
Paths to IT Performance:
A Configurational Analysis of IT Capabilities
François Bergeron
1
, Anne-Marie Croteau
2
, Louis Raymond
3
and Sylvestre Uwizeyemungu
3
1
Teluq, Université du Québec, 455 rue du Parvis, Québec, Québec, Canada
2
John Molson School of Business School, Concordia University, 1450 Guy St., Montréal, Québec, Canada
3
INRPME, Université du Québec à Trois-Rivières, 3351 Boul. des Forges, Trois-Rivières, Québec, Canada
Keywords: IT Performance, Environmental Uncertainty, IT Strategic Orientation, IT Capability, Qualitative Comparative
Analysis, QCA, SME.
Abstract: This study seeks to describe and explain the manner by which the environmental uncertainty, IT strategic
orientation and IT capabilities of manufacturing SMEs contribute to their IT performance, that is, to their
realization of benefits from the use of IT. A qualitative comparative analysis (QCA) allows to unveil three IT
capability configurations associated to high-IT performance firms. Dependent upon the configuration, the
core causal conditions involve an IT Defender strategic orientation, and various combinations of IT
managerial, functional, informational and technological capabilities. These results support the idea of a
gestalt alignment threshold for the IT capabilities of high-IT performance firms, that is, the idea that different
IT capability configurations can be equally effective.
1 INTRODUCTION
The need for information technology (IT) investment
in business enterprises keeps increasing and makes
growing demands on the information and
communication function of these organizations. This
is particularly true of manufacturing SMEs, who
recognize the challenge of investing in information
systems that provide the capacity to process the data
and generate the information that derive from their
dealings with their customers and other business
partners (Raymond et al., 2015). Many SMEs are
aware that investing in IT enables their survival and
competitiveness in a global, knowledge-based
economy, and allows them to benefit from their
product and process innovations (Marbert et al.,
2003). While IT-based solutions have considerably
increased the productivity and improved the
manufacturing process of these firms, they have also
provided them with greater flexibility by removing
the constraints of space and time, and by reinventing
organizational ways of doing business (Dibrell et al.,
2018)
With the opening of worldwide markets, SMEs
are affected by ongoing changes resulting in greater
environmental uncertainty and turbulence. If flexible
enough, IT can be a major change agent, allowing
SMEs to face uncertainty and quickly adapt to
changing market needs (Henderson and
Venkatraman, 1999). However, given the inherently
fragile nature of SMEs, the strategic role of IT is not
always fully exploited, giving rise to new managerial
challenges for these firms (Cragg, 2010). The barriers
to entry into emerging or existing markets are now
lower due to online offers and to customers being
more demanding and informed. In this context, IT
investments may quickly become obsolete
(Riemenschneider and Mykytyn, 2000).
Given the extensive investments in IT made by a
number of manufacturing SMEs, it is necessary to
anticipate the opportunities and threats that are
associated with these technologies, to discover the
mechanisms best suited to control and operate IT, and
to analyze their importance for the efficiency and
profitability of these enterprises (Kohli and Grover,
2008). The increasingly strategic role of IT within the
organization may give rise to problems related to the
management of IT that are not merely technical, but
also strategic and organizational in nature (Caldeira
and Ward, 2003). Therefore, it is of critical
importance for SMEs to have an understanding of
how their IT capabilities can provide them with the
294
Bergeron, F., Croteau, A-M., Raymond, L. and Uwizeyemungu, S.
Paths to IT Performance: A Configurational Analysis of IT Capabilities.
DOI: 10.5220/0006346702940305
In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2017) - Volume 3, pages 294-305
ISBN: 978-989-758-249-3
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

most business value from their investment in IT
(Clark et al., 1997, 2010).
In this regard, various configurations of IT
managerial, functional, informational and
technological capabilities (Raymond et al., 1995,
Sanders and Premus, 2005) should emanate from the
uncertainty perceived by an SME in its business
environment and the strategic role it assigns to IT,
that is, its IT strategic orientation (Philip and Booth,
2001, Venkatraman, 1994). Therefore, our research
question is the following: what are the appropriate
configurations of IT capabilities that allow SMEs to
be IT performing in various contexts of environmental
uncertainty and various types of IT strategic
orientation?
2 CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK
Given our research question, the conceptual
framework of this study combines theoretical
elements that underlie and integrate the following
notions in a configurational approach: IT
sophistication, to which are related environmental
uncertainty, IT strategic orientation and IT
performance. The theoretical background of this
study emanates first and foremost from Henderson
and Venkatraman’s conceptualization of the strategic
alignment of IT which means that the dynamic
coherence of the added-value obtained from IT is due
to an interplay between an organization’s business
strategy, organizational infrastructure, IT strategy
and IT infrastructure (Henderson and Venkatraman,
1999). These authors’ strategic alignment model
(SAM) emphasizes the need for coherence between
internal and external business activities in order to
meet the firm’s strategic objectives and improve its
organizational performance. While it has been
demonstrated that coherence between business
strategy and IT strategy contributes to both IT
performance and organizational performance
(Croteau and Bergeron, 2001, Kyobe, 2008), few
empirical studies have taken contextual factors into
account, i.e. factors that relate to the firm itself, its
business environmental, and its technological
context, that is, the well-known “TOE” framework
emanating from Tornatsky and Fleischer’s (1990)
work. While a number of empirical studies have
provided an understanding of the various contexts in
which the strategic alignment of IT contributes to the
attainment of business value from IT and to
organizational performance, many aspects of this
alignment have yet to be explored, such as the
alignment at the managerial, functional,
informational and technological levels (Bergeron et
al., 2004). Such a specific study of the alignment of
the IT capabilities has not been researched in the past
and filling this research gap will contribute to a better
management and use of IT in SMEs.
Our research aims to find efficient configurations
of IT capabilities, environmental uncertainty, and IT
strategic orientation that allow SMEs to attain
business value from IT. Hence, our main research
objective is to discover the various IT capability
configurations appropriate for various IT strategic
orientation of SMEs in contexts of high and low
environmental uncertainty that allow SMEs to realize
benefits from their use of IT, that is, to achieve IT-
business value.
2.1 IT Sophistication
The notion of IT sophistication refers to the way IT is
managed and used by an organization, including the
manner by which IT is aligned with the firm’s
strategic objectives (Henderson and Venkatraman,
1999). Raymond, Paré and Bergeron (1995) were
among the first to define the concept of IT
sophistication and validate its measurement. Their
conceptualization of IT sophistication was
subsequently used by other researchers (Iacovou et
al., 1995, Pflughoest et al., 2003, Rai et al., 2006). IT
sophistication is a notion that is meant here to
encompass the diverse nature and interrelationships
of the SME’s IT capabilities (Bharadwaj, 2000, p.
171). Within this conceptualization, IT sophistication
addresses four complementary IT capabilities: the
managerial, functional, informational, and
technological capabilities.
The firm’s IT managerial capability comprises
the planning, control and evaluation mechanisms
required to manage its IT-based applications portfolio
(Raymond et al., 1995). For its part, the IT functional
capability is related to the autonomy of the IT
function and the location of this function within the
organization (Blili and Raymond, 1993).
The firm’s IT informational capability refers to
the transactional and managerial nature of the
implemented applications as well as its coverage of
the functional organization areas. This capability also
refers to the quality of the information, its use and its
integration (Marbert et al., 2003). For its part, the IT
technological capability refers to the number or
variety of technologies used by manufacturing SMEs
for operational and managerial purposes, its
communication networks and the IT security
mechanisms (Riemenschneider and Mykytyn
, 2000).
While the concept of sophistication has been used
Paths to IT Performance: A Configurational Analysis of IT Capabilities
295

in earlier research on the IT function, it has not been
used to measure the appropriateness of specific IT
capabilities and to test for the fit of these IT
capabilities in a context of environmental uncertainty
and specific IT strategy orientation in manufacturing
SMEs. This research intends to fill this knowledge
gap.
2.2 Environmental Uncertainty
As an exogenous determinant of IT sophistication,
environmental uncertainty increases an SME’s need
for external information (Christopher and Lee, 2004,
Fiss, 2011, Liu et al., 2012, Raymond et al., 2015). To
better understand the way organizations should
handle such a need to maintain or even increase the
business value of their IT investment, we refer to
information processing theory, viewed initially as an
integrating concept in organizational design
(Tushman and Nadler, 1978). This theory posits that
in a case of disequilibrium between information
processing requirements and information processing
capabilities, which can occur after a change in
environmental uncertainty, performing firms must
properly fulfil the information requirements by
appropriate IT capabilities to keep an acceptable (or
high) level of organizational performance (Dutot et
al., 2014). Information processing theory also posits
that as environmental uncertainty increases,
information requirements intensify and thus the need
to enhance the sophistication of the organization’s IT
capabilities. An organization will thus perform better
when there is a “fit” between its information
requirements and its response in terms of
management and use of IT (Cegielski et al., 2012;
Dutot et al., 2014). The information requirements of
an organization thus rely on the level of uncertainty
related to various internal and external factors.
However, it is unknown what specific IT capabilities
should be enhanced and to what extent they should be
improved to respond to changes in environmental
uncertainty.
2.3 IT Strategic Orientation
As an endogenous determinant of its IT
sophistication, the IT strategic orientation of a SME
refers to the centrality and criticality of IT in the
achievement of its business goals and the
implementation of its strategies (Philip and Booth,
2001). This notion is thus focused on the “core
business” and success of these organizations
(Venkatraman, 1994). In this regard, Ward, Taylor
and Bond (1996) proposed that the firm’s IT strategic
orientation evolves in a three-period growth cycle: 1)
operational efficiency, 2) management and control of
the firm, and 3) strategic IS development. Similarly,
in the evolutionary model of the strategic role of IT
proposed by Philip and Booth (2001), each firm has
specific expectations with regard to IT that are
dependent upon its capacity to “align” these
technologies with its strategic goals. This alignment
may be difficult to attain given the ambidextrous
resolution strategies opposing short- and long-term IT
goals and IT project and program needs (Gregory,
2015). Although Miles and Snow (2003) suggest that
Prospectors differ from Defenders in their low
structure and low cost strategy (Fiss, 2011), it is still
unknown which IT capabilities or combinations of IT
capabilities should be enhanced to support Prospector
versus Defender types of strategy.
2.4 IT Performance
The performance of the organization’s IT function
lies in its realization of business value from IT
investments and is thus the expected outcome of its
IT capabilities (Guillemette and Paré, 2012). Given
the complexity of assessing the benefits gained from
IT, specifically in relation to organizational
performance, a SME must consider the technical
obsolescence of software, the declining cost of work
units and operating software, development flows, and
operating costs when it evaluates its IT costs (Kan et
al., 2016). In this regard, DeLone and McLean (2003)
observed that user satisfaction is the dimension that
remains most important to assess IT performance.
The user here may be a SME manager or other
employee. Furthermore, for SMEs in particular, user
satisfaction is usually associated with managerial and
organizational benefits, that is, to IT-business value
(Pflughoest et al., 2003, Shi et al., 2005). Despite this
possibility to measure performance, it is still a
challenge for many enterprises to quantify the
benefits obtained from organizational and
infrastructural changes, better follow-up of customers
or even improved internal and external
communications (Guillemette and Paré, 2012).
3 RESEARCH MODEL
As illustrated in Figure 1, our research model views
IT sophistication as an alignment (“fit”) of IT
managerial, functional, informational and
technological capabilities, a gestalt perspective of
alignment being taken here. In this perspective,
different internally consistent capability
ICEIS 2017 - 19th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
296

configurations may be equally effective (Bergeron et
al., 2001). This is in line with Fiss’s observation that
in an organizational context, several causal paths to
an outcome may lead to equifinal configurations,
each resulting in effective performance. Following
the developments presented in the conceptual
framework, the environmental uncertainty and its
strategic orientation with regard to IT are posited in
this research to be critical components of this gestalt,
while IT performance is posited to its outcome.
Consistent with the information processing theory
(Dutot et al., 2014, Gattiker, 2007, Venkatraman,
1994), our research model assumes that the level of
sophistication of IT capabilities is associated to the
level of environmental uncertainty. In the context of
high environmental uncertainty, be it market-related,
technological or competitive, the ambiguity
surrounding future increases in information
requirements pushes firms to develop a more
sophisticated management and usage of IT in order to
meet these requirements. Uncertainty can cause
actions, routines and practices to mutate (Miner,
1990). In the case of high uncertainty, a high IT
sophistication of capabilities could be needed even
with a high rate of change in the environment. In the
case of low environmental uncertainty, a lower level
of IT sophistication may be sufficient to meet
information requirements, given the relative stability
of the business environment. Based on literature, it is
not clear however when precisely and under which
circumstances a high or higher level of IT
sophistication is needed and which specific IT
capabilities should be altered in situations of high
versus low environmental uncertainty. This research
aims to clarify this specific research question by
providing evidence to support the link between the
sophistication of IT capabilities and the level of
environmental uncertainty.
IT strategic orientation is defined by analogy to
Miles and Snow’s (2003) typology which is deemed
to be the most appropriate to conceptualize and
operationalize strategic orientation in the context of
SMEs (Escribá-Esteve, 2009). At the core of this
typology is the adaptive cycle through which a firm
continuously realigns its decisions with regard to the
entrepreneurial problem (the firm’s product-market
domain), to the engineering problem (technologies
and processes for production and distribution), and to
the administrative problem (establishment of roles,
relationships, and business processes). To parallel
Miles and Snow’s typology, we label as IT
Prospectors SMEs that are inclined to strategically
consider IT as necessary means to enable their new
product/market endeavours. In the same way, IT
Defenders are SMEs that strategically conceive the
role of IT as one of supporting activities directed
towards satisfying the needs of current customers,
and ensuring production and organizational
efficiency. To some extent, the IT strategic
orientation is related to the environment forces and is
implemented through IT capabilities. Some gestalt
configurations will therefore be more effective than
others dependent upon the organizational context.
In the research model, we assume that a SME’s IT
strategic orientation will be associated to the
sophistication of its IT capabilities. More precisely,
IT Prospectors will be more likely to adopt or develop
IT aligned with product innovation and
organizational flexibility. By nature, IT Prospectors
are expected to experiment with a greater number of
technologies than IT Defenders, and to do so
effectively, they will need to enhance their
informational and technological capabilities. These
enhancements would aim at offering an effective but
not necessarily efficient response to the information
requirements given the exploratory nature of IT
Prospectors and the need to have short term effective
solution since projects can change on a regular basis.
Another point of view is that IT Prospectors should
be more inclined to enhance their managerial and
functional IT capabilities.
For a SME, the strategic alignment of IT
informational and technological capabilities should
be associated to the level of IT sophistication needed
to attain IT performance. Evolving in stable markets
in which they intend to reinforce their position, IT
Defender SMEs will likely less venture beyond the IT
solutions that have been well-proven within their
markets. However, in their quest for reliability and
efficiency with these IT solutions, they will need
greater IT managerial and functional sophistication.
The research model also suggests that the SME’s
IT performance is associated to the sophistication of
its IT capabilities. More precisely, the level of IT
performance achieved is linked to the firm’s
development of an appropriate mix of IT managerial,
functional, informational and technological
capabilities in line with its IT strategic orientation and
environment uncertainty. This calls upon the notion
of alignment which has been central for decades in
previous research on IT business value (e.g.,
Bergeron and Raymond, 1995, Charoensuk et al.,
2014) but limited itself to the management and use of
IT capabilities, without specifying which of the four
IT capabilities should be enhanced under various
organizational and extra-organizational conditions.
Following previous studies that have mainly
demonstrated the positive impact of IT strategic
Paths to IT Performance: A Configurational Analysis of IT Capabilities
297

alignment on IT business value, we surmise that
SMEs will achieve higher levels of IT performance
than the industry insofar as they develop the “right”
combination of IT capabilities, befitting both their IT
strategic orientation as well as their environmental
uncertainty. Higher environmental uncertainty
requires higher levels of IT sophistication, and we
expect that SMEs operating in highly uncertain
environments that have developed more sophisticated
IT to meet their information requirements will
achieve higher levels of IT performance than SMEs
that have not responded positively to these new
organizational needs. Independently of environment
uncertainty, higher levels of IT performance are
expected from IT Prospector SMEs that have
developed higher levels of IT usage sophistication
(i.e., informational and technological needs) in
response to their IT strategic needs. Similarly, IT
Defender SMEs that have developed higher levels of
IT managerial and functional sophistication to match
their IT strategic orientation are expected to achieve
higher levels of IT performance than IT Defender
SMEs that have not done so.
Synthesizing these considerations, it is expected
that various causal relationships between
organizational (environmental uncertainty and IT
strategic orientation) and IT capabilities can be
observed in SMEs whose attain high-IT performance.
Earlier studies have not considered the interaction,
moderation and mediation effects of all causal
conditions simultaneously. This complex interplay
can hardly be observed with conventional statistical
approaches that assume linearity (Ganter and Hecker,
2014, Ragin, 2000). Thus, given our research
question, objective and model, a QCA (qualitative
comparative analysis) approach is appropriate and is
used to unveil the gestalt of organizational and
ITcapability configurations that characterize high-IT
performance firms.
4 METHODOLOGY
4.1 QCA Approach
This study uses a set-theoretic approach based on
QCA, an analytic technique that provides suitable
means to accommodate complex complementarities
and nonlinear relationships among constructs
(Escribá-Esteve et al., 2009, Ragin, 2000, Rihoux and
Ragin, 2009, Woodside, 2013). As reported by Kan,
et al. (2016), scholars “now use QCA beyond its
original purposes in political and sociological
sciences and apply this method of analysis in the field
of management”. These authors add that “QCA
ITManagerial
Capability
ITInformational
Capability
FIT
(gestalt)
ITPerformance
ITFunctional
Capability
Environmental
Uncertainty
ITStrategic
Orientation
ITTechnological
Capability
ITSophistication
account ing,financeandHRM
applicationbenefits
logistics,productionand
distributionapplicationbenefits
marketing,salesandservice
applicationbenefits
e‐business,InternetandWeb
applicationbenefits
ITManagementSophistication ITUsageSophistication
Figure 1: Research model.
ICEIS 2017 - 19th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
298

extends beyond an empirical technique and this
method offers a genuine formalization of qualitative
analysis, which opens new ways of knowledge
production in management scholarship”. This type of
analysis is based on a configurational understanding
of how conditions or causes combine to produce a
specific outcome. QCA uses an approach to solve
causality that investigates an outcome as the product
of how conditions combine together. In seeking to
explain why certain cases have specific outcomes,
QCA uses Boolean algebra and algorithms that
change numerous complex causal conditions into a
reduced set of configurations leading to an outcome.
It combines the benefits of case-oriented and
variable-based methods (such as regression
techniques), and is particularly suited for small
sample sizes (Ragin, 1987, 2000, 2008). In QCA
terms, we report in this study the “parsimonious”
solutions produced by this analysis, wherein “core”
and “peripheral” conditions are presented. The truth
table algorithm used is the one described by Ragin
(2008), the originator of QCA. In terms of solution
coverage, we consider all configurations
characterized by one or more empirical observations.
The use of qualitative comparative analysis in
management is relatively new. Most research using
this method has been published since the year 2000.
Although the bulk of research using QCA has been
conducted in the fields of general management,
marketing, innovation, strategy, human resources,
and organization studies, only a few were applied to
production & operations, and public management.
Only one research addressed the sustainability issue
(Rekik and Bergeron, 2017). As reported by Kan et
al. (2016), the field of information systems, finance
and operations research reported only one research
each. Thus, it can still be considered as an innovation
to use the QCA method of analysis in information
systems. Since it is particularly appropriate for small
to medium sample, it offers a worthy perspective to
study IT capabilities configurations in an
organizational setting.
4.2 Data Collection
Data was provided by a database developed by a SME
research center for purposes of IT benchmarking and
IT management research. This database was created
in collaboration with business owner-managers
belonging to chambers of commerce in the Rhône-
Alpes region of France. These owner-managers as
well as their management team were solicited to
respond to a questionnaire on their firm’s IT strategy,
IT structure, IT management and usage practices, and
IT performance. The database thus contains
information gathered from forty-four SMEs whose
main activity is in manufacturing. The survey was
completed by the firms’ CEO or CFO, operations
manager, sales and marketing manager, and IT
manager. In this study, a SME is determined to have
more than 9 and less than 299 employees (median size
=38 employees). Various industry sectors are
represented, including metal products (27%), food
products (16%), wood products (9.5%), plastics
(8.5%), textile products (7%), mineral products (5%),
and various others (27%).
4.3 Measures
IT sophistication. The assessment of the
sophistication of IT capabilities emanates from
previously validated measures of IT management
sophistication and IT usage sophistication found in
the extant literature (Pflughoest et al., 2003,
Riemenschneider and Mykytyn, 2000). These
measures have been refined and validated to refer to
the sophistication of the SME’s IT functional,
managerial, informational and technological
capabilities. The IT managerial capability is
measured by six Likert-type items (see Table 1. The
IT functional capability is based on two categorical
items. The IT informational capability is measured
with six items. The IT technological capability is
formed of three Likert-type items (Riemenschneider
and Mykytyn, 2000).
Environmental uncertainty. This variable was
measured with 5 Likert-type items adapted from an
instrument validated by Miller and Dröge (1986)
evaluating the rate of change inside and outside the
firm.
IT strategic orientation. The strategic orientation
of the SME with regard to IT was assessed through a
self-typing measure developed on the basis of Philip
and Booth’s (2001) and Venkatraman’s (1994) stage
models. The chief executives were asked to choose
one statement among four that best describes their
understanding of the role that is assigned to
information technology-based applications (IT apps)
in their firm. The scale used is as follows. For IT
Defenders: IT applications are used to improve
managerial control and monitoring of the firm’s
manufacturing operations (IT strategy 1), or IT
applications are used to increase the flexibility of the
firm’s manufacturing operations and better respond to
its customers’ needs (IT strategy 2). For IT
Prospectors: IT applications are used to accelerate
and facilitate the firm’s development of new products
and to increase its market share (IT strategy 3), or IT
Paths to IT Performance: A Configurational Analysis of IT Capabilities
299

applications are used to increase the integration of the
firm’s manufacturing and business processes and to
improve relations with its business partners (IT
strategy 4). The statements were coded to form a
“crisp set” (0,1) in QCA terms (47).
IT performance. This variable is measured by the
level of attainment of the benefits associated with
four types of IT-based applications, following a
process-based approach wherein the respondents
evaluate the business value of IT for their firm
(Venkatraman, 1994). A list of expected benefits
specific to each type of application is presented to the
chief executive or to the concerned executive who
indicates on a 5-point scale the extent to which the
applications implemented contribute to the
attainment of such benefits.
5 RESULTS
The descriptive statistics of the research variables are
presented in Table 1. The discriminant validity of the
IT sophistication constructs was confirmed by two
principal component analysis (PCA). The first PCA
was applied to IT managerial and functional
capabilities as two sub-factors (constructs) grouped
under the more general concept of IT management
sophistication (Raymond et al., 1995). The second
PCA was applied to IT informational and
technological capabilities as two sub-factors grouped
under the more general concept of IT use
sophistication. In both cases, the two pairs of IT
sophistication constructs revealed to be orthogonal,
with each factor showing adequate reliability,
unidimensionality and convergent validity.
IT performance is conceptualized here as a
formative construct composed of four measures that
relate to the average benefits obtained from each type
of IT-based application. There was no
multicollinearity among these formative measures,
the highest correlation among them being equal to
0.19 (p > 0.1), thus confirming the last construct’s
validity. Furthermore, as presented in Table 2,
Cronbach’s α and intercorrelation values for the eight
research constructs confirm their internal consistency
and discriminant validity.
The aim of this study is to determine the causal
conditions associated with high-IT performance, i.e.
the IT capability configurations that, in line with the
SME's perceived environmental uncertainty and IT
strategic orientation, enable it to realize the most
benefits from its investment in IT. In order to test the
Table 1: Descriptive statistics of research variables.
Variable mean s.d. range
Environmental Uncertainty
2.6 2.6 1.0 - 4.6
IT Strategic Orientation
a
- - 1 - 4
IT Functional Capability
designated manager for IT
b
org. level of the IT function
c
.73
.55
-
-
0 - 1
0 - 1
IT Managerial Capability
IT development
IT evaluation
user participation
IT resources and competencies
IT support and appropriation
external consultants
3.0
2.8
2.9
3.4
3.7
2.4
0.8
1.2
0.9
0.9
0.8
1.8
1.0 - 5.0
0.0 - 5.0
1.0 - 5.0
1.2 - 5.0
1.7 - 5.0
0.0 - 5.0
IT Technological Capability
# of uses of IT
# of uses of e-bus/Internet/Web
quality of IT security
4.8
6.0
4.4
1.8
3.3
0.9
2 - 10
0 - 15
2.0 - 6.0
IT Informational Capability
# of accounting/fin./HRM apps
# of logistics/prod./distrib. apps
# of mark./sales/cust.serv. apps
# of ERP system modules
information output quality
user-system interaction quality
6.0
7.0
3.8
2.8
3.6
3.5
2.8
3.1
2.0
2.5
0.8
0.9
0 - 11
2 - 16
0 - 7
0 - 7
1.4 - 4.6
1.5 - 5.0
IT Performance
acc./fin./HRM app. benefits
log./prod./distrib. app. benefits
mark./sales/serv. app. benefits
e-bus./Net/Web app. benefits
3.3
3.3
3.0
2.6
1.2
0.6
1.1
0.7
0.0 - 5.0
2.0 - 5.0
0.0 - 5.0
0.0 - 4.1
a
1: IT for control (n = 14) 2: IT for flexibility (n = 9)
3: IT for product and market development (n = 4)
4: IT for internal and external integration (n = 17)
b
1: yes (n = 32) 0: no (n =12)
c
1: supervised by the chief-executive (n = 24)
0: supervised by another manager (n = 20)
Table 2: Intercorrelations of the research constructs.
research model, the sample was divided in three tiers
based on IT performance. The first tier represents the
high-IT performance firms (n=15), and the third tier,
the low-IT performance firms (n=15). The second-
tier is not used in the tests. In this research, the high-
IT performance firms are compared to low-IT
performance firms. This approach to forming sub-
samples is based on Fiss’ (2011) approach to study
organizational performance using QCA.
The variables were calibrated using crisp sets and
a
binary variable
b
inappropriate for formative constructs
Nota. Correlations greater than .25/.40/.45 are significant at p < .05/.01/.001.
ICEIS 2017 - 19th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
300
the truth tables were generated using the fs/QCA
software. The overall solution coverage indicates the
proportion of cases that are covered by all reported
configurations. The overall solution consistency
assesses the degree to which capability configurations
are subsets of the outcome (Ragin, 2008). In this
study, the consistency cut-off point was set at 0.80
and the minimum frequency equal to 1. All
configuration consistency values are equal to 1 and
the overall solution consistency is equal to 1,
satisfying the consistency threshold of 0.8 set by
Ragin (2000). The overall solution coverage is equal
to 0.93, indicating that these IT capability
configurations (or gestalts) represent the large
majority of SMEs that show a high level of IT
performance. The presence or absence of each IT
capability was determined by the level of
sophistication of each IT capability split in two
groups based on the median value and which was then
used to form crisp sets (0,1). The IT strategic
orientation used a crisp set classification: 1 for IT
Prospectors; 0 for IT Defenders. The black filled
circle means SMEs have an IT Prospective strategy
whereas the white crossed-out circle means SMEs
have an IT Defender strategy. The environmental
uncertainty and IT performance also used crisp sets
classification based on the median value of the scales.
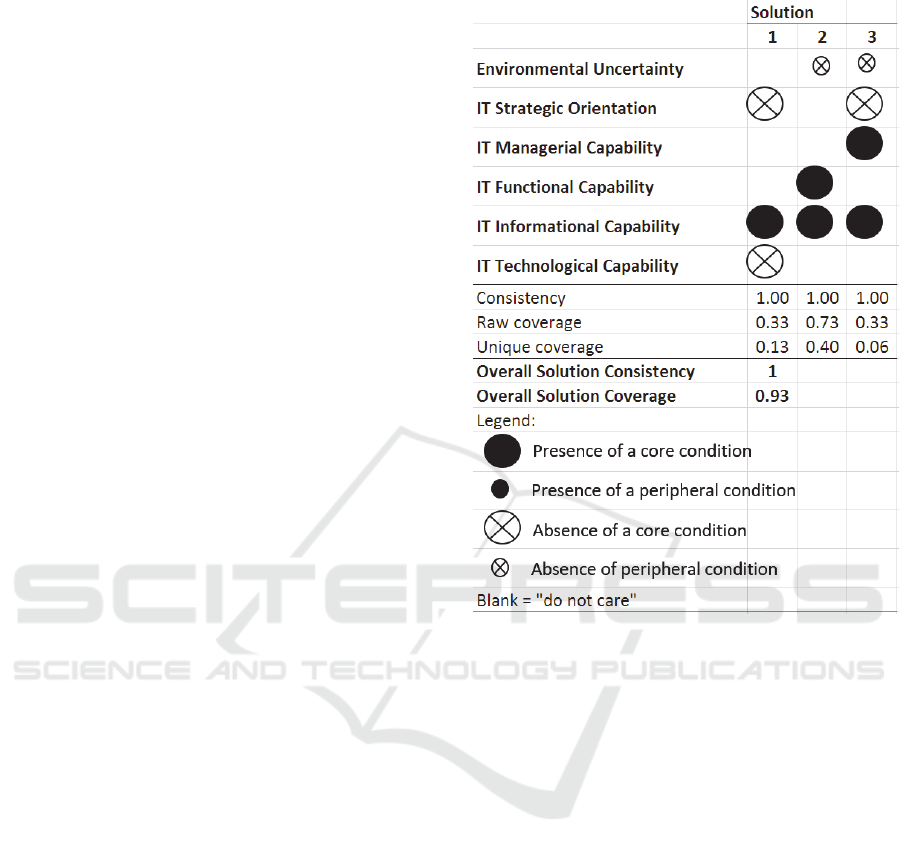
The results presented in Table 3 show three solutions
for achieving high-IT performance. The first solution
(#1) is characterized by three core conditions: an IT
Defender strategy, an IT informational capability and
the absence of (or unsophisticated) IT technological
capability. This solution has a raw coverage of 0.33
and a unique coverage of 0.13. The second solution
(#2) shows the absence of environmental uncertainty
as a peripheral condition and the presence of an IT
functional capability and an IT informational
capability as core conditions. This solution has a raw
coverage of 0.73 and a unique coverage of 0.40. The
third solution (#3) is also characterized by the
absence of environmental uncertainty as a peripheral
condition and the presence of a Defensive IT strategy,
an IT managerial capability and an IT informational
capability as core conditions. This solution has a raw
coverage of 0.33 and a unique coverage of 0.06.
We used the notation for solution tables
introduced by Ragin (2008), as used for example by
El Sawy et al. (2010) and Fiss (2011) (see Legend in
Table 3). A test of necessary and sufficient conditions
indicated that the IT informational sophistication is a
necessary condition in all reported configurations for
the outcome to exist (consistency = 1.0 and coverage
= 0.88). Note that a consistency threshold of 0.80
Table 3: Configurations for achieving high IT performance.
satisfied this condition (Ragin, 2008). The sufficient
conditions were identified by the configurations (or
solutions in QCA terms) obtained from the
parsimonious solutions generated to test the research
model, as presented in Table 3. Three IT
configurations were associated to high-IT
performance firms as parsimonious solutions.
6 DISCUSSION
The results revealed that the most frequent solution,
observed in 73% of the cases, is the solution #2. It is
not specific to any IT strategic orientation and thus
applies to both type of IT strategic orientation, be it
of a Defender or a Prospector one. Each of the two
other solutions (#1 and #3) are observed in 33% of the
cases and apply specifically to the IT Defender type.
While the presence (and absence) of IT capabilities as
core conditions and environmental uncertainty as a
peripheral condition differ among solutions, the
presence of IT informational capability is common to
all configurations. This indicates that there exist
various configurations for achieving high IT
performance and that the concept of a gestalt
Paths to IT Performance: A Configurational Analysis of IT Capabilities
301

alignment applies.
A first consideration in explaining these results
relates to the IT strategic types. One finds out at the
outset that two out of the three solutions (#1 and #3)
concern SMEs with an IT Defender strategic
orientation (i.e., crisp set where presence = IT
Prospector orientation, and absence = IT Defender
orientation) while no specific conclusion could be
drawn concerning IT Prospector strategic orientation
(#2). It might mean that IT Defender SMEs can define
more precisely what information they need and they
can be successful optimizing their management of the
information (through the IT managerial capability)
and their use of the information (through the IT
informational capability) of the information. This is
slightly different to what is reported by Miles and
Snow (2003) whose theory is that an organizational
Defender strategy should target a low cost strategy
and focus on the management of IT. Based on Miles
and Snow’s theory, IT Prospector SMEs evolve in
continuously changing markets, economic conditions
and organizational conditions, and should focus on
the use of IT capabilities which includes IT
informational and technological capabilities. This is
not observed here.
While all the solutions include the presence of IT
informational capability, these solutions do not relate
to any specific IT strategic orientation. Indeed,
solution #2 reports that IT informational capability is
a core condition of IT performance without
distinction for the IT strategic orientation. While the
presence of IT informational capability is in line with
the Miles and Snow’s theory for IT prospectors, the
IT functional capability should not be a characteristic
of IT Prospectors. This diversity in the configurations
of the two types of strategy has already been observed
by Fiss (2011) in a QCA research on large
organizations. He discussed his findings by reporting
that, at some point, there is no absolute configuration
for any strategic orientation and that variations may
exist among and within strategic types. Another
explanation is that the IT strategic orientation is not a
core causal condition to achieve high-IT performance
as long as the IT functional and informational
capabilities are present. This conclusion applies to the
solution #2 firms who represent a large majority of
the firms surveyed.
A second observation is that all solutions display
a necessary condition to be rated as a high-IT
performance SME. This core condition is the IT
informational capability. It is reported here as an
important characteristic of SMEs following an IT
Defender strategy. In set theoretic vocabulary, the IT
informational capability is a necessary (but not
sufficient) condition to be in the group of high-IT
performance organizations. It is a necessary
condition, in the sense that without IT informational
capability, no SME can be IT performing. It is not
sufficient since, as presented in the three solutions,
the IT informational capability has to be associated
with other characteristics. Note that these
characteristics differ among solutions. Again,
although the IT informational capability is a
characteristic of Miles and Snow’s Prospector
strategy, it is not a characteristic of Miles and Snow’s
Defender strategy. These results diverge from extant
theory.
In addition to the IT informational capability as a
necessary condition, the presence of IT managerial
and functional capabilities are core conditions in two
different solutions (#2 and #3). This corroborates the
importance of IT management capability as found in
earlier research (Raymond et al., 1995). However, it
could be noted that they are not simultaneously
present in the two solutions giving rise to a possibility
of only a partial alignment among IT capabilities to
be associated with high-IT performance SMEs as
long as the IT informational capability is present.
The IT technological capability is also reported as
a characteristic of one solution (#1) but in this case
(the IT Defender strategy), the solution indicates that
it is its absence that makes of it a core causal
condition. In this solution, an unsophisticated IT
technological capability characterize organizations
with an IT Defender orientation. In this case, the
absence of IT technological capability is in line with
what is reported in the literature (Miles and Snow,
2003).
The absence of environmental uncertainty is
another characteristic, of a peripheral type in this
case, of two (#2 and #3) out of three solutions for
high-IT performance SMEs. It means that among
high-IT performance firms, two observed solutions
concern SMEs in low environmental uncertainty. No
solution concerns a high environment uncertainty.
The gestalt form of alignment is appropriate for
the tested model since it allows to define three
different configurations of environmental
uncertainty, IT strategic orientation and IT
managerial, functional, informational and
technological capabilities, associated to high-IT
performance. As a necessary condition, the IT
informational capability matches the definition of a
moderator variable (Bergeron et al., 2004). In terms
of alignment of specific causal conditions, an IT
Defender strategy (as a core condition) (remind here
that in table 3, the “absence” of an IT strategic
orientation means the “presence” of firms with an IT
ICEIS 2017 - 19th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
302

Defensive strategy as a core condition), a low level of
environmental uncertainty (as a peripheral condition)
and various IT capabilities support a gestalt form of
alignment. The presence of a high level of
environmental uncertainty and an IT Prospector
strategic orientation did not show up as core
conditions in any of the three solutions. Moreover, the
simultaneous presence of all IT capabilities is not
necessary to achieve a high level of IT performance.
Indeed, each configuration relies on the alignment of
various combinations of IT capabilities, with two
capabilities suffice to allow an alignment of the
components. One configuration carry no specific IT
strategic orientation (be it Defender or Prospector),
and no specific level of environmental uncertainty (be
it high or low). Still, a partial level of alignment
between the presence of IT informational capability,
a necessary condition, and only one of the three other
IT capabilities is needed to be in the high-IT
performance SMEs. In all cases, it is the presence
(and not the absence) of IT capabilities that allow the
alignment while in one case (solution #1), it is the
absence (of sophistication) of a capability (the IT
technological capability) that allows the alignment.
This confirms that it is a mix of conditions that form
specific configurations, thus a gestalt type of
alignment.
7 IMPLICATIONS
In being among the first to answer El Sawy et al.’s
(2010) call for information systems researchers to
better study digital ecodynamics by using
configuration theory, this research has provided
evidence of a “holistic confluence” among
environmental uncertainty, IT strategic orientation
and IT capabilities in the context of manufacturing
SMEs. In so doing, we have gained initial insights as
to which types of IT strategy and IT capabilities are
critical to the IT performance of these firms in
uncertain (and more certain) business environments.
The three equifinal gestalts solutions identified
through the QCA approach were shown to constitute
a more likely source of IT performance for
manufacturing SMEs than any single type of IT
strategy and IT capability, given the complex
relationships and various interactions involved (Fiss,
2011).
This research contributes to the understanding of
the contribution of IT to firm performance. For
practitioners, it explains that there is no “one best
way” to perform in the management and use of IT.
SMEs have the choice of which IT capabilities they
want to emphasize and they do not need to attain a
high level on all four IT capabilities to become high-
IT performing firms. Instead, a gestalt perspective of
alignment wherein some IT capabilities are highly
developed while others are not is the solution. For
researchers, the results underline the analytical
possibilities offered by QCA to study small-sized
samples. QCA allows the researcher to achieve a
deeper understanding of the complexity faced by
SMEs when they attempt to strategically align their
management and use of IT. While specific results are
obtained for IT Defender SMEs, additional thoughts
should be made toward the appropriate capability
configurations for IT Prospector firms since no
specific configuration conclusion could be drawn that
would differentiate high-IT performance firms from
other firms. Finally, the gestalt alignment perspective
combined with QCA unveils results that have not
been observed before using traditional statistical
analysis. As noted by Fiss (2007, p. 1180), by using
QCA “researchers take a systemic and holistic view
of organizations where patterns or profiles rather than
individual independent variables are related to an
outcome such as performance”. Based on these
results, we call for more QCA research in the
management of information technology.
8 LIMITATIONS AND
CONCLUSION
As in all empirical research, this study has some
limitations. Given the size of the sample, its
representativeness in relation to manufacturing SMEs
is necessarily limited. A potential selection bias might
orient the results toward SMEs that are more
sophisticated in their management and use of IT. A
longitudinal study could also be needed for an in-
depth study of the IT alignment process. A more
complete formative model for measuring IT
performance could include information quality,
system quality, service quality and individual
benefits, in addition to organizational benefits. Its
limitations notwithstanding, this study has provided
further insight on the manner by which the
environmental uncertainty, IT strategic orientation
and IT sophistication of manufacturing SMEs
contribute to their IT performance, i.e. to their
realization of benefits from their investment in - and
use of - information technology.
In summary, the QCA approach allowed us to
unveil sets of core causal conditions characterizing
various solutions associated to a high level of IT-
Paths to IT Performance: A Configurational Analysis of IT Capabilities
303

business value for manufacturing SMEs. Among the
important observations are first, a sophisticated IT
informational capability as a necessary (but not
sufficient) causal condition for SMEs to realize the
most benefits from their investment in IT
independently from their IT strategic orientation and
the environmental uncertainty. Second, the strategic
alignment of all the IT capabilities (managerial,
functional, informational and technological) is a
condition that does not have to be fulfilled completely
to attain a high level of IT performance, as we
observed that only two of the four capabilities suffice.
Finally, two high-IT performance configurations
were identified for IT Defenders.
REFERENCES
Bergeron, F. and Raymond, L. (1995). The Contribution of
IT to the Bottom Line: A Contingency Perspective of
Strategic Dimensions. Proceedings of the 16th
International Conference on Information Systems,
Amsterdam, pp. 167- 181.
Bergeron, F., Raymond, L. and Rivard, S. (2004). Ideal
patterns of strategic fit and business performance,
Information & Management, 41 (8), pp. 1003-1020.
Bergeron, F., Raymond, L. and Rivard, S. (2001). "Fit in
Strategic Information Technology Management
Research: An Empirical Comparison of Perspectives",
Omega, 29 (2), pp. 125-142.
Bharadwaj, A. S. (2000). A resource-based perspective on
information technology capability and firm
performance: An empirical investigation. MIS
Quarterly, 24 (1), pp.169-196
Blili, S. and Raymond, L. (1993). Information technology:
Threats and opportunities for SMEs. International
Journal of Information Management, 13 (6), pp. 439-
448.
Caldeira, M.M. and Ward, J.M. (2003). Using resource-
based theory to interpret the successful adoption and
use of information systems and technology in
manufacturing small and medium-sized enterprises.
European Journal of Information Systems, 12, pp. 127-
141.
Cegielski, C. G., Jones-Farmer, L. A., Wu, Y. and Hazen,
B. (2012). Adoption of cloud computing technologies
in supply chains: An organizational information
processing theory approach. International Journal of
Logistics Management, 23 (2), pp. 184–211.
Charoensuk, S., Wongsurawat, W. and Khang, D. B.
(2014). Business-IT Alignment: A Practical Research
Approach. Journal of High Technology Management
Research, 25 (2), pp. 132-147.
Christopher, M. and Lee, H. (2004). Mitigating supply
chain risk through improved confidence. International
Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics
Management, 34 (5), pp. 388–396.
Clark, C. E., Cavanaugh, N. C., Brown, C. V. and
Sambamurthy, V. (1997). Building Change-Readiness
Capabilities in the IS Organization: Insights from the
Bell Atlantic Experience. MIS Quarterly, 21 (4), pp.
425-455.
Cragg, P.B., Mills, A. and Suraweera, T. (2010).
Understanding IT management in SMEs. Electronic
Journal of Information Systems Evaluation, 13 (1), pp.
27-34.
Croteau, A.-M. and Bergeron, F. (2001). An information
technology trilogy: Business strategy, technological
deployment and organizational performance, Journal of
Strategic Information Systems, 20 (2), pp. 77-99.
DeLone, W.H. and McLean, E.R. (2003). The DeLone and
McLean model of information systems success: a ten-
year update. Journal of Management Information
Systems, 19 (4), pp. 9-30.
Dibrell, C., Davis, P.S. and Craig, J. (2008). Fueling
innovation through information technology in SMEs,
Journal of Small Business Management, 46 (2), pp.
203-218.
Dutot, V., Bergeron, F., Raymond, L., (2014). Information
management for the internationalization of SMEs: An
exploratory study based on a strategic alignment
perspective. International Journal of Information
Management, 34 (5), pp.672-681.
El Sawy, O.A., Malhotra, A., Park, Y. and Pavlou, P.A.
(2010). Seeking the Configurations of Digital
Ecodynamics: It Takes Three to Tango. Information
Systems Research, 21 (4), pp. 835-848.
Escribá-Esteve, A., Sánchez-Peinado, L. and Sánchez-
Peinado, E. (2009). The Influence of Top Management
Teams in the Strategic Orientation and Performance of
Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises. British Journal
of Management, 20 (4), pp. 581-597.
Fiss, P. C. (2011). Building better causal theories: a fuzzy
set approach to typologies in organizational research.
Academy of Management Journal, 54 (2), pp. 393-420.
Fiss, P.C. (2007), A set-theoretic approach to
organizational configurations, Academy of
Management Review, 32 (4), pp. 1180-1198.
Flynn, B. B. and Flynn, E. J. (1999). Information processing
alternatives for coping with manufacturing
environmental complexity. Decision Sciences, 30 (4),
pp. 1021–1052.
Ganter, A and Hecker, A. (2014). Configurational paths to
organizational innovation: qualitative comparative
analyses of antecedents and contingencies, Journal of
Business Research, 67, pp. 1285-1292.
Gattiker, T. F. (2007). Enterprise resource planning (ERP)
systems and the manufacturing-marketing interface: An
information-processing theory view. International
Journal of Production Research, 45 (13), pp. 2895–
2917.
Guillemette, M.G. and Paré, G. (2012). Toward a new
theory of the contribution of the IT function in
organizations. MIS Quarterly, 36 (2), pp. 529-551.
Gregory, R.W., Keil, M., Muntermann, J., and Mähring, M.
(2015), Paradoxes and the Nature of Ambidexterity in
ICEIS 2017 - 19th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
304

IT transformation Programs, Information Systems
Research, 26 (1), pp. 57-80.
Henderson, J.C. and Venkatraman, N. (1999). Strategic
alignment: Leveraging information technology for
transforming organizations. IBM Systems Journal, 38
(2&3), pp. 472-484.
Kan, A.K.S., Adegbite, E., El Omari. S., and Abdellatif
(2016). On the use of qualitative comparative analysis
in management, Journal of Business Research, 69 (4),
pp. 1458-1463
Kohli, R. and Grover, V. (2008). Business value of IT: An
essay on expanding research directions to keep up with
the times. Journal of the Association for Information
Systems, 9 (1), pp. 23-39.
Kyobe, M. (2008). The influence of strategy-making types
on IT alignment in SMEs. Journal of Systems and
Information Technology, 10 (1), pp. 28-35.
Liu, G., Shah, R. and Babakus, E. (2012). When to mass
customize: The impact of environmental uncertainty.
Decision Sciences, 45 (5), pp. 851–887.
Marbert, V.A., Soni, A. and Venkataramanan M.A. (2003).
The impact of size on enterprise resource planning
(ERP) implementation in the US manufacturing sector.
Omega, 31, pp. 235-246.
Miles, R.E. and Snow, C.C. (2003). Organizational
Strategy, Structure, and Process, Stanford, California:
Stanford University Press.
Miller, D. and C. Dröge (1986). Psychological and
Traditional Determinants of Structure. Administrative
Science Quarterly 31, pp. 539–560.
Miner, A.S. (1990). Structural evolution through
idiosyncratic jobs: the potential for unplanned learning,
Organization Science, 1 (2), pp. 195 -210.
Pflughoest K.A., Ramamurthy, K., Soofi, E.S., Yasai-
Ardekani, M. and Zahedi, F. (2003). Multiple
conceptualizations of small business Web use and
benefit, Decision Sciences, 34 (3), pp. 467-512.
Philip, G. and Booth M.E. (2001). A new six ‘S’ framework
on the relationship between the role of information
systems (IS) and competencies in ‘IS’ management.
Journal of Business Research, 51, pp. 233-247.
Ragin, C.C. (1987). The Comparative Method, University
of California Press: Berkeley.
Ragin, C.C. (2000). Fuzzy Set Social Science, Chicago
University Press: Chicago.
Ragin, C.C. (2008). User’s Guide to Fuzzy-set / Qualitative
Comparative Analysis, Department of Sociology,
University of California.
Rai, A., Tang, X., Brown, P. and Keil, M. (2006).
Assimilation patterns in the use of electronic
procurement innovations: A cluster analysis.
Information & Management, 43, pp. 336-349.
Raymond, L., Bergeron, F., Croteau, A.-M. and St-Pierre,
J. (2015). Developing absorptive capacity through e-
business: The case of international SMEs. Journal of
Small Business Management, 53 (S1), pp. 75-94.
Raymond, L., Paré, G. and Bergeron, F. (1995). Matching
information technology and organizational structure:
Implications for performance. European Journal of
Information Systems, 4 (1), pp. 3- 6.
Rekik, L. and Bergeron, F. (2017). Green practices
motivators and performance in SMEs: A qualitative
comparative analysis, Journal of Small Business
Strategy, 27(1), pp. 1-17.
Riemenschneider, C.K. and Mykytyn, P.P. (2000). What
small business executives have learned about managing
information technology. Information & Management,
37, pp. 257-269.
Rihoux, B. and Ragin, C. (2009). Configurational
comparative methods: Qualitative comparative analysis
(QCA) and related techniques, Los Angeles: Sage.
Tornatsky, L.G. and Fleischer, M. (1990), The processes of
technological innovation, Lexington, Massachusetts:
Lexington Books.
Tushman, M. and Nadler, D. A. (1978). Information
processing as an integrating con-cept in organization
design. Academy of Management Review, 3 (3), pp.
613–624.
Venkatraman, N. (1994). IT-enabled business
transformation: From automation to business scope
redefinition, Sloan Management Review, 35 (2), pp. 73-
87.
Ward, J., Taylor, P. and Bond, P. (1996). Evaluation and
realisation of IS/IT benefits: An empirical study of
current practice. European Journal of Information
Systems, 4 (4), pp. 214-226.
Woodside, A.G. (2013) Moving beyond multiple regression
to algorithms: Calling for adoption of a paradigm shift
from symmetric to asymmetric thinking in data analysis
and crafting theory, Journal of Business Research, 66,
pp. 463-472.
Paths to IT Performance: A Configurational Analysis of IT Capabilities
305
