
Autonomous Semantic Structuring of Lecture Topics
Synthesis of Knowledge Models
Robin Nicolay, Nikolaj Troels Graf von Malotky, Tanja Auge and Alke Martens
University of Rostock, Institute of Computer Science, Chair of Practical Informatics, 18051 Rostock, Germany
robin.nicolay@uni-rostock.de, nikolaj.graf von malotky@uni-rostock.de
Keywords:
Latent Dirichlet Allocation, Topic Models, Mental Models, Knowlege Management, Force-directed Algo-
rithms.
Abstract:
Students attending lectures in universities suffer from a weak structural awareness on lecture content. Ac-
cording to learning theories, structural awareness is a relevant factor to association and comprehension of new
learning inputs. We synthesize semantic structures from non annotated lecture slides using Topic Modeling
algorithms to identify relevant terms and relate them in force-directed graphs. The synthesized graphs provide
a structural overview on the topic distribution and relations of non annotated sequential lecture slides.
1 INTRODUCTION
University teachers, aka lecturers, use lectures to
teach facts and concepts to students. From the per-
spective of the teacher, in the preparation phase the
relevant information of a lecture is analyzed, reduced
and sequenced into learning units and taught in a way
that is comparable to leading a path through a con-
strained area of knowledge. During a study a stu-
dent learns from many different lectures or knowledge
units. Some of these units reference each other, some
are partially overlapping or describe common topics
from different perspectives. An ideal situation would
be given, if the students identifies and understands the
key concepts plus their relations and their hierarchy
or topology. However, reality often leads to different
situations: Even if the teacher usually is preparing a
lecture via sequencing the important facts of an over-
all topic in a logical order, in quite a lot cases, lec-
tures are evolutionary grown over time. This results
in a situation, where the key concepts of a lecture are
somewhat hidden in the text. From the perspective
of the teacher, this is not so bad, as the overall pic-
ture shall not be influenced. However, in exams, we
were able to observe that students often miss impor-
tant items or misinterpret items. The situation grows
even worse, when students were asked to detect rela-
tions between different topics, i.e. different lectures
in different semesters. This seems to be a cognitive
step which is not directly supported in current lecture
formats. On the teacher’s side, an interconnection of
the topics or areas of study is seldom taking place.
This results in a situation where students are usually
missing the overall picture.
To develop a solution, i.e. to develop support
mechanisms and tools to support the student’s knowl-
edge construction in lectures, we have to take a look
at learning psychology. Learning theories such as
cognitivism describe the inner effects of processing
lecture information inputs by using cognitive models
(lernpsychologie.net, 2016). To understand, how pro-
cesses of knowledge construction could potentially
take place, we made several investigations together
with our students.
Our work started a while ago, when we developed
a tool for extracting knowledge from lectures with the
goal to support student’s annotation of lectures and
for giving support for learning (Nicolay et al., 2015).
To support our claim that understanding of the main
concepts and their interrelation is the key to under-
standing the lecture in a first step and to understand-
ing the overall picture in a study direction as a sec-
ond step, we investigated student’s intuitive method
of knowledge construction.
Our main study took place last semester, where
we made a structured investigation with a first grade
master course with 20 students from different depart-
ments. They were organized in teams of two to four
(mixed male and female). They got a free choice of
material (either digital or not), and free choice of most
important topics. Their task was to identify areas of
knowledge and relations in self designed knowledge
Nicolay, R., Malotky, N., Auge, T. and Martens, A.
Autonomous Semantic Structuring of Lecture Topics - Synthesis of Knowledge Models.
DOI: 10.5220/0006367903490355
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2017) - Volume 2, pages 349-355
ISBN: 978-989-758-240-0
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
349

management structures. We asked students, how they
identify key words, how they relate and organize them
and how they identify clusters or areas of topics. They
had to show and explain the results, e.g. in form
of a poster or slides. Additional to keywords, rela-
tions and clusters, they have to show us in a next step,
which system they use (e.g. mindmap, tables, other
graphs or trees). More information about this part
of our study and the related insights is described in
section 2. After we got insight to the student’s ideas
of organizing lecture knowledge, we applied this to
our tool described in section 3.1 and 3.2. We added a
mathematical algorithm to visualize the results using
force-directed graphs described in section 4 allowing
further inference of insights described in section 5.
2 STUDENT’S INTUITIVE
MANAGEMENT OF
KNOWLEDGE
We asked students how they process or recap the past
study course. Therefore we had 20 students from dif-
ferent fields of study, such as mathematics, ship build-
ing, teacher training and computer science. All stu-
dents recently finished their bachelors level and at-
tended some first master lectures. The Age of the stu-
dents where between 24 and 31. We asked the stu-
dents to invent a concept, with which they can man-
age and organize their experience of past courses.
They developed several different semantic knowl-
edge structures consisting of keywords and relations.
Hereby, we did not find significant differences be-
tween male and female students. The following para-
graphs summarize the outcomes in particular areas.
Students identified relevant topics and keywords
in two ways. First, the memorization of most rele-
vant terms, second the identification of keywords us-
ing past lecture material. The results of both tech-
niques where almost equal. While the memorized
terms show a tendency to specializations on interest-
ing and for the individual student relevant aspects, the
topics identified by lecture material showed a broader
coverage of the study course and reflected the char-
acteristics of the curriculum. All groups defined dif-
ferent hierarchies between terms. We identified two
main levels and call them: Thematic area terms for
higher more general terms and technical terms for
lower and more specific terms. Students used the-
matic area terms to group the more specific technical
terms in domains.
While students put a lot work on the specifica-
tion, and definition on keywords, they neglected the
specification of the relations. Students intuitively de-
fined relations to denote inheritance dependencies be-
tween area keywords and technical terms. Procedu-
ral descriptions between keywords as used in Concept
Maps defined in (Ca
˜
nas et al., 2004) where not used.
Students relate terms by declarative Associations. To
map learning resources, they link learning materials
as Occurrences to Topics. This intuitive approach is
very similar to the concept of Topic Maps defined in
(Marius et al., 2008).
For a cognitive description of relations between
important keywords, students needed to handle many
thematic areas and cross references on technical
terms. We identified two main approaches to layout
identified keywords.
The first approach shown in figure 1 defined sev-
eral thematic areas. These area keywords then where
surrounded by technical terms mapped to these ar-
eas. At a first glance, the first approach was sim-
ilar to Mindmaps. But students noted hierarchy of
an Mindmaps did lack in decentralization and a clean
cross referencing of dependencies between more than
one thematic areas and a single technical terms.
Figure 1: Example of student’s analog Mindmap approach
to organize learned knowledge (S. Brossmann, T. Auge).
The second approach shown in figure 2, provided
an interesting way to deal with cross referencing of
keywords. Students used dark colored sticker to de-
note thematic area keywords. In the middle is the
general thematic area. Matching this general thematic
area there are more specialized thematic areas placed
equally spaced around it. The all technical terms were
placed with a rule in mind: The level of dependency
of a technical term to a thematic area is described by
its distance. That means technical terms in the mid-
dle of the circle did not have a specified affiliation
and specialized techinal terms are placed in the areas
in the corresponding thematic area. The result is that
words with an affiliation to thematic areas built a lobe
from the center of the circle to the thematic area key-
word.
CSEDU 2017 - 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
350
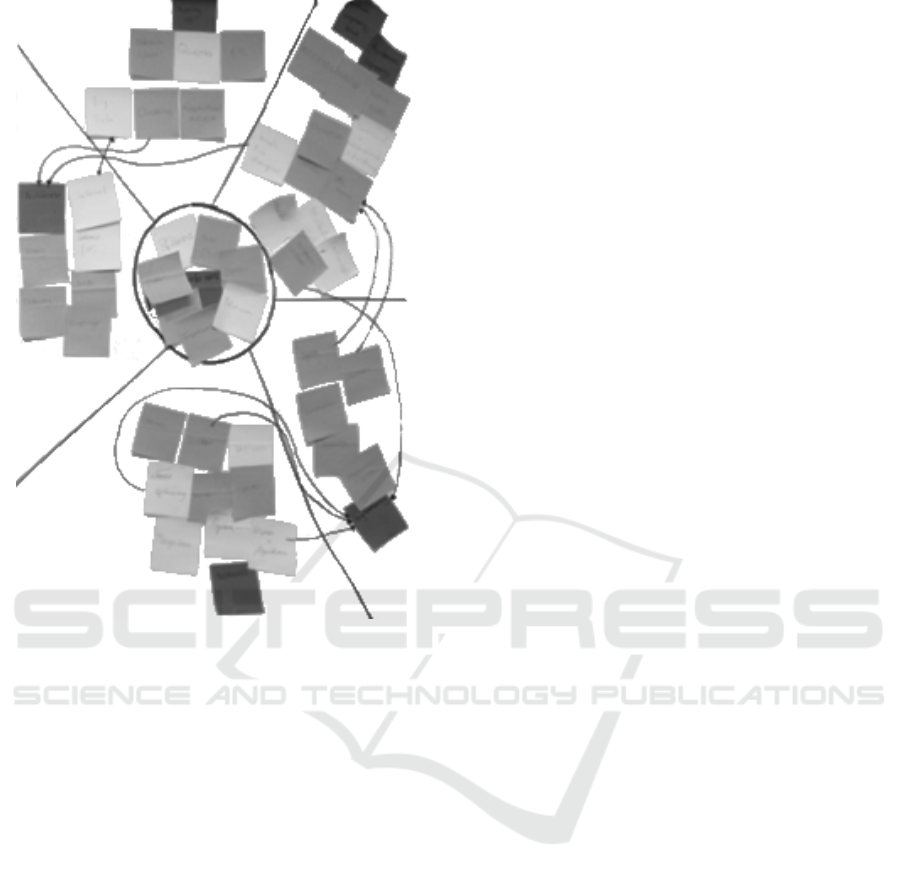
Figure 2: Example of a student’s analog approach to or-
ganize learned knowledge (J. Abel, S. Arth, T.Baudis, K.
Klohs).
Students claimed that the structure of a lecture is
not visible to a listener during lectures. Difficulties
arise in the identification of relevant topics, inference
of relations between topics, relations between topics
and lecture material as well as relations between lec-
tures themselves. Information in lectures are not pre-
sented in a structured way but in a sequences of lit-
tle annotated lecture slides. An option would be to
provide a structured, semantic overview about lecture
topics on an high abstraction level. This overview,
given by the lecturer, could be used by the students
to follow the structure and relations of topics during a
lecture while individually adding received stimuli and
associations to the provided skeleton.
In the next sections we describe our approach to
analyze sequential lecture material and synthesize the
identified structures shown in figure 1 and 2.
3 AUTOMATIC EXAMINATION
OF LECTURE’S TOPIC AREAS
AND SEMANTIC STRUCTURES
This section describes our system derived from two
parts: First, a system based on a former approach
to extract semantic topics from non annotated lecture
slides described in detail in (Nicolay et al., 2016).
Second, the identification of relations and semantic
structures between topics, keywords etc.
3.1 Inference of Topics from Lecture
Slides
To synthesize a model that approximates a lecturer’s
intended taught knowledge structure after attending
a lecture, we analyze the text on presented lecture
slides. We found in (Nicolay et al., 2016) that the text
on lecture slides allows us to identify semantic topics
or thematic areas during a lecture. Further steps will
include a synchronized transcription of the lecturers
verbally explanations during a lecture. The following
paragraphs provides a short overview about the used
algorithms.
Preparation of Text and Vocabulary. To prepare
and clean up the text on lecture slides, we imple-
mented a set of filters described below. To iden-
tify semantic topics from unstructured text, we used
the statistic topic modeling algorithm Latent Dirich-
let Allocation (LDA) introduced by Blei (Blei et al.,
2003) implemented using the Markov-Chain-Monte-
Carlo (MCMC) Gibbs Sampling algorithm (Griffiths
and Steyvers, 2004).
At first, we describe the implemented a set of fil-
ters. The system extracts all text without special char-
acters from the slides of a lecture and splits the text
into single words. Then the system removes gram-
matical deviations having a minor impact to seman-
tic meaning, such as a stemming (Yoshiki Shibukawa,
2015) and unifies all words to lowercase. Addition-
ally, it removes stopwords (Porter et al., 2015), short
words with less than 3 letters, numbers, and words
with a high occurrence on many different slides (e.g.
repeating footers). Then all words are added to an
word-slide adjacency matrix. Using the filters the av-
erage number of different words (or rank of matrix) is
reduced by 25 percent.
Common lecture slides consist of a low amount
of text. As shown in (Wallach et al., 2009) the use
of Dirichlet Priors introduced by LDA improves the
quality and convergence of inference on texts with
Autonomous Semantic Structuring of Lecture Topics - Synthesis of Knowledge Models
351

a lower number of words considerably. Neverthe-
less, we looked into ways of interpreting layout in-
formation and structure on lecture slides to improve
the inference with additional meta information. First
to be published results show, analyzing outline slides
that contain meaningful headings of a lecture, indicate
number and order of thematic areas. Further, corre-
lating size of words and importance added as weight
function to the Gibbs implementation improves the
separation between topics and their word distribu-
tions.
On the other hand, arrangement of text on lec-
ture slides is not easy to understand for automatic al-
gorithms. Factors such as layout templates, images
and aesthetics influence the position of words on a
slide. Here LDA supports a ”bag of words assump-
tion” and does not infer information from the position
of words within a text. As stated in (Blei, 2012, S.82)
this would be a disadvantage for synthesizing natural
speech, but is appropriate for semantic analysis.
Identifying Topics with Latent Dirichlet Alloca-
tion. In our approach LDA infers a fixed number
of topics T = t
1
, t
2
, ..., t
k
from a set of slides S . As
mentioned above, we keep the separation of lecture
information into separate slides. The filtered, relevant
subset of occurring words is V . LDA provides a dis-
crete distribution θ(s) denoting the proportion of ev-
ery topic t ∈ T on slide s ∈ S. Every topic t is defined
by a discrete distribution β(t) over the probability of
occurrence of every word w ∈ V . Both, the possible
random values of θ(s) and β(t) sum to one.
Figure 3: Intensity of 6 different topics t ∈ T to the slides
s ∈ S used during a lecture.
To get an impression of the result, figure 3 shows
the inferred distribution of six topics over a set of 43
lecture slides on Learning Theories at the University
of Rostock. The Bars in this figure lying above each
other, show the proportion of every topic to a slide
θ(s). The topics Topic0 to Topic5 are, as a result of
the sampling algorithm automatically named and only
defined by their probability of occurrence of semanti-
cally relevant words β(t), showing as Adjacency Ma-
trix indicated in figure 4. A MCMC sampling algo-
rithm uses a high number of randomly generated sam-
ples the initial distribution of topics on every lecture
slide and corrects the topics by a high number of iter-
ations fitting steps. The essence is, that the algorithm
does not include knowledge about lecture slides being
next to each other. However, figure 3 shows a mean-
ingful distribution of topics during a lecture. Nearby
slides tend to share the same topic. Furthermore, top-
ics show the trend to fade in and fade out during a
lecture. In conclusion, results on real data indicate
a well known pedagogical distribution of topics on a
sequence of lecture slides.
Figure 4: An excerpt of β(t). The probability of occur-
rences of vocabulary words w ∈ V on lecture topics t ∈ T .
3.2 Relating Slides by Topics
In section 3.1, we explained our approach to iden-
tify single topics in lecture slides. In (Nicolay et al.,
2016), we described a first approach to connect slides
with each other that share the same topics. Identified
connections, based on common topics, are meaning-
ful. Figure 5 shows, nearby slides have a higher pro-
portion of shared topics. Only a few cross references
bridge the chord diagram. Accordingly only a few
slides, lying far apart in a lecture, have high propor-
tions to a common topic.
CSEDU 2017 - 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
352
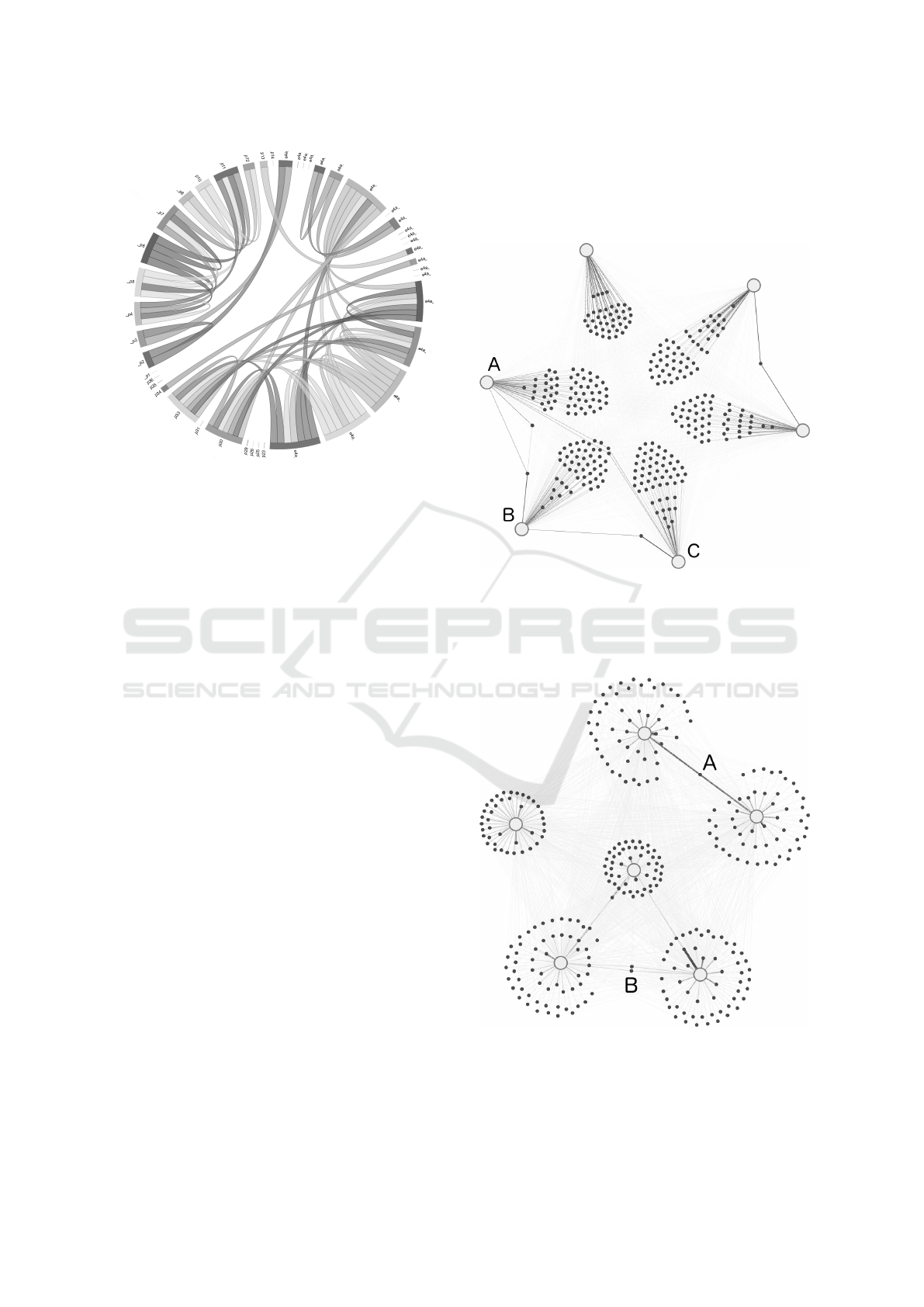
Figure 5: Relations between slides of a talk based on joined
topic assignments. Slides are arranged clockwise at the
outer ring of the graph. Lines indicate a shared topic of
over 65% for connected slides. (Nicolay et al., 2016).
4 MAPPING OF TOPICS AND
KEYWORDS
To fulfill the requirements indicated by the student
models described in section 2, we need to order tech-
nical terms to thematic areas by relations based on
affiliations. Therefore, we decided to interpret af-
filiations of technical keywords to thematic areas as
forces and examined two force-directed approaches.
First, the circular approach. We place area thematic
keywords around technical terms, as seen in figure 2.
Second, an extension of student’s Mindmap approach
by proximity concepts of the circular approach.
To graphically depict the results of LDA, we used
forced-directed graph models. Identified abstract top-
ics T were interpreted as abstract thematic clusters.
Their centers are shown as white points. The elements
of the filtered vocabulary V denote the unfiltered set
of technical terms indicated by smaller gray points.
The distribution β(t) defines the proportion of every
technical keyword w ∈ V to every topic t ∈ T .
While the sets of technical keywords and thematic
areas are defined, we need to convert β(t) (the knowl-
edge of affiliation of technical terms to thematic ar-
eas) to positions indicating proximity to thematic ar-
eas. Therefore we built a force-directed graph con-
taining vertices K = T ∪V and edges E = (w, t) ∈
β(t). The edges are weighted by the level of propor-
tion defined in β(t). Forces on the graph are denoted
by the weight of edges as an attraction strength factor,
a repulsion strength between two vertices and a grav-
ity to the center. The learning resources (not shown in
the following graphs) can be related to thematic areas
by θ(s) outlined in figure 3. Both figures 6 and 7 rep-
resents the network as a graph drawing, with different
success.
Figure 6: The first result on an force-directed graph of the
LDA results. The 6 topics (white points) placed on the outer
circle, words (dark points) oriented as lobes to their affili-
ated topics. Forces (edges) are determined by proportions
defined in β(t). We reduced visibility of weak connections.
Figure 7: The second result on a force-directed graph of the
LDA results. The words (dark points) are organized around
their most affiliated topics. Forces are determined by pro-
portions β(t). We reduced visibility of weak connections.
The different arrangement result in different force
Autonomous Semantic Structuring of Lecture Topics - Synthesis of Knowledge Models
353

models. Figure 6 shows ForceAtlas algorithm, fig-
ure 7 shows ForceAtlas 2. Both algorithms (described
in (Jacomy et al., 2014)) are implemented for the
open-source tool Gephi (v. 0.9.1) (Bastian et al.,
2009), a software to visualize and manipulate net-
works. ForceAtlas2 is developed by combining ex-
isting techniques as an improvement and extension of
the ForceAtlas algorithm. It simulates a physical sys-
tem with mutual repulsion of the nodes and attraction
towards their inzident edges. The lower based energy
model is inspired by real life: Forces of nodes de-
pends on the distance between the interacting entities.
The position of a node can’t be interpreted on its
own, it has to be compared to the other nodes in the
graph drawing. However, using ForceAtlas 2, the dis-
tance, edge weight and degree plays an important role
for positioning the nodes. In the classical case, the
attraction is linearly based on the distances
F(n
1
, n
2
) = d(n
1
, n
2
).
The edge weight influences the attraction multiplica-
tively
F(n
1
, n
2
) = w(e)
δ
· d(n
1
, n
2
)
with weight w(e) of the edge e and edge weight influ-
ence parameter δ (δ = 0: weights are ignored, δ = 1:
attraction is proportional to the weight, δ ≥ 2: strong
influences of the weights). And node degree is impor-
tant for the dissuade hubs:
F(n
1
, n
2
) =
d(n
1
, n
2
)
deg(n
1
) + 1
.
Here grant authorities (nodes with a high degree) get
a more central position than hubs (nodes with a small
degree). Whereas in the use of ForceAtlas, hubs are
pushed at the periphery and authorities more central.
5 INTERPRETATION OF
SYNTHESIZED
FORCE-DIRECTED SEMANTIC
NETWORKS
Looking into the interpretation of results, the circular
arrangement, approximates the student’s model from
figure 2. The force graph builds out a good visual-
ization of lobe based on pure LDA data. In figure
6, most of the words lie in a topic’s lobe. The dis-
tance to a topic node identify the attraction to the cor-
responding topic. The bigger the radius, the stronger
the affinity by other topics. On the first look, the in-
terpretation of keywords and their level of affiliation
to specific topics seems straight forward. However, 6
shows words belonging to two not-adjazent topics (A
and C), are likely to be pulled into the wrong topic’s
lobe (B). Furthermore, words oriented to the center
of the graph, either have no strong affiliation to one
of the topics, or have a strong affiliation to opposite
oriented topics. This issues leads to misleading inter-
pretations of affiliation.
In the case of the representation in figure 7, com-
bining aspects of Mindmap and proximity, the posi-
tion of the thematic area nodes is arranged by avoid-
ing foreign keywords. Each word is assigned unam-
biguously to the topic based on the strongest affili-
ation. Words in the inner circle indicate a high at-
traction to its topic; the larger the radius, the weaker
the affinity. Words that almost equally fit into multi-
ple thematic areas keywords as shown in figure 7 at
A and B are highlighted by their corresponding strong
edges. The more equal the affiliation to both topics is,
the more both topics share a keywords by pulling it
out of the corresponding circles. This representation
supports a more clear identification of thematic areas
and corresponding terminal keywords.
6 CONCLUSION AND FURTHER
WORK
In this paper we have synthesized a student’s intu-
itive model from a non annotated sequence of lec-
ture slides. We visualized semantic structures using
a force-directed graph drawing algorithms.
The possible application for teaching and learn-
ing are manifold. While the structure itself provides
an overview about the semantic structure of a cur-
riculum, it serves as an semantic index on learning
material. The proportional assignment of learning re-
sources to thematic areas support a semantic selection
of appropriate learning material across different lec-
tures.
As one aspect, we improve the visualization of
these results. To limit complexity, we need to filter
the view to show only currently relevant information
and resources. Based on a student’s currently marked
content, the structure needs to be dynamically reor-
ganized to accent relevant technical terms and inter-
topic relations. Our goal is to automatically synthe-
size an assistive map showing the completed path of
learning content as well as relevant relations between
current and past learning resources.
Another aspect is described in (Wittrock, 1989).
Learning is a process of associating input stimuli to
structures of internal knowledge. The structure syn-
thesized in this work, provides a step towards visu-
alizing and organizing an associative grid out of non
annotated, sequential learning material. On the one
CSEDU 2017 - 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
354

hand, it improves the structural awareness of students,
on the other hand the structure can be enhanced by
students during the processing of stimuli perceived in
the lecture. The observation of student’s annotation
of lecture content described as coding in (Lee et al.,
2008) enables an observation of student’s processing
of knowledge. Adding a semantic meta structure to
non annotated lecture material enables an observation
of student’s coding in connection to lecture topics and
relations.
Our next operative goals are to reduce the number
of words in our representation. We need to identify
relevant parameters, such as average importance, inter
topic relations and layout information, such as size of
text to weight identified technical terms by relevance.
Further, we look into time dynamics of these net-
works. Students and lecture structures develop over
time. New keywords and relation appear during a cur-
riculum. David Blei introduces dynamic topic models
in (Blei and Lafferty, 2006). These concepts allow an
observation of appearing new topics and distribution
of words over time. These changes lead to movements
in the force graph over time, providing insights in a
lectures teaching and later student’s learning process
and progress.
Acknowledgement: We thank all the students
of our course ”Indiviual Knowledgemanagement” in
Winterterm 2016 2017 for their enthusiasm, their in-
terest and their work in our course - and for allowing
us to use their insights and graphs for future research.
REFERENCES
Bastian, M., Heymann, S., Jacomy, M., et al. (2009). Gephi:
an open source software for exploring and manipulat-
ing networks. ICWSM, 8:361–362.
Blei, D. M. (2012). Probabilistic topic models. Communi-
cations of the ACM, 55(4):77.
Blei, D. M. and Lafferty, J. D. (2006). Dynamic topic mod-
els. In Proceedings of the 23rd international confer-
ence on Machine learning, pages 113–120.
Blei, D. M., Ng, A. Y., and Jordan, M. I. (2003). Latent
dirichlet allocation. the Journal of machine Learning
research, 3:993–1022.
Ca
˜
nas, A. J., Novak, J. D., and Gonz
´
alez, F. (2004). Con-
cept maps: Theory, methodology, technology.
Griffiths, T. L. and Steyvers, M. (2004). Finding scientific
topics. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sci-
ences, 101(Supplement 1):5228–5235.
Jacomy, M., Venturini, T., Heymann, S., Bastian, M., and
Muldoon, M. R. (2014). Forceatlas2, a continuous
graph layout algorithm for handy network visualiza-
tion designed for the gephi software. PLoS ONE,
9(6):e98679.
Lee, H. W., Lim, K. Y., and Grabowski, B. L. (2008). Gen-
erative learning: Principles and implications for mak-
ing meaning. Handbook of research on educational
communications and technology, 3:111–124.
lernpsychologie.net (2016). Lernpsychologie - Lernen und
Ged
¨
achtnis einfach erkl
¨
art: https://perma.cc/uc9w-
uzwp.
Marius, L., Moore, G., and Moore, G. (2008). ISO 13250-2:
Topic Maps — Data Model: http://perma.cc/MPT4-
MVLM.
Nicolay, R., Schwennigcke, B., Sahl, S., and Martens, A.
(2016). Visualisierung konzeptuellen lernens durch
semantische vernetzung sequenzieller lehrinhalte. In
Mayr, H. C., Pinzger, M., and Gesellschaft f
¨
ur Infor-
matik e. V. Bonn, Gesellschaft f
¨
ur Informatik e. V,
editors, GI Edition Proceedings Band 259 INFOR-
MATIK 2016, volume 259 of GI-Edition. Proceedings,
pages 1009–1016.
Nicolay, R., Schwennigcke, B., Vetterick, J., Sucharowski,
W., and H. Cap, C. (2015). Interlect - lecture content
interface. In 7th International Conference on Com-
puter Supported Education, pages 269–276.
Porter et al. (2015). Natural language toolkit - nltk 3.0 doc-
umentation: Stopwords corpus: https://perma.cc/f8l8-
kc96.
Wallach, H. M., Mimno, D. M., and McCallum, A. (2009).
Rethinking lda: Why priors matter. In Advances in
neural information processing systems, pages 1973–
1981.
Wittrock, M. C. (1989). Generative processes of compre-
hension. Educational Psychologist, 24(4):345–376.
Yoshiki Shibukawa (2015). Snowballstemmer 1.2.1:
https://perma.cc/xpj6-jnmf.
Autonomous Semantic Structuring of Lecture Topics - Synthesis of Knowledge Models
355
