
Where, Wherefore, and How?
Contrasting Two Surveillance Contexts According to Acceptance
Julia van Heek, Katrin Arning, and Martina Ziefle
Human-Computer Interaction Center, RWTH Aachen University, Campus Boulevard 57, 52074 Aachen, Germany
Keywords: Surveillance Technologies, Medical Vs, Crime Surveillance, Technology Acceptance, User Diversity, Con-
joint Analysis.
Abstract: Surveillance technologies are used all over the world for various reasons. In urban environments, surveil-
lance technologies are predominantly used for detecting or preventing crimes. Simultaneously, an increasing
number of technologies are used for medical monitoring at home, but also at clinical facilities, and at public
environments for assuring patients’ medical safety. An intensive policy discussion about perceived ad-
vantages (especially increasing safety) and perceived barriers (in particular the invasion of privacy) comes
along with the use of surveillance technologies. In this paper, it is examined where and for which contexts
the use of surveillance technologies is accepted and under which conditions safety or privacy is perceived as
more important. We investigate the acceptance of surveillance technologies for medical and crime surveil-
lance scenarios using a conjoint analysis approach including four relevant aspects: location of surveillance,
increase in safety, invasion of privacy, and the applied camera type. Results show both, context independent
findings as well as context-sensitive findings: e.g., for crime surveillance, the location is most important fol-
lowed by the trade-off between privacy and safety, while these three factors are of similar importance for
medical surveillance. From a practical viewpoint, the findings might contribute to a differentiated surveil-
lance policy in cities.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, modern societies face major challenges
in order to cope with on-going urbanization de-
mands: especially the demographic change, which
require novel care and adequate supply concepts as
well as enabling of living in smart, safe, and sustain-
able cities. Along with this comes the increasing
development that higher proportions of people will
live in cities than in all other regions. These substan-
tial urbanization processes lead to consecutive chal-
lenges, which are difficult to balance. Apart from
healthcare, economy, mobility, or governance issues,
the implementation of safe and also well-accepted
technical infrastructures and smart city concepts is
focused worldwide (Ziefle et al., 2014).
Most large cities around the world use surveil-
lance technologies (primarily video surveillance via
cameras) in order to prevent and detect crime for
increasing safety in cities and particularly at public
locations (Dailey, 2013; Barrett, 2013). Progressive-
ly, surveillance technologies in smart city concepts
(Filipponi et al., 2010; Dey et al., 2012) are increas-
ingly connected, integrated, and implemented. This
is especially driven by the motive to increase per-
ceived safety for city residents as this is the essential
condition for the participation in social and econom-
ic life and thus, it is a valuable asset for cities.
In spite of this undisputed positive aspect of sur-
veillance, the violation of public’s or city resident’s
privacy through recording, storage, and processing
of (video) data represents the most discussed draw-
back and barrier of using surveillance technologies
(Patton, 2000). The balance between both poles –
privacy as a value and safety as a value – is quite
intricate. A wide spectrum of resident’s needs, espe-
cially their attitudes towards and requirements for
safety and privacy have to be considered during the
development and implementation of smart city con-
cepts.
This trade-off is not only discussed for the crime
surveillance context, but also matters in the context
of medical surveillance. While surveillance technol-
ogies were mainly used for crime detection reasons
in recent decades, they have been increasingly used
for medical surveillance since the last years. Surveil-
lance technologies - in particular AAL systems
Heek, J., Arning, K. and Ziefle, M.
Where, Wherefore, and How? - Contrasting Two Surveillance Contexts According to Acceptance.
DOI: 10.5220/0006362400870098
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems (SMARTGREENS 2017), pages 87-98
ISBN: 978-989-758-241-7
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
87

(Ambient Assisted Living) - become more and more
popular in the context of chronic illness and medical
monitoring (Leonhardt, 2006; Klack et al., 2011). In
the medical context, one of the major goals of sur-
veillance or monitoring systems is the detection of
emergencies - especially falls - as falls are one of the
most serious health risks for seniors (Rubenstein,
2006). Thus, medical surveillance technologies do
increase not only perceived but also factual safety as
a fast detection of emergencies and falls and consec-
utively immediate help reduce the risk of death by
more than 80% (Gurley et al., 1996). Opposing this
benefit of medical surveillance, there are concerns
about an invasion of the own privacy in terms of a
protection of personal information, e.g., anonymity,
self-determination, personal control of data (Patton,
2000; Wilkowska & Ziefle, 2012). Thus, surveil-
lance generally represents a conflict between two
key motives: on the one hand, the wish to be safe as
well as increase safety in urban environments and,
on the other hand, the wish to stay private and to
protect the own privacy. This conflict is difficult and
almost impossible to address for city planners with-
out understanding the residents’ individual ac-
ceptance of surveillance technologies.
In this paper, the acceptance of surveillance
technologies is empirically investigated differentiat-
ing between two urban contexts. Using a conjoint
analysis, the critical trade-off between privacy and
safety is empirically addressed as well as different
locations of surveillance and different camera types
are taken into account. Comparing a medical and a
surveillance context allows to find out if the ac-
ceptance of surveillance technologies is a context-
sensitive phenomenon. This way, it is examined to
what extent city residents’ evaluation of the trade-off
between safety and privacy varies depending on the
context, the type of technology, and the city location
in which surveillance is applied.
2 ACCEPTANCE OF
SURVEILLANCE SYSTEMS
Currently, more and more different surveillance
technologies are used and integrated into surveil-
lance concepts not only to generate smart houses,
but also to build smart city networks. Thus, this
section presents an overview of the technologies that
are applied for different surveillance contexts as well
as their advantages and drawbacks (2.1). Further, the
current state of the art concerning research on the
acceptance of surveillance is detailed focusing on
which technologies are accepted at which locations,
for which context, and under which conditions (2.2).
2.1 Context-specific Use of Surveillance
Technologies
For the context of crime surveillance, the currently
most applied safety measure in urban environments
is video surveillance (Koh et al., 2016). Video sur-
veillance strongly differs with respect to the camera
type enabling diverse functions (compounded with
other technologies) such as face recognition or pre-
cise location determination. These types of video
surveillance are used in many cities exhaustively
enabling a detailed tracking of criminals and detec-
tion of crimes (La Vigne et al., 2011). Some theoret-
ical research approaches focus also on the integra-
tion of crime surveillance into smart city concepts
(Fyfe, 2004; Dey et al., 2012). So far, many studies
investigated the effectiveness of safety measures
such as improved lighting of public places or video
surveillance for enhancing safety especially at public
high-frequented locations (e.g., La Vigne et al.,
2011, Welsh & Farrington, 2004; Welsh et al.,
2015): all of them found an increased safety percep-
tion by city residents but also a higher “real” safety
in terms of crime reduction and higher rates of crime
detection. In contrast, an invasion of privacy is the
main drawback of (video-based) crime surveillance
as recording, processing, and storage of data is heav-
ily scrutinized (e.g., Welsh et al., 2015; Schwartz,
2012).
For medical reasons, surveillance technologies
were mainly used in the private home environment,
in health facilities, and retirement homes in the last
years. A wide variety of AAL technologies exists
mainly developed to detect falls and enable fast
assistance in emergencies (Cardinaux et al., 2011;
Memon et al., 2014). Using video-based technolo-
gies is in particular advantageous as it enables con-
tactless observation without the necessity to equip
patients with further technologies (e.g., help button,
tag, sensors). Thus, a high number of video-based
health surveillance systems was developed to date
that primarily focus on fall detection in order to
increase safety (e.g., Fleck & Strasser, 2008; Yu et
al., 2012; Chen et al., 2013). Although AAL tech-
nologies were predominantly used at private envi-
ronments, it is reasonable to integrate medical sur-
veillance technologies at public urban environments
to expand existing (crime) surveillance technologies
with regard to medical surveillance as a high number
of emergencies happen in public. In accordance with
demographic change and an aging society, the needs
SMARTGREENS 2017 - 6th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
88

for public medical surveillance in cities increase
continuously. Hence, there are also first approaches
to integrate medical or health surveillance into smart
city concepts in order to increase medical safety
(Solanas et al., 2014).
Besides the main benefit of increased safety, pri-
vacy concerns are of major importance in the health
or medical surveillance context (Wilkowska & Zief-
le, 2012). In particular, privacy is a highly relevant
topic for video surveillance, since people in the area
covered by cameras have no option to avoid being
monitored. There are some technical approaches that
try to integrate measures to protect privacy within
the surveillance systems, e.g., by recording and
storage of video data only if accidents were detected
(Aghajan et al., 2007).
Summarizing so far, the use of surveillance tech-
nologies implies a sensitive and critical trade-off
between an increase in safety and the protection of
privacy in a crime as well as a medical surveillance
context.
2.2 Technology Acceptance
Usually, the development and integration of surveil-
lance technologies is a policy decision of planning
authorities in cities and communes without integrat-
ing residents during the technical development and
decision-making process. However, the controver-
sial public discussion about surveillance shows that
it might be supportive to consider resident’s needs
and concerns in early phases of the decision process
in order to enable a pleased and safe life in cities
(Slobogin, 2003; Surette, 2005). While there are a
plenty of studies focusing on technical characteris-
tics of surveillance or the efficiency of applied sur-
veillance technologies (e.g., La Vigne et al., 2011;
Welsh et al., 2015), sparse social science research is
available in this regard. Previous acceptance studies
primarily focus on single surveillance contexts: a
study on crime surveillance acceptance found high-
est acceptance scores for video surveillance at highly
frequented public places, such as train stations, as
well as comparatively higher needs for safety at
public and higher privacy needs at private environ-
ments (van Heek et al., 2015). Another single case
study focused on medical surveillance and also
found higher acceptance scores for video surveil-
lance at public environments. However, general
acceptance for medical surveillance was rather low
due to strong privacy concerns of the participants
(Himmel et al., 2013).
A direct comparison of different surveillance
contexts has not been investigated so far. It would be
useful to analyze whether the acceptance of surveil-
lance technologies and the evaluation of the trade-
off between safety and privacy is a generic or a
context-sensitive phenomenon. As privacy and safe-
ty proved to be important factors of surveillance
acceptance (see 2.1), their understanding is essential
for a successful adoption of surveillance technolo-
gies (Rogers, 2003).
The Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) is
the most known and best-established model explain-
ing and predicting the adoption of technologies and
serves as a basis for numerous subsequent and
adapted models (Davis et al., 1989). However, these
acceptance models cannot be simply applied to the
acceptance of video-based surveillance technologies:
A first reason is that conventional acceptance mod-
els enable an evaluation of complete technologies,
systems, or applications, but they do not allow an
evaluation of single technical functions or character-
istics of a system. Hence, it is not possible to derive
which characteristics of a system lead to adoption or
non-adoption of the complete system yet. As a re-
sult, it is also not possible to derive concrete design
guidelines, e.g., where, how, and under which condi-
tions a video-based surveillance system should be
used. Secondly, questionnaires, designed on the
basis of TAM or adapted acceptance models, do not
allow a simulation of complex decision scenarios, in
which several decision criteria are weighted against
each other. Hence, it is also not possible to infer
statements about relative importance, relationships,
and interactions of several factors.
Summarizing, acceptance, conceptualization, and
integration of video-based surveillance systems in
smart cities could be improved, if designers and
(city) planners could revert on city residents’ prefer-
ences. Thus, the goal of our study was to capture
preferences for video-based surveillance scenarios at
different locations (private vs. public), under consid-
eration of different camera types, benefits in terms
of increased safety, and privacy concerns due to
different data handling purposes. By applying a
conjoint analysis, decision scenarios were simulated
and different attributes’ acceptance as well as their
interrelations were analyzed in detail. In order to
fulfill a direct comparison of surveillance context,
the approach was carried out for a medical (study 1)
and a crime surveillance (study 2) context.
3 METHODOLOGY
In order to understand if acceptance for surveillance
depends on the context, the conjoint analysis ap-
Where, Wherefore, and How? - Contrasting Two Surveillance Contexts According to Acceptance
89

proach was applied to a medical and a crime surveil-
lance scenario. The factorial design of the conjoint
analysis in both contexts (surveillance vs. medical)
included four attributes that had been identified as
important impact factors on surveillance acceptance
in preceding studies (van Heek et al., 2015; Arning
& Ziefle, 2015): 1) locations of surveillance, 2)
increase in safety operationalized as detection rates
of crimes and medical emergencies, 3) privacy in
terms of different handlings of the recorded data
material, and 4) different camera types. These attrib-
utes were used to identify the most important pa-
rameters and to examine to which extent surveil-
lance scenario decisions based on these attributes
were linked to the surveillance context.
3.1 Conjoint Analysis
Conjoint analyses were developed by Luce and Tuk-
ey in the 1960s and combine a measurement model
with a statistical estimation algorithm (Luce & Tuk-
ey, 1964). Within a conjoint analysis, respondents
assess specific product or scenario configurations
that consist of different attributes and differ from
each other in the attribute levels. This way, conjoint
analyses go beyond the possibilities of conventional
survey-based research approaches: they enable not
only an evaluation of single product or scenario
characteristics, but allow a holistic evaluation of
decision scenarios, a weighting of different attributes
against each other, and a direct simulation of rela-
tionships and interactions (Orme, 2010). Decision
processes and scenario preferences can be simulated
and separated into part-worth utilities of the attrib-
utes and their levels. In this process, the relative
importance of attributes delivers information about
which attribute affects the participants’ choice the
most. The part-worth utilities characterize the most
important or unimportant attribute levels. Further,
preference ratings and preference shares can be
consulted as indicators of acceptance.
For this study, a choice-based conjoint analysis
approach (CBC) was chosen in order to analyse
scenario decisions in which - most probably - more
than one attribute affects the final respondent’s
choice (Sawtooth Software, 2009).
3.2 Attributes and Attribute Levels
The identification and selection procedure of attrib-
utes and attribute levels is the first - and highly im-
portant - step for the conceptualization of a conjoint
analysis, since it affects the generalizability, validity,
and significance of the findings (Rao, 2014). It has
to be ensured that all attributes are considered that
are relevant for the preferences of respondents as
well as for city-planers, policy-makers, or other
important stakeholders. In order to identify the at-
tributes, the results of extensive literature analyses
and preceding studies were used - in which relevant
parameters for the acceptance of surveillance tech-
nologies (crime surveillance (van Heek et al., 2015)
and medical surveillance context (Arning & Ziefle,
2015)) were identified as a basis for the selection of
attributes and levels.
The following four attributes were assessed in
our conjoint study: locations of surveillance, camera
types, increase in safety, and invasion of privacy.
Within the attribute locations, the private home
environment was contrasted with different public
locations as place for camera installation: store,
market, and train station.
Increase in Safety as major benefit of imple-
mented surveillance technologies was operational-
ized as different detection rates of crimes in the
crime surveillance and of medical emergencies in
the medical surveillance context. The attribute levels
were specified as detection rates of 0% (no im-
provement), 5%, 10%, and 20% in both contexts.
Invasion of Privacy as major concern of imple-
mented video-based surveillance technologies was
operationalized as different ways and intensities to
handle and process recorded video data and included
the following levels: merely archiving data (police
and patient data bases), storage in profile data bases
(open to institutions, e.g., health insurance compa-
nies, security services), enabling position determina-
tion, and allowing face recognition.
As last attribute Camera Type was integrated in-
to the study differing in size, visibility, an obtrusive-
ness of the technology: a conventional, clearly visi-
ble, large and tracking camera, a large and visible
dome-camera, a small mini-dome-camera, and a
hidden, integrated, not visible camera.
3.3 Conjoint Questionnaire Design
In both contexts - medical (study 1) and crime (study
2) - identical questionnaire designs were developed
using the SSI web Sawtooth Software (SSI Web,
2016) and consisted of four parts.
The first part addressed demographic characteris-
tics such as age, gender, educational level, type of
residence, and area of residence. Afterwards, the
participants had to answer some context-specific
questions. For the medical surveillance context, the
participants were asked for details concerning health
status and experience with medical emergencies. For
SMARTGREENS 2017 - 6th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
90

Figure 1: Example of a choice task (crime surveillance context).
the crime surveillance context, the participants indi-
cated if they have already fallen victim to offenses.
In the second part, the respondents indicated
their perceived threat (of crimes or medical emer-
gencies) and their needs for privacy (measured each
with four items on six-point Likert scales). The
items were checked for reliability and subsequently
summed up resulting in a “need for privacy” and a
“perceived threat” score.
Next, the participants were introduced in the re-
spective scenario. The medical scenario dealt with
the installation of video cameras for medical surveil-
lance purposes at different locations. The cameras
were able to sent an emergency signal to a medical
institution. Similarly, the cameras introduced in the
crime surveillance scenario were also installed at
different locations and should help to detect and
prevent crime by enabling to send alarm signals to
security institutions.
In the fourth part, the CBC choice tasks with four
attributes and each four levels were presented. As a
control, the participants were asked to imagine that
they would be alone during the day. Then, they
should decide under which conditions and at which
locations they would accept the installation of video
cameras and were instructed to select the scenario in
each choice task, that met their individual needs
most closely. An example for a choice task is shown
in Fig. 1. As a combination of all attribute levels
would have let to 256 possible combinations
(4x4x4x4), the number of choice tasks was reduced
and overall, 10 random and one fixed task were
presented to the participants. A test of design effi-
ciency confirmed that the reduced, randomized de-
sign was sufficient and comparable to the hypothet-
ical orthogonal design regarding a sample of at least
100 respondents.
3.4 Data Analysis
For analysing the conjoint data (i.e. estimation of
part-worth utilities, preference simulations) the Saw-
tooth Software was used (SSI Web, 2016)(SMRT,
2016). First, the relative importance of attributes was
calculated, that deliver information about which
attribute affected the participants’ choice the most.
The computed part-worth utilities of all attribute
levels characterize the most important or unim-
portant attribute levels. Finally, preference simula-
tions were run estimating the impact on preferences
if single attribute levels change within a predefined
specific scenario (Orme, 2010). Preference ratings
and shares can be interpreted as indicators of ac-
ceptance. Data was analysed descriptively and, with
respect to the effects of surveillance context and user
diversity, by (M)ANOVA procedures (significance
level at 5%).
3.5 Sample Study 1 and 2
Data was collected in an online survey in Germany
and completion of each questionnaire took on aver-
age 15 minutes.
In study 1, overall 119 participants fully com-
pleted the questionnaire and were included in statis-
tical analyses. 52.9% of these participants were
Where, Wherefore, and How? - Contrasting Two Surveillance Contexts According to Acceptance
91

female and 47.1% male. The mean age was 28.5
years (SD=11.7) and ranged from 18 to 75 years.
The educational level was high with 38.7% of partic-
ipants holding a university degree and 45.4% a qual-
ification for university entrance. The participants’
majority lived in apartment buildings (60.5%, n=79),
while far fewer people indicated to live in detached
(14.3%), semi-detached (4.2%), or row houses
(15.1%). Most of the participants lived in the city
centre (60.5%), 23.5% on the outskirts, 7.6% in
suburbs, and 8.4% in a village. Further, 29.4% of the
participants indicated to have no experiences with
medical emergencies at all. Nearly half of the partic-
ipants (48.7%, n=58) reported to have already expe-
rienced a medical emergency in their family and
15.1% have been in a medical emergency situation
themselves. Participants indicated to feel only little
threatened by medical emergencies (M=2.3;
SD=1.1; min=1; max=6), but showed very high
needs for privacy (M=5.5; SD=0.6; min=1; max=6).
In study 2, 130 participants completed the ques-
tionnaire and were included in further statistical
analyses. 60.0% of the participants were female,
40.0% were male. The mean age was 32 years
(SD=12.2), ranging from 16 to 77 years. The educa-
tional level was also high with 48.5% holding an
university degree and 26.9% an university entrance
qualification. Similar to study 1, the majority of
participants lived in apartment buildings (60.0%),
and far fewer people lived in a detached (20.0%), a
semi-detached (6.9%), or a row house (13.1%).
43.1% of the participants lived in a city centre, while
22.3% lived on the outskirts, 20.0% in suburbs, and
14.6% in a village. 32.3% (n=42) had no experiences
with crimes at all, while 67.7% had a least fallen
victim to “slight” offenses (e.g., theft). On average,
participants indicated to feel only slightly threatened
by crime (M=2.5; SD=0.9; min=1; max=6). Similar
to study 1, the participants of study 2 showed very
high needs for privacy (M=5.5; SD=0.6; min=1;
max=6). ANOVAs revealed that the samples of
study 1 and 2 did not differ regarding gender, educa-
tional level, type of residence, perceived threat (of
crimes or emergencies), previous experiences, and
privacy needs. However, the results showed signifi-
cant differences only for age (F(1,248)=5.389;
p<.05) and place of residence (F(1,248)=10.436;
p<.05): compared with study 1, the participants of
study 2 were on average a little older and lived more
often outside the city centre.
4 RESULTS
First, the relative importance of attributes is present-
ed for the medical and crime surveillance context.
Afterwards, the part-worth utilities are presented for
all attribute levels comparing medical and crime
surveillance. Further, the results of preference simu-
lations analyses with regard to the trade-off between
safety and privacy are described.
4.1 Context-Specific Acceptance
Factors
The relative importance of attributes was calculated
for the medical and the crime surveillance context
and is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Relative importance of attributes for medical and
crime surveillance.
Overall, (M)ANOVA analyses revealed significant
differences between the medical and the crime sur-
veillance context concerning the relative importance
of the attributes (F(4,249)=21.610; p<.01). For the
medical surveillance context, increase in safety was
the most important attribute (29.5%), directly fol-
lowed by invasion of privacy and locations of sur-
veillance (each 27.0%), which were also very im-
portant. The camera type is comparatively the least
important attribute (16.4%) for medical surveillance
scenarios.
This is in line with the crime surveillance scenar-
io results, where camera type was the least important
attribute (14.4%) as well (F(1,249)=2.725; p=.10;
n.s.). Concerning the other three attributes, a more
heterogeneous picture emerged: in contrast to the
medical surveillance scenario, locations of surveil-
lance was the most important attribute for scenario
decisions (F(1,249)=79.588; p<.01), followed by
increase in safety (23.1%) (F(1,249)=12.300; p<.01),
42,4%
23,1%
20,2%
14,4%
27,0%
29,5%
27,0%
16,4%
0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50%
locations
increase in safety
(detection rate)
invasion of privacy
(data handling)
type of camera
Relative Importance (%)
medical (n=120)
crime (n=130)
SMARTGREENS 2017 - 6th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
92
44,0
20,9
10,6
-75,5
33,7
14,9
-7,4
-41,2
21,7
-4,4
1,9
-19,2
-14,6
-4,5
3,9
15,2
25,8
18,1
11,4
-55,2
48,5
20,7
-17,3
-51,9
-6,0
4,9
25,4
-24,3
-14,1
0,5
10,4
3,2
-100,0 -80,0 -60,0 -40,0 -20,0 0,0 20,0 40,0 60,0 80,0 100,0
train station
market place
shopping mall
own home
20%
10%
5%
0%
archiving (police, emergency)
storage (profile data bases -
insitutions)
position determination
face recognition
integrated, hidden
mini dome
dome
conventional
Locations
increase in safety
(detection rate)
invasion of privacy
(data handling)
type of camera
Average Utilities
medical (n=120)
crime (n=130)
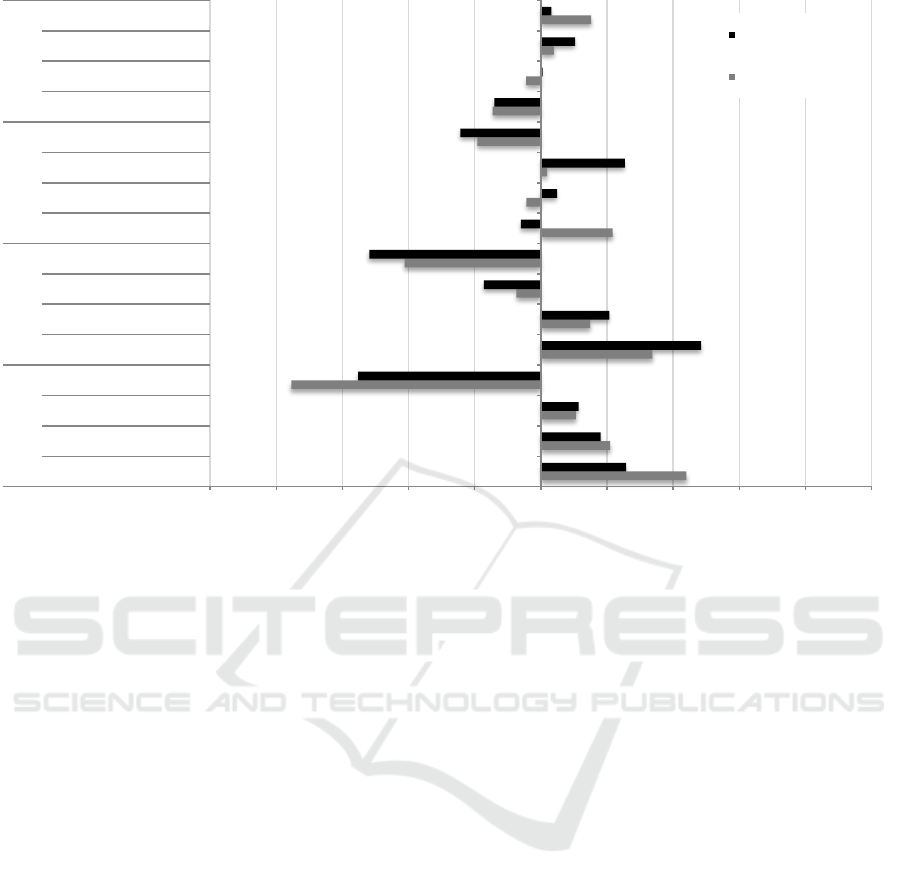
Figure 3: Part-worth utilities of all attribute levels for medical and crime surveillance.
and invasion of privacy (20.2%) (F(1,249)=13.908;
p<.01) which were of similar importance in the
crime surveillance scenario.
4.2 Context-Specific Acceptance
Characteristics
MANOVA analyses were calculated for each attrib-
ute level as dependent and the surveillance context
as independent variable. Figure 3 presents the results
of the part-worth utilities for medical and crime
surveillance.
The results showed a similar evaluation pattern
across scenarios, however, also significant differ-
ences for the attribute locations, (F(3,245)=4.055;
p<.01): surveillance at a store (F(1,248)=0.058;
p=.85; n.s.) or a market (F(1,248)=0.063; p=.42;
n.s.) revealed both rather positive utility values in-
dependent of the surveillance context.
In contrast, surveillance at a train station re-
ceived a significantly higher utility value in the
crime context (44.0) than in the medical context
(25.8) (F(1,248)=11.914; p<.01), while surveillance
at the own home received a clearly lower utility
value for the crime (-75.5) than the medical (-55.2)
context (F(1,248)=5.878; p<.05).
The evaluation pattern of the increase in safety
attribute levels was similar for both contexts, but
differed with regard to the amounts of values
(F(3,245)=3.770; p<.05) due to the higher attribute’s
importance for the medical surveillance context:
detection rates of 0% (F(1,248)=4.809; p<.05) and
5% (F(1,248)=9.986) obtained more negative utility
values for the medical (0%: -51.9; 5%:-17.3) com-
pared to the crime surveillance context (0%: -41.2;
5%: -7.4). Instead, detection rates of 10%
(F(1,248)=5.455; p<.05) and 20% (F(1,248)=8.176;
p<.01) received obviously higher positive utility
values for the medical (10%: 20.7; 20%: 48.5) than
the surveillance context (10%: 14.9; 20%: 33.7).
The most diverse evaluation pattern emerged for
the invasion of privacy attribute levels (F(2,244)=
13.047; p<.01). As the worst way of data and priva-
cy handling, face recognition achieved negative
utility values regardless of the surveillance context
(F(1,248)=0.906; p=.34; n.s.). For the crime surveil-
lance context, archiving of data (by police and
emergency services) obtained the highest positive
utility values (21.7), while it received slightly nega-
tive values for the medical context (-6.0)
(F(1,248)=25.444). Storage of data in profile data
bases (by medical or crime institutions) was rated
with rather positive utility values for the medical
(4.9), but with rather negative values for the crime (-
4.4) surveillance context (F(1,248)=4.143; p<.05).
Finally, position determination received the highest
positive utility values for the medical (25.4) and
Where, Wherefore, and How? - Contrasting Two Surveillance Contexts According to Acceptance
93

only neutral values for the crime (1.9) surveillance
context (F(1,248)=19.282; p<.01).
The levels of the attribute camera type were part-
ly rated differently for both contexts
(F(4,244)=3.202; p<.05). The hidden and integrated
camera received high negative utilities for both
groups (F(1,248)=0.027; p=.83; n.s.). Further, the
mini-dome camera was not evaluated differently as
well (F(1,248)=2.740; p=.1; n.s.). The dome camera
obtained slightly positive values for the crime (3.9),
but the attribute’s highest positive values for the
medical (10.4) surveillance context (F(1,248)=8.323;
p<.01). In contrast, the conventional large and track-
ing camera received the highest utility values for the
crime (15.2) and only slightly positive values for the
medical (3.2) surveillance context (F(1,248)=7.018;
p<.01).
4.3 Safety Vs. Privacy Decisions
Overall, the results (see 4.1) showed that the safety
and privacy attributes were significantly more im-
portant for medical than for crime surveillance.
What both contexts have in common is that there is
no clear distinction concerning the importance of the
safety and the privacy attribute (Fig. 2).
To examine the trade-off between increase in
safety and invasion of privacy in detail, sensitivity
analyses were carried out using the Sawtooth market
simulator (SMRT, 2016). In these simulations, it is
possible to examine to which extent respondents’
relative preferences for a scenario change if the
levels of an attribute vary while other specific attrib-
ute levels were kept constant. To directly contrast
safety and privacy, two opposite safety and privacy
scenarios with constant attribute levels were formed,
based on the findings of the previously reported
part-worth utilities:
1. high increase in safety + high invasion in pri-
vacy: with the constant levels “detection rate of
20%” and “face recognition”
2. low invasion in privacy + low increase in safe-
ty: with the constant levels “detection rate of
0%” and “archiving of data”
These levels were kept constant while all other
attribute levels (locations and camera type) changed.
The results are pictured in Fig. 4 for the medical and
in Fig. 5 for the crime surveillance context.
For the medical surveillance context (Fig. 4), the
“high safety” scenario (max. 61.6%) reached higher
average preferences compared to the “high privacy”
scenario (max. 20.2%). For all single attribute levels
in the medical surveillance context, the preferences
were significantly higher for the “high safety” than
for the “high privacy” scenario. The acceptance of
the “high safety” and also of the “high privacy”
scenario rose, when surveillance was carried out at
public locations. Changing the attribute level from
private home (32.9%) to a public location (store:
57.5%) in the high safety scenario, caused the high-
est difference in the share of preference (+24.5%),
while the differences between the various public
locations were rather small. Concerning all camera
types in the medical surveillance context, the “high
safety” scenario was consistently favoured by at
least 49.7% difference.
Overall, the decisions in the crime surveillance
context showed a similar pattern (Fig. 5). The ”high
safety” scenario (max. 66.5%) was clearly preferred
compared to the “high privacy” scenario (max.
20.0%) for all attribute levels (locations and camera
types) except of surveillance at the private home
environment (“high safety”: 15.3%; “high privacy”:
14.3%). Here, surveillance for crime detection rea-
sons was not desired and accepted regardless of
different safety and privacy scenarios. Similar to the
results in the medical surveillance context, the high-
est difference (+46.3%) occurred in the “high safe-
ty” scenario, when surveillance at the private home
(15.3%) was changed to a public location (store:
51.6%). In the “high privacy” scenario, there were
only small differences between the various locations
and almost no differences between the camera type
Figure 4: Results sensitivity analyses for medical surveil-
lance.
SMARTGREENS 2017 - 6th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
94

Figure 5: Results sensitivity analyses for crime surveil-
lance.
levels. In contrast, the camera types were evaluated
differently in the “high safety” scenario: the large
tracking camera obtained the highest share of prefer-
ences (66.5%), while less visible cameras received
lower agreement (e.g., the invisible, integrated cam-
era 55.8%).
5 DISCUSSION
This study revealed insights into the acceptance of
surveillance technologies for two different surveil-
lance contexts. Using a conjoint analysis approach
and involving the location of surveillance, the ap-
plied camera type, and the trade-off between safety
and privacy as acceptance parameters, decision sce-
narios were simulated for a medical and a crime
surveillance context. The results showed which
acceptance parameters are relatively most important
and which characteristics lead to adoption or non-
adoption of surveillance technologies in urban envi-
ronments. The findings provide valuable insights for
the conceptualization and planning of smart cities
regarding an acceptable implementation and use of
surveillance technologies in urban environments.
5.1 Context-sensitive Acceptance of
Surveillance Technologies
For the crime surveillance context, the location of
surveillance clearly is the most important determi-
nant of surveillance acceptance, while increase in
safety and protection of privacy are of secondary
importance. In contrast, these three parameters are
nearly of equal importance for medical surveillance.
One explanation for the greater importance of loca-
tions in the crime surveillance context could be that
crimes were stronger associated with special loca-
tions than medical emergencies. In contrast, for
medical surveillance, the interaction of perceived
benefit (increased safety, perceived barrier (privacy),
and location of surveillance is important. What both
contexts have in common is that the applied type of
camera technology is comparatively unimportant in
relation to the other three aspects. In contrast to
previous studies, which identified safety and protec-
tion of privacy as important factors for acceptance
without weighting them directly (Slobogin, 2002;
Welsh and Farrington, 2009; Welsh et al., 2015),
this study revealed that acceptance depends on per-
ceived benefits in terms of increasing safety and to a
slightly lesser extent on privacy-related issues. The
rather similar evaluation of safety and privacy for
both contexts shows the importance to analyse this
trade-off in detail and to consider this complex phe-
nomenon in future studies as well as conceptualiza-
tions of surveillance systems in urban environments.
5.2 Context-sensitive Characteristics of
Acceptance
Confirming previous research results (e.g., Welsh &
Farrington, 2009), the use of surveillance technolo-
gies is generally accepted at public locations in ur-
ban areas. In contrast, our findings demonstrate that
surveillance technologies are not accepted at all at
private locations such as the own home. Interesting-
ly, the same acceptance pattern was found for the
crime as well as the medical surveillance context.
Although previous research also indicated this pat-
tern for medical surveillance (Himmel et al., 2013),
we assumed differences between both contexts and
preferences for the home environment in the medical
context as most AAL technologies were used and
were planned to be used in private home environ-
ments.
Concerning the increase in safety, a similar ac-
ceptance pattern was found for both surveillance
contexts as well. The pattern was merely a bit
stronger pronounced for the medical surveillance
Where, Wherefore, and How? - Contrasting Two Surveillance Contexts According to Acceptance
95

context due to the higher relative importance of the
attribute: the higher the detection rates and thus, the
increase in safety, the higher the acceptance. Low
detection rates of 0% or 5% were completely reject-
ed. Hence, the perceived benefit of surveillance
(increased safety) has to be noticeable for ac-
ceptance and is more important for the medical than
the crime surveillance context.
The most contrary acceptance pattern was re-
vealed for the privacy attribute. For the medical
surveillance context, position determination is the
best evaluated way of handling video data, which is
in line with previous research results. Archiving and
storage of recorded data is not desired for medical
surveillance. In contrast, archiving of data is the
most desired way of data handling in the surveil-
lance context. Interestingly face recognition is per-
ceived as invasion in privacy and is the most reject-
ed way of data handling for medical as well as crime
surveillance.
Although the camera type was relatively unim-
portant, a tendency of preferences for both contexts
can be derived: for crime surveillance, conventional
large cameras are preferred, while a bit smaller and
discrete cameras are desired for medical surveil-
lance. However, hidden and integrated camera tech-
nology is strictly rejected for both surveillance con-
texts. This is surprising and has to be considered, as
current technological developments – in particular in
the field of AAL environments – aim for designing
small, less visible or invisible and seamlessly inte-
grated technologies (e.g., Kim et al., 2012).
5.3 Trade-off between Safety and
Privacy
Previous research results on the trade-off between
privacy and safety indicated that the will to abandon
a piece of privacy for increased safety depends on
the degree of increased safety (Bowyer, 2004). Our
study revealed that only a noticeable increase in
safety (detection rate at least 10%) is perceived
positively independent of the surveillance context.
Although, the analysis of relative importance re-
vealed only slightly higher importance of increase in
safety (crime: 23.1%; medical: 29.5%) in contrast to
the privacy attribute (crime: 20.2%; medical:
27.0%), the sensitivity analyses showed that secure
scenarios were clearly preferred compared to scenar-
ios that focused on privacy.
Thus, safety is much more preferred in a direct
confrontation of safety and privacy for medical as
well as crime surveillance. Thus, safety issues are
more important criteria for the acceptance of surveil-
lance technologies than privacy issues, provided the
technology is efficient and causes a noticeable in-
crease in safety.
5.4 Limitations and Further Research
Although, the applied conjoint analysis approach
was useful to evaluate preferences in different sur-
veillance scenarios and enabled a comparison of
surveillance, there are some limitations that should
be considered for further studies.
A first limitation is that the estimated preference
ratings are ratings on a hypothetical level and do not
mirror actual behaviour. Hence, agreement or rejec-
tion might be higher or lower in real situations
(Ajzen & Fishbein, 1977). A second limitation af-
fects the limited number of attributes in a choice-
based conjoint analysis. It had to be found the right
balance between an economic research design with a
limited number of attributes and a not to high com-
plexity of the research issue. The participants sug-
gested other interesting attributes, which could be
integrated in future research, such as the period of
data storage.
Further, there are some limitations with respect
to the samples of this study. So far, a highly educat-
ed participants group was examined. It is not clear if
the results can be simply transferred to other educa-
tion levels, therefore, future studies will aim at sam-
ples with a more diverse educational level. In addi-
tion, the samples did not have much experience with
crime offenses and medical emergencies. Hence, it
cannot be excluded that the trade-offs between safe-
ty and privacy are quite theoretically evaluated,
without the true understanding of own experience.
As the approach focused on video-based surveil-
lance, it would be useful to analyse the acceptance
of other surveillance technologies with respect to
different surveillance contexts in detail.
Further, it is assumed that the evaluation of sur-
veillance technologies is influenced by current
events such as terrorist attacks and crimes in the
local environment. Hence, longitudinal studies and
comparisons of surveillance acceptance represent an
interesting approach for further research.
Finally, as the approach represents the ac-
ceptance of surveillance with a perspective of a
single country, it would be useful and interesting to
compare surveillance needs and wishes of city resi-
dents of different countries, backgrounds, and cul-
tures.
SMARTGREENS 2017 - 6th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
96

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors thank all participants for their patience
and openness to share opinions. Furthermore, the
authors want to thank Valentina Kneip for research
assistance. This work was funded by the Excellence
Initiative of the German State and Federal Govern-
ment (Project Urban Future Outline).
REFERENCES
Aghajan, H., Augusto, J. C., Wu, C., McCullagh, P., &
Walkden, J.-A. 2007. Distributed vision-based acci-
dent management for assisted living. In International
conference on Smart homes and health telematics, pp.
196–205, Springer.
Ajzen, I., Fishbein, M. 1977. Attitude-behavior relations:
A theoretical analysis and review of empirical re-
search. Psychological Bulletin, 84(5), 888–918.
https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.84.5.888.
Arning, K., Ziefle, M., 2015. “Get that Camera Out of My
House!” Conjoint Measurement of Preferences for
Video-Based Healthcare Monitoring Systems in Pri-
vate and Public Places. In Inclusive Smart Cities and
e-Health, pp. 152–164. Springer.
Barrett, D., 2013. One surveillance camera for every 11
people in Britain, says CCTV survey. Telegraph. 10
th
July 2013.
Bowyer, K. W., 2004. Face recognition technology: secu-
rity versus privacy. IEEE Technology and Society
Magazine, 23(1), 9–19.
https://doi.org/10.1109/MTAS.200 4.1273467.
Cardinaux, F., Bhowmik, D., Abhayaratne, C., Hawley,
M. S., 2011. Video based technology for ambient as-
sisted living: A review of the literature. Journal of
Ambient Intelligence and Smart Environments, 3(3),
253–269.
Chen, B.-W., Chen, C.-Y., & Wang, J.-F., 2013. Smart
homecare surveillance system: Behavior identification
based on state-transition support vector machines and
sound directivity pattern analysis. IEEE Transactions
on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 43(6),
1279–1289.
Dailey, K., 2013. The rise of CCTV surveillance in the
US. BBC News. 29
th
April 2013.
Davis, F. D., Bagozzi, R. P., Warshaw, P. R., 1989. User
acceptance of computer technology: a comparison of
two theoretical models. Management Science, 982–
1003.
Dey, S., Chakraborty, A., Naskar, S., Misra, P., 2012.
Smart city surveillance: Leveraging benefits of cloud
data stores. In 37th Conference on Local Computer
Networks Workshops (LCN Workshops), 2012, pp.
868–876. IEEE.
Filipponi, L., Vitaletti, A., Landi, G., Memeo, V., Laura,
G., Pucci, P., 2010. Smart city: An event driven archi-
tecture for monitoring public spaces with heterogene-
ous sensors. In Fourth International Conference on
Sensor Technologies and Applications
(SENSORCOMM), 2010, pp. 281–286. IEEE.
Fleck, S., Strasser, W., 2008. Smart camera based moni-
toring system and its application to assisted living.
Proceedings of the IEEE, 96(10), 1698–1714.
Fyfe, N., 2004. Zero tolerance, maximum surveillance?
Deviance, difference and crime control in the late
modern city. The Emancipatory City, 40–56.
Gurley, R. J., Lum, N., Sande, M., Lo, B., Katz, M. H.,
1996. Persons Found in Their Homes Helpless or
Dead. New England Journal of Medicine, 334(26),
1710–1716.
https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199606273342606.
Himmel, S., Ziefle, M., Arning, K. (2013). From Living
Space to Urban Quarter: Acceptance of ICT Monitor-
ing Solutions in an Ageing Society. In Human-
Computer Interaction. Users and Contexts of Use, pp.
49–58. Springer.
Kim, J. E., Boulos, G., Yackovich, J., Barth, T., Beckel,
C., Mosse, D., 2012. Seamless Integration of Hetero-
geneous Devices and Access Control in Smart Homes.
In 2012 Eighth International Conference on Intelligent
Environments, pp. 206–213.
https://doi.org/10.1109/IE.2012.57.
Klack, L., Schmitz-Rode, T., Wilkowska, W., Kasugai, K.,
Heidrich, F., Ziefle, M., 2011. Integrated Home Moni-
toring and Compliance Optimization for Patients with
Mechanical Circulatory Support Devices. Annals of
Biomedical Engineering, 39(12), 2911.
https://doi.org/10. 1007/s10439-011-0407-1.
Koh, Y., Mohan, A., Wang, G., Xu, H., Malik, A., Lu, Y.
H., & Ebert, D. S. (2016, May). Improve safety using
public network cameras. In Technologies for Home-
land Security (HST), 2016 IEEE Symposium on (pp.
1-5). IEEE.
La Vigne, N. G., Lowry, S. S., Markman, J. A., & Dwyer,
A. M. (2011). Evaluating the use of public surveil-
lance cameras for crime control and prevention. Wash-
ington, DC: US Department of Justice, Office of
Community Oriented Policing Services. Urban Insti-
tute, Justice Policy Center.
Leonhardt, S. (2006). Personal Healthcare Devices. In S.
Mukherjee, R. M. Aarts, R. Roovers, F. Widder-
shoven, & M. Ouwerkerk (Eds.), AmIware Hardware
Technology Drivers of Ambient Intelligence, pp. 349–
370. Springer Netherlands.
Luce, R. D., Tukey, J. W., 1964. Simultaneous conjoint
measurement: A new type of fundamental measure-
ment. Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 1(1), 1–
27.
Memon, M., Wagner, S. R., Pedersen, C. F., Beevi, F. H.
A., & Hansen, F. O., 2014. Ambient assisted living
healthcare frameworks, platforms, standards, and qual-
ity attributes. Sensors, 14(3), 4312–4341.
Orme, B. K., 2010. Getting started with conjoint analysis:
strategies for product design and pricing research, 77–
89.
Patton, J. W., 2000. Protecting privacy in public? Surveil-
lance technologies and the value of public places. Eth-
Where, Wherefore, and How? - Contrasting Two Surveillance Contexts According to Acceptance
97

ics and Information Technology, 2(3), 181–187.
https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010057606781.
Rao, V. R., 2014. Theory and Design of Conjoint Studies
(Ratings Based Methods). In Applied Conjoint Analy-
sis, pp. 37–78. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Rogers, E., 2003. Diffusion of innovations. (5th ed.). New
York: NY Free Press.
Rubenstein, L. Z., 2006. Falls in older people: epidemiol-
ogy, risk factors and strategies for prevention. Age and
Ageing, 35(suppl 2), 37–41.
Sawtooth Software. (2009). The CBC/HB System for
Hierarchical Bayes Estimation Version 5.0 Technical
Paper. 2015, from http://www.sawtoothsoftware.com/
products/advanced-analytical-tools/cbc-hierarchical-
bayes-module/167-support/technical-papers/sawtooth-
software-products/128-cbc-hb-technical-paper-2009.
Schwartz, A., 2012. Chicago’s Video Surveillance Camer-
as: A Pervasive and Poorly Regulated Threat to Our
Privacy. Northwestern Journal of Technology and In-
tellectual Property, 11, 9.
Slobogin, C., 2003. Public Privacy: Camera Surveillance
of Public Places And The Right to Anonymity (SSRN
Scholarly Paper No. ID 364600). Rochester, NY: So-
cial Science Research Network.
SMRT, 2016. SMRT - Sawtooth Software Market Simula-
tor. Sequim, WA, USA: Software Software Inc.
Solanas, A., Patsakis, C., Conti, M., Vlachos, I. S., Ramos,
V., Falcone, F., 2014. Smart health: a context-aware
health paradigm within smart cities. IEEE Communi-
cations Magazine, 52(8), 74–81.
SSI Web, 2016. SSI Web Sawtooth Software. Software for
online conjoint survey developement. Sequim, WA,
USA: Software Software Inc.
Surette, R., 2005. The thinking eye: Pros and cons of
second generation CCTV surveillance systems. Polic-
ing: An International Journal of Police Strategies &
Management, 28(1), 152–173. https://doi.org/10.1108/
13639510510581039.
van Heek, J., Arning, K., & Ziefle, M., 2015. Safety and
Privacy Perceptions in Public Spaces: An Empirical
Study on User Requirements for City Mobility. In R.
Giaffreda, D. Cagáňová, Y. Li, R. Riggio, & A.
Voisard (Eds.), Internet of Things. IoT Infrastructures,
pp. 97–103. Springer International Publishing.
Welsh, B. C., Farrington, D. P., 2004. Surveillance for
Crime Prevention in Public Space: Results and Policy
Choices in Britain and America. Criminology & Pub-
lic Policy, 3(3), 497–526.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-9133.2004.tb00058.x.
Welsh, B. C., & Farrington, D. P., 2009. Making Public
Places Safer: Surveillance and Crime Prevention. Ox-
ford University Press.
Welsh, B. C., Farrington, D. P., Taheri, S. A., 2015. Effec-
tiveness and social costs of public area surveillance for
crime prevention. Annual Review of Law and Social
Science, 11, 111–130.
Wilkowska, W., Ziefle, M., 2012. Privacy and data securi-
ty in E-health: Requirements from the user’s perspec-
tive. Health Informatics Journal, 18(3), 191–201.
Yu, M., Rhuma, A., Naqvi, S. M., Wang, L., Chambers, J.,
2012. A posture recognition-based fall detection sys-
tem for monitoring an elderly person in a smart home
environment. IEEE Transactions on Information
Technology in Biomedicine, 16(6), 1274–1286.
Ziefle, M., Schneider, C., Vallée, D., Schnettler, A.,
Krempels, K.-H., Jarke, M., 2014. Urban future Out-
line-A Roadmap on Research for Livable Cities. Smart
Cities, 9.
SMARTGREENS 2017 - 6th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
98
