
Process Development for the Liquid-sensing Enterprise
Carlos Agostinho
1,2
, José Ferreira
1,2
, Joaquim Pereira
2
, Catarina Lucena
1
and Klaus Fischer
3
1
Centre of Technology and Systems, CTS, Uninova, 2829-516, Caparica, Portugal
2
Department of Electrical Engineering, FCT, NOVA University of Lisbon, 2829-516, Caparica, Portugal
3
DFKI GmbH, 66123, Saarbrucken, Germany
Keywords: MDA, MDSEA, Enterprise Interoperability, Liquid-sensing Enterprise, Business Process.
Abstract: Servitization and product-based services are used to support the integration of products and services with
customers, enabling companies to maintain a competitive advantage in their markets. However, in order to
achieve these capabilities is necessary to have flexible processes and services. The enterprise needs to
become self and context aware to meet these new challenges, and with the Internet-of-Things development,
resources can be shared across companies to reduce costs. Enterprise integration is an essential component
of enterprise and service engineering but traditional modelling techniques need to evolve and become more
dynamic, separating concerns but at the same time promoting knowledge reuse. This paper contributes to a
more flexible environment for information systems and service development, proposing a model-driven
framework for dynamic process development in the enterprise of the future. It applies the concept of the
liquid-sensing enterprise following the Osmosis processes paradigm, supporting the enterprises to model
and design their processes at business and technical level. With the support of a modelling toolbox the
enterprises are able to parameterize their processes and accelerate the advancement from the design phase
into services execution phase.
1 INTRODUCTION
In today’s economy, to achieve customers’
satisfaction, enterprises need to be able to deliver
products tailored specifically to each customer’s
needs. However, this can result in a challenging
environment that mixes manufacturing flexibility
with constantly evolving information systems and
services characterized by high volumes of
information (Friedman, 2006). A single final
manufactured product is often processed in many
companies, countries, and crossing several systems
in a collaborative process. Hence, a growing
servitisation is shaping today’s manufacturing sector
(Baines and W. Lightfoot, 2013), enabling to focus
on the services these companies are providing to the
value chain or to the end customer.
Enterprise integration is an essential component
of enterprise and service engineering (Panetto and
Molina, 2008), concerning the usage of specific
methods, models and tools to design and to
continually maintain an enterprise and the services it
provides constantly updated and integrated with the
domain objectives. However, from a technical point
of view, traditional information systems and service
development techniques are rigid, designed from the
planning stages with predefined functionality. This
makes them less sustainable to face the dynamicity
requested by the evolving market (Honour, 2008).
This concern is shared by a number of
communities and is reflected in the 2025 roadmap
for Future Internet Enterprise Systems (FInES
Research Roadmap Task Force, 2012), which
considers that today’s business process modelling
techniques do not appear adequate to address
today’s systems. Methods based on advanced
modelling techniques and model-driven
development are required to allow users to properly
address different levels of concerns (from business
goals to development), and at the same time reuse
the knowledge acquired between modelling levels
and teams. This idea was implemented in the
OSMOSE Project (www.osmose-project.eu) with
design and development of a reference architecture
for modelling and managing the Liquid Sensing
Enterprises (LSE) with the aim of design, execute
and monitor the processes and services of
enterprises. This architecture was designed having in
mind the integration of the several components and
Agostinho C., Ferreira J., Pereira J., Lucena C. and Fischer K.
Process Development for the Liquid-sensing Enterprise.
DOI: 10.5220/0006331602390249
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Model-Driven Engineering and Software Development (MODELSWARD 2017), pages 239-249
ISBN: 978-989-758-210-3
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
239

services of an enterprise. This paper contributes to a
more flexible environment for information systems
and service development, proposing a model-driven
framework for dynamic process development in the
enterprise of the future, where business experts,
system architects and developers are involved on the
development process and can contribute to any
design/re-design activity. This design follows the
Osmosis processes paradigm, allowing the business
experts to represent business process model at a high
level, describing knowledge in terms of the
enterprise of future notions of Real, Digital, and
Virtual World activities. This facilitates transference
of requirements to the technical experts and
accelerates LSE services development.
The paper starts by presenting the liquid–sensing
enterprise concept for the future enterprise, and in
section 2 it recalls the model-driven paradigm
developed previously, relating it the other related
initiatives. Section 3 presents the process
development framework proposed and developed
with the support of the OSMOSE European project.
Finally, section 4 presents the details about the
proof-of-concept developed and section 5 draws the
final considerations.
1.1 Liquid-sensing Enterprise
In face of the enduring economic crisis, shortness of
resources, and increasing demands for customization
and flexibility highlighted before, our enterprises are
in need of innovative ideas to adapt to these changes
and remain competitive. To meet these
requirements, the concept of Sensing Liquid
Enterprise was introduced as a fusion of the Sensing
Enterprise (Santucci et al., 2012) with the fact that
the enterprise is losing it fixed boundaries, in terms
of human resources, markets, products and processes
(FInES Cluster, 2010). Hence, the LSE is as an
attempt to reconcile traditional (non Internet-driven)
organisations with the tremendous possibilities
offered by the cyber worlds where objects,
equipment’s, and technological infrastructures are
shared by many exhibiting advanced networking and
processing capabilities, actively cooperating in a sort
of 'nervous system' (Arthur, 2011; FInES Cluster,
2010; Santucci et al., 2012; Moisescu & Sacala,
2016).
1.2 OSMOSE Metaphor and Processes
The OSMOsis applications for the Sensing
Enterprise - OSMOSE (FP7 610905) project aimed
at developing a reference architecture, a middleware
and some prototypal applications for the Sensing-
Liquid Enterprise, by interconnecting Real, Digital,
and Virtual Worlds in the same way as a semi-
permeable membrane permits the flow of liquid
particles through itself (Agostinho et al., 2015). The
worlds represent a way of organizing the structure of
an entire manufacturing enterprise, and the business
applications in three types of data management
environments: Real World (RW) - related to data
that comes directly from devices that is handled by
physical components; Digital World (DW) - related
to data management available in data and knowledge
bases or Internet (big data); and Virtual World
(VW) - related to specific management of data with
the support of future projections or specific
simulations (Spirito et al., 2014).
Following the LSE paradigm, osmosis processes
are a special type of business processes used to
moderate the information exchanged among the
worlds. The six Osmosis processes considered are
detailed in (Marques-Lucena et al., 2015):
Digitalization (RW-DW) – Model and
represent RW data in a computer-tractable form;
Actuation (DW-RW) – Plan and implement
highly distributed decision-making;
Enrichment (VW-DW) – Extends the
computational capabilities of the DW with
annotations and projections coming from
simulations and what-if hypothetical scenarios;
Simulation (DW-VW) – Instantiate and run
hypothetical VW scenarios based on historical
data;
Virtualization (RW-VW) – Provides real-time
data for simulation of hypothetical simulations;
Augmentation (VW-RW) – Annotates Real
World objects with Virtual World information.
2 MODEL-DRIVEN PARADIGM
FOR THE LSE
A business process can be seen as a set of internal
activities performed to serve a customer (Jacobson
et al., 1994). It is characterized by being: a purposed
activity; carried out collaboratively by a group; it
often crosses functional boundaries; it is invariably
driven by outside agents or customers (Ould and
Ould, 1995). This means that, to accomplish a
business process, especially in manufacturing, it is
necessary to involve several partners or user
profiles, and manage knowledge across different
boundaries of the enterprise (Zdravkovic et al.,
2013), much alike the LSE.
MODELSWARD 2017 - 5th International Conference on Model-Driven Engineering and Software Development
240

To better align the implementation and support
of a process lifecycle, a separation of concerns
starting from business goals down to the consequent
physical means to realize it is required (Ducq et al.,
2012). It can be accomplished if a model driven
approach is applied. Thus, instead of writing the
code directly, such approach enables services to be
firstly modelled with a high level of abstraction in a
context independent way. The main advantages of
applying model driven approaches are the
improvement of the portability, interoperability and
reusability through the architectural separation of
concerns (Grangel et al., 2008).
The work presented in this paper was inspired by
the one presented in (Ducq et al., 2012), which
adapted the model driven concept to manufacturing
services development, with the definition of Model
Driven Service Engineering Architecture (MDSEA)
concept. It followed the Model Driven Architecture
(MDA) and Model Driven Interoperability (MDI)
principles (Lemrabet et al., 2010), supporting the
modelling stage and guiding the transformation from
the business requirements (Business Service Model,
BSM) into detailed specification of components that
need to be implemented (Technology Specific
Models, TSM). This approach proposes that each
model, retrieved by the model transformation from
an upper-level model, should use a dedicated service
modelling language, which represents the system
containing the level of description needed. MDSEA
was the chosen method because is already oriented
to the development of services for business
processes and identifies the concepts IT, Physical
Mean and Human used to describe the processes.
However, for such approach to be successfully
applied to the LSE concept, it should be enriched
with the capability of represent concerns related
with the LSE-enabled real, digital and virtual worlds
of the Liquid-Sensing Enterprise (Agostinho &
Jardim-Goncalves, 2015). Following this
requirement, three levels of abstraction where
adapted from the MDSEA (see Figure 1):
Osmosis Business Models (OBM), where the
business case is defined. OBM extends the
BSM in the sense that this abstraction level
envisages meta-information not only about
components (e.g. actors, resources, etc.) but also
about activities and the world in which it is
active (e.g. “schedule maintenance” is an
activity from the DW and “clean machine” is
from the RW), The representation of the world
in each activity is called OBM Annotated,
enabling the system to identify osmotic
processes.
OSMOSE Technology Independent Models
(OTIM), that like the MDSEA TIM is
complementing the upper level model with
detailed technology independent functionally.
OTIM is optimized for the osmostis processes
representation, detailing such behaviour
(OSMOSE membrane) and the interactions
between the source and target world. For
instance, in a digitalization process, OTIM
represents three pools of activities (one the RW,
one for the DW and one for the membrane).
OSMOSE Technology Specific Models
(OTSM), which is the last level and consists in
the instantiation and parameterization of the
identified activities with services needed for the
the process execution.
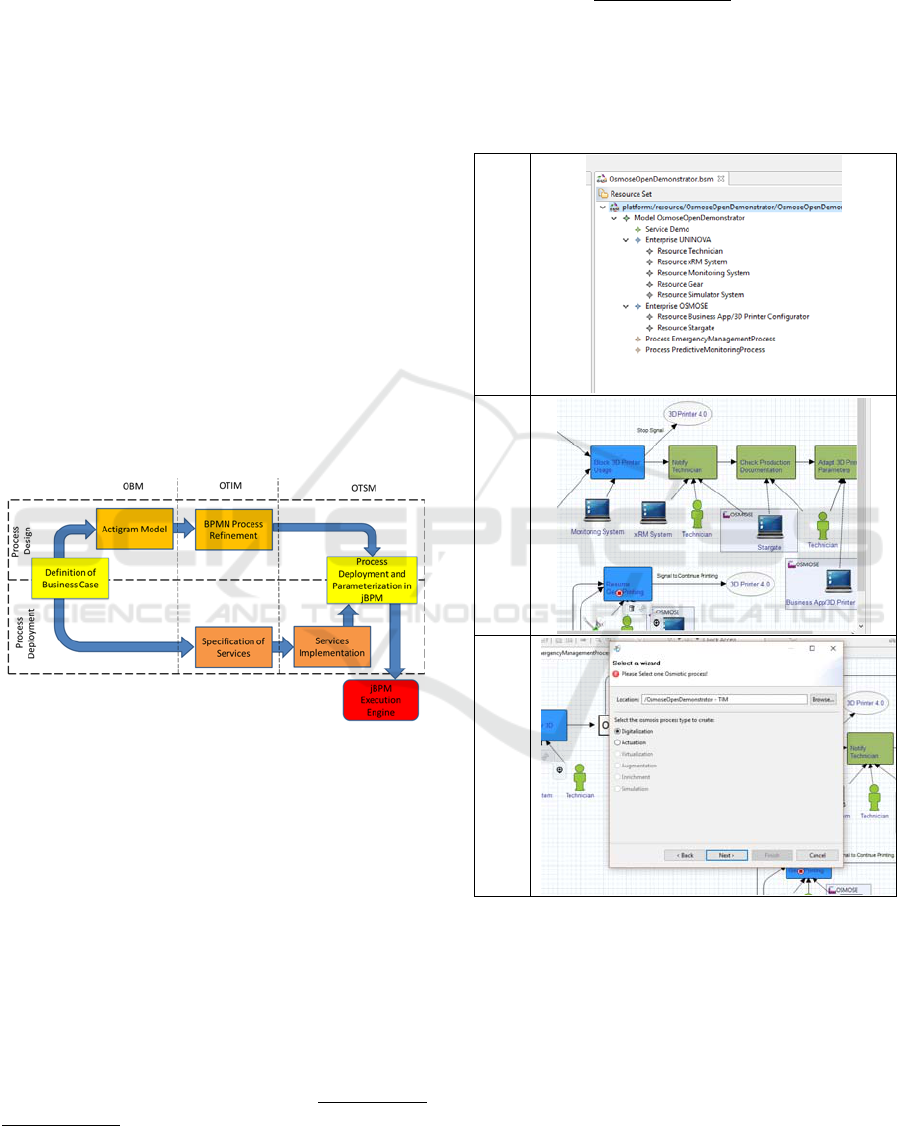
Figure 1: OSMOSE Process Design Methodology.
2.1 Discussion and Similar Approaches
The usage of model driven approaches applied to
processes modelling is not a novelty per se. Several
related works can be found in the literature. In the
work presented in (Mili et al., 2004), the authors
propose a method for classifying and specializing
generic business processes. With that method, the
authors aim to derive, from a catalogue of generic
processes and process specialization operators, an
enterprise-specific process, which corresponds
closely to MDA’s computation independent models
or CIMs. In (Bouchbout & Alimazighi, 2011), the
authors propose a framework for Inter-
Organizational Business Processes based on MDA.
Thus, it considers three levels in a top-down
manner: business (organizational), conceptual
(logic) and technical (execution). Other relevant
works are (Bouchbout et al., 2012; Rodríguez et al.,
2010; Rodr’iguez et al., 2007).
Based on the presented successful applications of
MDA techniques in processes modelling, the authors
consider that LSE design could benefit from the
methodology behind MDA and MDSEA in order to
accelerate the transition of the traditional enterprise
to the “internet-friendly” and context-aware
organization envisaged in OSMOSE. The major
Process Development for the Liquid-sensing Enterprise
241
question resides on the fact whether the LSE concept
and MDSEA strategy are compatible. This papers
contributes to prove this hypothesis, continuing the
work of (Marques-Lucena et al., 2016) and
contributing to the implementation of the model-
driven paradigm for the LSE. In detail, this work
complements the existing ones, identifying a
concrete LSE process development framework and
updated models transformation methodology.
3 OSMOSIS PROCESS
DEVELOPMENT
FRAMEWORK
As introduced in section 1.2, the osmosis processes
are a special type of process used to moderate the
information exchange among the real, digital, and
virtual worlds. When instantiated, these processes
will enable to seamlessly integrate the LSE,
connecting events across the 3 worlds, and
triggering services to provide the enterprise full
knowledge about its inner systems and interactions.
Figure 2: Overall Structure of Process Development.
The process design framework allows companies
to take the most out of LSE and the OSMOSE
project, being able to carefully plan the new
business strategies or specify the new services
clearly differentiating activities and events in
different worlds. Next section describes how the
process design methodology is combined with the
services specification and deployment, used at
execution time (Figure 2). It is divided into 2 phases,
the Process Design and the Process Deployment.
3.1 Process Design
The Process Design starts with the Definition of
Business Case, which is a high-level description of
the business case/service to be implemented. It can
be made in the form of textual description of the
user story, or a more formal definition following
models. After that and illustrated in Figure 3, the
design of the Actigram Model is conducted (EA*
(Extended Actigram Star) language is used (H.
Bazoun, G. Zacharewicz, 2013)). It represents the
initial part of the OBM level, starting with the
specification of the enterprise, collecting meta-
information about the organization and the resources
(as illustrated in the upper figure of Figure 3).
Identifying Resources of
Business Case
Modelling Actigram
(worlds identified in different colour)
Transforming to OTIM
(select from the existing osmosis processes)
Figure 3: OBM Modelling Activities.
Then, it is specified the business perspective of
the process model (as illustrated in the middle figure
of Figure 3), by identifying the innovation
requirements and expected behaviour. Using this
model, the user visualizes in a simple form, which
activities will go into processes between the
different worlds. The worlds identification
procedure at the OBM initiates the model-driven
paradigm explained in section 2, enabling the system
MODELSWARD 2017 - 5th International Conference on Model-Driven Engineering and Software Development
242
to identify osmosis processes and ask to the user the
type of osmosis event that can occur (see last figure
of Figure 3). This gives the possibility to change
from the OBM level into the OTIM level, through an
automated model transformation that transforms the
Actigram into a 3-parts BPMN model (BPMN 2.0 is
used to instantiate OTIM in this work) representing
the OSMOSE membrane and the respective worlds
processes. The transformation used in this process is
described in section 3.1.2.
The next step is the BPMN Process Refinement;
at this phase is possible to specify additional details
for service integration and extended business logic.
This represents the OTSM level of the methodology
preparing the BPMNs for execution.
3.1.1 Algorithm for Osmosis Process
Detection
To facilitate the identification of the osmosis
processes between different OBM activities, the user
should select to which world the activity belongs.
This option changes the colour of the activity in the
diagram, hence facilitating the visualization of the
worlds by the user, and providing the system the
necessary information for it to compute the existing
osmosis processes in a single business case (see the
middle part of Figure 2). When more than one
exists, the user should address them separately in
different OTIM models.
To support this process identification, an
algorithm has been specified and implemented. It
detects the world transitions and asks the user which
osmosis process he wants to work on. This new
feature improves the transformation between the
EA* and BPMN instances of OBM and OTIM,
following the concept presented in Figure 2. For
example, looking to Figure 5, the algorithm is going
to ask to user to select between two transitions
(which correspond the transitions between Blue-
Green and Green-Blue), i.e., Digitalization and an
Actuation processes.
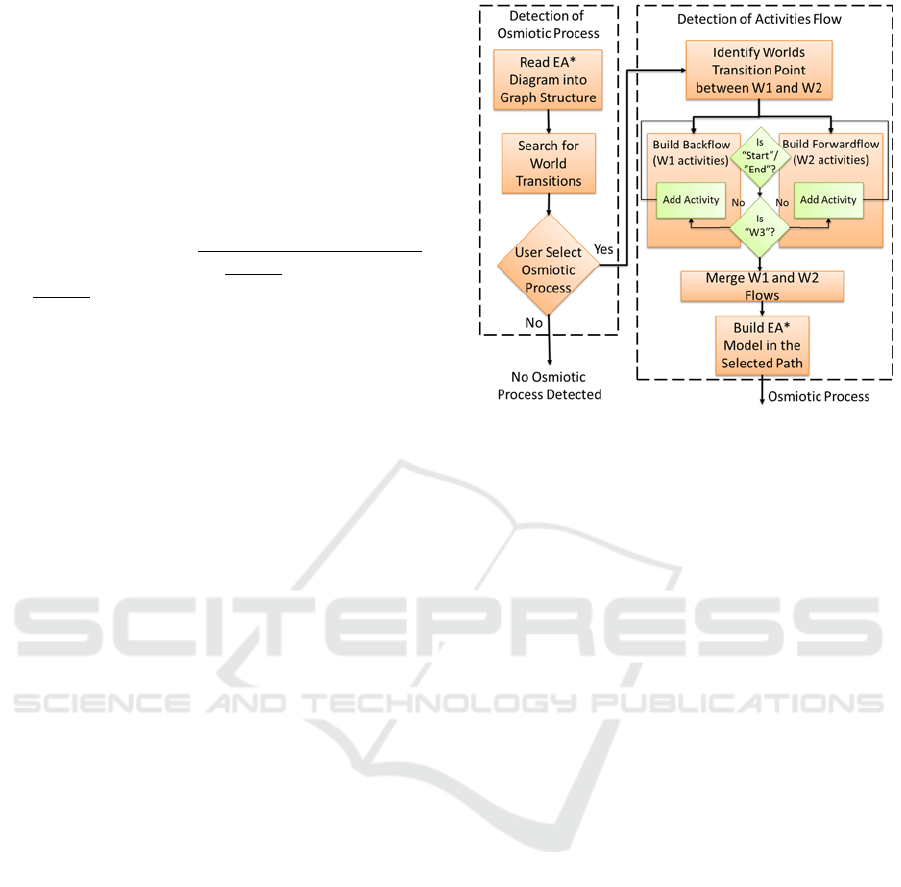
Figure 4 describes the algorithm dividing it into
two phases. First phase is about the detection of the
transitions between the worlds, and the second part
about the detection of the Activities flow within the
process. The algorithm reads the EA* diagram into a
graph structure to search for world transitions. It
does this by applying the following rules to the EA*
model:
A start and stop events needs to exist;
At least one world transitions need to exist.
Figure 4: Algorithm for Osmosis Process Detection.
In the case of the model does not respect these
rules, the algorithm is invalid.
After the user selects which osmosis process he
wishes to further specify at OTIM, the second phase
starts to iterate the graph and will identify all the
Activity blocks that belong to the selected osmosis
process. It starts detecting the Activities Blocks back
and forth from the world transition point (e.g. RW-
>DW). It follows the graph until it detects the
start/end of the diagram or a different world (RW
backflow; DW forward flow). In the end, it merges
the two flows into the osmosis EA* model to be
transformed.
As in the first phase, there are also some rules:
Detect if an activity is already included in the
flow and stop the iteration (it avoids to repeat it
the case the graph iterates through the same
activity more than once),
“And” or an “Or” connections points respect the
same rules as the Activities.
3.1.2 EA* to BPMN 2.0 Transformation
(Evolved)
To support the modelling and model transformation
process, the authors continued to develop the
MSEE’s Toolbox for service modelling (H. Bazoun,
G. Zacharewicz, 2013; Wiesner et al., 2014) which
is using ATL (https://eclipse.org/atl/) engine to
automatically execute the predefined transformation
rules between OBM and OTIM models. Since, the
MSEE Toolbox did not have the OSMOSE
processes concept implemented, (Marques-Lucena
et al., 2016) started to make the update which is here
Process Development for the Liquid-sensing Enterprise
243

continued with the new transformation rules
identified in Table 1.
Table 1: Summary of changes made in EA* to BPMN2.0
Transformation.
Source
Concept
Target Concept
EA* (OBM) BPMN2.0 (OTIM)
Resource
Material Data Object
Human Lane
IT Lane
Osmosis
Process
(Digitalization,
Virtualization,
etc…)
Pool
Source
(Real,
Digital,
Virtual)
world
End Event
Source Lanes
Source Tasks
Osmosis
membrane
Predefined Pool,
Events and Tasks
Target
(Real,
Digital,
Virtual)
world
Start Event
Target Lanes
Target Tasks
The changes made to the transformation are
divided into two parts, the first one is related with
the changes made in the resource, the first version of
the Toolbox was made to do the transformation of
the Human and IT resource, and at this moment the
Material resource is also being contemplated. The
second part is the big change, since at this moment
each activity is being transformed into task and
being allocated in the respective world. For
example, in the case of being a Digitalization
process, three different pools are created, one for the
Real World, other for the Digital World, and the last
for the Osmosis Membrane. Then in each pool is
allocated the respective lanes (each lane represents
the resource which is being used in that world), the
tasks. In the case of the Start or End event is due to
the rules of the BPMN, as each pool needs to have a
start and an end event (missing in the previous
version).
3.2 Process Deployment
The Process Deployment, as illustrated in the bottom
part of Figure 2 is made to support process
execution. In our implementation, the jBPM (Del
Fabro et al., 2009) environment has been selected,
since it is an open environment and being widely
used by the community. A straight forward manner
to start process execution is to use the jBPM Web
console. This step represents the Code level in the
model-driven paradigm.
The processes from the Toolbox are transformed
into BPMN processes that are uploaded into the
jBPM repository, from where they are deployed in
the jBPM process execution engine. In the jBPM
execution engine the processes can be further
refined (OTSM) and executed, when they are
eventually completed. For now, a command line
interface is available for interacting with the jBPM
git repository. The usual clone, commit, pull and
push commands are used for download of the jBPM
git repository content and to upload modifications or
new process models appropriately. The address of
the jBPM git repository is
ssh://[username]@[host]:[port]/jbpm-playground.
During the preparation of the jBPM to execute
the processes, it is necessary to specify and
implement the services in order to get or set data
used during the monitoring processes. The service
part of the design framework can be handled in
parallel with the OTIM and OTSM definition. These
services are register in an enterprise service bus
being available to entities in the OSMOSE
architecture to invoke process execution of these
services. With this approach, the services are
available anytime to be used in the processes,
allowing the system to have two types of services: a)
Services for invoking process execution; and b)
Services for delivering messages to specific
processes which are already in execution. Indeed,
the specification of user and service tasks begins to
be detailed in the BPMN model at the OTIM level
(see Figure 2). Then using a standard IDE
(Integrated Development Environment) is possible
to generate the skeleton of the code to be applied on
the service tasks, which then needs to be finalized
using the usual programming rules and approaches.
These services have to be specified and
implemented mapping the input/output of the service
specification to the input/output of the process.
4 OSMOSE OPEN
DEMONSTRATOR
The process of the framework is a complete
integrated process allowing, starting from a business
case, to get to the conclusive execution of the
Osmosis business processes. This section describes
an example showing how the different steps of
Figure 2 are instantiated to be used by a user. The
reference scenario is the OSMOSE open
demonstrator demonstrating the core steps to follow
in terms of process modelling (applying the design
framework), and at same time validating them.
MODELSWARD 2017 - 5th International Conference on Model-Driven Engineering and Software Development
244
4.1 Description of Business Case
The emergence of 3D Printers has made the market
of customizable products grows exponentially,
providing anyone (end user or manufacturing
stakeholder) with the possibility to print a custom
piece on demand. However, printers (especially low
cost ones) are still far from being a reliable option
due to production times, very delicate conditions and
configuration, and high failure rates. Hence,
depending on the size or quality of the piece,
printing can take many hours, and whenever an
undetected problem occurs in the printing process, in
addition to the huge waste of time there is the
amount of wasted raw material. For this reason, it is
important to monitor the printing and ensure the best
possible approach to save time and material in face
to such situations.
In open demonstrator scenario, OSMOSE is
applied to better manage the process of monitoring a
standard 3D printer that is producing a gear,
providing the solutions to handle predictive
maintenance and emergency management. In an
emergency situation, the printer has to stop to ensure
that the current the work is not ruined, and
potentially saving many working hours. Also, if it is
possible to predict possible printing error or
hardware failure, then maintenance procedure can be
triggered, avoiding significant losses.
4.2 OBM Models – Business Actigram
Instances
In this phase, the OSMOSE middleware framework
enables to design and specify in a business-friendly
interface, the activities that describe the different
flows of monitoring 3D Printer process. The
OSMOSE Process Modelling Toolbox is used to
design and specify the OBM Model in EA* notation.
For the specific user story described before, two
main process flows have been identified: a)
Emergency Management and b) Predictive
Maintenance (only the Emergency Management
example is going to be demonstrated in this paper).
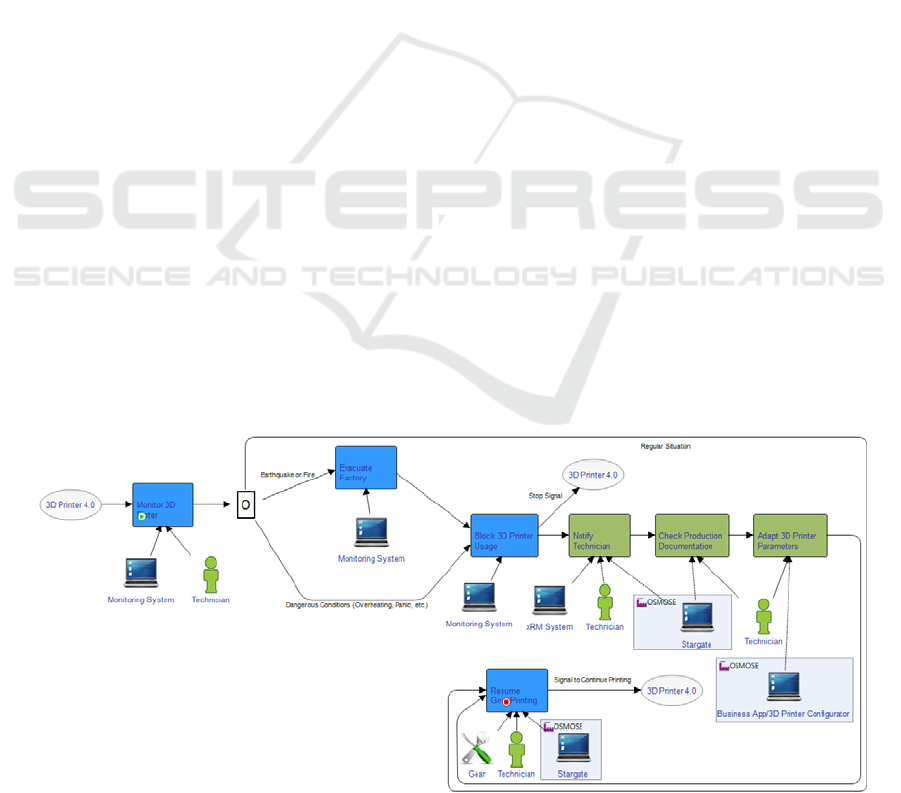
Figure 5 depicts the high-level overview of the
Emergency Management process, where sensors
available in the printer are used to track and monitor
the Gear printing, hence enabling to detect when and
which problems occur. The sensors used for this
process are the temperature sensor, accelerometer
sensor, gas sensor and a panic button. Using these
sensors, the idea is to develop a system capable of
detecting the real world events bellow and managing
the subsequent activities to prevent material waste:
Earthquake – In this situation an accelerometer
is used to detect abrupt oscillations to determine
if it is an earthquake, stopping the production in
the case of occurring one. This prevents the
workers, product and the printer itself from
damage (external to the earthquake);
Fire – In this situation the temperature and gas
sensors are used to detect a fire. This is made by
validating a high temperature together with an
increase of CO2 in the air. In the case of
detecting a fire the system stops the production;
Panic Button – In the case of a dangerous
situation (e.g. burnt hand in the printer bed;
hand stuck in the printer, etc.) or if the worker
identifies that the piece presents flaws during
the printing, he/she can press the panic button in
order to pause the production and resolve the
situation;
Figure 5: Actigram for an Emergency Management Process.
Process Development for the Liquid-sensing Enterprise
245
Printer Overheating Detection – The system
is prepared to detect whether the printer reaches
very high temperatures, which can cause long
term damage. This option prompts the user to
check what is happening to the printer and if
possible return it to the ideal temperature.
4.3 OTIM – BPMN Process
Refinement
In this stage, one automatically derives BMPN2.0
Technical Models from the Actigram Business
Process Models, reusing concepts already defined
and simplifying the design of the detailed osmosis
behaviour. Each BPMN process represents an
Osmosis process defined.
Figure 5 represents the Actigram model of the
Emergency Management process. By looking to the
model, it is possible to identify two Osmosis
Processes (a Digitalization Process – from blue to
green activities - and an Actuation Process – from
green to blue activities). Figure 6 represents the
refined Digitalization process, defining the printer
monitoring activities and identifying situations in
which the system can block the printer (described in
the previous section). It is possible to see that
comparing with the Actigram model, this includes
much more detail specified by the system architect.
At same time, OTIM describes the transition
between worlds. In this case one can see that the
Digitalization crosses the boundaries of the Real
World into the Digital World going through the
OSMOSE membrane (the transition is made by the
detection of osmosis events).
Once, the process has identified the problem
(real world event) and the printer is locked, the
technician is notified and he becomes responsible to
restore the production following a certain set of
actions. This is an Actuation process that is not
represented in this paper.
Figure 6: Digitalization Process to Notify Technician.
MODELSWARD 2017 - 5th International Conference on Model-Driven Engineering and Software Development
246
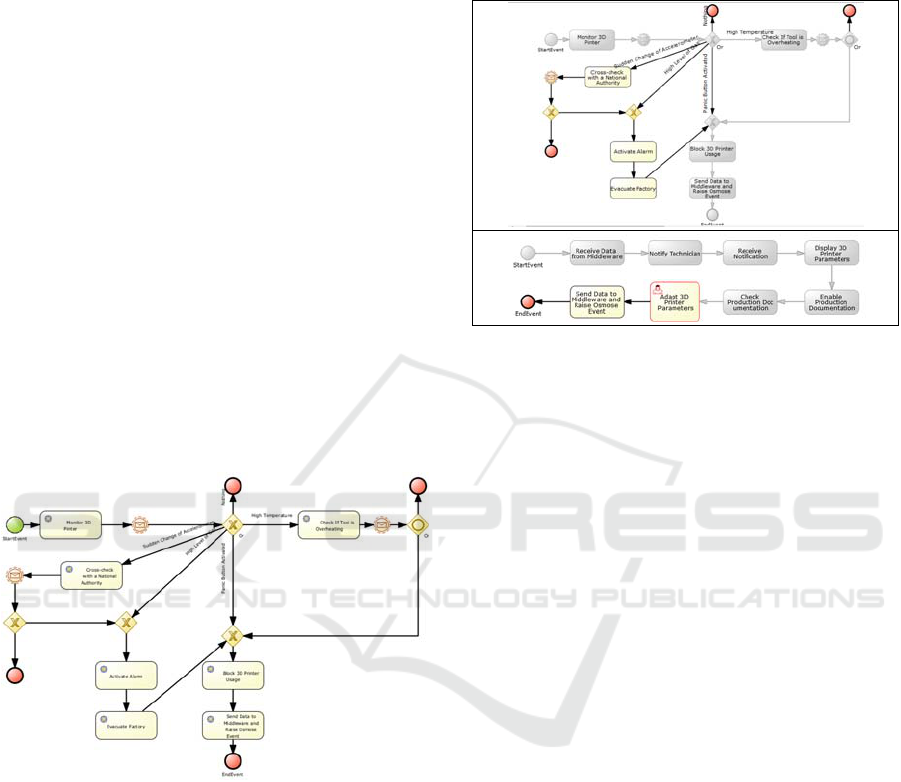
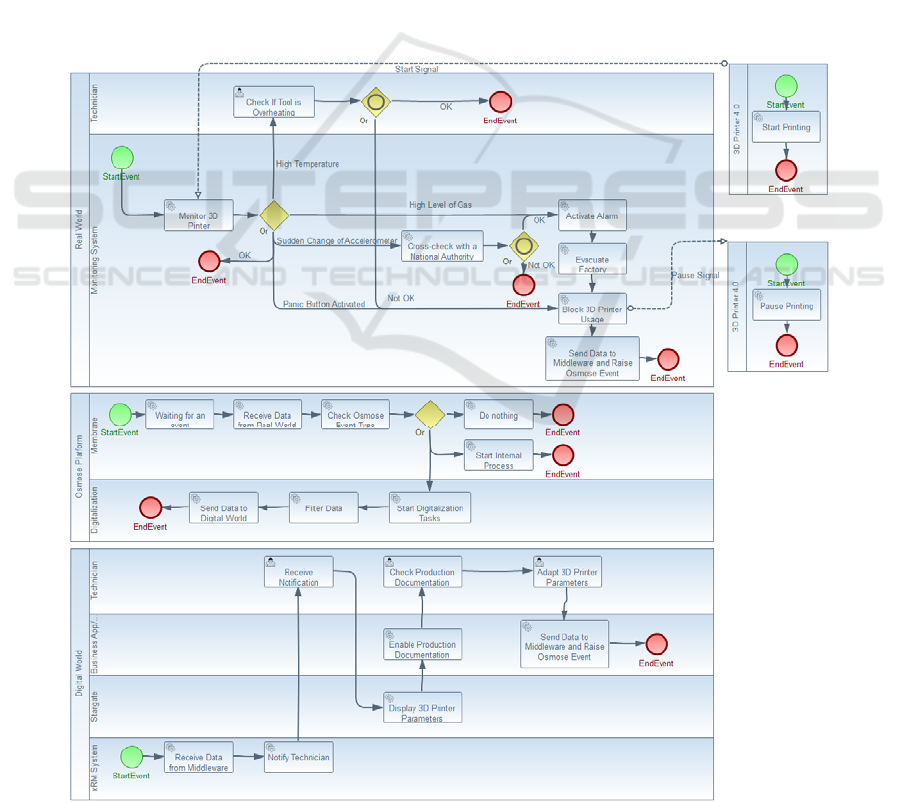
4.4 OTSM – BPMN Process
Deployment and Parameterization
in jBPM
The last phase is the implementation model, which
is the refinement of the BPMN so that in can be
executed in jBPM concurrently. In this model the
configuration of the BPMN with the services and
events is made, to be used in the run-time mode. The
representation of the executable Real World
processes is illustrated in Figure 7
(for space
restrictions we did not include the DW and the
OSMOSE membrane, where the model is
complemented with more detail and ready to be
launched and tested in jBPM, making the osmosis
process runnable.
The process is divided into three different
processes, as illustrated in
Figure 7. In this case, the
Digitalization process is going to be divided into,
Real World, Osmosis World and Digital World
processes. For each situation, it was needed to
identify the services needed and configure them in
the BPMN to be ready for execution. After this, it is
ready for deployment and them for execution.
Figure 7: RW BPMN Emergency Management Process.
4.5 Open Demonstrator Process
Execution
In this section, we briefly describe the execution of
the processes in the jBPM process execution engine.
It is important to note that this step requires that the
ones described in the previous sections need to be
properly designed and implemented.
Figure 8 shows a screen shot of the execution of
the digitalization process in the emergency
management. In the first image is represented the
Real world process, and it is monitoring the 3D
printer was started and the process waits for events
from the monitoring. In this example (following the
dark tasks), it was detected a high temperature in the
extruder, in response the system blocks the printer,
with this the Real world process ends.
Figure 8: Execution of Real and Digital Worlds
Emergency Management Process.
At this moment, the Osmosis Membrane started
and it is executing the middleware actions to allow
to proceed into the next phase of the Digitalization,
which in this case is the Digital World Process. In
the Digital world, the technician is notify about the
possible problem and he is called to verify the state
of the printer. Until the technician checks and
detects the problem and solve it, the process is
blocked until the user check the validation option.
The process finish with the confirmation by the user,
then it restarts to continue to monitor the printer.
5 CONCLUDING REMARKS
This paper presents the Osmosis Processes concept
and its associated modelling challenges for the
liquid-sensing enterprise. This objective was
achieved by following the three-layer paradigm
based on MSDEA approach, which the supports
potential coordination and cooperation between
multi-disciplinary teams. It starts by defining the
process application goals, to identify the activities
for each world, in a business and technical language,
ending with the osmosis process execution.
The modelling tool was adapted from MSEE’s
project results. In (Marques-Lucena et al., 2016) was
presented a first version of the OSMOSE Toolbox
explained the changes made in the MSEE’s tool to
follow the need to model the osmosis processes
concept, namely the interactions between worlds,
and the middleware membrane decision logic. In this
Process Development for the Liquid-sensing Enterprise
247

new version, the objective was to improve the
experience of the user, by giving the option to
specify the worlds in the EA* model, facilitating
with this approach the redesign in the BPMN2.0
model. For that, it was needed to change the
transformation code, improving the transformation
and accelerate the design time. These changes
allowed to include in the business process model a
more detailed information about the involved
worlds. It facilitated, technical teams, with their
knowledge about the osmosis worlds’ concept and
technical modelling skills, to enrich the business
process model with the osmosis behaviours and
constrains. This new version of the Toolbox
improved user experience as well as the integration
between the business level and the technical level.
The notion of the worlds in the transformation rules
improved the resulting BPMN process, causing the
user to make fewer changes in it. At same time, due
to the fact that the Toolbox follows the MDA
paradigm, it gives the capability (at the design phase
of the processes models) to re-adapt over time,
allowing to evolve when occurring a change in the
process or service, which need to be changed.
As future work, the authors intend to enrich LSE
environment tool with the osmosis events pallet, so
the osmosis processes modelling can be facilitated.
The authors also want to improve the deployment to
jBPM, enabling the import of the BPMN directly to
the jBPM reducing the time to execution and
improving the instantiation and parametrization of
the activities, since it is made at same level.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Authors would like to acknowledge the European
funded Projects OSMOSE (FP7 610905) and
C2NET (H2020 636909) that supported the
development of various ideas, concepts and use case
presented.
REFERENCES
Agostinho, C. & Jardim-Goncalves, R. (2015) Sustaining
interoperability of networked liquid-sensing
enterprises: A complex systems perspective. Annual
Reviews in Control, 39, pp.128–143.
Agostinho, C., Sesana, M., Jardim-Gonçalves, R. &
Gusmeroli, S. (2015) Model-driven Service
Engineering Towards the Manufacturing Liquid-
sensing Enterprise. In: {MODELSWARD} 2015 -
Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on
Model-Driven Engineering and Software
Development, ESEO, Angers, Loire Valley, France, 9-
11 February, 2015. pp.608–617.
Arthur, W.B. (2011) The Second Economy. McKinsey
Quarterly.
Baines, T. & W. Lightfoot, H. (2013) Servitization of the
manufacturing firm. International Journal of
Operations & Production Management, 34 (1), pp.2–
35.
Bouchbout, K., Akoka, J. & Alimazighi, Z. (2012) An
MDA-based framework for collaborative business
process modelling. Business Process Management
Journal, 18 (6), pp.919–948.
Bouchbout, K. & Alimazighi, Z. (2011) Inter-
organizational business processes modelling
framework. In: ADBIS (2). pp.45–54.
Ducq, Y., Chen, D. & Alix, T. (2012) Principles of
Servitization and Definition of an Architecture for
Model Driven Service System Engineering. In: M. van
Sinderen, P. Johnson, X. Xu, & G. Doumeingts eds.
Enterprise Interoperability. Lecture Notes in Business
Information Processing. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,
pp.117–128.
Del Fabro, M.D., Albert, P., Bézivin, J. & Jouault, F.
(2009) Achieving Rule Interoperability Using Chains
of Model Transformations. In: pp.249–259.
FInES Cluster (2010) FINES Research Roadmap.
Retrieved, August, 24, p.2013.
FInES Research Roadmap Task Force (2012)
FInESResearch Roadmap 2025: version 3.0.
Friedman, T.L. (2006) The World is flat : a brief history of
the twenty-first century. New York, Farrar, Straus and
Giroux.
Grangel, R., Bigand, M. & Bourey, J.-P.J.P. (2008) A
UML profile as support for transformation of business
process models at enterprise level. 1st International
Workshop on Model Driven Interoperability for
Sustainable Information Systems, MDISIS 2008 - Held
in Conjunction with the CAiSE 2008 Conference, 340,
pp.73–87.
H. Bazoun, G. Zacharewicz, Y.D. and H.B. (2013)
Transformation of Extended Actigram Star to BPMN
2.0 in the frame of Model Driven Service Engineering
Architecture. In: Symposium on Theory of Modeling
and Simulation (TMS/DEVS 2013). San Diego, USA.
Honour, E. (2008) Systems Engineering and Complexity.
INCOSE Insight, 11 (1), p.20.
Jacobson, I., Ericsson, M. & Jacobson, A. (1994) The
Object Advantage: Business Process Reengineering
with Object Technology. New York, NY, USA, ACM
Press/Addison-Wesley Publishing Co.
Lemrabet, Y., Bigand, M., Clin, D., Benkeltoum, N. &
Bourey, J.-P. (2010) Model Driven Interoperability in
Practice: Preliminary Evidences and Issues from an
Industrial Project. In:
Proceedings of the First
International Workshop on Model-Driven
Interoperability. MDI ’10. New York, NY, USA,
ACM, pp.3–9.
Marques-Lucena, C., Agostinho, C., Marcelino-Jesus, E.,
Sarraipa, J. & Jardim-Goncalves, R. (2015)
MODELSWARD 2017 - 5th International Conference on Model-Driven Engineering and Software Development
248

Collaborative Management of Requirements Using
Semantic Wiki Modules. In: Control Systems and
Computer Science (CSCS), 2015 20th International
Conference on. pp.665–672.
Marques-Lucena, C., Ferreira, J., Sesana, M., Fischer, K.
& Agostinho, C. (2016) Process Modelling Approach
for the Liquid-Sensing Enterprise. In: I-ESA’16 -
Interoperability for Enterprise Systems and
Applications. Guimarães, Portugal.
Mili, H., Jaoude, G.B., Lefebvre, É. & Tremblay, G.
(2004) Going beyond MDA: Business process
modeling for software reuse. In: Proceedings of the
Workshop on Legacy Transformation: Capturing
Business Knowledge from Legacy Systems-
OOPSLA’2004.
Moisescu, M.A. & Sacala, I.S. (2016) Towards the
development of interoperable sensing systems for the
future enterprise. Journal of Intelligent
Manufacturing, 27 (1), pp.33–54.
Ould, M.A. & Ould, M.A. (1995) Business processes:
modelling and analysis for re-engineering and
improvement. Wiley Chichester.
Panetto, H. & Molina, A. (2008) Enterprise integration
and interoperability in manufacturing systems: Trends
and issues. Computers in Industry, 59 (7), pp.641–646.
Radder, L. & Louw, L. (1999) Mass customization and
mass production. The TQM Magazine, 11 (1), pp.35–
40.
Rodr’iguez, A., Fernández-Medina, E. & Piattini, M.
(2007) Towards CIM to PIM Transformation: From
Secure Business Processes Defined in BPMN to Use-
Cases. In: G. Alonso, P. Dadam, & M. Rosemann eds.
Business Process Management: 5th International
Conference, BPM 2007, Brisbane, Australia,
September 24-28, 2007. Proceedings. Berlin,
Heidelberg, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp.408–415.
Rodríguez, A., de Guzmán, I.G.-R., Fernández-Medina, E.
& Piattini, M. (2010) Semi-formal transformation of
secure business processes into analysis class and use
case models: An {MDA} approach. Information and
Software Technology, 52 (9), pp.945–971.
Santucci, G., Martinez, C. & Vlad, D. (2012) The Sensing
Enterprise. In: In FInES Workshop at FIA 2012.
Available from:
<http://www.theinternetofthings.eu/sites/default/files/
%5Buser-name%5D/Sensing-enterprise.pdf>.
Spirito, M., Pastrone, C., Soldatos, J., Giaffreda, R.,
Doukas, C., Muñoz, L., Polidura, V.G., Gusmeroli, S.,
Sola, J. & Agostinho, C. (2014) Internet of Things
Applications - Research and Innovation to Market
Deployment (Chapter 7). In: O. Vermesan & P. Friess
eds. Internet of Things – From Research and
Innovation to Market Deployment. River Publishers,
pp.243–286.
Wiesner, S., Guglielmina, C., Gusmeroli, S. &
Doumeingts, G. (2014) Manufacturing Service
Ecosystem: Achievements of the European 7th
Framework Programme FoF-ICT Project MSEE:
Manufacturing Service Ecosystem (Grant No.
284860). Bremer Sch. http://www.verlag-mainz.de.
Zdravkovic, M., Panetto, H. & Trajanovic, M. (2013)
Semantic Interoperability for Dynamic Product-
Service. In: International Conference on Information
Systems and Technology (ICIST 2013)
. Kopaonik,
Serbia.
Process Development for the Liquid-sensing Enterprise
249
