
Using Facebook to Transfer Knowledge into
Practice and Aid Student, Lecturer and Content Interaction
A Case of Bachelor of Information Technology Undergraduate Students
at Makerere University
Emily Bagarukayo
1
, Dick Ng’ambi
2
, Rehema Baguma
1
and Proscovia Namubiru Ssentamu
3
1
Department of Information Systems, Makerere University, Kampala, Uganda
2
School of Education, University of Cape Town, Capetown, South Africa
3
Quality
Assurance Department, Uganda Management Institute, Kampala, Uganda
Keywords: Knowledge Transfer, Facebook, Interaction, Collaboration, Operating Systems.
Abstract: Employers have criticised graduates for inadequate skills to apply knowledge into practice due to the
traditional teaching and learning methods which concentrate more on theory than practice. Technology
affords several teaching and learning methods like social media which students are already motivated to use.
The research therefore used Facebook technology to facilitate students’ application of operating systems
knowledge to record and upload a video installing a virtual machine and operating system onto a group; to
promote content access, and interactive and cooperative learning. The results from the study show that the
overall effect of Facebook on students learning process and experience was positive because it enabled
putting knowledge into practice, sharing, collaboration, interaction, flexibility and learner – centred
activities, among others. Therefore, to increase learning outcome, motivation, desire and interest, new
educational technologies should continuously be explored by educational institutions, educators and learners
for teaching and learning in the digital era. In this light we recommend that Facebook should be assessed in
more studies and integrated as a tool for learning at the university since students appreciate it, find it easy to
use and familiar.
1 INTRODUCTION
Although social media, like Facebook, is used for
sharing learning experiences, research, academic
events and getting latest information (Hussain et al.,
2012), its use for learner-centric teaching is
underutilized. Facebook has potential of sharing of
videos, which can aid in transferring knowledge into
practice, which is a challenge today. In Uganda there
is more concentration on theory compared to
practice, which leads to a mismatch between what
students expect and what educationists deliver. The
education system currently does not emphasize use
of technology and practical skills development.
Facebook technology is an online application that
students are familiar with and can support, connect
and engage students outside formal in-class hours
(Monopolis, 2014). Facebook has stronger roots in
the academic community, since it was developed as
a university project (Bosch, 2009). Beldarrain
(2006) notes that today’s workplace requires
individuals who can create and collaborate within
constraints of time and place. Therefore, he
highlights the need for real-time communication and
tools to create a stronger learning community where
members can build expertise and develop problem-
solving skills. For students to be prepared for the
complex and rapid changing work demands, they
need a variety of skills including analysis, critical
thinking, decision-making and problem solving
(Mbarika et al., 2010). Therefore, educationists need
to tap into technology that affords students the
ability to learn effectively learning and be
productive to address this mismatch.
2 BACKGROUND
Makerere University has not yet embraced e-
learning to its full potential since technology use in
402
Bagarukayo, E., Ng’ambi, D., Baguma, R. and Ssentamu, P.
Using Facebook to Transfer Knowledge into Practice and Aid Student, Lecturer and Content Interaction - A Case of Bachelor of Information Technology Undergraduate Students at Makerere
University.
DOI: 10.5220/0006329104020410
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2017) - Volume 1, pages 402-410
ISBN: 978-989-758-239-4
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

teaching and learning is noncompulsory. An optional
e-learning policy exists for the individual Colleges
or lecturers. A customized Moodle, Makerere
University E-learning Environment (MUELE), is
used to disseminate notes to students, however,
collaboration tools are not used. The lecturers only
upload notes which students access at convenience,
therefore, there is limited interaction, engagement,
and collaboration.
2.1 Context, Problem and Goal
Bachelor of Information Technology second year
students undertaking the Operating Systems (OS)
course unit took part in the study. The course unit
provides basic knowledge and skill in using,
evaluating and managing existing OSs. Employers
have expressed concern that graduates hardly apply
knowledge and skills acquired to solve real life
problems at work (Bagarukayo et al., 2012; Mbarika
et al., 2010). The education system concentrates
mainly on theory and not practice, which contributes
to this problem. Therefore the mismatch between
teaching methods in the digital era does not address
different learning styles. Therefore, there is need to
develop learning activities where students can
transfer knowledge into practice to develop skills to
address real world issues and yield greater
productivity and return on investment. Therefore,
the goal was facilitating students’ application of OS
knowledge to record and upload a video installing a
virtual machine and OS onto a Facebook group; to
promote content access, and interactive and
cooperative learning.
3 LITERATURE REVIEW
3.1 Transferring Knowledge into
Practice
Learning is acquiring new information, knowledge
and sharing best practices and for a permanent
learning process, time should be invested in
transferring knowledge into practice and
understanding the outcomes (Tenkasi and Hay,
2004). Hands-on opportunities provide a rich
learning space in supporting students to transfer
knowledge into practice and test newly acquired
skills. Applying newly learned skills and behaviors
for the workplace greatly enhances knowledge
retention. The gap between knowledge generated
through studies, evaluations and application of
these findings in practice needs to be addressed.
Bloom’s Taxonomy emphasizes the need for
holistic learning (Churches, 2001). Before one
analyzes a concept, they must be able to apply it and
before they can evaluate its impact, they must have
analyzed it and before they create it they must have
remembered, understood, applied, analyzed and
evaluated it. Therefore, before students create an
artifact, they should remember, understand, apply,
analyze and evaluate it. Bloom notes that applying
knowledge is using information, concepts and ideas
in a new situation and includes implementing,
carrying out, using, executing, doing, running,
loading, playing, operating, uploading, sharing and
editing (Churches, 2001). Applying involves digital
activities of running and operating, playing,
uploading, and editing.
3.2 Research Studies That Have Used
Facebook
Murumba et al., (2015) noted that integrating social
networking tools into learning is beneficial to
students for better engagement and motivation,
better instructional materials, better communication
and interaction, increased family involvement and
application of real world skills. They state that
teachers enhance professionalism and collaboration
with peers and gain opportunities to build
relationships with students. Bagarukayo and Kalema
(2015) advocate for social software approach to
promote learning activities that improve the learning
process since there is a paucity of research on its use
for academic purposes in Africa as compared to the
developed world. Students are engaged in social
media platforms and therefore educators need to tap
these spaces for the learning process. Monopolis
(2014) said Facebook facilitates communication and
collaboration between faculty and students, allows
interaction and information sharing. Bosch (2009)
reported that learners are more engaged with
Facebook and prefer it to the Vula Learning
Management System (LMS) and a lecturer said it
was quicker to ‘talk’ to learners on Facebook than
finding them in class. Facebook enabled lecturers to
be more accessible and approachable in a less formal
environment and made students ask questions freely.
Facebook is effective for academic discussions
because students find it familiar and easy to navigate
(Hurt et al., 2012). Ractham et al., (2012) reported
that 55% of the students found Facebook helpful in
learning and 78% found it a useful supplemental
learning tool. Facebook facilitates interactive
communication, enhances participation and
Using Facebook to Transfer Knowledge into Practice and Aid Student, Lecturer and Content Interaction - A Case of Bachelor of Information
Technology Undergraduate Students at Makerere University
403

discussion, and provides personal and professional
growth (Barczyk and Duncan, 2013). It facilitates
the development of community of practice that
pinnacles in knowledge sharing, collaboration and
interaction, and learner-centered activities. Rinco
and Sandoval (2014) say Facebook was the greatest
host (81%) therefore, making it the most popular
social network. Learners were more familiar with
Facebook and preferred it for discussions (Brady et
al., 2010). Cloete et al., (2009) notes the benefits of
Social Networking Sites like Facebook as a higher
level of engagement, development of digital literacy
skills, and integration in learners’ daily practices,
potential to make identity information more relevant
during class discussions, adding a ‘social’ peer to
peer component and managing alumni through the
group.
According to Beldarrain (2006), technology as a
delivery method should encourage contact between
students and faculty, develop reciprocity and
cooperation among students, use active learning
techniques, give prompt feedback, emphasize time
on task, communicate high expectations, and respect
diverse talents and ways of learning. Facebook as a
tool affords these 7 principles and was used as an
interaction tool to increase collaboration between
learners and lecturer.
In conclusion, Facebook was used because it is
the most popular social media platform, students
were already motivated to use it, makes it easy to
combine teaching and learning with social
interaction which makes learning interesting,
facilitates students’ engagement with one another
and instant access to lecturers, brings interaction and
collaboration with content, peers, and teachers into
the classroom and forms communities of practice,
which facilitates development of Higher Order
Cognitive Skills.
4 APPROPRIATE
FRAMEWORKS TO DEFINE
EDUCATIONAL GOAL
4.1 Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy
Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy (BDT) addresses new
objectives, processes and actions presented by
emergence of ICTs into the classroom and their
impact on students’ lives. BDT introduced new
digital verbs that aid collaboration, which are
elements to facilitate higher order thinking and
learning. Collaboration is a 21
st
century skill integral
to the learning process and has an increasing
influence on learning. Collaborating and sharing are
higher order thinking skills, which are facilitated by
digital media and increase learning influence. Social
networking is a key element of collaborating and
networking because it forms links between people
and helps to develop networks.
4.2 Anderson’s Interactions
Framework
Anderson (2008) states that for learning to be
effective, there has to be interaction between
students, teachers and content. Therefore, the tool
identified needed to afford these interactions. The
task of facilitating students’ application of OS
knowledge emphasized teacher –content, teacher-
student, student- student and student –content
interactions using technology to enhance effective
learning.
5 METHODOLOGY
5.1 e-Learning Design Methodology
Framework
Bowers Affordance analysis framework was used to
match requirements of this task with affordances of
the tool (Bower, 2008). Affordances refer to the
perceived and actual properties of the thing. Bower
(2008) classified affordances of e-learning
technologies to include Media, spatial, temporal,
navigation, emphasis, synthesis, access control,
technical, usability, aesthetics and reliability
affordances. Facebook has the affordances required
to facilitate achievement of the learning and teaching
objectives. Affordance analysis was used as follows:
1. Identify the Educational Goals
The intentions of the learning design were
facilitating students’ application of operating system
(OS) knowledge to record and upload a video
installing a virtual machine (VM) and OS onto a
Facebook group; to promote content access,
collaborative and cooperative learning.
2. Postulate the Suitable Tasks to Satisfy the
Educational Goals
a) Understand the key concepts
Students needed to research on ‘how to install
CSEDU 2017 - 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
404

Virtual box software and UNIX OS and download
an ISO image of Ubuntu 14.04 OS’. Students were
required to explain in video - what file systems they
chose for the OS to use, justify their choice and
explain use of swap space.
b) Apply knowledge acquired to install the Virtual
Machine and OS and Record and Upload Video
Students needed to use knowledge from research to
practically install VM and OS onto VM while video
recording themselves and upload the video on the
Facebook group.
3. Determine the Affordance Requirements
of the Tasks
a) Understand the key concepts
In order for students to research about installation of
the VM and OS, read-ability, write-ability, search-
ability, view-ability, listen-ability, access-ability,
browse-ability, data-manipulation-ability, link-
ability, download-ability were necessary for
reviewing, searching, downloading, adjusting and
relating information.
b) Apply knowledge acquired to install Virtual
Machine and OS and Record and Upload video
In order for students to install the VM and OS they
needed to set up the software and create Video
installing the OS on VM. Therefore, Record-ability,
watch-ability, move-ability, combine-ability, listen-
ability, view-ability, video-produce-ability, focus-
ability, resize-ability, playback-ability share-ability,
and permission-ability were necessary for recording,
playing back, editing, putting together the video and
posting it on the group.
4. Determine affordances from Facebook
The technology considered for this task was
Facebook because it has affordances of
‘uploadability’, ‘downloadability’,
‘commentability’, ‘sharability’ and ‘likability’ to
enable this task to be accomplished.
a) Understand the key concepts
The tool needed to afford read-ability, write-ability,
search-ability, view-ability, listen-ability, access-
ability, data-manipulation-ability, link-ability and
browse-ability by allowing students to research and
‘download-ability’ for OS and Virtual box software,
which were necessary for
reviewing, searching,
downloading, adjusting and relating information.
b) Apply knowledge acquired to install Virtual
Machine and OS and Record and Upload video
A tool was needed to enable students’ record
themselves installing the OS and VM and upload the
video on Facebook group. The technology needed to
afford Record-ability, video-produce-ability,
combine-ability, watch-ability, move-ability, resize-
ability, focus-ability, listen-ability, view-ability,
playback-ability, share-ability, and permission-
ability necessary for recording, playing back,
editing, putting together the video and posting it on
the group.
5. e-Learning Task Design
The task required students to create a video
recording installing a VM and OS and post it for
peers and lecturers to comment and interact thereby
learning from peers and lecturers online as a
supplement to classroom. The process of integrating
available and required affordances, that is, selecting
the appropriate tool to match tasks was as follows:
a) Understand the key concepts
Facebook is a tool, which enables students to
research and understand key concepts. It provides
affordances for reviewing, searching, downloading,
adjusting and relating information.
b) Apply knowledge acquired to install Virtual
Machine and Operating System and Record and
Upload video
Students installed the OS and VM on their machines
and used their phone or computer cameras to record
the video. Facebook provides affordances for
recording editing, putting together the video.
Facebook provides affordances necessary for
playing back the video and posting it on the group.
The researcher chose Facebook which students are
already motivated to use to account for motivation
and student ability.
Facebook affords social networking, seeking
peer support, community building, student activism,
general communication, sharing information and
maintaining group and personal communication on
public spaces. Facebook also affords students with a
shared connection and collaboration with students,
lecturers and communities of practice, Interaction
and engagement with students, teachers and content
and Chatting, liking, posting, uploading and
downloading video, text and audio file.
Using Facebook to Transfer Knowledge into Practice and Aid Student, Lecturer and Content Interaction - A Case of Bachelor of Information
Technology Undergraduate Students at Makerere University
405

6 DATA COLLECTION AND
ANALYSIS
a) Questionnaire to Determine Students’
Attitudes and Perceptions on Facebook
Use
A validated questionnaire was used to determine
attitudes and perceptions of students on the use of
Facebook to accomplish the video upload
assignment. The results are presented in section 10.
b) Data Analysis
The qualitative data collected was analyzed by
reading individual responses as summarized in 10.1.
The quantitative data collected was analyzed using
MS Excel to total up the number of responses on
each question as presented in table 2.
7 RESULTS
The researchers created a Group page in Facebook
for students taking OS course unit. Through the
group students had discussions, commented on
posts, posted videos, links, uploaded and shared
created videos. The task required students to create a
video, using mobile phones or cameras, installing
OS and uploading it to the group to enable peers
interact, critique it and learn from one another in the
process. They learnt by doing, by creating the video,
from peers, lecturers, and content uploaded by peers
and lecturers which promoted use of educational
technologies for learning and teaching. It was
important to use Facebook because it affords
students the ability to communicate, interact, and
collaborate which enabled them to put knowledge
into practice in a new context.
BDT helped understand that students needed to
attain higher levels of thinking skills to enable them
acquire practical skills. Therefore, it was necessary
to create learning activities that make students put
knowledge into practice to develop hands on skills.
BDT was applied to train students holistically to
attain knowledge, skills and attitudes, which
addressed all levels of three domains. Students were
trained from lowest to highest levels of the BDT by
teaching them theory about installing an operating
system and virtualization in an introduction lecture,
which enabled them to gain skills at lower levels of
Remembering and Understanding. At ‘Applying’
level digital activities were carried out by students
during video creation and upload on Facebook.
Activities that enabled ‘applying’ include
demonstration by video, collaboration by students
interacting and sharing ideas, playing and editing.
Digital additions include commenting and
reflecting, reviewing, posting, moderating,
collaborating and networking, testing (alpha and
beta) and validating. The activities that promoted
this level include chat rooms, discussions,
collaborating tools, camera, searching, presentation,
recorders, posting, collaborating and networking.
Students attained ‘Evaluating’ level by commenting,
posting, testing, and experimenting during the task.
The creating level involves designing, constructing,
planning producing, inventing, devising and making
the video which students acquired during video
creation, editing and upload on Facebook.
The students put together their ideas from
research on VM and OS installation, and created and
posted the video on Facebook. Facebook was used
as a tool for collaborating and sharing or publishing
the video, therefore, HOCS were achieved in the
task. Students did the assignment practically, which
enabled them gain skills at higher levels of Analysis,
Applying, Evaluating and Creating. This helped
students to practically install the OS onto VM
thereby applying knowledge into practice. Ensuring
that students produced video as a final product
enabled them to gain ‘creating’ skills, at the highest
level of taxonomy, therefore practical skills were
attained to address industry needs of putting
knowledge into practice. Therefore, before students
created the video, they had to remember, understand,
apply, analyze and evaluate it. Collaborating,
commenting, posting, networking, chatting, texting,
reviewing, questioning, replying which are
collaboration spectrum of BDT at all levels of
cognitive domain happened. For effective learning,
students required skills of interaction and
engagement provided by the platform because it
affords collaboration and communication needed for
uploading and presenting video recording, sharing
ideas, and commenting on peers’ videos to enhance
the learning process.
Facebook has facilities which introduced agents
that increased interaction, it is not dependent on
institution’s infrastructure and empowers both
educator and student. Students also have face-to-face
interactions with lecturers and peers as emphasized
by Anderson’s (2008) interaction framework for
effective learning. Students interacted and
‘followed’ their mentors and society leaders who
influenced learning. Facebook promotes innovative
and transformative learning. Students were involved
CSEDU 2017 - 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
406
in choosing the cover photo for the group to
personalize the ‘BIT II CSC 2200 Operating
Systems class’ page and feel at ‘class’. The peers,
lecturer and systems administrator followed
students’ discussions to monitor progress.
a) Facebook Usage Findings
Students were actively engaged, appreciated and
enjoyed use of Facebook as a communication and
interaction platform basing on participation.
Students were very excited and interactive. They
created a video and posted it on the group to
supplement and complement collaborative activities
introduced in classroom. Students learnt at all levels
of cognitive domain of BDT (Churches, 2001)
because the task enabled them to carry out different
activities.
Post-Assignment Questionnaire Responses
a) Quantitative Findings
A validated students’ questionnaire used to
determine ‘perceptions and attitudes about use of
Facebook for the assignment’ basing on a likert
scale ranging from Strongly Disagree, Disagree,
Neutral, Agree and Strongly Agree, was filled by 48
students after uploading video. The results of the
number of individual responses per question are
shown in Table 2 as follows (Where S= strongly
disagree; D= disagree; N= neither agree nor
disagree; A= agree; SA= strongly agree; FB=
Facebook) 523 responses positively (Strongly Agree
and Agree) rated Facebook as a convenient platform
for classroom discussions and allowed them to
interact with classmates. Students noted that
Facebook should be used as a learning tool, since it
had changed their view of the course, was well
integrated into assignment, was more effective and
preferred than MUELE, had an overall positive
experience, made students feel more connected,
enhanced their OS understanding, enabled lecturer-
student interaction, enhanced experience of
participation, allowed finding and sharing of
resources, provided collaborative opportunities,
encouraged learner-centered activities and allowed
flexibility in learning. However, 123 responses were
neutral, while 89 either disagreed or Strongly
disagreed with the statements. Therefore, the overall
effect of Facebook on students learning process and
experience was positive because it enabled putting
knowledge into practice, sharing, collaboration,
interaction, flexibility and learner – centered
activities, among others. In addition, the
questionnaire had open-ended questions to capture
students’ views regarding their experience,
challenges and recommendations using Facebook for
the assignment.
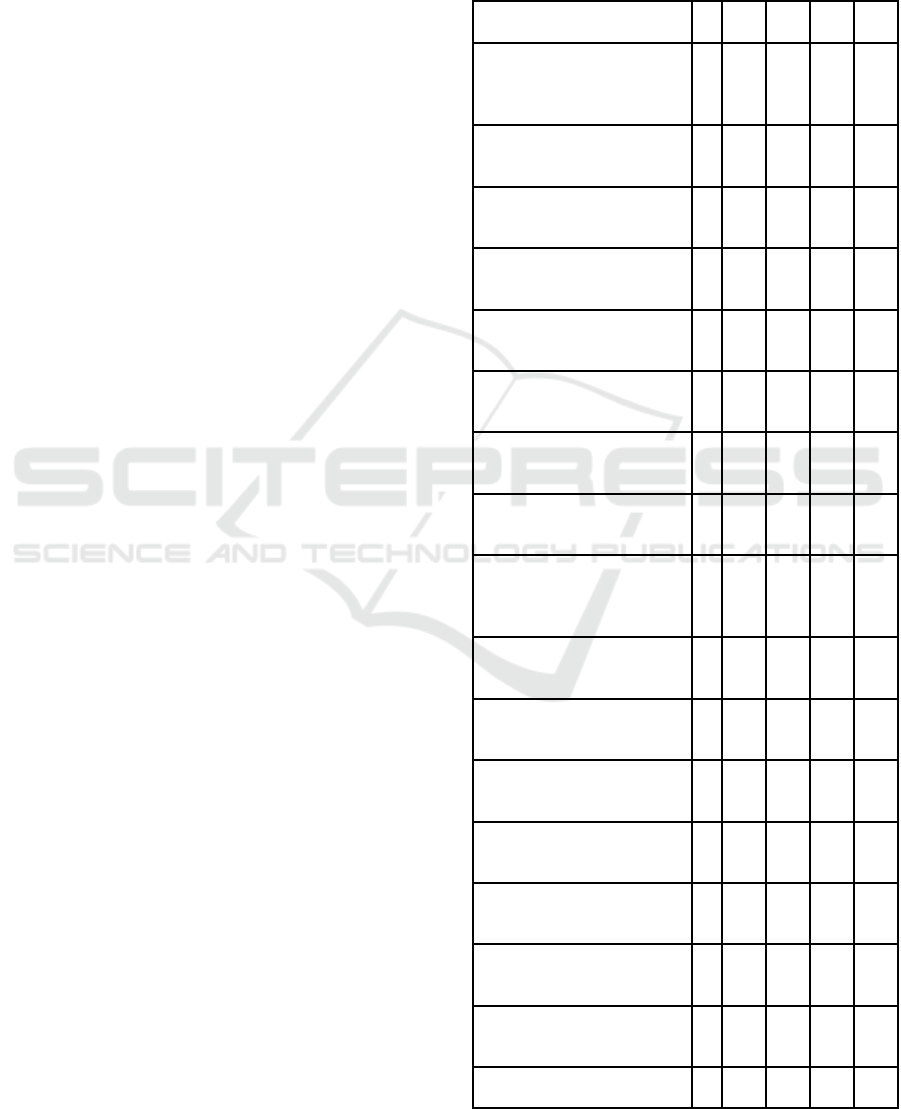
Table 1: Total of individual responses per question.
Question / Response S D N A SA
1. Facebook for classroom
discussions is very
convenient
3 4 3 19 18
2. Facebook allows me to
interact with classmates
0 3 4 20 18
3. Facebook should be used
as a learning tool
1 5 6 28 10
4. Facebook changed my
overall view of the course
1 8 17 14 6
5. Facebook was well
integrated into the assignment
3 3 6 26 6
6. Facebook was more
effective than MUELE
1 2 7 15 20
7. I preferred using Facebook
over MUELE
3 2 8 15 19
8. Overall experience using
Facebook was very positive
2 5 3 22 15
9. I felt more connected to
fellow students using
Facebook
2 2 7 20 16
10.FB enhanced my
understanding of OS
3 8 11 17 8
11.FB enabled me to interact
with the lecturer more
2 3 5 20 13
12. FB enhanced my
experience of participation
1 3 9 22 13
13. FB allows me to find and
share educational material
2 4 8 20 10
14. FB provided collaborative
learning opportunities
1 4 9 19 14
15. FB encourages learner-
centred activities
2 2 12 22 7
16. FB allows me flexibility
in learning
1 3 8 27 4
Total 28 61 123 326 197
Using Facebook to Transfer Knowledge into Practice and Aid Student, Lecturer and Content Interaction - A Case of Bachelor of Information
Technology Undergraduate Students at Makerere University
407

b) Qualitative Findings
i) Students’ Experience using Facebook
The students noted that it was a good experience
because it made them active, learning was more
effective, convenience of time and place, interaction,
information distribution was easy, getting notes was
faster. Facebook was easy to use, access and
familiar, promoted peer and self-learning, and
instant updates. It was better for mobility purposes,
availability and accessibility, was not limited and
enabled bonding with classmates and Online
discussions, Interactions with lecturer and constant
communications. The experience was educative
because even without prior knowledge they clearly
understood concepts, and changed overall view of
learning.
One student noted that using Facebook was not a
good experience because of waiting for approval to
join. However, majority of students characterized
the affordances of Facebook as per Anderson (2008)
and the tool bringing fun in learning.
ii) Conceptual Understanding
Majority of students positively rated using Facebook
as improving their conceptual understanding because
it was good, exciting, interesting, practical and
interactive, and helped understand concepts,
approach made students more involved, promoted
multiple views of activities and connecting with
peers helped them learn better, promoted Learning
by doing, and built confidence. Facebook is a good
platform and greatly improves teacher-student
interaction, research-intensive and more
participatory, promoted access to educational
materials from anywhere, good lecturer-student
relationship, idea generation, technical skills,
knowledge sharing, Peers approached others which
helped them learn more. Although one student noted
he did not learn the concepts better because
explaining in person would have been a better
option, the rest found the use of Facebook as further
promoting their practical, research, communication
and interpersonal skills, and consequently improving
their conceptual understanding.
iii) Students’ Challenges using Facebook
Students noted the challenges of time, cost and
difficulty in uploading large videos, some phones
could not support Facebook, poor network
connections, Privacy of information shared, not all
students were on Facebook, pseudo names usage,
few students on platform at times, others did not
want to mix social life with academic purposes, and
lack of personal computers. Most challenges were
related to resource constraints, implying that limited
resources are a hindrance in using social media for
learning.
iv) Students’ Recommendations on using
Facebook for Learning
Students made recommendations that Facebook
should be used for future assignments and learning
opportunities because it is simple to use, enables
interaction, peer learning for understanding concepts
easily. It should be customized for academic work
and lecturers should use it as a learning and grading
tool. In summary, students recommend the use of
Facebook and its integration with other tools to
enhance research, teaching, learning and assessment.
8 PROOF OF CONCEPT
The tool in action provides evidence of the prototype
test and show that students put knowledge acquired
into practice by uploading videos of installation of
VM and OS on VM and show interaction between
students, peers and lecturers and using Facebook to
solve learning problems. Some students uploaded
videos after a struggle thereby learning by doing.
Uploading of videos show the educational goal was
achieved since students managed to learn how to
install VM and OS and recorded, uploaded or posted
the video on Facebook. Facebook affords interaction
relevant for effective learning by lecturers
commenting on students’ posts and student to
student interactions and problem inquiry.
9 DISCUSSION
The students researched and uploaded a video
recording installing a VM and installed the UNIX
(Ubuntu 14.04) OS onto VM and the class Facebook
group ‘BIT II CSC2200 Operating Systems Class’.
Since students were already familiar with Facebook,
they did not hesitate using it and enjoyed the
experience. From the results, it is clear that the
overall experience was positive. Most students
indicated increase in motivation, collaboration, and
interaction and believed they learned better through
this approach. Therefore, use of Facebook in
teaching and learning has potential to facilitate
application of knowledge to solve real world
problems.
CSEDU 2017 - 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
408

The student who observed that Facebook was not
a good experience because of waiting for approval to
join the group is unfortunate because the
administrator was online and approved requests
immediately. The student who said they did not
learn concepts better because explaining in person
would have been a better option emphasizes that
students have various learning styles, which need to
be addressed in the learning process. The Web
provides several tutorials on YouTube where this
student could have found explanations as required of
them. The lecturer also explained in class in the
general introduction to operating systems and
virtualization.
10 CONCLUSION AND
RECOMMENDATIONS
The research focused on Student’s inadequacy to
transfer knowledge acquired in class into practice.
Further, lecturers teach practical courses in a
theoretical way curtailing students’ acquisition of
the expected practical skills. The lecturer gave an
introductory lecture about OSs, and installations.
Students carried out research on how to install OS
and VM, and recorded a video installing OS and
uploaded it on Facebook group, and uploaded the
videos and later presented them in class. From the
perceptions, majority thought they learnt better with
this approach and therefore, it curbs the problem.
Technology affords new ways of learning using a
variety of tools and media that address different
needs of digital learners and provide various skills
required. Technology provides knowledge sharing
opportunities where students and educators can
access content and network with peers to share best
practices from different institutions to develop deep
learning approaches amongst students and lead to
production of new knowledge and artifacts and
transform institutions and society. Therefore, to
increase learning motivation, desire and interest it is
important to design meaningful learning tasks and
use of new educational technologies should
continuously be explored by institutions, educators
and learners for teaching and learning in this digital
era.
The current experiment enabled students to
transfer knowledge acquired in class into practice
and thereafter upload the video onto Facebook
where they interacted with peers, content and
lecturer. In future the study should be repeated with
more course units and topics to assess Facebook
effectiveness, integrated as a tool for learning.
Students without Facebook accounts should be
accommodated, and challenges of network
connectivity and shortage of computers addressed.
REFERENCES
Anderson, T. (2008). Toward a theory of online learning,
Theory and practice of online learning, 2(2008): 15-
44.
Author unknown (n.d). Putting Knowledge into Action to
Prevent Violence. Applying Science Advancing
Practice (ASAP). Enhanced Evaluation and Actionable
Knowledge for Suicide Prevention Series.
Bagarukayo E., & Kalema, B.M. (2015). Evaluation of
eLearning Usage in South African Universities: A
Critical Review. International Journal of Education
and Development using Information and
Communication Technology (IJEDICT), 2015,
11(2):168-183, ISSN: 1814-0556.
Bagarukayo, E., Weide, Th. P. van der., Mbarika, V. W.,
& Kim, M. S. (2012). The Impact of Learning Driven
Constructs on the Perceived Higher Order Cognitive
Skills Improvement: Multimedia vs. Text.
International Journal of Education and Development
using Information and Communication Technology
(IJEDICT), 8(2):120-130, ISSN: 1814-0556.
Barczyk, C. C. & Duncan, D. G. (2013). Facebook in
Higher Education Courses: An Analysis of Students’
Attitudes, Community of Practice, and Classroom
Community. International Business and Management,
6(1):1-11; DOI: 10.3968/
j.ibm.1923842820130601.1165; ISSN 1923-841X
[Print] ISSN 1923-8428 [Online]
Beldarrain, Y. (2006). Distance Education Trends:
Integrating new technologies to foster student
interaction and collaboration. Distance Education,
27(2): 139–153. ISSN 0158-7919 (print); 1475-0198
(online) /06/020139–15 © 2006 Open and Distance
Learning Association of Australia, Inc. DOI
10.1080/01587910600789498.
Bosch, T. E. (2009). Using online social networking for
teaching and learning: Facebook use at the university
of Cape Town. Communication: South African Journal
for Communication Theory and Research, 35:185–
200.
Bower, M. (2008). Affordance Analysis – matching
learning tasks with learning technologies. Educational
Media International, 45(1): 3-15.
Brady, K. P., Holcomb, L. B., & Smith, B. V. (2010). The
Use of Alternative Social Networking Sites in Higher
Educational Settings: A Case Study of the E-Learning
Benefits of Ning in Education. Journal of Interactive
Online Learning, 9: 151-170. www.ncolr.org/jiol,
accessed 20 November 2014.
Churches, A. (2001). Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy.
Cloete, S., de Villiers, C., & Roodt, S. (2009). Facebook
as an academic tool for ICT lecturers. SACLA '09
Using Facebook to Transfer Knowledge into Practice and Aid Student, Lecturer and Content Interaction - A Case of Bachelor of Information
Technology Undergraduate Students at Makerere University
409

Proceedings of the 2009 Annual Conference of the
Southern African Computer Lecturers' Association,
16-22 ACM, New York, US.
Hurt, N. E., Moss, G. S., Bradley, C. L., Larson, L.R.
Lovelace, M. D., Prevost, L. B., Riley, N., Domizi, D.,
& Camus, M. S. (2012). The Facebook Effect: College
Students’ Perceptions of Online Discussions in the
Age of Social Networking. International Journal for
the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning, 6(2):1-24.
Hussain, I., Gulrez, N., & Tahirkheli, S.A. (2012).
Academic Use of Social Media: Practices and
Problems of University. 2012 international conference
on Education and Management Innovation. IACSIT
Press.
Mbarika, V., Bagarukayo, E., Hingorani, V.,Stokes, S.,
Kourouma, M., & Sankar, C. (2010). A Multi-
Experimental Study on the Use of Multimedia
Instructional Materials to Teach Technical Subjects.
Journal of STEM Education: Innovations and
Research. Special Edition Winter 2010. 9(3).
Monopolis, A. (2014). Interactive Collaboration Using
Facebook. The innovative educator. Center for
educational resources. Pedagogy Forum.
Murumba, J., Micheni, E., & Njuguna, A. (2015).
Evaluating Preparedness for Social Networks
Integration into Learning: A Case Study of Inoorero
University. 3rd IST Africa International Conference.
6-8 May, Lilongwe, Malawi, ISBN:
DOI:10.1109/ISTAFRICA.2015.7190523 Publisher:
IEEE.
Ractham, P., Kaewkitipong, L., & Firpo, D. (2012). The
Use of Facebook in an Introductory MIS Course:
Social Constructivist Learning Environment. Decision
Sciences Journal of Innovative Education, 10(2):165-
188.
Rinco, J. G. C. & Sandoval, J. A. L. (2014). Use of social
networks, a path to training in blended learning
community. Proceedings of the third international
conference on informatics and applications.
Tenkasi, R. V., & Hay, G. W. (2004). Actionable
Knowledge and Scholar-Practitioners: A Process
Model of Theory-Practice Linkages. Systemic Practice
and Action Research, 17(3):177-206.
CSEDU 2017 - 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
410
