
RSSI-based Device Free Localization for Elderly Care Application
Shaufikah Shukri
1,2
, Latifah Munirah Kamarudin
1,2
, David Lorater Ndzi
3
, Ammar Zakaria
2,4
, Saidatul
Norlyna Azemi
1
, Kamarulzaman Kamarudin
2,4
and Syed Muhammad Mamduh Syed Zakaria
2
1
School of Computer and Communication Engineering, Universiti Malaysia Perlis, Arau, Perlis, Malaysia
2
Centre of Excellence for Advanced Sensor and Technology, University Malaysia Perlis, Jejawi, Perlis, Malaysia
3
School of Engineering and Computing, University of the West of Scotland, Paisley, Scotland
4
School of Microelectronic Engineering, University Malaysia Perlis, Arau, Perlis, Malaysia
Keywords: Device-free Localization, Elderly Care Application, Indoor Detection, IoT, RSSI, WSN.
Abstract: Device-Free Localization (DFL) is an effective human localizing system that exploits changes in radio
signals strength of radio network. DFL is playing a critical role in many applications such as elderly care,
intrusion detection, smart home, etc. DFL is ideal for monitoring the elderly activities without causing any
physical discomfort with the wearable devices. It is challenging for elderly to remember each day to wear or
to activate those devices. The purpose of this study is to select the best DFL methods in term of detection
and tracking accuracy, which is suitable for human monitoring application especially for elderly and disable
people. This paper proposes an RSSI-based DFL system that can be used to detect and locate elderly people
in an area of interest (AoI) using changes in signal strength measurements. An attenuation-based and
variance based methods have been introduced in the proposed DFL system. In stationary people scenario,
attenuation-based method managed to accurately detect the presence of human, which is very suitable for
elderly care application compared to variance-based DFL. The result shows that attenuation-based method
managed to detect all trajectories of moving people with 100% detection accuracy while variance-based
method only give 71.74% accuracy.
1 INTRODUCTION
Device Free Localization (DFL) is a passive indoor
localization system that uses the changes in the
Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI)
measurement to form the location information
metric about the location of person or object being
tracked. The DFL system monitors the fluctuation in
the received signal strength caused by the presence
of a human body in an indoor environment. More
than 70% of human body contains water that can
absorb and attenuate the radio signal wave at the
frequency of 2.4 GHz which is also the resonance
frequency of water (Deak et al., 2013). Several terms
has been used by the researcher to described DFL
system. Patrawi et al. (2010) defined DFL research
area as radio frequency (RF) tomography, RF sensor
network, and sensorless sensing. Due to the
increasing number of elderly and disabled people
population whom requiring better quality of life and
demand more healthcare and assistance services,
Internet of Things (IoT) has great potential to
support the society and health care providers by
introducing the combination of Ambient Intelligence
and DFL technology into residential monitoring
system known as Ambient Assisted Living (AAL).
The Ambient Intelligence vision is to build an
intelligent home with the help of smart devices and
appliances in order to increase the safety and
wellbeing in that particular home (Rose et al., 2015).
The basic idea of IoT is the transformation of
everyday devices into smart things which have the
ability to sense, interpret and react to the
environment through application by utilizing the
embedded technology (Domingo, 2012).The main
strength of IoT is to create smart environment
applications that will give significant impact to the
real world scenarios and bring improvement in
people's daily lives as well as provide intelligence
and comforts to the end user especially the disabled
by saving times and resources. Vermesan et al.
(2014) stated that at the year of 2011 the number of
Shukri, S., Kamarudin, L., Ndzi, D., Zakaria, A., Azemi, S., Kamarudin, K. and Zakaria, S.
RSSI-based Device Free Localization for Elderly Care Application.
DOI: 10.5220/0006361901250135
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security (IoTBDS 2017), pages 125-135
ISBN: 978-989-758-245-5
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
125

available IoT devices has already exceeded the
number of human being on planet Earth, and he
estimated by the year of 2020 the IoT devices are
expected to number in range of 26 billion to 50
billion. Examples of IoT application area include
Building, Healthcare, Lifestyle, Transportation, City,
Factory, Agriculture, Supply chain, Environment
and Energy and Tourism (Vermesan et al., 2014).
We strongly believe that the Internet of Things
can offer elderly people the assistance and support
they need to achieve a better quality of life.
Therefore, in this paper we proposed RSSI based
indoor localization system that is able to estimate the
location of people by monitoring the changes in RF
signal field occurring in the monitored network area.
This paper introduces a similar concept of device
free human presence detection system using
attenuation-based and variance based methods that
varies in terms of experimental designs. The aim of
this paper is to evaluate and compare the
performance of attenuation-based and variance-
based method in DFL system in detecting moving
and static entities inside a building for elderly care
application. The remainder of this paper is organized
as follows: Section 2 described the existing works
related to elderly care applications, Section 3
presents the proposed model-based methods used to
design algorithms using signal strength
measurements, Section 4 describe the experimental
setup, hardware, and development of algorithm, and
Section 5 reports in details the result and analysis of
the experiment. Finally, Section 6 concludes and
discusses the recent improvement strategies of DFL
system for elderly care application.
2 RELATED WORKS
Elderly care applications has been introduced to
improve the quality of life of seniors citizen whose
health is deteriorating due to increasing of age, and
at the same time reducing healthcare resources as
well as costs. The detection and tracking accuracy of
moving people in indoor and domestic environment
is one of the most important requirement in elderly
care application. The information gathered from
sensor nodes implemented for indoor localization
are multiple purposes and useful for elderly care
application to monitor daily activities, observe
tendencies of people, and alert the caretaker or
doctors in the case of abnormal behaviour of events
(Chironi et al., 2015).
In recent years, DFL for indoor environment
topic has become increasing popular among research
community and different detection system and
sensing technology have been developed in the
context of elderly care application. DFL technology
provides considerable advantages over other
technologies since there is no requirement for the
tracked entities to carry or wear any radio device or
sensor. This advantage makes DFL system very
suitable for monitoring the elder people activities
without causing them physical discomfort with the
wearable devices or sensors. It is challenging for
elder people to remember each day to wear or to
activate those devices.
Kaltiokallio et al. (2012) presented an RSS-based
DFL system for long-term residential monitoring
purpose that is able to provide accurate location
estimation. An online recalibration method was
proposed which enable proposed system to adapt to
the small changes in the real radio network
environment cause by daily routines for the long-
term deployment. They introduced a Finite-state
Machine (FSM) model which defines the location
specification of the person at different AoI inside the
house and linked the system to a Twitter account to
update the affected AoI. The proposed system was
able to accurately locate the monitored person while
carried out his daily routine.
Jin et al. (2015) proposed a passive elderly care
localization system using Nearest Neighbour-based
(NN) method to estimate the person location in the
monitored area and compared with Support Vector
Machine (SVM) method. They divided their
experiment into offline and online phase where
indoor position information was utilized to construct
the daily motion pattern of an elderly person. They
show that NN method performs better than SVM in
more complex environment and it is able to estimate
on average the location of tracked person with a very
high accuracy, 93.0655%.
Bocca et al. (2012) explore the use of Radio
Tomographic Imaging (RTI) in the context of
assisted living application. RTI is a technique that
produces real-time images of the changes in received
signal strength caused by human presence in the
monitored radio network environment which can be
used to estimate the location of people. They found
out that the change in RSSI depends on measured
frequency channel and proposed “fade level”
concept to their attenuation based RTI system. The
regularized least-square approach was selected as
regularization method to solve the ill-posed inverse
problem when estimating the real-time image. They
demonstrated that the average localization error of
the system is 0.23m. The proposed system can
accurately localize a target without participating in
IoTBDS 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
126

the localization process, hence makes the RF
technology a very attractive solution for elderly-care
application.
3 DFL CONCEPT
DFL is an effective human presence detecting
technology that does not require the tracked entities
to carry any additional radio devices or to be
cooperatively participating with the localization
process. It performs on the principle that the human
body will absorb/reflect the signal strength of indoor
wireless links being transmitted, when moving
across the Line-of-Sight (LoS) link of a transmitter
and receiver. By exploiting the changes on the
received signal strength of a given radio link, the
DFL system is able to detect the area where the
tracked entity is moving into. For example, if a
person enters a room as shown in Figure 1, the
algorithm of detection system will automatically
detect that there is a changes on the signal strength
on the LoS link between node N1 and N2 hence the
localization system will conclude that the user is
entering the area A1.
Figure 1: The proposed RSSI-based DFL system.
The advantage of model-based methods reported
by Kanso et al. (2009), Chen et al. (2011),
Kaltiokallio et al. (2011), Wilson et al. (2010, 2011),
and Zhao et al. (2011), is that training data of each
possible location in AoI is not required. These
methods use an elliptical model to relate people’s
location to different forms of RSSI measurements.
Wilson et al. (2010) use the model to relate the
location of a person with the absolute RSSI changes
from an “empty-room” calibration, where there is no
human presence in the network area. The model is
based on the fact that if a person stands inside an
elliptical area covered by a link between two nodes
within N voxel of network region, the person has
certain effect on the RSSI link measurement;
otherwise, there is no effect from the person.
3.1 Attenuation-based Method
For attenuation-based model, let consider an empty
room scenario of radio network for certain period of
time. During this period, the RSSI of L radio links
are measured. The average RSSI of unaffected link
is represented using the sample mean, denoted as ̂
.
In real environment, the RSSI measured by the
receiver of link l at time t can be described as
(
)
=
−
−
(
)
−
(
)
−
(
)
(1)
where
is the transmitted power,
(
)
is the
shadowing loss,
(
)
is fading loss from multipath
signals,
is static losses, and
(
)
is the
measurement noise. Let consider that changes in
attenuation has great impact to the received signal,
hence static losses
which caused by distance,
antenna patterns, device performance, etc. can be
removed over time to simplify the problem. The
shadowing loss
(
)
due to objects that attenuate
the signal for a link can be described as
(
)
=
(
)
−
(
)
(
)
. (2)
The fading loss and measurement noise can be
grouped as noise
and described as
=
()
(
)
(3)
hence
(
)
can be written as
(
)
=
(
)
−
(
)
. (4)
Due to the presence of noise
(
)
, the
shadowing loss cannot be measured directly. Thus,
the shadowing loss is estimated using the average
RSSÎ
, measured during empty room scenario
(
)
=
(
)
−̂
. (5)
The RSSI attenuation or difference between the
current RSSI measurement and the average RSS
measured during empty room scenario when no
person is in the monitored area at time t is calculated
as
∆
(
)
=
(
)
−̂
. (6)
3.2 Variance-based Method
The attenuation-based method requires an initial
calibration of the system in an empty room scenario
with no objects present in the monitoring area.
Recalibration is required when there is changes in
the environment, e.g., when any objects are placed
to other position, otherwise the system will lose its
accuracy. Variance-based method can be applied
since the changes in RSSI due to human presence on
RSSI-based Device Free Localization for Elderly Care Application
127

the link can be quantifies as the unbiased sample
variance of windowed RSS variance (McCracken et
al., 2013). Zhao et al. (2011) described the
windowed RSSI variance as
(
)
=
1
−1
(
̅
(
)
−
( − ))
(7)
where is the window length, and ̅
(
)
is the
average sample in this window period and can be
written as
̅
(
)
=
1
(
−
)
(8)
Variance-based RTI does not require empty room
scenario training data of the system and can easily
adapt to the changes in the environment.
4 EXPERIMENTS
In the previous work (Shukri et al., 2016), we
proposed a RSSI-based DFL system using a pair of
IRIS mote to study the impact of human body to the
signal strength in static and moving condition on
single network link. The proposed system proved
that the signal strength tends to fluctuate by average
of 3.97 dBm with the presence of static human body
on the LOS link and human detection and tracking
of stationary target is possible to within 1.0 m
distance from LOS link. Meanwhile, human
movement across the LOS link can cause significant
signal variation ranging from 10 to 15 dBm. In this
paper, we proposed an RSSI-based DFL system with
the configuration of multiple nodes (multiple
network links).
The experiments were conducted in Research
Room located at the first floor of Centre of
Excellence for Advanced Sensor and Technology
(CEASTech), University of Malaysia Perlis
(UniMAP), and the test-bed setups are illustrated in
Figure 2. The area of the Research Room is 2.5 m by
5.0 m and the ceiling height is 2.5 m. Three of the
walls are made of concrete, and one is containing
glass window. A wireless radio network consists of
six XM2110 IRIS motes (Memsic Inc.) made by
MEMSIC configured as the transmitters (N1, N2,
N3, N4 and N5) and a receiver (Rx). Each node
comprises of 1.2 inch 3 dBi omni-directional
antenna gain in azimuth with transmission rate of
250 kbps.
Figure 2: Test-bed setups for Exp.2 (Setup A) and Exp.3
(Setup B).
The nodes were placed at different position in the
room with different distance from the receiver. Each
node, placed with height of 1m above the floor,
operated in the 2.4 GHz frequency band and used
IEEE 802.15.4 (Zigbee) standard for the
transmission protocol. The receiver was mounted on
a MIB520 interface board and connected to a laptop
via USB port. The XM2110 IRIS for the transmitters
was programmed to transmit an empty packet every
1s. The receiver was programmed with Xsniffer
firmware to sniff and collect the received signal
strength from the transmitting nodes.
The collected information was transferred to a
laptop to be processed by a DFL detection algorithm
developed using LabVIEW programming language.
The RF power level was set to 3.2 dBm transmitting
at the strongest power level. RF channel 26 (2.48
GHz frequency band) was used to avoid co-channel
interference to the radio signal during experiment
since this channel 26 is proven as the most stable
with least interference among other available
channel based on the wireless network coexistence
study performed by Guo et al. (2012). Each node
was programmed with the same Group IDs, RF
channels and RF power for successful radio
communication.
During RF packets transmissions, the receiver
will automatically detect the RF strength level of
each node and send the information to a laptop for
processing. The nodes are placed at the height of 1.0
m above the floor to eliminate the Fresnel Zone
effect. Turner et al. (2013) studied the allowable
height for obstruction within the clear Fresnel Zone
is when both transmitter and receiver are mounted 1
.0 m above the floor. They also stated that to ensure
IoTBDS 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
128

the optimum radio performance, the motes must be
kept clear from the wall, ceiling and floor for about
0.2 m.
4.1 RSSI Analysis
To study and analyse the RSSI attenuation and
variance patterns of human presence in the indoor
environment of multiple nodes, we have decided to
record the RSSI information under the following
scenarios:
No obstruction was present (Exp.1): 3600
samples (for duration of 1 hour) of RSSI
measurements were taken to analyse the RSSI
trend during day time. This experiment was
carried out to monitor the baseline reading of
all network environments.
A body stands at pre-defined positions
(Exp.2): A person was instructed to walk from
point A to point B and stand at a pre-defined
position without moving for pre-determined
amount of time before walking to the next
position as shown in Setup A of Figure 2. The
pre-defined positions labeled as ‘X’ were
denoted as P1 and P2. Position of P1 is
located in Area B between link N2 and N3.
Position of P2 is located in Area C between
link N3 and N4. The objective of this third
experiment is to compare the detection result
and localization accuracy between
attenuation-based DFL and variance-based
DFL for human presence in static condition.
A body crossed the network link (Exp.3): A
person was instructed to walk from point A to
B as shown in Setup B of Figure 2, and
walked back to point A at a moderate pace
across the network links. This experiment was
carried out to monitor significant signal
attenuation when a person crossed the LoS
links. Experiment was repeated and the
number of crossing was increased from two to
ten times. This experiment was carried out to
monitor the RSSI pattern when a person
crossed the LoS links and measured nodes
sensitivity in detecting movement.
All RSSI information collected from the
experiment were transferred to a laptop to be process
using a DFL detection system developed using
LabView programming language. For attenuation-
based DFL system, it is important to obtain the
baseline or average RSSI during the monitored area
is empty. The baseline indicates the reference level
which will be used to estimate the attenuation in
RSSI signal when person entered the monitored area
or crossed the radio links. The attenuation, α is
estimated as the difference between RSSI measured
at time t, ri(t) and the baseline of RSSI, ȓ :
=
(
)
−̂ (9)
where ȓ computed using mode function which
selects the value that occur the most often
ȓ=
(10)
If the person moving across the radio network
area, the signal will experience large attenuation in
RSSI as the obstruction by human body contributes
to signal degradation for a certain time frame. The
baseline will give very small attenuation values
(small fluctuations), thus indicating the absence of
people. If the person is moving across the network
several times, the graph of RSSI value will show
declines in reading according to the number of
crossing.
4.2 Detection Algorithm
The attenuation-based method requires an initial The
proposed detection algorithm used in the LabView
program is based on the observation of RSSI
attenuation. RSSI attenuation is one of the valuable
parameters to detect activities or any changes
occurred in wireless radio network. The RSSI
attenuation reading shows that there are changes in
the RSSI behaviour where the radio links of the
network were obstructed or blocked. In this study,
the value of RSSI attenuation increases (in negative
reading) when a person walked across the network
links of wireless nodes. When the person walked
away from the monitored area, the RSSI attenuation
reads zero readings shows that there are no changes
in the monitored area. The threshold value for
attenuation, denoted as ᾱ is determined by taking the
average attenuation when people crossing the
network links.
Based on the above consideration, a detection
algorithm has been deployed and the process flow is
shown in Figure 3. When the receiver received RSSI
from each node, it sends the information to laptop
for data processing and analysis. Baseline reading of
each node is computed using mode function and
RSSI graphs of each node are updated for viewing
purposes. RSSI measurements from each window
are stored and updated. The attenuation of each link
is evaluated. When ∆ɑ > ᾱ, the link between node i
and receiver is assumed to be unaffected and go
back to the initial step for the measurement of next
window. When ∆ɑ ≤ ᾱ, human crossing is detected,
RSSI-based Device Free Localization for Elderly Care Application
129

the LED that show human presence is blinked, the
counter for occurrence is increased, and go back to
the initial step to measure RSSI of next window.
Figure 3: Process flow of proposed detection system.
5 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
AND ANALYSIS
The following results are presented in three sections;
empty room scenario, human presence with
movement scenario and human presence with static
scenario. The empty room scenario only focuses on
the RSSI measurement during daytime since
previous work (Shukri et al., 2016) has covered
RSSI measurement during both day time and at
night. For human presence with movement scenario,
a person walks across the network link two times
and ten times at a moderate pace. In human presence
with static scenario, a person stands at different
positions for certain period of time. The differences
in the signal attenuations can be observed when
there is human presence in the different
environments. All the RSSI measurements from
each experiment were automatically plotted on
graph which is available on the Front Panel of
LabVIEW program. The day results allow the
analysis of human presence on WSN and show the
effect of building materials, other WiFi devices, and
node battery strength on the signal strength.
5.1 Empty Room Scenario
In empty room scenario where no obstruction
presence in the Research Room, the day time
reading were taken during working hours from 9:00
to 17:00. Figure 4 shows the RSSI values of each
node measured during day time. The RSSI values
measured for 3600 samples range from -51d to -56
dBm for node N1, from -52 to -57 dBm for N2, from
-49 to -52 dBm for N3, from -51 to -55 dBm for N4,
and from -46 to -47 dBm for N5, respectively. In
previous work (Shukri et al., 2016), the RSSI
measurements for empty room scenario were
collected during daytime and at night; and the signal
strength were found to be unstable with several
small fluctuations during daytime due the presence
of several wireless devices operating for data
collection, human movement inside the building,
and moving vehicles on the nearby road (Kassem et
al., 2012), compared to the signal strength which are
more stable at night.
In this work, the experiment for empty room
scenario only focuses on the RSSI measurement
during daytime to monitor the stability of the nodes
in transmitting packets and the reliability of the data
collected. The baseline was computed using mode
function which selects the value that occurs the most
often for every node as shown in Table 1. The RSSI
and baseline readings for each links are different
since the nodes were placed at different position
inside the room. The battery performance has a
significant impact to the RSSI readings as well
where signal degradation happens when the battery
is low since the node does not have enough power to
transmit or received the signal.
Figure 4: RSSI measured in the monitored area during day
time.
-80
-70
-60
-50
-40
0 400 800 1200 1600 2000 2400 2800 3200 3600
RF Signal [dBm]
Time [s]
RSSI N1
RSSI N2
RSSI N3
RSSI N4
RSSI N5
IoTBDS 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
130

Table 1: Baseline reading measured for each node.
Node Baseline (dBm)
N1 -52
N2 -54
N3 -50
N4 -52
N5 -46
5.2 Stationary People Scenario
Exp.2 focuses on monitoring the changes in received
signal strength of multiple network links in the
presence of human without movement. In the real
world scenario, people living in a house always
performed activities that did not required them to
move at considerable amounts of time such as sitting
or lying on the coach while watching television,
sleeping on bed, sitting at dining table and etc. This
section discussed on the capabilities of attenuation-
based and variance-based DFL system in localizing
stationary people.
Figure 5 and Figure 6 show the attenuation and
variance values of the network links when a person
stand at pre-defined position P1 and P2 as depicted
in Setup A of Figure 2 for about 20 sec, respectively.
As illustrated in Figure 5, the attenuation of the
RSSI values decreases at pre-determined times
showing that a person standing at fixed position P1
and P2. When the person moved away from the
positions leaving the area empty, the attenuation
reading of affected links goes back to the normal
(empty area) readings. For eg., when a person is
standing at position P1 (Area B) for about 20 sec
starting at t=30 sec, there are changes on the
attenuation values of N1, N2 and N3 since these
three nodes located near to position P1. When the
person started to move and stand at position P2 after
20 sec, the attenuation values of nodes N1, N2 and
N3 experience normal (empty area) value. The
presence of human near to the network links changes
considerably the RSSI and attenuation measured on
the affected links.
For each sample window, the collected RSSI
values been averaged for every four second, and the
variance of each sample window have been
computed. As per illustrated in Figure 6, the
variance values only experiences peaks which
indicate that the person moved crossed the network
links into and away from the pre-defined position P1
and P2, but did not show that the person was
standing at Position P1 and P2 at pre-determined
times. For eg., the variance value of N2 is expected
to show changes from 7th to 13th sample window
interval which indicates that a person is standing at
Position P1 (Area A), however it only shows two
peaks at 7th and 13th sample window interval which
indicate that the person is crossing the network link
of node N2. This proved that variance-based DFL is
not capable of localizing stationary people since the
measurements are based on a windowed variance of
RSSI.
The experiments conducted in these section
shows that human presence in stationary condition
contributes to the changes of signal strength by
introducing the shadowing and multipath effect. The
results proved that localization and detection of
stationary people in multiple network links
environment is possible using attenuation-based.
However, the variance-based DFL is not suitable for
elderly-care application due to its incompetency of
localizing stationary people.
Figure 5: Attenuation values of the network links in Setup
B when a person stands at pre-defined position.
Figure 6: Variance values of the network links in Setup B
when a person stands at pre-defined position.
5.3 Moving People Scenario
In this section, the changes on received signal
strength due to human movement across the LoS
links are discussed. Two experiments have been
conducted in this section with different number of
-30
-25
-20
-15
-10
-5
0
5
10
0 20406080100120140160
RF Signal [dBm]
Time [s]
ɑ N1
ɑ N2
ɑ N3
ɑ N4
ɑ N5
-10
-5
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
0 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36 40 44
RF Signal [dBm]
Sample Window
Var N1
Var N2
Var N3
Var N4
Var N5
RSSI-based Device Free Localization for Elderly Care Application
131

crossing. In the first experiment, a body was
instructed to cross the monitored area twice while in
the second experiment the number of crossing was
increased to ten times. The results have been
analyzed in both attenuation-based and variance-
based DFL.
5.3.1 Two Times Crossing
Figure 7 shows the RSSI attenuation values of each
network links in the monitored area when a person
crossed the network links twice. It can be observed
that the signal strength of affected network links
decrease when the person crossed the network links
from point A to B and back to point A. The affected
network links are N2, N3 and N4.
Figure 7: Attenuation value of the links in Setup B when a
person crossed the link 2 times.
Figure 8: Variance of the links in Setup B when a person
crossed the link 2 times.
The graph from Figure 7 shows that the
attenuation-based DFL system can accurately detect
the sequence of affected links when a person moving
across the network, hence the area of interest can be
determined. From point A to B, a person will first
cross the link of node N2 at time equal to 11 sec
which determined that the person moved from Area
A to Area B. The person then walked from Area B
to Area C by crossing N3 link at time equal to 19
sec, and at time equal to 23 sec the person crossed
N4 link indicates that he moved from Area C to
Area D. Significant signal attenuations are observed
to be range from -11 dBm to -18 dBm when the
person crossed the network links.
Figure 8 shows the variance values of the same
scenario computed using variance-based DFL. The
first crossing was detected to be at 2nd, 4th and 5th
sample windows for N2, N3 and N4 links with the
variance values of 49, 32.9 and 72.9 respectively.
The second crossing was detected to be at 7th, 9th
and 10th sample windows for N4, N3 and N2 links
with the variance values of 52.3, 60.7 and 24.3
respectively. The attenuation and variance values of
affected links from both Figure 7 and Figure 8
experiences two peaks, as expected since during
experiment the user crossed the link two times. No
signal large fluctuation observed on links N1-Rx and
N5-Rx since there is no human presence across these
links.
5.3.2 Ten Times Crossing
Exp. 3 was repeated and the number of crossing was
increased from two to ten times. Figure 9 shows the
RSSI attenuation values of multiple network links
when a person crossed the link ten times. It can be
observed that the signal strength of affected network
links N2, N3 and N4 decrease when the person
crossed the network area ten times. Similar to
previous experiment with less number of crossings,
the attenuation-based DFL system can accurately
detect the number of crossing as well as sequence of
affected links with 100% accuracy when a person
moving across the network several times; hence can
the area of interest can be determined. As per
expected, ten decreasing peaks experienced by the
attenuation values of affected links in Figure 9 since
during experiment the user crossed the network links
ten times. The variance values computed using
variance-based method of the same scenario is
depicted in Figure 10. It can be observed that the
variance values of affected network links N2, N3
and N4 varies when the person crossed the network
area ten times. As per expected, ten peaks
experienced by the variance values of affected links
ranging from 8.25 to 157.33 as shown in Figure 10
since during experiment the user crossed the
network links ten times.
-14
-11
-12
-14
-18
-15
-30
-25
-20
-15
-10
-5
0
5
10
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
RF Signal [dBm]
Time [s]
ɑ N1
ɑ N2
ɑ N3
ɑ N4
ɑ N5
49,0
24,3
32,9
60,7
72,9
52,3
-10,0
10,0
30,0
50,0
70,0
90,0
110,0
0123456789101112
RF Signal [dBm]
Sample Window
Var N1
Var N2
Var N3
Var N4
Var N5
IoTBDS 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
132
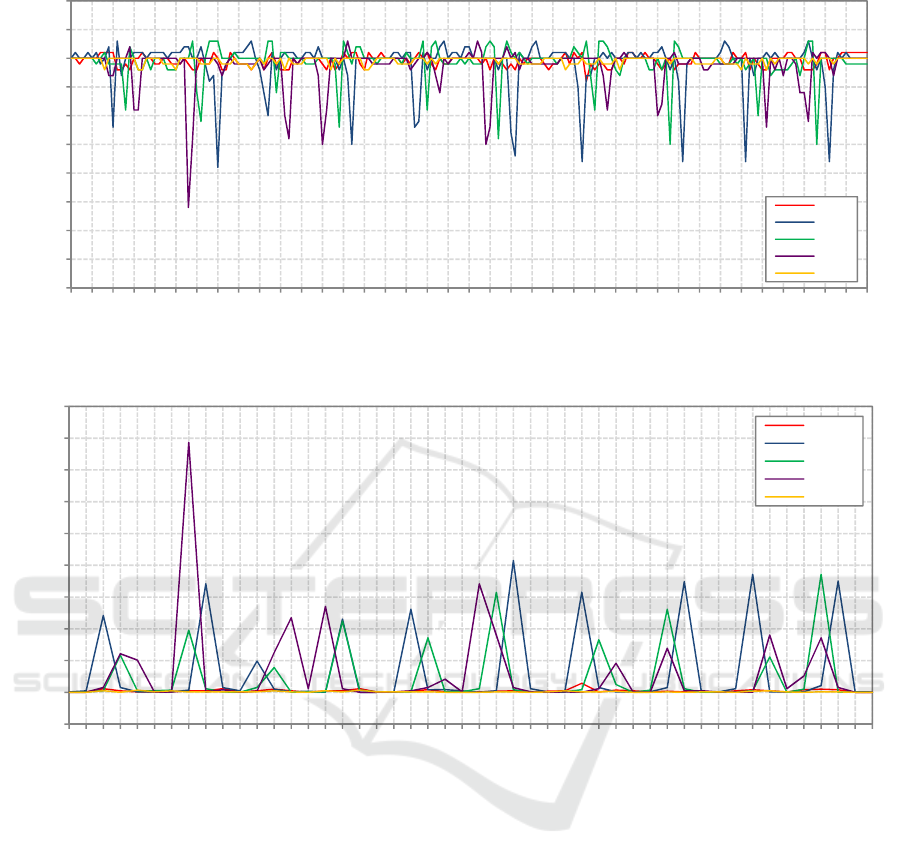
Figure 9: Attenuation values of the link in Setup A when a person crossed the link 10 times.
Figure 10: Variance value of the link in Setup B when a person crossed the link 10 times.
In contrast with previous experiment with less
number of crossings, the variance-based method
only able to detect the presence of human across the
network links with less accuracy, 71.74%. As per
illustrated in Figure 10, variance-based method
unable to accurately detect the sequence of affected
links when a person moving across the network
several times. For example in sample window
intervals equal to 7th, 16th, 35th, 41st and 44th, the
variance values experience overlapping peaks at the
same window interval indicated that two links are
effected but unable to identify which link was
crossed first, hence variance-based DFL unable to
correctly identify the affected area of interest of
radio network environment. For example, at 7th
sample window interval, the user is expected to
move from Area D to Area C, and the variance
graph indicates that the user probably located at
Area C or Area B since there are increasing in
variance values of links N3 and N4 which indicate
that the person already crossed both links at the
same window interval. The variance-based DFL
system produced 28.26% of the result as overlap and
false detection.
All experiments conducted show that human
movement or any moving objects across the network
links will introduce shadowing and multipath effect
on the radio signal strength. Both attenuation-based
and variance-based DFL results proved that the
presence of moving people across network links has
cause significant signal degradation. The number of
peaks experienced by the attenuation and variance
-12
-19
-10
-15
-12
-17
-18 -18 -18 -18
-9
-11
-6
-12
-9
-14
-9
-15
-10
-15
-9
-26
-14
-15
-6
-15
-9
-10
-12
-11
-40
-35
-30
-25
-20
-15
-10
-5
0
5
10
0 102030405060708090100110120130140150160170180190
RF Signal [dBm]
Time [s]
ɑ N1
ɑ N2
ɑ N3
ɑ N4
ɑ N5
48,25
68,25
19,67
52,25
82,92
63,00
69,58
74,25
70,00
23,33
39,00
15,58
44,92
34,25
62,92
33,00
52,25
22,25
74,25
24,25
157,33
46,92
54,00
8,25
68,25
18,25
27,67
36,00
34,25
-20
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
180
0246810121416182022242628303234363840424446
RF Signal [dBm]
Sample Window
Var N1
Var N2
Var N3
Var N4
Var N5
RSSI-based Device Free Localization for Elderly Care Application
133

values agrees with the number of crossing in the
network environment; however the variance-based
method give overlapping peaks result at particular
window intervals resulting in false human detection.
This proved that localization and detection of human
moving in moderate pace across multiple network
links is better using attenuation-based and variance-
based DFL. However variance-based DFL will give
less localization accuracy if the number of crossing
is increased.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, an RSSI-based DFL system has been
proposed for elderly care application. The effects of
human presence in both moving and static scenarios
have been presented and compared between
attenuation-based and variance-based method. The
result shows that, attenuation-based method able to
accurately detect the presence of stationary people
compared to variance-based method which unable to
detect stationary people in presence in monitored
area. Since people living in house always performed
daily activities which spend considerable amounts of
time without moving, the attenuation-based is more
suitable for elderly care application compared to
variance-based DFL. In the case of moving people
scenario, both attenuation-based and variance-based
methods able to localize moving people. The
attenuation-based method successfully detects the
number of crossing and the sequence of trajectories
with 100% accuracy while variance-based only
gives 71.74% accuracy. Work is in progress to
optimize the network links so that each node can
communicate with each other to create more
network links that can improve the localization
accuracy. Further work will involve exploring
attenuation-based DFL system in larger area which
might not only focus on localizing, but as well as
fall-detection that is very useful in elderly-care
application
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported in part by the Fundamental
Research Grant Scheme (FRGS), Grant No. 9003-
00548. Authors would like to thank all research
members, cliques and others who have involved and
make this experiment successful.
REFERENCES
Bocca, M., Kaltiokallio, O. and Patwari, N., 2012. Radio
tomographic imaging for ambient assisted living. In
International Competition on Evaluating AAL Systems
through Competitive Benchmarking (pp. 108-130).
Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Chen, X., Edelstein, A., Li, Y., Coates, M., Rabbat, M.
and Men, A., 2011. Sequential Monte Carlo for
simultaneous passive device-free tracking and sensor
localization using received signal strength
measurements. In IPSN’11, 10th International
Conference on Information Processing in Sensor
Networks, (pp. 342-353). IEEE.
Chironi, V., Pasca, M., D’Amico, S., Leone, A. and
Siciliano, P., 2015. IR-UWB for Ambient Assisted
Living Applications. In Ambient Assisted Living (pp.
209-218). Springer International Publishing.
Deak, G., Curran, K., Condell, J., Asimakopoulou, E. and
Bessis, N., 2013. IoTs (Internet of Things) and DfPL
(Device-free Passive Localisation) in a disaster
management scenario. Simulation Modelling Practice
and Theory, 35, pp.86-96.
Domingo, M.C., 2012. An overview of the Internet of
Things for people with disabilities. In Journal of
Network and Computer Applications, 35(2), pp.584-
596.
Guo, W., Healy, W.M. and Zhou, M., 2012. Impacts of
2.4-GHz ISM band interference on IEEE 802.15. 4
wireless sensor network reliability in buildings. In
IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and
Measurement, 61(9), pp.2533-2544.
Jin, Z., Bu, Y., Liu, J., Wang, X. and An, N., 2015.
Development of Indoor Localization System for
Elderly Care Based on Device-Free Passive Method.
In ISDEA’15, 6th International Conference on
Intelligent Systems Design and Engineering
Applications, (pp. 328-331). IEEE.
Kaltiokallio, O. and Bocca, M., 2011. Real-time intrusion
detection and tracking in indoor environment through
distributed RSSI processing. In RTCSA’11, 17th
International Conference on Embedded and Real-Time
Computing Systems and Applications, (Vol. 1, pp. 61-
70). IEEE.
Kaltiokallio, O., Bocca, M. and Patwari, N., 2012.
Follow@ grandma: Long-term device-free localization
for residential monitoring. In LCN Workshops’12,
37th Conference on Local Computer Networks
Workshops, (pp. 991-998). IEEE.
Kanso, M.A. and Rabbat, M.G., 2009. Compressed RF
tomography for wireless sensor networks: Centralized
and decentralized approaches. In International
Conference on Distributed Computing in Sensor
Systems (pp. 173-186). Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Kassem, N., Kosba, A.E. and Youssef, M., 2012. RF-
based vehicle detection and speed estimation. In VTC
Spring’12, 75th Vehicular Technology Conference
(pp. 1-5). IEEE
McCracken, M., Bocca, M. and Patwari, N., 2013. Joint
ultra-wideband and signal strength-based through-
IoTBDS 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
134

building tracking for tactical operations. In
SECON’13, 10th Annual IEEE Communications
Society Conference on Sensor, Mesh and Ad Hoc
Communications and Networks, (pp. 309-317). IEEE.
Memsic Inc., 2009. MEMSIC IRIS datasheet, Doc. Part
No.: 6020-0124-01 Rev B.
Patwari, N. and Wilson, J., 2010. RF sensor networks for
device-free localization: Measurements, models, and
algorithms. In Proceedings of the IEEE, 98(11),
pp.1961-1973.
Rose, K., Eldridge, S. and Chapin, L., 2015. The internet
of things: An overview. The Internet Society (ISOC),
pp.1-50.
Shukri, S., Kamarudin, L.M., Goh, C.C., Gunasagaran, R.,
Zakaria, A., Kamarudin, K., Zakaria, S.M.M.S.,
Harun, A. and Azemi, S.N., 2016. Analysis of RSSI-
based DFL for human detection in indoor environment
using IRIS mote. In ICED’16 3rd International
Conference on Electronic Design, (pp. 216-221).
IEEE.
Turner, J.S., Ramli, M.F., Kamarudin, L.M., Zakaria, A.,
Shakaff, A.Y.M., Ndzi, D.L., Nor, C.M., Hassan, N.
and Mamduh, S.M., 2013. The study of human
movement effect on Signal Strength for indoor WSN
deployment. In ICWISE’13, Conference on Wireless
Sensor, (pp. 30-35). IEEE.
Vermesan, O. and Friess, P. eds., 2014. Internet of things-
from research and innovation to market deployment
(pp. 74-75). Aalborg: River Publishers.
Wilson, J. and Patwari, N., 2010. Radio tomographic
imaging with wireless networks. In IEEE Transactions
on Mobile Computing, 9(5), pp.621-632.
Wilson, J. and Patwari, N., 2011. See-through walls:
Motion tracking using variance-based radio
tomography networks. In IEEE Transactions on
Mobile Computing, 10(5), pp.612-621.
Zhao, Y. and Patwari, N., 2011. Noise reduction for
variance-based device-free localization and tracking.
In SECON’11, 8th Annual IEEE Communications
Society Conference on Sensor, Mesh and Ad Hoc
Communications and Networks, (pp. 179-187). IEEE.
RSSI-based Device Free Localization for Elderly Care Application
135
