
Detection of Runtime Normative Conflict in Multi-Agent Systems
based on Execution Scenarios
Mairon Belchior
1
and Viviane Torres da Silva
2
1
Computer Science Department, Fluminense Federal University, Niterói, Brazil
2
IBM Research (on leave from Fluminense Federal University), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Keywords: Norms, Normative Conflict, Runtime Conflict, Multi-Agent Systems, OWL, SWRL.
Abstract: Norms in multi-agent systems are used as a mechanism to regulate the behavior of autonomous and
heterogeneous agents and to maintain the social order of the society of agents. Norms define what is
permitted, prohibited and obligatory. One of the challenges in designing and managing systems governed by
norms is that they can conflict with another. Two norms are in conflict when the fulfillment of one causes
the violation the other and vice-versa. Several researches have been proposed mechanisms to detect
conflicts between norms. However, there is a kind of normative conflict not investigated yet in the design
phase, here called runtime conflicts, that can only be detected if we know information about the runtime
execution of the system. This paper presents an approach based on execution scenarios to detect normative
conflicts that depends on execution order of runtime events in multi-agent systems.
1 INTRODUCTION
Norms have been used in open multi-agent systems
(MAS) as a mechanism to regulate the behavior of
autonomous and heterogeneous agents without
directly interfering with their autonomy. They are
system-level constraints that are independent from
the implementation of specific agents and represent
the ideals of behavior of these agents (Aphale et al.,
2012). They represent a way for agents to
understand their responsibilities and the
responsibilities of the others. Norms describe actions
that must be performed (obligations), actions that
can be performed (permissions) and actions that
cannot be performed (prohibitions) by a given entity
in a certain situation.
An important issue that must be considered while
specifying the norms is the conflicts that may arise
between them. Due to the numeral norms that may
be necessary to govern a normative MAS, the
normative conflict might not be immediately
obvious to the system designer. Two norms are in
conflict when the fulfillment of one causes the
violation of the other and vice-versa. For example,
there is a conflict when a norm prohibits an agent
from performing a particular action and another that
requires the same agent to perform the same action
at the same period of time.
There are many approaches in the literature that
deal with conflicts between norms in MAS. As
stated in Santos and Silva (2016), a normative
conflict can be classified as direct conflict and
indirect conflict. Direct conflict involves two norms
that are associated with the same entity, regulate the
same behavior, have contradictory deontic concepts,
and are defined in the same context. The detection of
this conflict can be done by simply comparing the
norm elements. Indirect conflict involves two norms
whose elements are not the same but are related. Its
detection requires that the relationships among the
norm elements are known.
However, there is another kind of normative
conflict not investigated yet in the design phase that
can only be detected when we know information
about the runtime execution of the system. We will
call this kind of conflict as runtime conflict. This
kind of conflict depends on events that only happen
at runtime. For example, let us suppose that N1 is a
norm that prohibits an agent Ag from performing the
action Ac after the execution of action X. Moreover,
suppose that N2 is another norm that obligates the
same agent to perform the same action before the
execution of another action Y. The execution of the
actions X and Y are runtime situations and we do not
646
Belchior, M. and Silva, V.
Detection of Runtime Normative Conflict in Multi-Agent Systems based on Execution Scenarios.
DOI: 10.5220/0006368306460652
In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2017) - Volume 1, pages 646-652
ISBN: 978-989-758-247-9
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

know when they will be performed by the agents in
the system. However, analyzing the execution order
of them, we can say that if event Y would happen
first compared to event X, we could assert that N1
and N2 will be not in conflict. Otherwise, there will
be a conflict between N1 and N2. Therefore, if we
know the information about when the conditions that
make the norm active, it would be possible to detect
the existence of the conflict. We defined six types of
conditions that define the activation period of a
norm, which are (i) the execution of an action by an
agent, (ii) a fact that become true for an agent, (iii)
the fulfillment or (iv) violation of a norm and (v) the
activation or (vi) deactivation of a norm.
In this paper, we propose an approach based on
execution scenarios to detect normative conflicts
that depend on execution order of runtime events in
MAS. The system designer may want to evaluate a
possible sequence of actions in the system and know
if that sequence would cause any normative conflict.
The conflict detection approach identifies normative
conflicts in case such scenario would be executed in
the system. The propose approach uses Semantic
Web technologies, such as, SWRL rules, OWL DL
and SPARQL query language.
This paper is organized as follows. Section 2
presents the ontology-based definition of a norm and
the execution scenario representation. Section 3
describes the normative conflict detection approach
and gives an example of detection of this kind of
conflict. Our proposal is compared to related works
in Section 4, and conclusions and future works are
presented in Section 5.
2 ONTOLOGY-BASED NORM
REPRESENTATION
Ontologies are used to capture knowledge about
some domain of interest. They describe the domain
concepts and relationships between these concepts.
We propose to use OWL DL and SWRL and
reasoning tools to represent the main concepts of a
norm in MAS. With this representation we are able
to detect norm violations and norm conflict. The
OWL Web Ontology Language is an expressive
knowledge representation language endorsed by the
World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). OWL DL is a
sublanguage of OWL that is based on Description
Logic (DL), a decidable fragment of the first-order
logic (Rudolph, 2011). The Semantic Web Rule
Language (SWRL) is a Horn clause rules extension
to OWL (Horrocks at al., 2004). One of the most
powerful features of SWRL is its ability to support
user-defined built-ins functions to perform
operations for comparisons, mathematical, strings,
date, and others.
2.1 Norm Definition
The main classes represented in the norm ontology
are Norm, Context, DeonticConcept, Entity, Action,
Condition, FulfillmentStatus and ActivationStatus.
The class Norm represents a norm definition used as
a mechanism to regulate the behavior of agents in
MAS and is defined in DL, as follows.
Norm ≡ ∀ hasContext.Context ⊓
=1 hasDeonticConcept.DeonticConcept ⊓
=1 hasEntity.Entity ⊓
=1 hasAction.Action ⊓
≤1 hasBefore.Condition ⊓
≤1 hasAfter.Condition ⊓
=1 hasActivationStatus.
ActivationStatus ⊓
=1 hasFulfillmentStatus.
FulfillmentStatus ⊓
∀ hasConflict.Norm
According to the definition above, a norm can be
related to instances of the classes Context,
DeonticConcept, Entity, Action, ActivationStatus and
FulfillmentStatus through the object properties
hasContext, hasDeonticConcept, hasEntity,
hasAction, hasActivationStatus and hasFulfillment
Status, respectively. It also can be connected to the
Condition class via two object properties: hasBefore
and hasAfter. Moreover, a norm can have a
relationship to order instances of norm by using the
hasConflict property.
The class Context determines the application area
of a norm. Norms can be defined usually in two
different contexts: Environment and Organization
contexts. They are defined in the norm ontology as
subclasses of the Context class, as shown below.
Organization ⊑ Context
Environment ⊑ Context
The class DeonticConcept describes behavior
restrictions for agents in the form of obligations,
permissions and prohibitions. Thus, the individuals
Obligation, Permission and Prohibition were
introduced in the norm ontology, and the class
DeonticConcept was defined as the enumeration of
its members using Nominals in DL, as shown below.
DeonticConcept ≡
{Obligation,Permission,Prohibition}
The Entity class describes the entities whose
behavior is being controlled by a norm. An entity is
the subject of a norm-controlled action. It has a
relationship with a context, via the actsIn object
Detection of Runtime Normative Conflict in Multi-Agent Systems based on Execution Scenarios
647

property, to determine in which context an entity is
acting. The entities represented in this paper are
single agents. Instances of the Entity class can
perform an action in the MAS. Thus, they can have a
relationship along the object property perfomAction
to individuals that are members of the Action class.
An entity can also participate in a situation, instance
of Situation class. A situation is one kind of
activation condition that represents a fact in the
knowledge base (e.g., an agent has a car, lives in
New York or is graduated from a college). An agent
can participate in zero, one or many situations by
using the object property participateIn. Activation
conditions will be explained latter in this section.
The class Entity is defined in DL as follows.
Entity ⊑ ∀ actsIn.Context ⊓
∀ perfomAction.Action ⊓
∀ participateIn.Situation
The behavior been controlled by the norm is
defined by the Action class. An action can be
performed by individuals that are members of the
Entity class via isPerformedBy object property,
which is the inverse property of the perfomAction
property. The Action class is defined as follows.
Action ⊑ ∀ isPerformedBy.Agent
The class Condition determines the period during
which a norm is activated. A norm has a relationship
with a condition via two object properties, namely,
hasBefore and hasAfter, which are used to delimitate
its activation period. For example, let n1 and n2 be
two norms, and n1 is defined to be activated after
norm n2 is been fulfilled. Thus, the fulfilment of n2
is the condition of norm n1 and the activation period
of n1 is whenever norm n2 is fulfilled until +infinite.
A norm can have no relationship with any
condition. When that happens, its activation period
is since the beginning of the system’s execution until
+infinite, i.e., the norm is always active. There are
six types of condition defined in the norm ontology
as subclasses of the Condition class. They are
ExecutionOfAction, ActivationOfNorm, Deactivation
OfNorm, FulfillmentOfNorm, ViolationOfNorm and
Situation, and are defined as follows.
ActivationOfNorm ⊑ Condition ⊓
=1 hasRelatedNorm.Norm
DeactivationOfNorm ⊑ Condition ⊓
=1 hasRelatedNorm.Norm
FulfillmentOfNorm ⊑ Condition ⊓
=1 hasRelatedNorm.Norm
ViolationOfNorm ⊑ Condition ⊓
=1 hasRelatedNorm.Norm
ExecutionOfAction ⊑ Condition ⊓
=1 hasRelatedAction.Action ⊓
=1 hasRelatedEntity.Entity
Situation ⊑ Condition
Individuals that are members of any of the
classes ActivationOfNorm, DeactivationOfNorm,
FulfillmentOfNorm and ViolationOfNorm must
specify a norm that is related to the condition
through the object property hasRelatedNorm. The
class ExecutionOfAction was defined as subclass of
Condition that has exactly one relationship to the
Action and Entity classes through hasRelatedAction
and hasRelatedEntity object properties, respectively.
The Situation class is one type of condition that
represents a fact in the knowledge base.
The class ActivationStatus represents the
activation status of a norm and can be either
activated, deactivated or none. When a norm is
activated, it means the norm becomes active and
must be somehow fulfilled. Once a norm is
activated, it can be deactivated at some time and no
action is required anymore. The none activation
status means that the norm has not been neither
activated nor deactivated yet. All instance of Norm
are started in the system with none value for its
activation status. This status is useful to let the
agents know about the existences of the norms. The
individuals Activated, Deactivated and None were
introduced in the ontology, and the class
ActivationStatus was defined as the enumeration of
its members, as shown below.
ActivationStatus ≡
{Activated,Deactivated,None}
The class FulfillmentStatus describes the
fulfillment status of a norm, which can be either
fulfilled, violated or unknown. The unknown
fulfillment status means that the norm has not been
neither fulfilled nor violated yet. For example, let us
suppose we have an activated obligation norm
stating that a given action must be performed, but
that action has not been execute yet. Hence, in that
case, the fulfillment status is unknown. However, if
that action is executed, the fulfillment status will
become fulfilled. But if that norm turns into
deactivated and the action has not been executed yet,
then the fulfillment status would be violated. All
norms are started with unknown value for its
fulfillment status. The individuals Fulfilled, Violated
and Unknown were introduced in the ontology, and
the class FulfillmentStatus was defined as the
enumeration of its members, as follows.
FulfillmentStatus ≡
{Fulfilled,Violated,Unknown}
A norm can have a relationship to individuals
that are members of the Norm class by using the
object property hasConflict, which represents a
normative conflict between two instances of norms.
In order to classify the norms regarding their
compliance, the classes FulfilledObligationNorm,
ICEIS 2017 - 19th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
648

ViolatedObligationNorm, FulfilledProhibitionNorm,
ViolatedProhibitionNorm and ViolatedPermission
Norm were introduced in the norm ontology as
subclass of Norm class, as follows.
FulfilledObligationNorm ⊑ Norm ⊓
hasDeonticConcept.(Obligation) ⊓
hasFulfillmentStatus.(Fulfilled)
ViolatedObligationNorm ⊑ Norm ⊓
hasDeonticConcept.(Obligation) ⊓
hasActivationStatus.(Deactivated) ⊓
¬ ObligationNormFulfilled
FulfilledProhibitionNorm ⊑ Norm ⊓
hasDeonticConcept.(Prohibition) ⊓
hasActivationStatus.(Deactivated) ⊓
¬ ProhibitionNormViolated
ViolatedProhibitionNorm ⊑ Norm ⊓
hasDeonticConcept.(Prohibition) ⊓
hasFulfillmentStatus.(Violated)
ViolatedPermissionNorm ⊑ Norm ⊓
hasDeonticConcept.(Permission) ⊓
hasFulfillmentStatus.(Violated)
Due to the open word assumption of OWL, in
order to the classification of the classes
ViolatedObligationNorm, FulfilledProhibitionNorm
work properly, it is necessary to explicitly limit the
universe of known individuals of the classes
FulfilledObligationNorm and ViolatedProhibition
Norm by setting them equivalent to the enumeration
of their members. Thus, suppose that the class
FulfilledObligationNorm has two individuals, called
oblig1 and oblig2. Therefore, the following axiom is
added to the norm ontology.
FulfilledObligationNorm ≡
{oblig1, oblig2}
2.2 Execution Scenario Ontology
The norm ontology allows to represent an agent
performing an action, participating in a situation,
and a norm being fulfilled, violated, activated and
deactivated. However, in order to detect normative
conflict that depends on execution order of runtime
events in MAS, it is not enough to know only that
those events occurred in the system. More them that,
it is necessary to know when such events were
executed in the system and if them happened before
or after another one. In other words, if we know the
time when each condition of the system norms
happened in the system, then it is possible to ensure
if such norms are in conflict or not.
Therefore, the execution scenario ontology
extends the norm ontology in order to add the notion
of time. The time when a condition of a norm
happens in the system is captured by the
hasConditionTime datatype property and is
represented by an integer value. The range of this
property is an xsd:integer. The following axiom was
added to the Condition class.
Condition ⊑ ∀ hasConditionTime.Integer
The execution scenario ontology also introduced
the class Time to represent the moment when an
action is performed by an agent and when a situation
becomes true in the system for an agent. The Time
class is related to hasTime datatype property, which
range is an xsd:integer. The following axioms were
added to the classes Entity, Action and Situation, and
the Time class is defined as follows.
Entity ⊑ ∀ entityTime.Time
Action ⊑ ∀ actionTime.Time
Situation ⊑ ∀ situationTime.Time
Time ⊑ ∀ hasTime.Integer ⊓
(∀ timeEntity.Entity ⊔
∀ timeAction.Action ⊔
∀ timeSituation.Situation)
As described in section 2.1, a norm is activated
during a period of time, which is determined by the
Condition class along with hasBefore and hasAfter
object properties. An agent can perform an action at
any time in the system. However, in order to an
obligation norm to be fulfilled by the agent, the
regulated action must be performed only while the
norm is active, i.e., during the period of time where
the norm is active. It is necessary to know when the
norm start and finish its activation. Therefore, the
datatype properties hasStart and hasEnd were
included to the execution scenario ontology. Their
domain and range are the ActivationPeriod class and
xsd:integer, respectively. The class ActivationPeriod
represents the timeline period during which a norm
is active. The following axiom was added to the
Norm class and the ActivationPeriod class is defined
as follows.
Norm ⊑ ∀ hasActvPrd.ActivationPeriod
ActivationPeriod ⊑
∀ hasStart.Integer ⊓
∀ hasEnd.Integer
In this paper, we are considering that a norm can
have at most one before condition and one after
condition. Therefore, a norm can have one of the
five types of activation intervals showed in Figure 1.
The first type is when a norm has no condition and is
always active, i.e., its activation interval starts at
time zero and lasts until +infinite. The second type
refers to a norm associated with only one before
condition. This interval starts from zero and lasts
until whenever that condition happens in the system.
The third type represents a norm with only one after
condition and the interval starts whenever that
condition happens and lasts until +infinite. The
Detection of Runtime Normative Conflict in Multi-Agent Systems based on Execution Scenarios
649

fourth and fifth types refer to a norm associated with
both before and after conditions. They differ each
other by when each condition happens in the system.
If the before condition happens first, then the norm
activation period is characterized by the fourth
interval type. Otherwise, the norm activation period
is represented by the fifth interval type.
Figure 1: Five types of activation intervals.
The fourth interval type is the only one which a
norm has two activation periods, i.e., from zero to
whenever the before condition happens and from
whenever the after condition happens to +infinite.
Therefore, the norms can have one or at most two
activation intervals.
In the norm ontology, six conditions were
defined as subclass of Condition class, which were
the classes ExecutionOfAction, ActivationOfNorm,
DeactivationOfNorm, FulfillmentOfNorm, Violation
OfNorm and Situation. The time when such
conditions happen in the system can be inferred
automatically from the normative system, if the
times when an action was performed by an agent and
when a situation became true to an agent are known
in advance. Assuming these times are known, the
remaining times can be inferred by using SWRL
rules, as follows. The time of the conditions
ExecutionOfAction and Situation can be easily
inferred by using the following rules, respectively.
Rule1: ExecutionOfAction(?c) ∧
hasRelatedAction(?c, ?a) ∧ Action(?a) ∧
hasRelatedEntity(?c, ?e) ∧ Entity(?e) ∧
entityTime(?e, ?t) ∧ Time(?t) ∧
timeAction(?t, ?a) ∧ hasTime(?t, ?ti)
⟶ hasConditionTime(?c, ?ti)
Rule2: Situation(?c) ∧ participateIn(?e,
?c) ∧ Entity(?e) ∧ entityTime(?e, ?t) ∧
Time(?t) ∧ timeSituation(?t, ?c)∧ hasTime
(?t, ?ti) ⟶ hasConditionTime(?c, ?ti)
The norm’s fulfillment depends on its deontic
concept, i.e., if the norm is an obligation, prohibition
or permission. As described in section 2.1, the
fulfillment can be unknown, fulfilled or violated.
When the norm is an obligation, it becomes fulfilled
when the agent performed the action while the norm
is active. If the norm was deactivated, but the agent
did not perform the action, then the norm becomes
violated. If the norm is a prohibition, then the
opposite behavior can be observed. It becomes
violated when the agent performed the action while
the norm is active, and fulfilled when the norm was
deactivated, but the agent did not perform the action.
When the norm is a permission, it becomes violated
when the agent performed the action, but he/she has
no permission to do that, i.e., the norm is not active.
A permission norm never becomes fulfilled because
a permission is an authorization and it is not
expected to be perform by the agent. The condition’s
time for fulfilment and violation of an obligation
norm are shown in rules 3 and 4, respectively.
Rule3: FulfillmentOfNorm(?c) ∧
hasRelatedNorm(?c, ?n) ∧ Norm(?n) ∧
hasDeonticConcept(?n, Obligation) ∧
hasAction(?n, ?a) ∧ Action(?a) ∧
hasEntity(?n, ?e) ∧ Entity(?e) ∧
entityTime(?e, ?t) ∧ Time(?t) ∧
timeAction(?t, ?a) ∧ hasTime(?t, ?ti) ∧
hasActvPrd(?n, ?ap) ∧ hasStart(?ap,
?ts) ∧ hasEnd(?ap, ?te) ∧
swrlb:greaterThanOrEqual(?ti, ?ts) ∧
swrlb:lessThan(?ti, ?te) ⟶
hasConditionTime(?c, ?ti) ∧
hasFulfillmentStatus(?n, Fulfilled)
Rule4: ViolationOfNorm(?c) ∧
hasRelatedNorm(?c, ?n) ∧ Norm(?n) ∧
hasDeonticConcept(?n, Obligation) ∧
ViolatedObligationNorm(?n) ∧ hasActvPrd
(?n, ?ap) ∧ hasEnd(?ap, ?te) ⟶
hasConditionTime(?c, ?te) ∧
hasFulfillmentStatus(?n, Violated)
In a similar manner, the condition’s time for
fulfilment and violation of a prohibition norm can be
inferred, but in the opposite way. The rules 5 and 6
calculates the condition’s time for activation and
deactivation of a norm.
Rule5: ActivationOfNorm(?c) ∧
hasRelatedNorm(?c, ?n) ∧ Norm(?n) ∧
hasActvPrd(?n, ?ap) ∧ hasStart(?ap,
?ts) ⟶ hasConditionTime(?c, ?ts)
Rule6: DeactivationOfNorm(?c) ∧
hasRelatedNorm(?c, ?n) ∧ Norm(?n) ∧
hasActvPrd(?n, ?ap) ∧ hasEnd(?ap, ?te)
⟶ hasConditionTime(?c, ?te)
The start and end times of a norm activation
period cannot be inferred by using SWRL, because
in SWRL there is no way to check the existence of
only one if these relationships: hasBefore and
hasAfter. This verification can be done by using
NOT EXISTS filter expression in SPARQL queries
[Harris at al., 2013]. For example, suppose that n1 is
a norm that has only a relationship with hasBefore
condition, named c1. The activation interval of that
ICEIS 2017 - 19th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
650
norm starts at time zero and the end time will
depend on whether or not the condition c1 was
satisfied. If not, the end time is unknown. Otherwise,
the end time is the time when the condition c1
became true in the knowledge base.
3 CONFLICT DETECTION
The execution scenario ontology can be used by the
system designer as a means for providing an
example of execution scenario performed by the
agents in the system. The system designer may want
to evaluate a possible sequence of actions in the
system and know if that sequence would cause any
normative conflict. The conflict detection rule uses
the times provided by the execution scenario
ontology in order to detect conflicts between the
norms in case such execution scenario would be
executed in the system. As described in section 2.2,
the designer only needs to provide the time when an
action would be performed by an agent and when a
situation would become true to an agent. The
remaining times are automatically calculated.
Two active norms are said to be in conflict when
they are associated with the same entity, regulate the
same behavior, have contradictory deontic concepts
(i.e., prohibition versus permission or prohibition
versus obligation), and are defined in the same
context. To detect conflict between two norms that
depends on execution order of runtime events, we
have to compare the activation periods two by two in
order to find intersections between them. The rule 7
shows the detection of normative conflict between
an obligation and a prohibition.
Rule7: Norm(?n1) ∧ Norm(?n2) ∧
hasEntity(?n1, ?e) ∧ hasEntity(?n2, ?e)
∧ hasAction(?n1, ?a) ∧ hasAction(?n2,
?a) hasContext(?n1, ?c) ∧ hasContext
(?n2, ?c) ∧ hasDeonticConcept(?n1,
Obligation) ∧ hasDeonticConcept(?n2,
Prohibition) ∧ hasActvPrd(?n1, ?ac1) ∧
hasStart(?ac1, ?st1) ∧ hasEnd(?ac1,
?ed1) ∧ hasActvPrd(?n2, ?ac2) ∧
hasStart(?ac2, ?st2) ∧ hasEnd(?ac2,
?ed2) ∧ swrlb:lessThan(?st1, ?st2) ∧
swrlb:greaterThanOrEqual(?ed1, ?st2)
⟶ hasConflict(?n1, ?n2)
This rule verifies if any activation periods of two
norms intersects each other by comparing the initial
and final times of their activation intervals. If that
happen, then they are in conflict. A similar rule must
be created in order to identify conflicts between a
permission and a prohibition.
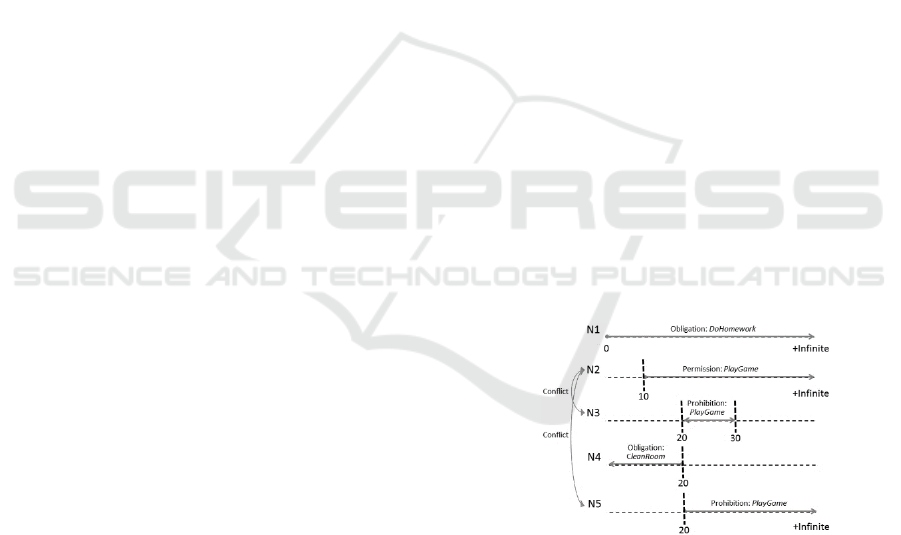
3.1 Conflicting Norms Example
This section presents an example of the detection of
this kind of conflict. Let us assume a daily home
rules for a family with a child called Riley. The
following norms are defined for him.
Norm1: Agent Riley are obligated to perform the
action doHomework.
Norm2: Agent Riley are permitted to perform the
action playGame after fulfill the norm Norm1.
Norm3: Agent Riley are prohibited to perform
playGame after he performs haveLunch and before
the situation doneLunching becomes true for him.
Norm4: Agent Riley are obligated to perform the
action cleanRoom before he performs haveLunch.
Norm5: Agent Riley are prohibited to perform the
action playGame if he violates the norm norm4.
Let us suppose now that the designer provided
the following execution scenario and wanted to
know if there is any normative conflict in case this
scenario would be executed in the system.
Riley performs doHomework at time 10;
Riley performs haveLunch at time 20, and;
The situation doneLunching becomes true for
Riley at time 30.
According to the proposed conflict detection
approached, there is a normative conflict between
the norms N2 and N3, and between N2 and N5
because they are applied to the same agent and
action, they have contradictory deontic concept, and
their activation interval intersect each other. Figure 2
depicts the activation periods for each norm.
Figure 2: Example of norms in conflict.
4 RELATED WORK
Several researchers have investigated mechanisms to
detect normative conflicts in MAS. Some of them
deal with the identification of direct conflicts (Li et
al., 2014, Dos Santos Neto et al., 2013, Uszok et al.,
2008), and others can also detect indirect conflicts
(Aphale et al., 2012; Sensoy et al., 2012 Santos and
Silva, 2016; Da Silva et al., 2015, Lam et al., 2008).
Detection of Runtime Normative Conflict in Multi-Agent Systems based on Execution Scenarios
651

However, to the best of our knowledge, none of
them is able to detect runtime normative conflicts,
i.e., conflicts that may occur depending on execution
order of runtime events, in the design phase.
Lam et al. (2008) proposed an approach that uses
SWRL and OWL DL to represent norm-governed
organizations. A conditional norm with a deadlines
was specified where the condition is only a
xsd:dateTime associated with either before or after
object properties. This approach does not allowed a
norm to have a relationship with both before and
after properties. Also, the authors did not show how
to detect a conflict between norms with conditions.
Moreover, runtime conditions such as those
described in this paper are not supported.
Sensoy et al. (2012) developed a framework for
representing OWL-based policies for distributed
agent-based systems called OWL-POLAR. The
activation and expiration conditions of a norm in
OWL-POLAR are represented by a conjunctive
semantic formula, which are facts in the knowledge
base. However, the authors did not take into account
before and after conditions.
Uszok et al. (2008) developed a policy
framework called KAoS that uses OWL ontology-
based representation and reasoning to specify,
deconflict, and enforce policies. KAoS supports two
main types of norms: (positive and negative)
authorization and (positive and negative) obligation.
However, KAoS does not provide mechanisms to
represent deactivation condition of a norm. Also,
before and after conditions are not supported.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Normative conflicts is an important issue in the
design of multi-agent systems. In this paper, we
have presented an approach to deal with the
detection of normative conflicts that depends on
information about the runtime execution of the MAS
based on execution scenarios. The proposal allows
the designer to provide examples of execution
scenarios of the system and evaluate the conflicts
that may arise if those scenarios would be executed
in the system.
There are several extensions we continue to work
on. Since multi-agent systems are composed of
multiple autonomous and heterogeneous agents,
there is a huge amount of possibilities of execution
scenarios to happen in the system. We would like to
investigate how the proposed approach can be
extended in order to automatically generate
execution scenarios and provide to the designer
potential normative conflicts in the system.
Moreover, we want to extend the proposed approach
to support repetition of before and after conditions.
REFERENCES
Aphale, M. S., Norman, T. J., and Sensoy, M. Goal
directed conflict resolution and policy refinement, In
14th International Workshop on Coordination,
Organizations, Institutions and Norms in Agent
Systems, Valencia, Spain, 2012.
Da Silva, V. T.; Braga, C.; Zahn, J. Indirect Normative
Conflict: Conflict that Depends on the Application
Domain. In: International Conference on Enterprise
Information Systems (ICEIS), 2015, Barcelona.
Dos Santos Neto, B. F., Da Silva, V. T., and De Lucena,
C. J. P. (2013). Developing goal-oriented normative
agents: The NBDI architecture. In Filipe, J. and Fred,
A., editors, Agents and Artificial Intelligence, volume
271 of Communications in Computer and Information
Science, pages 176–191. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Harris, S., Seaborne, A., & Prud’hommeaux, E. (2013).
SPARQL 1.1 query language. W3C recommendation,
21(10).
Horrocks, I., Patel-Schneider, P. F., Boley, H., Tabet, S.,
Grosof, B., & Dean, M. (2004). SWRL: A semantic
web rule language combining OWL and RuleML.
W3C Member submission, 21, 79.
Lam, J. S. C., Guerin, F., Vasconcelos, W., & Norman, T.
J. Representing and Reasoning about Norm-Governed
Organisations with Semantic Web Languages. In Sixth
European Workshop on Multi-Agent Systems. Bath,
UK. December, 2008.
Li, T.; Jiang, J.; Aldewereld, H.; De Vos, M.; Dignum, V.;
Padget, J. Contextualized institutions in virtual
organizations. In: Coordination, Organizations,
Institutions, and Norms in Agent Systems IX. Springer
International Publishing, 2014. p. 136-154.
Rudolph, Sebastian. Foundations of description logics.
Reasoning Web. Semantic Technologies for the Web of
Data. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2011. 76-136.
Santos, J. S., and Silva, V. T. (2016). Identifying Indirect
Normative Conflicts using the WordNet Database. In
Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on
Enterprise Information Systems - Volume 2: ICEIS,
ISBN 978-989-758-187-8, pages 186-193.
Sensoy, M., Norman, T. J., Vasconcelos, W. W., and
Sycara, K. Owl-polar: A framework for semantic
policy representation and reasoning. Web Semantics:
Science, Services and Agents on the World Wide Web,
12:148–160, 2012.
Uszok, A.; Bradshaw, J. M.; Lott, J.; Breedy, M.; Bunch,
L.; Feltovich, P.; Johnson, M.; Jung, H. New
developments in ontology-based policy management:
Increasing the practicality and comprehensiveness of
KAoS, in: POLICY ’08: Proceedings of IEEE
Workshop on Policies for Distributed Systems and
Networks, 2008.
ICEIS 2017 - 19th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
652
