
Using Educational Robotics with Primary Level Students
(6-12 Years Old) in Different Scholar Scenarios: Learned Lessons
Alfredo Pina
1
, Gabriel Rubio
2
and Ainhoa Moreno
3
1
Math & Computer Engineering department, Public University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain
2
Filology & Language Didactics department, Public University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain
3
Colegio Cardenal Ilundain, Avenida de Don Marcelo Celayeta, 117, 31014 Pamplona, Spain
Keywords: Educational Robotics, Real/Virtual Robots, Key Competences, Standard Curricula, Primary.
Abstract: In this paper, we describe the experiences we have been carrying out the last years using educational robotics
in classroom at the primary level, mainly with boys and girls from 6-7 to 12-14 years old. We have set up a
constructivist Problem Based Learning Approach in order to use robotics to teaching/learning key
competences and standard curricula topics. We have introduced the possibility of working with virtual robots
as well as with real robots. In order to achieve that, firstly we chose real robots (Beebot and Lego Mindstorms
NXT/EV3 respectively). Secondly we implemented software tools for the virtual robots using either our own
developed software or Scratch or Byob/Snap, and thirdly we designed different projects and materials that
could work with all those technological artifacts. Afterwards, and in order to validate such tools and such
methodological approach, we used all of them in three different educational environments: firstly in a series
of teacher’s training summer courses (11, 12 years old, in August from 2012 until 2016), secondly in the First
Lego League (FLL) contests (10-14 years old, which took place from 2009 until 2016) and then with a
teacher’s teams network we promoted (7-14 years old, consolidated in 2014- 2015 and still in place up to
date). The results are promising as we have managed to create a sustainable network of schools and a
significant group of people working in a coordinated way. The Educational authorities support our work and
we have set up a binding agreement between the university, the schools and the Planetarium of Pamplona, in
order to work both in the school and out of the school (the Planetarium plays the role of a Science and
Technological Museum).
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Context and Literature Review
Rocard’s report (where the main issue is that the
European countries are experiencing serious
shortages in the scientific labor market) claims that “a
reversal of school science-teaching pedagogy from
mainly deductive to inquiry-based methods provides
the means to increase interest in science”.
Teaching programming at the primary level is a
critical issue as it is stated in the Report of the joint
Informatics Europe & ACM Europe Working Group
(Informatics education: Europe cannot afford to miss
the boat, April 2013, http://europe.acm.org/iereport/).
The report (focused on primary level students) makes
a clear difference between Digital Literacy or Digital
Competencies and Education in Informatics (specific
science behind information technology, characterised
by its own concepts, methods, body of knowledge and
open issues).
In the last years, Educational Robotics has been
introduced as a powerful, flexible teaching/learning
tool stimulating learners to control the behaviour of
tangible models using specific programming
languages (graphical or textual) and involving them
actively in authentic problem-solving activities
(Alimisis et al, 2010).
Inquiry Based Learning, Problem Based
Learning, Constructivist or Constructionist learning
paths are valid approaches to manage Learning
through robotics (demo, Moro, Pina & Arlegui,
2012).
Nevertheless, we do not need always to use
physical robots to create real learning environments.
Scratch is a visual programming environment that
allows users (10-12 years old) to learn computer
programming while working on personally
196
Pina, A., Rubio, G. and Moreno, A.
Using Educational Robotics with Primary Level Students (6-12 Years Old) in Different Scholar Scenarios: Learned Lessons.
DOI: 10.5220/0006381501960208
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2017) - Volume 1, pages 196-208
ISBN: 978-989-758-301-8; ISSN: 2184-5026
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

meaningful projects such as animated stories and
games (Maloney, Resnick, Rusk, Silverman, &
Eastmond, 2010). It has been shown in (Arlegui,
Moro & Pina a, 2012) through a sequence of
documented examples, some engaging learning
experiences for using Scratch to have an initial,
deeper robotic experience before starting with a
physical robot.
Using BYOB (Harvey & Möning, 2010)), through
the construction of suited custom blocks and, in some
cases, of supporting service scripts, and including
several fundamental robotic sensors, a rather
complete 2D robotic simulator has been presented in
(Arlegui, Moro & Pina b, 2012). Some practical
experiences were implemented using BYOB and
LEGO NXT robots for primary level are presented in
(Arlegui, Moro & Pina, 2013). Currently all these
tools have been adapted and extended to SNAP and
EV3.
Some of the different experiences of robotics
found in the literature, describe the kind of robots and
didactical approach they use, others focus on the
different applications contexts and there are a few that
describe research studies on using robotics in
Education. The literature review has been organized
in three main blocks related with scholar experiences,
robotics clubs/ camps or competitions and
miscellaneous aspects.
Benitti (2012) has shown that educational robotics
has an enormous potential as a learning tool,
including supporting the teaching of subjects that are
not closely related to the Robotics field. This study
points out that there are no studies on the experiences
of using robotics with students aged 11-12 (neither
for less age). Another important question for us is that
he demonstrates that there are no empirical research
involving the use of low cost robots in education
(most of the experiences are using Lego NXT).
Bers, Flannery, Kazakoff & Sullivan (2014) argue
that engaging in construction-based robotics
activities, children as young as four can help to learn
a range of concepts related with computational
thinking, robotics, programming and problem
solving. Even the early childhood classroom is not
typically a place where we find students
programming robots, with the availability of
developmentally appropriate technologies it is
possible, and the result may be the technological
fluency for our youth students. The authors show in
this paper that with age-appropriate technologies,
curriculum and pedagogies, young children can
actively be engaging in learning programming.
Parents, educators, policymakers and researchers are
responsible to assure that our children receive the
technological education needed for healthy
development and successful future.
Fridin (2014) presents “Kindergarten Social
Assistive Robotics (KindSAR)”, a novel technology
that offers kindergarten staff an innovative tool for
achieving educational aims through social
interaction. The basic principle of constructivist
education is that learning occurs when the learner is
actively involved in a process of knowledge
construction. In this study, storytelling was used as a
paradigm of a constructive educational activity. An
interactive robot served as a teacher assistant by
telling prerecorded stories to small groups of children
while incorporating song and motor activities in the
process. Their results show that the children enjoyed
interacting with the robot and accepted its authority.
Johnson (2003) was stating some questions
already not completely answered about teaching with
robotics at the schools. The main question he had at
that moment was: if we could show that robotics has
sustained potential in education, we should integrate
it into the curriculum. Currently a few scholar
curriculum include robotics. In Sweden for example,
in 2006 a study (Hussain et al, 2006) shown that it
was possible to use Robotics at school for improving
Maths learning and they were able to demonstrate that
it was true. Most of the issues in applying robotics as
a learning tool are today well known. For example,
Pitti et al. (2014) made a study in Latin America and
Spain about the perception of teachers (from Schools
and Universities) and most of the issues are explained
(like methodology, types of robots or teachers &
school’s needs). The results could be easily
generalized to other parts of the world. Focusing on
Europe in 2010 some experts (Bredenfeld et al, 2010)
were stating that the long-term goal is to make
robotics in education stronger, more serious and
evaluated and thus sustainable in order to achieve
increasing technology competence of young people
and to attract them for technical professional careers.
Some of the educative experiences in applying
robotics we can found are in schools like the study
that made Chin et al. in Taiwan (Kai-Yi Chin et al,
2014). The main conclusion was that using
educational robot-based learning systems in
classrooms demonstrates a significant advantage for
students, by improving overall learning interest and
motivation. We have several examples of educative
experiences for University undergraduate students
(Jung, 2013; Riek, 2013; Alvarez, Larrañaga, 2016),
but the results in such contexts cannot be applied to
primary school.
If we switch to other fields of application, robotics
has shown a great value in complementary education
Using Educational Robotics with Primary Level Students (6-12 Years Old) in Different Scholar Scenarios: Learned Lessons
197

through the use of it in Contests, Competitions, Clubs
or Tech Camps at earlier ages. The motivation to do
such activities can be that robotics can provide a
vehicle for guiding primary and secondary school
children toward an effective understanding of
programming and engineering principles (Petre et al,
2004: He et al, 2014)). It is a way to encourage and
promote computing and engineering education
among its young generations, and in particular for
female students (Alhumoud et al, 2014). The lack of
interest in Science and technology among young
people is a fact and robotic events help to try to
change such potential problem (Riedo et al a, 2012;
Chan et al, 2013).
There are other important issues to take into
account if we want to manage to introduce robotics
education at schools. Teacher’s schools training and
supporting is a key aspect and sometimes this can be
done out of the school, for example in robotic
festivals (Riedo et al b, 2012). Another key factor is
to get the engagement of the families in such
processes (Cuellar et al, 2013) or event to try to create
collaborations between universities and schools. In
(Bers et al, 2005) an example is given; the approach
involves the creation of partnerships between pre-
service early childhood and engineering students to
conceive, develop, implement and evaluate
curriculum in the area of math, science and
technology by using robotics. The type of robots we
can use is also very important. In general, we need to
have a robot every 3-4 students and the cost of it can
be high. In (Korsh et al, 2013) they present the 10
Dollar Robot Design Challenge to encourage new
designs for extremely low-cost robots that can be
made globally available to attract primary and
secondary- level student interest in engineering.
Related with that we may use also virtual robots (as
we propose in this paper). It has been stated the need
of having direct manipulation environments for
learning (Slangen et al, 2010), like robots.
Nevertheless, other virtual environments could be
used for such purposes.
1.1 Aims of Our Work
Analysing the previous state of the art we can observe
that only a few of the educational robotics initiatives
are addressing the target ages we are working with (6-
12 years old). So the double hypothesis of our paper
is, on the one hand, that learning using digital and real
technological artefacts (robots in this paper) can be
done at earlier ages and on the other hand this learning
can be done with almost all kind of students’ groups
and in different contexts and course formats.
In order to carry out such objectives we have
developed an Educational/Pedagogical theoretical
framework. Based on such framework we have
constructed a learning model producing specific
materials and proposing a methodology to be used
during the teaching/learning process.
In this paper we give an overview of such a model and
we show and discuss three practical cases where we
have applied it (first cycle of primary school, summer
course and the teachers’ team network). The results
are analysed and discussed in order to give answer to
the hypotheses and to summarise other findings and
reflections.
The rest of the paper outlines the theoretical
framework, explaining the didactical and
technological tools we use, and how we can create
materials for both virtual and real robotics
teaching/learning environments. Then we describe
the teaching/learning activities we have carried out,
showing the experimental results. The following
section (discussion) focus on how the results
contribute in reaching the stated research goals. The
paper ends with the conclusions and future work
section.
2 THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
AND EDUCATIONAL
MATERIALS
2.1 The Didactical Approach &
Technological Tools
Our learning strategy consists of a Project Based
Learning (PBL) approach, which means that we will
be working on planned specific projects. Meanwhile,
our intention is to promote and carry out Inquiry
Based Learning (IBL) Activities. The methodological
approach is based on the Constructivism Theory of
Learning. The way to combine those three aspects is:
• to propose different Projects as the main
educational material,
• for every Project we need to propose several
Problems to be solved, starting from a simple
problem, and when the problem is solved we
propose the next one, very similar, but with one
additional issue to be solved/learnt: constructivist
path
• During the solving process we need to guide the
students, offering alternatives but not
solutions…just hints…. promoting self-learning
or Inquiry Based Learning.
CSEDU 2017 - 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
198
We propose to use different technological tools
(software & hardware). In general, we use
Scratch/BYOB/Java simulator and BeeBot robots in
the first primary cycle (6-7 years old) and
BYOB/SNAP and Lego Mindstorms NXT/EV3
robots in the third cycle (10-11 years old). In both
cases we are using a graphical formal programming
language and we have several programming tools and
tips to make the necessary blocks or procedures
(primitives) in order to implement the previous
didactical approach.
More details of the didactical framework can be
found in (Arlegui et al, 2013); you can find also more
details on how to use Real Lego Robots, virtual robots
and sensors created with BYOB in order to make
constructivist PBL learning paths for 11-12 years old
students. We outline in the next section an example
of how we can do a similar thing for 6-7 years old
students, integrating PBL, IBL, soft skills, teamwork,
logical programming, key competencies and
curricular topics.
2.2 Example: First Primary Cycle
(6-7 Years Old)
The public school Cardenal Ilundain, one of the
schools we are working with belongs to the British
Educational Programme, which is worldwide
recognised as a leading educational centre of
excellence, and as a key innovator in British and
Spanish bilingual and multicultural education. British
schools in Spain must follow not only the Spanish
national curriculum but also the UK syllabus and
almost half of the lessons are taught in English;
mandatory those subjects: Science, Maths and
Literature. One of the key features of the Science
British syllabus is the importance it gives to apply the
scientific method, in which the educational robotic
experiences fits perfectly.
We have been working with the above mentioned
school for two years with Robotics in the first cycle
of Primary level (6-7 years). The first year only one
teacher participated in the program with one group of
24 students. In the second year there were 6 teachers
involved and 3 groups of students (75 students). The
robotic activities have been combined with
Programming in Scratch and with playing with
logical games. In fact one group is splitted in three
and in parallel they work in turns in one of the 3
activities proposed. Robotics is in this way integrated
with the rest of “thinking & programming” activities
and at the same time smaller groups work with any of
the activities. In this way you need more teachers and
more room; in fact, they are using the classrooms and
other common areas of the school (the hall) and at the
same time some parents are engaged in helping the
teachers in order to be able to monitor the different
groups.
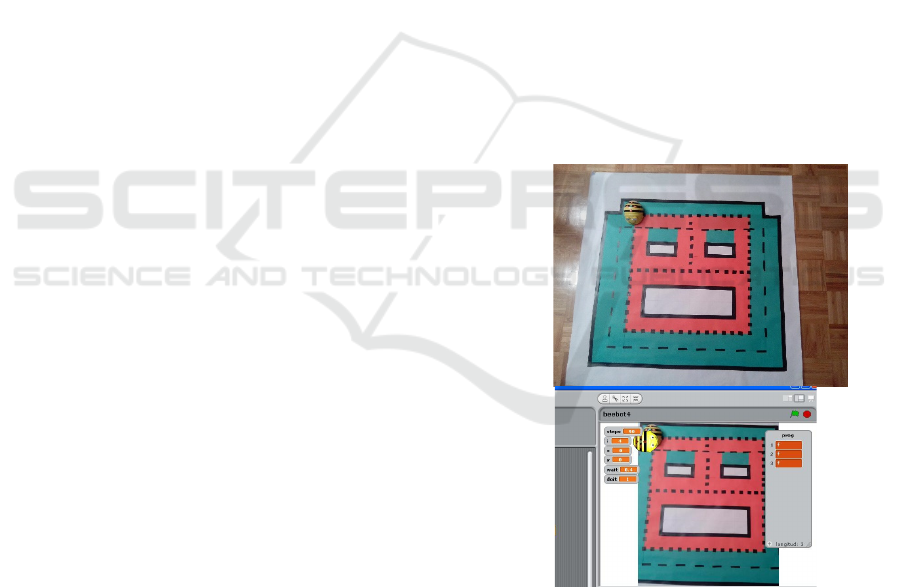
We use the mini robot Bee-Bot, ad-hoc prepared mats
and Scratch (figures 1 & 2) in order to work with the
curricular topics and key competencies by means of
programming robots or simulators. Bee-bot is a big
bee with buttons on its back produced by the TTS
group. The bee can be programmed by pushing the
six buttons on its back to make it move forward or
backward (15 cm), turn left or right a quarter of a
circle (“a pizza” for the children), start to move after
one or several buttons have been pushed one after the
other or all of the previous commands can be deleted.
Scratch includes several features which can be
attributed to usual robotic behaviours. Carefully
exploiting these features makes it possible for a
student to have a significant experience of ‘virtual’
robotics in a ‘virtual’ environment. Therefore, before
working with a real robot, the most important aspects
of robotics can be easily taught. In our case we have
developed a simple simulator of Bee-Bot robots with
Scratch. It is very simple but it allows us to have an
alternative to real robots.
Figure 1 and 2: The BeeBot robot, one mat and both
integrated within the Scratch environment.
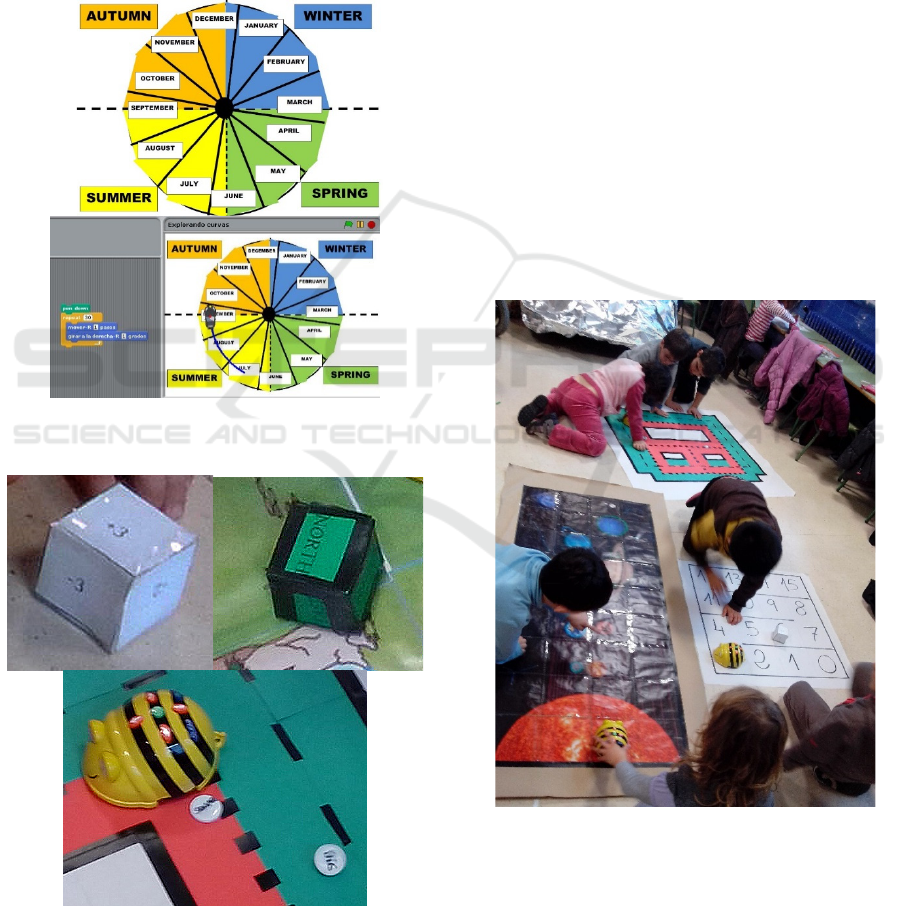
Bee-Bot is suitable when making linear movements,
but if we need to make curved trajectories the
physical Bee-bot robot is not valid (in general robots
are not very precise with curved trajectories). For that
we need to use Scratch to create primitives that can
follow curve trajectories (see figure 3)
Using Educational Robotics with Primary Level Students (6-12 Years Old) in Different Scholar Scenarios: Learned Lessons
199
Finally, we have implemented one complete Bee-
bot simulator with Java in order to be able to work
both in virtual or real environments. The main reason
for that is that we have a limited number of robots, so
the use of Scratch and/or the simulator helps to make
all the students to work on the same activity in
different stages. Before starting designing the
activities, there is a planning process to set the
contents, the objectives and the assessment. The main
goal is to be able to work on curricular topics, key
competences and soft skills (as mentioned before).
Figure 3: A “seasons” mat and one Scratch simulator for
curve trajectories using this mat.
Figure 4: Materials: dices, the robot and one mat.
We are using 12 Bee-bots, mats, spinning-wheels,
dices and counters (figure 4). Except the robots, all
the objects are “student made materials”. At this
moment we have several “educative kits” to work on
several topics: “Solar System”with mat and spinning
wheel;“Desert Island” with mat, dice and spinning-
wheel; “A Year Round”with mat and 2 spinning
wheels depending on the aim of the activity;
“Navarra, our region”with mat, dice and spinning
wheel;“Basic Maths” with mat and dice; “Easy
Geometry” with mat and counters; “Object relative
position” with mat and cards.
Flexibility is a key aspect of this approach,
allowing students to participate individually, in pairs
or small groups (see figure 5) in order to complete a
task guided by the teacher and working for an
extended period of time, to investigate and respond to
a simple or more complex questions, problems, or
challenges. Pupils are engaged in a rigorous process
of asking questions, using resources, and developing
answers. They are allowed to make some choices
(about the movements or paths) which contribute to
develop their knowledge on basis of exploration and
experiences.
Figure 5: Working in small groups & Observation as the
assessment process method.
The first day students meet the robot, PBL
methodology is again applied. The teacher does not
say anything so they show their own expectations,
then they have the opportunity of touching and also
CSEDU 2017 - 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
200

they are guided through small challenges and
attainable goals. They discover different possibilities
that the Bee-bot offers or the lack of them (impossible
curved trajectories). Next step is to reach an
agreement and set the rules to use the robot: handle
with care, take turns....etc. Beginning in such way we
generate interest and curiosity, thus they are ready to
tackle future activities. Observation has been until
now the assessment tool used (figure 5).
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The employed research methodology is case study.
Using the previous didactical ideas, we have
organized/followed different learning activities in
order to collect data to support or no the paper
hypothesis.
3.1 Description of the Experiments
The three formats and different contexts we have
been working with are:
• First Lego League competition (FLL) (2010-
2015)
• Summer courses open to teachers and students
(10-12 years old) (2012-2014)
• Schools Network (and teacher’s teams) making
robotic projects at the primary level (10-12 years
old). In the network we have at least one case
where a team of teachers who are working at the
first cycle of primary level (6-7 years old). (2013-
2015).
The FIRST Lego League (also known by the acronym
FLL) is an international competition for elementary
and middle school students (ages 9-14 in the USA and
Canada, 9-16 elsewhere). In fact, in Navarra we have
mostly students between 10 and 14 years old.
Each year the contest focuses on a different real-
world topic related to Science. There is a scientific
project related to the chosen year´s topic to be
developed and presented. The robotics part of the
competition involves designing, building and
programming the Lego robots in order to complete
certain tasks. Once the tasks have been completed,
you get some points. The students work out solutions
to the various problems they are given and then go to
regional tournaments to share their knowledge,
compare ideas, and show their robots completing the
tasks.
We have a 2-week summer course. During the first
week “trainees” are trained by lecturers in a very
practical way (“making projects”), with several
theoretical reflections or insights. The second week
the trainees have to apply their newly acquired
knowledge with students (about 5 students for every
teacher) and they have to teach/guide them through
the project’s completion (4 days). Then the 5th and
last day we all gather at the Planetario of Pamplona,
where every group of teacher/students has to explain
what they have achieved by means of demos of the
virtual robot and the physical one. For that event the
families and general public are invited to participate.
The families of the students agree on participating
in such training teacher’s course by means of letting
their children to participate in the course and getting
involved in the learning process (in fact for the
students it was a kind of Tech Camp).
The courses have been organized in collaboration
with the Public University of Navarra, Planetarium of
Pamplona and the Education Department of the
Navarra Government (Educational Authorities).
After the first summer course (August 2012) we
have decided to deep dive in the experience but in this
case with the regular teachers and the regular classes
of the educational system in Navarra. The aim was to
involve not only teachers (we wanted more than the
summer course) but also the schools (including
school principals) and the Education department of
Navarra Government (educative authorities).
Trainers from UPNA participated as well.
The proposal was put forward for every academic
year and organized as follows:
First stage (September-October): Trainee’s
training (Lecturers and Teachers)
Second stage (November-December): The
teachers’ teams design a robotic project to be
carried out with their students at the schools.
Third stage (January): All projects are discussed
in one seminar, where all the teachers participate.
At the end of this stage every team of teachers
know their project and also the materials needed
like software and robots.
Fourth stage (February-May): every team of
teachers organises and teaches the practical
lessons with their students (an agreed number of
lessons).
Fifth stage (June): All the completed projects are
discussed and shared during a seminar where all
the teacher’s teams participate.
3.2 Data Collection Process
After several years working we have collected data
related to those experiences; the main aspects we
have focused on and therefore measured (with
different surveys at different times) are:
Using Educational Robotics with Primary Level Students (6-12 Years Old) in Different Scholar Scenarios: Learned Lessons
201
• Gender, Age and Number of people participating
(students & teachers)
• Type of schools
• Frequency and amount of time they work on
robotics
• Relation with standard curriculum
• Motivation of the students towards science &
technology
• Methodology and learning strategies
• Competences they work
• Outcomes of the students
Table 1: Summer Course survey for teachers & for pupils.
Q1
Date of the
course Q8
Course
expectations Q1
How did you
like the course?
Q2 Timetable Q9 Contents Interes
t
Q2
Did you learn a
lot?
Q3
Lenght of
the course Q10 Course Syllabus Q3
What did you
miss?
Q4
Course
Location Q11 Speakers Rating Q4
Will you repeat
a summer
course?
Q5
Classrooms
facilities Q12
Material’s
quality Q5
If yes, on what
topic?
Q6
Technical
facilities Q13
Course
Interactivity
Q7
Personal
Attention
The participants in the surveys are teachers or
coaches involved in the robotic training activities
(Summer Courses, FLL and Schools Network), the
students that have been following the robotic
activities (Summer Courses and Schools Network)
and the families (Summer Courses).
In all the cases we have gathered all the
information about number, genre or age of the
persons involved, contextual scenarios and other
general information. Apart from that we have used
specific surveys for teaching-learning information.
We explain those surveys in the next paragraphs.
To collect data about the summer courses we have
used 2 questionnaires just at the end of the course, one
for the teachers another for the students.
Table 2: Summer Course survey for families (motivating
stem activities).
Q1 Have your son/daughter made similar courses afterwards?
Q2
Do you think that robotic activities have improved their
motivation on Maths and/or Sciences?
Q3
Do you think that robotic activities have improved their
motivation on technology and/or Computer Science and/or
Programming?
To complete that after the third edition (in 2014) we
have made a survey to the families, to know if the
course has been perceived by them as a turning point
in motivating the students towards science and
technology subjects. Moreover, we have also
measured separately the global satisfaction for
teachers and students after every course.
Regarding the First Lego League we have
collected qualitative and quantitative data regarding
the last tournament (2014-15) among the coaches.
The main specific questions are organized around
several topics like key competences involved in the
training, didactical approaches, curricular topics
related with the activity and outcomes of the students.
The following tables show the questions we have
used (the answers are in a 5-likert scale except in the
case of curricular topics; in this case the teachers used
check box being able to choose one or more topics).
Table 3: Key Competencies survey.
Q1 Linguistic communication
Q2
Mathematical competence and basic competences in
Science and Technology
Q3 Digital competence
Q4 Learning to learn
Q5 Social and Civic competencies
Q6 Sense of Iniciative and Entrepreuneurship
Q7 Cultural Awareness and Expression
Table 4: Didactical approaches survey (5-likert scale) &
Curriculum topics related with the robotic activities
(multiple checkbox).
Q1
Natural
Sciences
Q2 Social Sciences
Q1 Inquiry based Learning Q3 Mathematics
Q2 Structured Learning (step by step) Q4
Mother
language
Q3 Project Based Learning Q4
Foreign
languages
Q4 Problem Solving Based Learning Q5 Arts Education
Q6 Technology
Q7 Others
Finally, and related with the school’s network, we
have collected qualitative and quantitative data after
two complete years working with them. Nevertheless,
some of the schools were working before, and others
have been integrated within the network in the last
months. We have used the same questions that in the
previous case of the FLL that have been answered by
the teachers.
CSEDU 2017 - 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
202
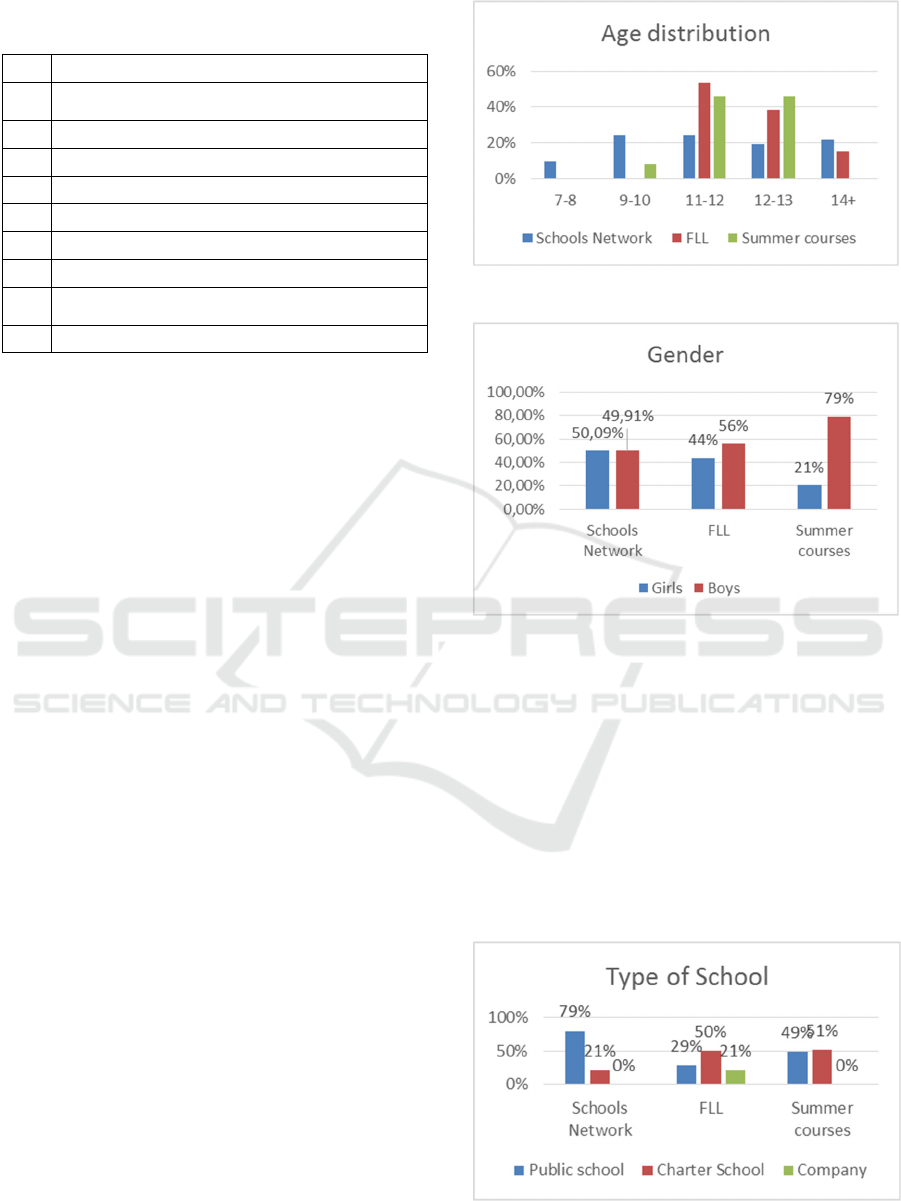
Table 5: Outcomes of students (gain in motivation,
competencies, skills, etc…).
Q1 Motivation towards Maths and/or Sciences
Q2
Motivation towards Technology and/or Computer
Science
Q3 Team work capacity
Q4 Analysis capacity (i.e. Problem decomposition)
Q5 Abstraction capacity (i.e. Generalizing solutions)
Q6 Initiative and Autonomy
Q7 Creativity and innovation when searching for solutions
Q8 Explaining and arguing problems and solutions
Q9
Persistency when achieving goals, overcoming
difficulties
Q10 Specific programming concepts (Loops, Ifs, etc..)
4 RESULTS
The three issues of the summer courses (August
2012-2013-2014) had a total number of 36 teachers
(average age of 34,52) and a total number of 126
pupils. The satisfaction degree for the teachers is 9,13
(10-scale) and 3,59 (4-scale) for the pupils.
During the FLL 2014-15 28 teams from Navarra,
Aragon and La Rioja were participating in Pamplona.
About 51 coaches were involved and the teams had
about 224 students.
4.1 General Results: Age, Gender,
Type of School and Working
Language
The age and gender information is shown in the next
figures. For the summer courses, the age of the
students has been evolving from 2012 (where we did
not have any students of 10 years old) to 2014 (where
some of the students from 2013 where repeating the
course during 2014). For the FLL we only have range
ages. The schools’ network is the only experience
where we have 7 years old pupils. In the case of
gender, we see that the results are clearly different
depending on the context of application.
Figure 6: Age comparison.
Figure 7: Gender comparison.
Navarra has a long history of private subsidized
schooling, and those schools are integrated in the
educational public system. They are similar to a
charter school, nevertheless they have to follow the
same general rules about curricular aspects that the
rest of the public schools. Another important feature
within the educational system in Navarra is that we
work with two official languages, Spanish and
Basque; in the last years English has also been
introduced as a third linguistic approach at the
schools.
Figure 8: Type of school comparison.
Using Educational Robotics with Primary Level Students (6-12 Years Old) in Different Scholar Scenarios: Learned Lessons
203
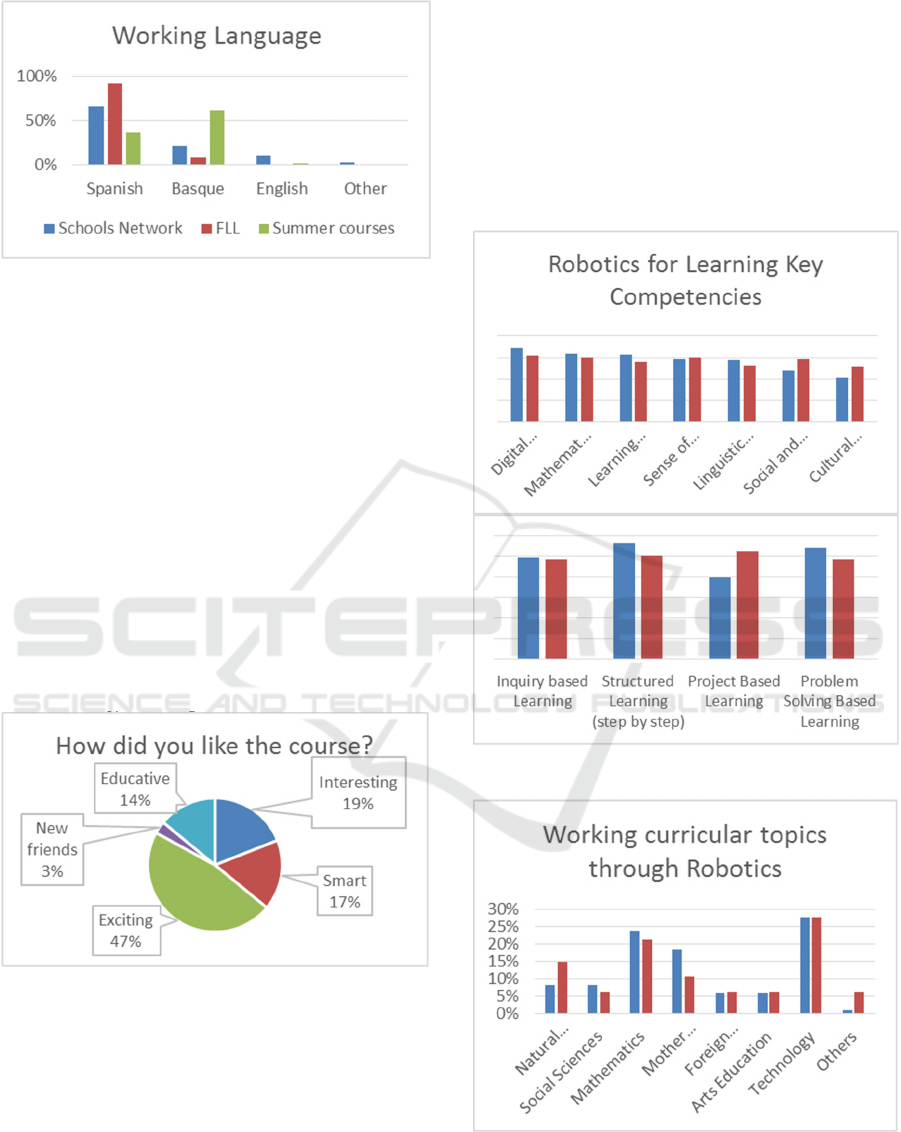
Figure 9: Working language comparison.
4.2 Teachers, Students and Families’
Feedback for the Summer Course
After every summer course edition, we get feedback
from students & teachers through tests. Teachers gave
us their opinion about course organization and
teaching learning contents. In general, they are happy
with both issues (between 3.5 and 4 and between 3
and 4, out of 4 respectively). Pupils are very happy
with the course and have different opinions on it
(figure 10). After the third issue (2014) we have made
a survey to the families in order to get some feedback
from them, a few years after the course in some of the
cases. Only 35% of the families answered to the
survey, and 60% of the families agree that the course
increased their motivation towards Math & Sciences
and technology & Computer Science.
Figure 10: Students survey for the summer courses.
4.3 Didactical Approach, Curricular
Topics, Key Competencies and
Students Outcomes for the Schools’
Network and the FLL
First of all, we can see in figure 11 (FLL in Blue) that
Educational Robotics can be a “tool for learning any
Key competency” (not only Digital or Math
competencies). And thus can be done using different
didactical approaches.
Secondly we can observe in figures 12 & 13 that
the teachers have managed to work several topics
(apart Computer Science and Math) through
Robotics. At the same time the teachers have
considered that the students, through the robotic
activities, are improving their outcomes in several
critical aspects that are not only related to Computer
Science nor to the Curriculum.
Figure 11: Competencies & Didactical approach.
Figure 12: Learning & Students Outcomes.
CSEDU 2017 - 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
204
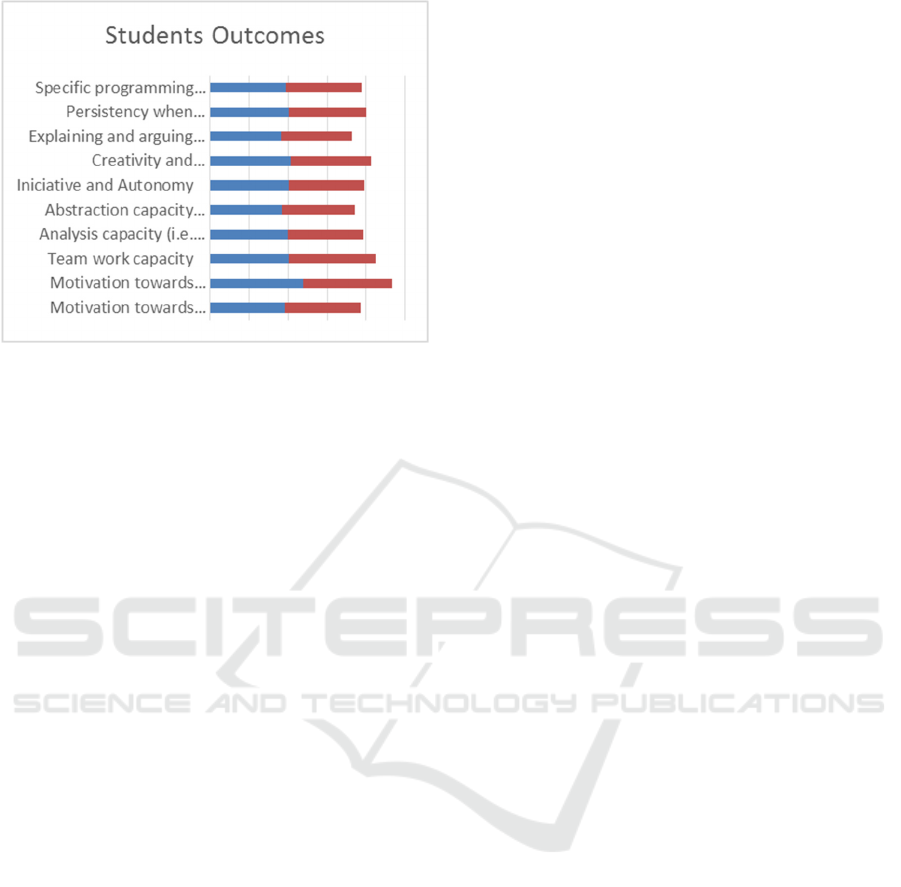
Figure 13: Learning & Students Outcomes (cont.).
5 DISCUSSION
We have categorized the results trying to answer two
broad questions: What is the student’s profile:
gender, age, language or kind of school? Influence on
the learning processes? Answering these two
questions will give us valuable information to
measure to what extent learning using digital and real
technological artefacts (robots in this paper) can be
done at an earlier age, with almost all kind of group
of students, and in different scenarios.
5.1 What Is the Student’S Profile:
Gender, Age, Language or Kind of
School?
For the first question, the results of the surveys that
have been carried out show clear differences.
Gender: the presence of female students in voluntary
experiences (as FLL or Summer Course) is small. For
the Summer Courses we had an enrollment of 21%
female students and 79 % male students. In FLL
teams we discovered that the female participation was
slightly higher than 30% while the male one was of
70%. In comparison, in the Network of Schools the
female presence was 50%. This data has to be
analyzed in close relationship with other questions
that were asked in the Network Survey and FLL
Survey: Girls and Boys are equally motivated? Here,
while the FLL coaches responded yes in 38% and no
in 31% of the answers, in the Network of School
teachers chose 52% of the answers were affirmative
and only 17% of them negative. Another 31% of
teachers said the answer depended on individual
features as: perseverance, curiosity...
Age: within the Network of schools, students are
younger. 50% of the FLL teams are in 10 to 12 range
and the rest (50%) up to 16. Nevertheless, most of the
students in Network of Schools scenario are from 7 to
11 years old (68,54%), and the rest are up to 13 or
early 14 (41,46%). So we are finding here a younger
population that is facing programming problems and
topics with teacher's guidance and at an appropriate
level for them. When we asked teachers if this
approach should be continued 100% of the teachers
said yes.
Type of school: the percentage of public schools
enrolled in the Network is 77,27%. That is the
opposite of what happened in FLL, as non-public
(charter schools) enrolled in it are 79,31%. Most of
the schools in Network of Schools are, therefore,
public schools whereas most of the schools enrolled
in FLL are non-public schools. From the point of
view of educational policies, this fact is remarkable
and supports the efforts done to spread educational
robotics through this Network, as the impact in areas
and population where charter schools are not reaching
now can be achieved
Working language: The surveys show differences in
this aspect, as well. According to the answers
received, most of the teams are working in Spanish in
the FLL (92,30%). Nevertheless, under the Network
of Schools, this percentage is lower (65,5%) and
reflects better the reality of the Navarrese educational
system, where Basque and English are strong
vehicular languages. Besides, in the case of Basque,
is one of the official languages in the region. For this
reason, it is quite relevant that 20,7% of students in
the Network of Schools has Basque as working
language, and 10,3% English.
5.2 Teaching/Learning Processes
For the second question, learning outcomes, the
surveys left interesting considerations. First of all, it
has to be said that by learning outcomes we are
including two major areas: basic competences (as
defined by the EU and the Spanish educational laws)
and a set of observable gains or general outcomes as
motivation towards Maths and/or Sciences,
motivation towards Technology and/or Computer
Science, team work capacity, analysis capacity (i.e.
Problem decomposition), abstraction capacity (i.e.
Generalizing solutions), initiative and autonomy,
creativity and innovation when searching for
solutions, explaining and arguing problems and
solutions, persistency when achieving goals,
overcoming difficulties, specific programming
concepts (Loops, Ifs, etc..). Teachers or coaches,
Using Educational Robotics with Primary Level Students (6-12 Years Old) in Different Scholar Scenarios: Learned Lessons
205
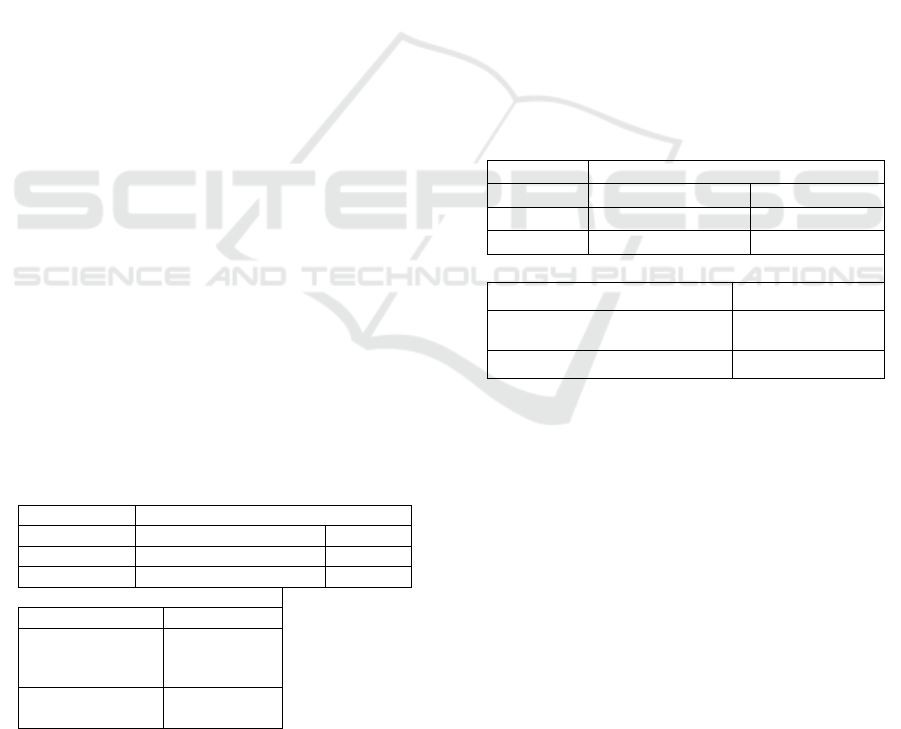
depending on the survey, selected in Likert scale up
to 5 the intensity they thought the educational
robotics program they were involved in was
impacting in their students or teams.
About general outcomes, FLL results show that
for most coaches, the learning outcomes observed
were more focused on teamwork (maybe an influence
of the competition context), whereas Network results
showed the importance of perseverance, which is an
important individual value that is responsible of most
of dropouts. As PISA (Program for International
Student Assessment) data shows, perseverance, drive
and motivation are essential for doing well in and out
of school (Skills for Social Progress: The Power of
Social and Emotional Skills, OECD Skills Studies,
OECD Publishing, Paris. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/
10.1787/9789264226159-en). It is highly remarkable
that the second important outcome in both cases is
creativity and innovation. In Network Survey, student
autonomy scored very high too. We could say, from
the results, that the general learning outcomes that
arise working in both settings with educational
robotics, demonstrate that “hard skills” closely
related to computing or mathematics are only a small
part of the picture. In fact, social skills compound
another big part of the picture and further empiric
research should be done in this respect to discover
how these skills are influencing other areas of
learning in educational robotics programs.
Regarding basic competences, FLL results
highlighted STEM and entrepreneurship -influence of
contest rules probably-, and the Network results
preferred Digital Competence, which is speaking
about a more global approach to educational robotics
inside schools. In any case, both surveys selected in
second place the competence selected in first one in
the other survey. That points a total agreement about
the main competences impacted.
Table 6: learning Competences and Outcomes.
Competences
First Second
Network Digital STEM
FLL STEM‐Entrepreneurship Digital
Outcomes
First Second
Perseverance
Initiative,
Creativity,
Autonomy
Teamwork
Creativity,
innovation
In order to provide more insights into this issue, it is
interesting to check the answers to the question
“Robotics for working curricular topics”. In the top
five list, in both scenarios Technology and Math are
at the top, as expected, but Mother Language is the
third one in Network Survey and fourth one in FLL
results. Again, we have to consider and shape
adequately this fact: learning through robotics implies
other transversal and social skills that have to be bore
in mind while planning and designing didactical
units.
Apart from these two big questions that have been
discussed, the results gave us relevant information
about the way teachers and coaches are organizing
their Teaching-Learning process. Although our
learning strategy preferred is Project Based Learning,
which means that we are going to work on projects
and we want to promote an Inquiry Based Learning,
with a constructivist/constructionist path in the
background, we discovered that structured or step by
step learning, is a popular strategy in both settings.
Maybe, the nature of the contest tends to organize
learning as projects but, then, uses step by step
learning as a way to scaffold teamer’s progress. In the
case of Network results, it has to be subject of further
research why step by step learning is so prominent.
Table 7: Didactical approach comparison.
Motivation
Math/Sciences Computing‐Tech
Network 96% 62%
FLL 61% 76,90%
Methodology
First Second
StructuredLearning
ProblemBased
Learning
ProjectBasedLearning StructuredLearning
6 CONCLUSIONS
All the participants agreed on the fact that the
educative materials end the proposed learning
methodology is suitable to be used in classroom or out
of the classroom. The trainees (school teachers) have
adapted the materials and methodology taught by
trainers (lecturers) to their own situation (schools
pupils).
The use of both technological tools with the
methodological approach, the constructivist PBL, has
allowed us to create flexible materials to teach the
school teachers who will also use them with the be
teaching learning activities used by pupils in the
classroom.
We have showed that it is possible to work with
such materials and methodology in several different
CSEDU 2017 - 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
206

context. In all cases it was possible to work with
either standard curricula topics or key competencies.
Finally and hypothesis related, through the
description and analysis of the different experiences
we have find out that it is possible to do the
educational robotics we propose at earlier ages
(starting 6-7 years old) and in different contexts (in
school, out of the school, summer courses or tech
camps, competitions, etc…). Every scenario has his
own features and outcomes and all of them seem
necessary and complementary.
REFERENCES
Alimisis, Arlegui, Fava, Frangou, Ionita, Menegatti,
Monfalcon, Moro, Papanikolaou, Pina (2010).
Introducing robotics to teachers and schools:
experiences from the TERECoP project. Proceedings of
Constructionism 2010 (Aug. 2010).
Demo, G. B., Moro, M., Pina, A., &Arlegui, J. (2012). In
and out of the School Activities Implementing IBSE
and Constructionist Learning Methodologies by Means
of Robotics. In B. S. Barker, G. Nugent, n.
Grandgennet, & V. I. Adamchuk (Eds.), Robots in K-12
Education: A New Technology for Learning (pp. 66-
92). IGI Global.
J.Maloney, M. Resnick, N. Rusk, B. Silverman, and E.
Eastmond (2010). The Scratch Programming Language
and EnvironmentACM Transactions on Computing
Education, Vol. 10, No. 4, Article 16.
J. Arlegui, M. Moro and A.Pina (2012). How to enhance the
robotic experience with Scratch. Proceedings of
Constructionism 2012 (Aug. 2012).
B. Harvey, J. Mönig (2010). Bringing “No Ceiling” to
Scratch: Can One Language Serve Kids and Computer
Scientists?.Proceedings of Constructionism 2010 (Aug.
2010).
J. Arlegui, M. Moro and A.Pina (2012). Simulation of
Robotic Sensors in BYOB. Proceedings of Robotics In
Education 2012 (Sept. 2012).
J. Arlegui, M. Moro and A.Pina (2013). A PBL approach
using virtual and real robots (with BYOB and LEGO
NXT) to teaching learning key competences and
standard curricula in primary level. TEEM '13
Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing
Multiculturality (2013), pp 323-328.
Benitti, F.B.V. (2012). Exploring the educational potential
of robotics in schools: a systematic review. Computers
& Education, 58 (3), pp. 978-988.
Bers M. U, Flannery L., Kazakoff E.R., Sullivan A. (2014).
Computational thinking and tinkering: exploration of
an early childhood robotics curriculum. Computers &
Education, 72 , pp. 145-157.
Fridin M. (2014). Storytelling by a kindergarten social
assistive robot: a tool for constructive learning in
preschool education. Computers & Education, 70 , pp.
53-64.
Johnson J. (2003). Children, robotics, and education. Artif
Life Robotics (2003) 7:16-21.
Hussain H. et al. (2006). The effect of LEGO Training on
Pupils’ School Performance in Mathematics, Problem
Solving Ability and Attitude: Swedish Data.
Educational Technology & Society, 9 (3), 182-194.
Kathia Pittí Patiño et al. (2014). Using Robotics as a
Learning Tool in Latin America and Spain. IEEE
Revista Iberoamericana de Tecnologias del
Aprendizaje, VOL. 9, NO. 4, NOVEMBER 2014.
Bredenfeld et al. (2010). Robotics in Education Initiatives
in Europe - Status, Shortcomings and Open Questions.
Proceedings of SIMPAR 2010 Workshops, Intl. Conf.
on Simulation, Modeling and Programming for
Autonomous Robots, Darmstadt (Germany) November
15-16, 2010, ISBN 978-3-00-032863-3, pp. 568-574.
Kai-Yi Chin et al. (2014). Impact of Using an Educational
Robot-Based Learning System on Students’ Motivation
in Elementary Education. IEEE Transactions on
Learning Technologies, VOL. 7, NO. 4, October-
December 2014, pp. 333-345.
Seul Jung (2013). Experiences in Developing an
Experimental Robotics Course Program for
Undergraduate Education. IEEE Transactions on
Education, VOL. 56, NO. 1, February 2013, pp. 129-
136.
Laurel D. Riek (2013). Embodied Computation: An Active-
Learning Approach to Mobile Robotics Education.
IEEE Transactions on Education, Vol. 56, NO. 1,
February 2013, pp.67- 72.
Ainhoa Alvarez & Mikel Larrañaga (2016), Experiences
Incorporating Lego Mindstorms Robots in the Basic
Programming Syllabus: Lessons Learned. J Intell Robot
Syst, DOI 10.1007/s10846-015-0202-6.
Petre et al. (2004). Using Robotics to Motivate ‘Back Door’
Learning, Education and Information Technologies 9:2,
147–158, 2004.
He et al. (2014). Teaching K-12 Students Robotics
Programming in Collaboration with the Robotics Club.
4th IEEE Integrated STEM Education Conference.
AlHumoud et al. (2014). Using App Inventor and LEGO
mindstorm NXT in a Summer Camp to attract High
School Girls to Computing Fields. 2014 IEEE Global
Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON), pp.
173-177.
Riedo et al. (2012). Analysis of Impact of an Annual
Robotics Festival, Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE
International Workshop on Advanced Robotics and its
Social Impacts, Technische Universität München,
Munich, Germany, May 21 - 23, 2012.
Chan et al. (2014). Integrated STEAM Education through
Global Robotics Art Festival (GRAF), 4th IEEE
Integrated STEM Education Conference.
Riedo et al. (2012). Involving and training public school
teachers in using robotics for education. Workshop on
Advanced Robotics and its Social Impacts, Technische
Universität München, Munich, Germany, May 21 - 23,
2012, pp. 19-23.
Cuellar et al. (2013). Robotics Education Initiative for
Parent-Children Interaction. 2013 IEEE RO-MAN: The
Using Educational Robotics with Primary Level Students (6-12 Years Old) in Different Scholar Scenarios: Learned Lessons
207

22nd IEEE International Symposium on Robot and
Human Interactive Communication Gyeongju, Korea,
August 26-29, 2013. pp. 364-365.
Bers et al. (2005). Teaching Partnerships: Early Childhood
and Engineering Students Teaching Math and Science
Through Robotics. Journal of Science Education and
Technology, Vol. 14, No. 1, March 2005, pp. 59-73.
Korsah et al. (2013). The African Robotics Network and the
10 Dollar Robot Design Challenge. IEEE Robotics &
Automation Magazine • March 2013, pp. 116-118.
Slangen et al. (2010). What pupils can learn from working
with robotic direct manipulation environments.
International Journal of Technology and Design
Education, Springer, Vol. 21, Issue: 4, Pages: 449-469.
CSEDU 2017 - 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
208
