings of the 15th inter-
national academic MindTrek conference: Envisioning
future media environments, pages 9–15. ACM.
Dicheva, D., Dichev, C., Agre, G., and Angelova, G. (2015).
Gamification in education: a systematic mapping
study. Educational Technology & Society, 18(3):1–14.
Fredes, C. A., Hernández, J. P., and Díaz, D. A. (2012).
Potencial y problemas de la simulación en ambientes
virtuales para el aprendizaje. Formación universitaria,
5(1):45–56.
Gibson, J. J. (2014). The ecological approach to visual per-
ception: classic edition. Psychology Press.
Gobbetti, E. and Scateni, R. (1998). Virtual reality: Past,
present, and future. Virtual environments in clini-
cal psychology and neuroscience: Methods and tech-
niques in advanced patient-therapist interaction.
Helsel, S. (1992). Virtual reality and education. Educa-
tional Technology, 32(5):38–42.
Laffont, P.-Y., Martin, T., Gross, M., Tan, W. D., Lim, C.,
Au, A., and Wong, R. (2016). Rectifeye: a vision-
correcting system for virtual reality. In SIGGRAPH
ASIA 2016 Posters, page 8. ACM.
MacIsaac, D. et al. (2015). Google cardboard: A vir-
tual reality headset for $10? The Physics Teacher,
53(2):125–125.
Mazuryk, T. and Gervautz, M. (1996). Virtual reality-
history, applications, technology and future.
Ohta, Y. and Tamura, H. (2014). Mixed reality: Merging
real and virtual worlds. Springer Publishing Com-
pany, Incorporated.
Ott, M., FREINA, L., et al. (2015). A literature review
on immersive virtual reality in education: state of
the art and perspectives. In Conference proceedings
of» eLearning and Software for Education «(eLSE),
number 01, pages 133–141. Universitatea Nationala
de Aparare Carol I.
Saxena, N., Kyaw, B. M., Vseteckova, J., Dev, P., Paul,
P., Lim, K. T. K., Kononowicz, A., Masiello, I., Tu-
dor Car, L., Nikolaou, C. K., et al. (2016). Virtual re-
ality environments for health professional education.
The Cochrane Library.
Steuer, J. (1992). Defining virtual reality: Dimensions de-
termining telepresence. Journal of communication,
42(4):73–93.
Evaluation of a Gamified 3D Virtual Reality System to Enhance the Understanding of Movement in Physics
401
