
A Multi-dimensional Peer Assessment System
Usman Wahid, Mohamed Amine Chatti, Uzair Anwar and Ulrik Schroeder
Informatik 9 (Learning Technologies), RWTH Aachen University, Germany
Keywords:
Open Learning Environments, Open Assessment, Peer Assessment, Peer Feedback, Scalable Assessment.
Abstract:
Modern day education and learning has moved on from brick and mortar institutions to open learning envi-
ronments. This recent shift in education has had its effects on the field of assessment and feedback as well.
The traditional methods of assessment are being replaced by new methods from the field of open assessment.
One such assessment method for open learning environments is peer assessment. Peer assessment is a crowd
sourcing technique which lessens the teacher workload and gives students a voice in the assessment process.
Despite being the leading assessment method in open learning environments, the tools available for peer as-
sessment are lagging far behind. Most peer assessment tools are context and domain specific which hinders
their uniform adoption across different fields of study. This paper introduces the core peer assessment module
in the Peer Assessment & Learning Assessment System (PALAS). The module is a flexible, customizable and
multi-dimensional peer assessment system which allows the teachers to configure the peer assessment process
according to their liking and requirements without any changes required to the system design.
1 INTRODUCTION
Assessment and feedback are an integral part of the
learning process. It is widely recognized that the
teach-learn-assess cycle in education cannot function
in the absence of quality assessment (Frederiksen and
Collins, 1989). Without quality assessment and feed-
back, the learning outcomes of any course could not
be judged in an adequate manner. Assessment nowa-
days has transformed from the usual assessment of
learning to a more advanced assessment for learn-
ing strategy. The end of course summative tests have
given way to formative assessments that happen dur-
ing the course and keep the learners engaged and im-
prove their overall learning. The field of education
has transformed in recent years as well, with a grow-
ing interest in learner-centered, open, and networked
learning models. These include Personal Learning
Environments (PLEs), Open Educational Resources
(OER) and Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs).
With these new learning models, the assessment car-
ried out in these environments has to adapt to the open
nature as well, in turn paving the way for Open As-
sessment (Chatti et al., 2014).
Open Assessment as defined by (Chatti et al.,
2014) is ”an all-encompassing term combining differ-
ent assessment methods for recognizing learning in
open and networked learning environments. In open
assessment, summative, formative, formal, informal,
peer, network, self-, and e-assessment converge to al-
low lifelong learners to gain recognition of their learn-
ing. It is an agile way of assessment where anyone,
any time, anywhere, can participate towards the as-
sessment goal. Open assessment is an ongoing pro-
cess across time, locations, and devices where every-
one can be assessor and assessee”.
The importance of assessment in the education cy-
cle is paramount and it holds true in the case of open
learning environments as well, but there are a num-
ber of issues associated with assessment. The most
obvious and critical issue in providing quality assess-
ment and feedback in these environments is scale, as
a large number of resources are required to provide
good quality feedback to such large number of learn-
ers.
Researchers have been working on ways to im-
prove the quality of education in these open learn-
ing environments by working on more scalable as-
sessment techniques like automated assessment, self-
assessment and e-portfolios, reflective networks and
peer assessment to name a few (Costello and Crane,
2013), (Suen, 2014). Automated assessment tech-
niques like online tests with multiple choice questions
that are machine scored are generally used as progress
checks and to give instant feedback to students. The
intent of these quizzes is to gauge the level of students
mastery of the concepts and contents presented in any
module (Suen, 2014). Despite the ease of implemen-
Wahid, U., Chatti, M., Anwar, U. and Schroeder, U.
A Multi-dimensional Peer Assessment System.
DOI: 10.5220/0006390006830694
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2017) - Volume 1, pages 683-694
ISBN: 978-989-758-239-4
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
683
tation, this technique is appropriate only for certain
types of courses. For courses where learners have to
demonstrate an ability to generate ideas or produce
a product, such as answer open ended questions this
method of assessment leaves a lot to be desired.
The more suited and widely applicable method of
assessment in open learning environments is to use
peer assessment and peer discussion forums to pro-
vide formative feedback to students (Suen, 2014).
Peer assessment offers a scalable and cost effective
way, where fellow learners are asked to evaluate stu-
dent assignments and provide feedback to their peers.
It also encourages the learners to take an active part
in the assessment process (O’Toole, 2013).
Although, peer assessment is the most viable as-
sessment method in open learning environments but
still there are a number of apprehensions about the
method itself from the learners and teachers alike.
Certain issues like validity, quality of feedback and
most importantly the lack of a general purpose peer
assessment tool cloud the use of this method on a
larger scale. The peer assessment tools available in
different learning platforms normally cater to a partic-
ular audience and can only be used in a certain context
(Wahid et al., 2016b). This lack of adaptability makes
it impossible to use any peer assessment tool in a wide
range of subject areas and reflects the need for a flexi-
ble and customizable solution which could be used in
every context.
In this paper, we introduce the core peer assess-
ment module in the Peer Assessment & Learning An-
alytics System (PALAS). The module provides a cus-
tomizable, flexible and multi-dimensional platform to
conduct peer assessment in any learning environment
(traditional and open learning environments alike).
The remainder of this paper is structured as fol-
lows: Section 2 introduces peer assessment and Sec-
tion 3 provides a comparison of the available peer as-
sessment tools in the state of the art. In sections 4 and
5 we discuss the conceptual framework and imple-
mentation details of the peer assessment component
in PALAS. Section 6 presents the evaluation results of
the system and finally, Section 6 gives a conclusion of
the main findings of this paper along with some future
work.
2 PEER ASSESSMENT
Peer assessment has a long standing history in tradi-
tional classroom instruction, where it has often been
used in class or group discussions, normally under
the supervision of the teacher and is augmented by
teacher assessment (Falchikov and Goldfinch, 2000),
(Gielen et al., 2011), (Topping, 2005). But recent
shift in the nature of assessments from the traditional
testing of knowledge to the culture of learning as-
sessments has changed the whole paradigm. This
new assessment culture thrives on students taking an
active part in the learning and assessment processes
(Planas Llad
´
o et al., 2014), hence the assessment
methods have to adapt as well to this new shift in
paradigm.
Peer assessment is the front runner in this new as-
sessment culture by involving and giving voice to stu-
dents in the assessment process. Peer assessment has
been used in a wide range of subject areas including
but not limited to natural sciences, business, medicine
and engineering (Luo et al., 2014).
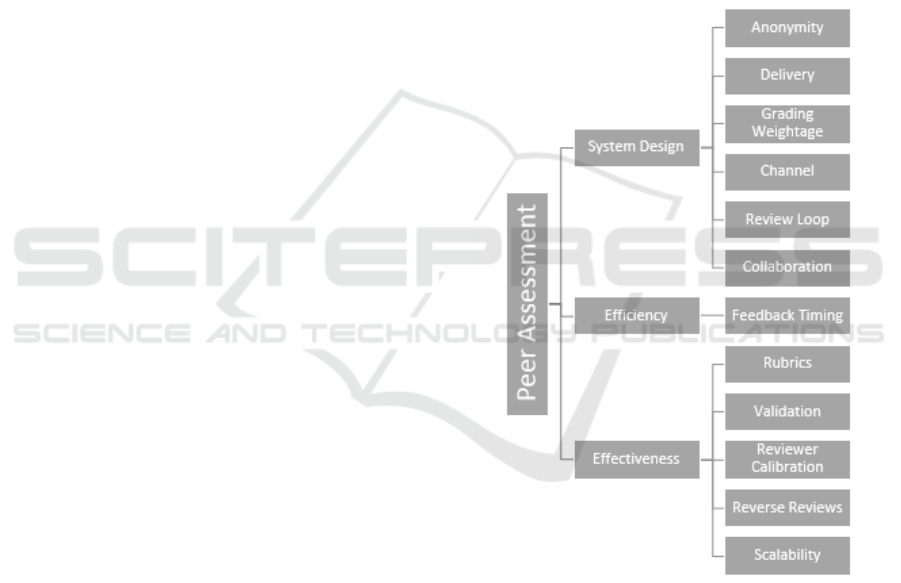
Figure 1: Peer Assessment Cognitive Map (adapted from
(Wahid et al., 2016b)).
A few systematic comparisons have been made
on the available peer assessment tools. The study in
(Luxton-Reilly, 2009) compares a number of online
tools for peer assessment and groups them together
based on certain features and criterion. A recent study
by (Wahid et al., 2016b) focuses on tools being used
in the open learning platforms (e.g. MOOCs) and pro-
vide a number of dimensions using cognitive mapping
for a more systematic comparison of the tools. The
study highlights three main classification dimensions,
LLL 2017 - Special Session on Lifelong Learning
684

namely system design, efficiency, and effectiveness.
These main categories are further sub-divided into 11
dimensions which are used to compare the peer as-
sessment tools available in open learning platforms.
The provided dimensions form a good basis for tool
comparison and at the same time highlight key re-
search areas in peer assessment. We have further ex-
tended the classification dimensions by adding Scal-
ability to the effectiveness category as well. Scala-
bility is an important aspect, and any effective peer
assessment tool should be able to provide scalable as-
sessment and feedback features. Figure 1 shows the
updated peer assessment classification dimensions.
2.1 Peer Assessment Dimensions
The systematic comparison made by (Wahid et al.,
2016b) provides us with a set of features/dimensions
which are vital to any modern day peer assessment
system. The identified dimensions are further ex-
plained below:
2.1.1 Anonymity
Anonymity in peer assessment refers to the level of
secrecy in the review process. There are three dif-
ferent levels of anonymity in peer reviews, namely,
single blind: one way knowledge, the reviewer knows
the original author of the submission but the author
has no idea of the assessor, double blind: complete
secrecy, both reviewer and author are unaware of each
other and finally no anonymity in which the identity
of both parties is known to each other. Anonymity is
an important feature to consider in peer assessment as
it allows the teachers to remove obvious bias (gender,
nationality, friendship etc.) from the system.
2.1.2 Delivery
Delivery mode in peer assessment refers to whether
the review is provided to the peers directly i.e. face
to face or indirectly via the system. Although, the
indirect method seems to be the logical choice but
in some blended learning environments the teachers
might want to introduce the direct feedback method
based on their course structure.
2.1.3 Grading Weightage
The purpose of this dimension is to find out whether
the reviews provided by peers actually count towards
the final grade of the reviewed student or not. It refers
to the weightage given by the teacher or system to the
reviews provided by the peers. If a grading weightage
is assigned, then the system calculates the final grade
of the submission using the assigned weights for the
teacher and peer reviews.
2.1.4 Channel
The channel in peer assessment refers to the number
of reviews provided by the peers. In a single chan-
nel (1 to 1) system, every submission is reviewed
by exactly one peer or peer group. Whereas, in a
multi-channel (m to n) setting the number of review-
ers varies and is normally grater than one. The prob-
lem with a multi-channel setting is that it puts addi-
tional burden on the students to review multiple works
from their peers increasing the time requirements.
2.1.5 Review Loop
The purpose of this feature is to improve the learning
outcome of the students by allowing them to submit
an initial draft of their submission and get feedback
from peers on their submission. The students can then
improve their submission based on the feedback from
peers and later submit an improved final version for
further reviews. The peer assessment system could
either have a double/multi loop functionality to sup-
port this intermediate feedback or only provide a sin-
gle loop feedback cycle with no possibility of an in-
termediate feedback.
2.1.6 Collaboration
The collaboration in peer assessment reflects the abil-
ity of the peer assessment tool to allow students to
form and work in small groups. The formation of stu-
dent groups promotes a healthy learning environment
by encouraging them to share ideas within the group,
promote team work and improve their interpersonal
skills.
2.1.7 Feedback Timing
This feature of peer assessment tools refers to the av-
erage time it takes for a student to get a review of
their submission, particularly in a multi-review loop
setting. The main focus is to decrease the feedback
time to a minimal level, as it gives the learners more
time to react and improve their final submission.
2.1.8 Rubrics
Rubrics are task specific questions, which the re-
viewer has to answer as part of their review allow-
ing the teachers to get fair and consistent feedback
for all course participants. The assessment rubrics are
an easy way to introduce transparency in the review
A Multi-dimensional Peer Assessment System
685

process by directing the students to look for certain
key aspects in the reviewed submission and provide
them with an evaluation guideline.
2.1.9 Validation
Validation of the reviews submitted by peers is a ma-
jor research area in peer assessment. It refers to the
steps taken by the peer assessment system to make
sure that the feedback provided by the peers is actu-
ally valid and of a certain value.
2.1.10 Reviewer Calibration
In this method, the reviewers are required to grade
some sample solutions that have been pre-graded by
the instructor to train them in the process of provid-
ing reviews. The reviewers are not allowed to review
the work of their peers, unless they achieve a certain
threshold in the review of the sample submission and
only then can they review the work of their peers. In
the end, the system takes into account the calibration
accuracy of the reviewer by assigning weightage to
each submitted review.
2.1.11 Reverse Reviews
Another interesting method to verify the effectiveness
of the reviews is to use the reverse review method.
Certain tools make use of this method to allow the
original authors of the reviewed submissions to rate
the reviews they received from their peers. The stu-
dents can specify, whether the review helped them in
improving their submission, or was of a certain qual-
ity, or helped them understand the topic clearly. This
review is then taken into consideration at the time of
calculation of the final grade, so the peers who pro-
vided better reviews have a chance to improve their
assignment score.
2.1.12 Scalability
Any modern day peer assessment system used in
open learning environments should provide methods
to scale the feedback process. The number of stu-
dents in open learning environments is usually large
and the feedback scalability is a must have feature
to reduce the time required by the teacher to provide
quality feedback to all course participants.
2.2 Peer Assessment Challenges
Peer assessment is a crowd sourcing technique which
not only lessens the teacher’s workload; it brings
many potential benefits to student learning as well, in-
cluding a sense of ownership and autonomy, increas-
ing the motivation for learning and high level cogni-
tive and discursive reasoning (Luo et al., 2014). But
despite these potential benefits, peer assessment still
isn’t the optimal choice for teachers and students. The
most glaring and obvious problem with peer assess-
ment is the quality and validity of the reviews pro-
vided by the peers. The issue at hand stems from the
fact that the performance of a novice is being judged
by other novices rather than an expert on the subject
matter (Falchikov and Goldfinch, 2000), (McGarr and
Clifford, 2013). Researchers have highlighted a num-
ber of other challenges for peer assessment, which
should be addressed by the peer assessment tools in
an effective way for improving the overall process.
The general list of challenges in peer assessment
includes transparency, credibility, accuracy, reliabil-
ity, validity, diversity, scalability, efficiency and flex-
ibility (Wahid et al., 2016a). Transparency refers to
the fact that the assessee is aware of how the re-
view process works and has confidence in it. The
credibility refers to the issue whether the reviewing
person has sufficient knowledge in the subject area
and is capable enough of providing credible feedback.
Accuracy is closely linked to credibility in a sense
that if the reviewer has a good mastery of the sub-
ject then his/her reviews would tend to be more accu-
rate. Reliability is the consistency of grades that dif-
ferent peers would assign to the same assessment, or
in other words as inter-rater reliability. Whereas, va-
lidity is calculated as a correlation coefficient between
peer and instructor grades, assuming that the instruc-
tor grade is considered a trustworthy benchmark (Vo-
gelsang and Ruppertz, 2015). Diversity refers to the
different educational backgrounds of the assessors.
Scalability is inherent to open learning environments
with a large number of participants. The efficiency in
peer assessment is related to feedback timing. Studies
have shown that the earlier the learners get feedback
to their work, the more time they have to improve the
final product. Reducing the time it takes to get feed-
back to a draft submission automatically allows for
a better final product. And last but not the least, the
flexibility challenge in peer assessment applies to the
peer assessment tools which are used to carry out the
process and whether they allow the teachers to adapt
the system to their own particular needs or not.
A good peer assessment tool, while providing the
features/dimensions explained earlier should also be
able to overcome most peer assessment challenges in
an effective way to help students and teachers in the
learning process. There are a number of peer assess-
ment tools available in different learning platforms
LLL 2017 - Special Session on Lifelong Learning
686

which are being used in traditional and open learning
environments alike. Despite the large number of tools
available for peer assessment in open learning envi-
ronments, the assessment method is not uniformly
adapted due to certain limitations in every tool. Most
of the tools are rigid in their design and offer certain
features in a fixed way and it is not possible to change
the system behaviour according to user needs. In this
paper, we present a new multi-dimensional peer as-
sessment system, PALAS, which could be easily con-
figured by the teachers for use in any context and sce-
nario.
3 STATE OF THE ART
The use of peer assessment in open learning environ-
ments is growing and this interest leads to an increase
in the number of peer assessment tools that are avail-
able in different learning environments. In this sec-
tion, we focus on some of the leading peer assessment
tools identified by (Wahid et al., 2016b) and their fea-
tures in a bit more detail.
Table 1 provides the results of the systematic com-
parison of peer assessment tools from another study
(Wahid et al., 2016b). The core peer assessment mod-
ule in PALAS is also added to the list to highlight the
major differences between PALAS and other systems.
The comparison from Table 1 shows that most
peer assessment tools follow a similar system design
pattern to offer different features in a similar man-
ner. Most peer assessment tools implement a Double
Blind setting for Anonymity, to eliminate obvious bias
from the system. There are some tools which also rely
on Single Blind method but they are very few in num-
ber and tools like Organic PA (Komarov and Gajos,
2014) and GRAASP Extension (Vozniuk et al., 2014)
do not have a mention of the feature at all. Deliv-
ery mode for all the tools is indirect, since they are
online systems and are generally used in open learn-
ing environments. However, an instructor could still
use them in blended learning environments and could
have in place a direct mode of delivery, which is be-
yond the scope of the assessed tools. For Grading
Weightage, there are two types of implementations
found in different tools. A number of systems offer
a fixed grading weightage which is incorporated in
the system design and cannot be altered during usage.
The examples of such systems include CTAS (Vo-
gelsang and Ruppertz, 2015), CPR (Walvoord et al.,
2008) and Peer Scholar (Joordens et al., 2009) among
others. This gives some importance to the reviews
from peers, as they influence the final grade of the
submission. But on the other hand, a few systems do
not offer this feature at all and use the teacher grade as
the final grade of the submission. A notable variation
is found in L
2
P Peer Reviews (Yousef et al., 2015)
which allows the teacher to set a variable percentage
for the grades from peers and do it on a task by task
basis.
All the peer assessment systems used in the study
offer a m to n mapping for the Channel feature, as it
can be used to mimic a 1 to 1 mapping as well. This
multiple review strategy in turn puts extra burden on
the students as each student has to review multiple
works from their peers. Peer Studio tries to create an
automated mapping based on an algorithmic scoring
of the submission to reduce the number of required
reviewers to some extent (Kulkarni et al., 2014). The
system predicts the student grade by using a machine
learning algorithm, which then estimates the confi-
dence value. This value is used to determine the re-
quired number of peer graders for that submission.
This automated process aims at putting manageable
load on peers by trying to reduce the number of peers
required for each submission.
The Review Loop dimension of system design is
an important feature for any peer assessment tool but
only a handful of tools offer more than one review
loop. Peer Studio (Kulkarni et al., 2015) and Peer
Grader (Gehringer, 2001) are unique in this regard as
they offer a multiple loop strategy instead of a double
loop which means the students get multiple feedbacks
and chances to improve their work. Both tools han-
dle it in different ways, Peer Grader opens up a line
of communication between the author and reviewer
so they can communicate until the final submission
deadline. Whereas, the Peer Studio tool relies on a
give and take method to provide multiple reviews.
The idea behind it is that a student who wants an inter-
mediate review has to review two works from his/her
peers to get a review of their own work.
A major area where almost all the peer assess-
ment tools are lagging behind is the Collaboration
dimension. The tools rely heavily on the learning
management system features like discussion forums
and wikis for enabling collaboration and idea sharing
between the students. There is no actual implemen-
tation in the tools for the students to work together
and submit their solutions in groups. The only tools
that allow such collaboration are Web-PA (Willmot
and Pond, 2012), Web-SPA (Sung et al., 2005), L
2
P
Peer Reviews (Yousef et al., 2015) and Team Mates
(Goh et al., 2011).
The area, where all the tools are lagging behind
is the Rapid Feedback. Only Peer Studio (Kulkarni
et al., 2015) offers this feature by making use of the
information of the currently logged in users and re-
A Multi-dimensional Peer Assessment System
687
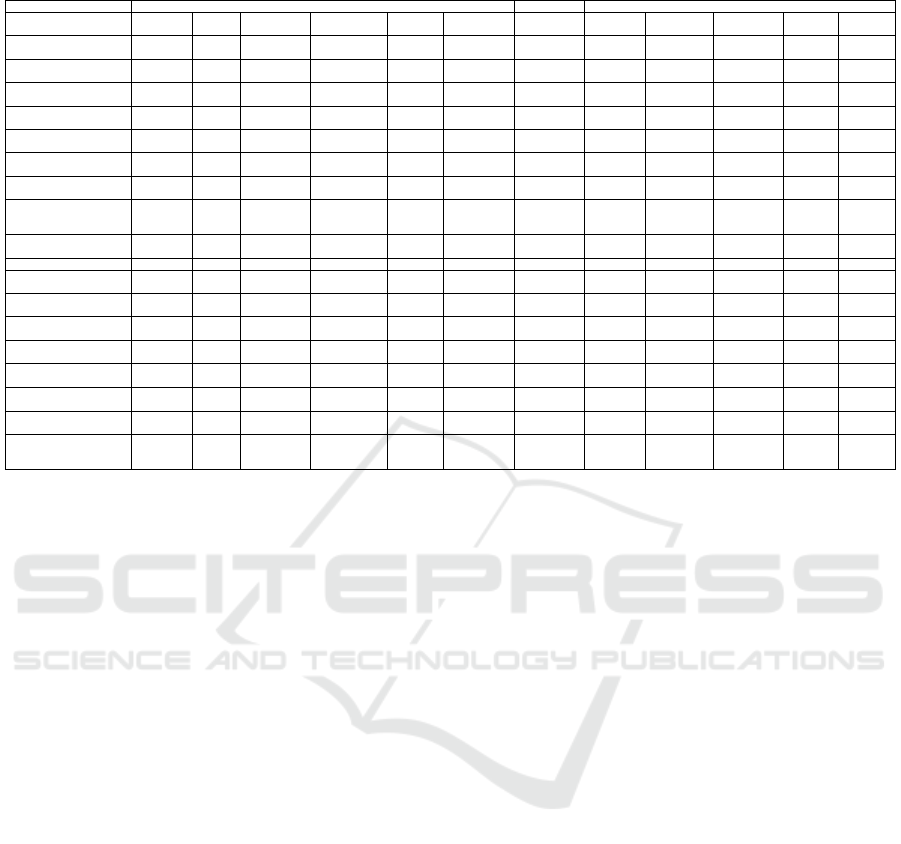
Table 1: A systematic comparison of peer assessment tools (adapted from (Wahid et al., 2016b)).
System Design Efficiency Effectiveness
Tools Anonymity Delivery Grading
Weightage
Channel Review
Loop
Collaboration Time/Rapid
Feedback
Rubrics Validation Reviewer
Calibration
Reverse
Reviews
Scalability
Peer Studio (Kulkarni
et al., 2015)
Double Indirect Yes Multiple Multiple No Yes Yes Yes No No Yes
CTAS (Vogelsang and
Ruppertz, 2015)
Double Indirect Yes Multiple Single No No Yes Yes No No No
ITPA (Lehmann and
Leimeister, 2015)
Yes Indirect No Multiple Single No No Yes Not measured No No No
Organic PA (Komarov and
Gajos, 2014)
None Indirect No Multiple Single No No No Yes No No No
EduPCR4 (Wang et al.,
2014)
Double Indirect Yes Multiple Double No No Yes Not measured No Yes No
GRAASP Extension
(Vozniuk et al., 2014)
None Indirect Yes Multiple Single No No Yes Yes No No No
Web-PA (Willmot and
Pond, 2012)
Yes Indirect Yes Multiple Single Yes No Yes Not measured No No No
SWORD/Peerceptiv
(Kaufman and Schunn,
2011)
Double Indirect Yes Multiple Double Yes No Yes Yes No No No
CPR (Walvoord et al.,
2008)
Double Indirect Yes Multiple Single No No Yes Yes Yes No No
Arop
¨
a (Hamer et al., 2007) Yes Indirect Yes Multiple Double No No Yes Yes No Yes No
Web-SPA (Sung et al.,
2005)
Yes Indirect No Multiple Double Yes No Yes Yes No No No
Peer Scholar (Joordens
et al., 2009)
Double Indirect Yes Multiple Single No No Yes Yes No No No
Study Sync (McCrea and
Weil, 2011)
Single Indirect No Multiple Single No No Yes Yes No No No
Peer Grader (Gehringer,
2001)
Double Indirect Yes Multiple Double No No No Yes No Yes No
L
2
P Peer Reviews (Yousef
et al., 2015)
Double Indirect Yes Multiple Single Yes No Yes Yes No No No
Team Mates (Goh et al.,
2011)
Double Indirect No Multiple Single Yes No Yes Not measured No No No
TurnItIn (Draaijer and
van Boxel, 2006)
Single Indirect No Multiple Single No No Yes Yes No No No
PALAS Single/
Double/
None
Indirect Configurable Single/ Multiple Single/
Multiple
No No Yes(Shared) No No No No
quiring the author to review others work to get feed-
back on their own submission. All the reviewed sys-
tems provide an implementation for Rubrics in one
way or the other. Most of them make use of shared
rubric libraries to access the rubrics across different
tasks inside a course.
Validation of the reviews is an important feature in
peer assessment as it ensures that students get a qual-
ity feedback from their peers. Most of the peer as-
sessment systems tend to implement a multiple chan-
nel review system and in the end measure the valida-
tion of reviews to a submission by simply calculating
the agreement rate between different reviewers (Kauf-
man and Schunn, 2011). Despite it being a minimal-
istic approach, it still provides a good starting point
for other measures to be carried out, to judge the va-
lidity of reviews in detail. Reverse Reviews are also
an important feature of peer assessment tools, which
could also help in ensuring the validity of reviews.
Scalability is an inherent trait in the peer assess-
ment tools used in open learning environments, but
oddly there are no actual implementations to scale
the feedback process in the tools. Only Peer Studio
(Kulkarni et al., 2014) offers a primitive solution to
scale short answer grading by combining algorithmic
scoring with peer assessment.
The rigidity of system design in all the available
tools gives rise to the need for a flexible peer assess-
ment system, which can be easily configured by the
teachers according to the need of their context for use
in their learning environments. The core peer assess-
ment module in PALAS, handles the system design
dimensions in a flexible way as shown in Table 1.
The module gives control to the teacher to choose be-
tween the available variations of each dimension set-
tings, e.g., the teacher could chose between the sin-
gle, double or no anonymity setting to hide/show the
identities of reviewer and author in different ways de-
pending upon their requirements. Similarly, the other
dimensions like grading weightage, channel, review
loop and rubrics are designed in a way that allows the
teacher to customize the review process according to
their own preferences. In the next sections, we discuss
the system design and implementation of the peer as-
sessment module in PALAS, explaining how it tries to
overcome the shortcomings of the existing systems.
4 CONCEPTUAL APPROACH
In this section, we focus on the basic application
design for the proposed peer assessment module in
PALAS. The system consists of several smaller com-
ponents, which are shown in Figure 2.
The interaction between the main components
of the peer assessment module are depicted in Fig-
ure 2, namely: Task Manager, Solution Management,
Review Management and Review Settings. Task
Management and Review Settings(/Dimensions) are
closely coupled together as they form the base for
LLL 2017 - Special Session on Lifelong Learning
688

Figure 2: Peer assessment system: Conceptual Model.
defining the assignment task for students and config-
uring the review related settings from a single place.
The solution management handles the solution sub-
mission from the students based on the settings de-
fined in task definition by the teacher. And lastly, the
final component, Review Management handles the
peer and teacher reviews. This component is closely
linked to review settings to enforce task based peer
review settings.
The basic workflow of peer assessment module in
PALAS is shown in Figure 3. The application fol-
lows a simple flow starting from task definition by
the teacher and configuring the review related settings
(could be added later, as well). Once the task is de-
fined, it is published to the students and they are al-
lowed to submit their solutions. After the solution
submission phase is over, the teacher can assign the
submitted solutions to random peers and start the re-
view phase. The review phase could lead back to so-
lution submission in case of multiple review loop set-
tings, otherwise it is followed by the teacher review
and publishing of results.
The multi-dimensional aspect of the peer assess-
ment module is highlighted in Figure 3, which lists
the various dimensions implemented in the system.
The core peer assessment module implements most of
the system design dimensions highlighted in Figure 1,
by allowing the teacher to customize them on a task
by task basis introducing flexibility and adaptability
to the system.
Figure 3: Peer assessment workflow in PALAS.
5 IMPLEMENTATION
The peer assessment module in PALAS is a Web
based application developed using open source tech-
nologies in the MEAN Stack (Mongo DB, Express
JS, Angular JS, Node.JS), along with some other
javascript libraries. The use of MEAN Stack offers
a number of advantages including scalability, security
and customization among others. The application fol-
lows a Model View View Model (MVVM) architec-
ture, which is based on the widely known Model View
Controller (MVC) design pattern (Osmani, 2012).
It is developed using the Test-Driven Development
(TDD) approach (Astels, 2003), which allows the pro-
grammers to divide the system in smaller compo-
nents. In our system, the different components have
already been defined as shown in Figure 2. The com-
ponents were then sub-divided into even smaller tests,
to facilitate the TDD approach.
In the next sections, we discuss the implementa-
tion details of the core peer assessment module in
PALAS using the system workflow, as shown in Fig-
ure 3. It also covers the features/dimensions of the
system in detail with their implications on the system
workflow.
5.1 Task Definition
Task definition refers to the basic assignment cre-
ation where a teacher can define simple attributes like
name, description, publish and due dates along with
uploading assignment documents and other resources.
The teacher could define these settings using the basic
tab in the ”New Peer Review” form as shown in Fig-
ure 4. Once the basic task settings have been defined,
the system automatically takes care of publishing the
task to students at the publish date and enforces that
A Multi-dimensional Peer Assessment System
689

no solutions are submitted after the deadline.
Figure 4: Task Definition.
5.2 Review Settings
Once the basic assignment task has been defined, the
teacher could move forward to define task specific re-
view settings for the peer assessment process using
the ”Review Settings” tab in the ”New Peer Review”
form. This form allows the teachers to configure the
peer assessment process based on the dimensions pre-
sented in Figure 1. The system successfully imple-
ments the following dimensions:
Figure 5: Review Settings.
5.2.1 Anonymity
The teacher can select between three available
anonymity settings, namely: single, double and none
as shown in Figure 5. The selection of any of these
settings has its effects on the way the submissions and
reviews are shown to the reviewers and authors. For
example, if we select single blind setting then the re-
viewer can also see the identity of the original author
of the submission he/she is reviewing. Similarly, for
anonymity setting ”none”, the reviewer can see the
author’s identity while reviewing and also the author
gets to see the reviewer’s identity while looking at the
provided review. The double blind setting enforces
secrecy of both the reviewer and author identities.
5.2.2 Delivery
The peer assessment component in PALAS, imple-
ments the indirect delivery of reviews as the system
acts as an intermediary between the original authors
of the submission and the reviewers. The reviewers
add their review to the system which is made avail-
able to the authors, hence, there is no direct interac-
tion between the two parties.
5.2.3 Grading Weightage
There is no fixed weightage assigned to the peer re-
views, instead the teacher can choose any percentage
ranging from 0 to 100. A value of ”0” means, no
weightage is given to peer reviews and the final grade
of the submission is the one given by the teacher. For
any other percentage value, the final grade is calcu-
lated by giving the said weightage to the peer review
and (100 - percentage value) to the teacher review. In
case of multiple reviews from peers, an average grade
is calculated from the peer grades which is then used
to calculate the final grade.
5.2.4 Channel
The review settings page offers two options for set-
ting the review channel/mapping. These options are:
1-to-1 and M-to-N. These settings have a direct im-
pact on the assign reviews functionality, as in case
of 1-to-1 mapping, the assign review page hides the
submission and reviewer who have already been as-
signed and only shows the remaining submissions and
reviewers in the respective columns for the teacher
to create more mappings. Whereas, in the case of
M-to-N mapping, the submissions and reviewers re-
main available for further assignments and the teacher
could assign as many submissions as he wants to a
particular reviewer for a review or vice versa.
5.2.5 Review Loop
The system offers two variations of the review loop to
the teachers. One is the single review loop, in which
case the teacher has to set two additional dates for the
start and end of review phase. In this scenario, the
review assignments are made available to students at
LLL 2017 - Special Session on Lifelong Learning
690

the start of the review phase and they can add their re-
views for the submission(s) until the review end date.
The reviews are then made available to the teachers
and once they add their own review of the submis-
sion, both teacher and peer reviews are shown to the
students.
Secondly, the teacher could also select the option
of a double review loop. This setting requires two sets
of additional dates from the teacher namely the review
start and end dates for both review cycles, as well as
an additional deadline for students to submit their im-
proved work again after the first review loop. The
first loop works the same as the single review loop,
but the reviews from peers are made available to au-
thors without requiring a review from the teacher. The
authors can see the reviews from their peers and try to
improve their submission based on the provided feed-
back before the second submission deadline. Once
the second deadline has passed, the normal review cy-
cle resumes with reviews from peers and the teacher
on the final submission from the students.
5.2.6 Rubrics
Review rubrics are a very useful construct available to
teachers to bring transparency to the review process,
and to guide the students in the review process. The
review settings page allows the teacher to define new
rubrics or select from existing ones, which are shown
to the students at the time of creating reviews. The
students are required to answer the rubric questions,
to complete the review. The review rubrics are stored
in a shared library for the course room and could be
re-used across multiple tasks.
Apart from the above mentioned dimensions, the
future versions of the peer assessment system intend
to add further dimensions in a similar configurable
way. The teachers can configure the available dimen-
sions in the system on task level, allowing for distinct
settings per assignment task.
5.3 Solution Submission
After the assignment has been published, the students
are allowed to submit their solutions for the given
task. The solution management component allows the
students to work on their solutions until the deadline
proposed by the teacher. The students could add so-
lution files and additional resources along with their
comments using the Add/Edit Solution form. The
system carries a time based check on all solution sub-
missions to enforce the submission deadline.
5.4 Assign Reviews
Once the solution submission phase is over, the teach-
ers could assign the submitted solutions to different
peers for review by selecting the solution and re-
viewer from a list as shown in Figure 6. The assign-
ment of solutions and reviewers varies based on the
channel settings for the peer review. If the review
channel is 1 to 1 then the solution and reviewer are
removed from the available lists automatically as they
can no longer take part in any other review assign-
ment. In case of m to n channel, the solution and
reviewer remain available for further review assign-
ments.
Figure 6: Assign reviews.
An automatic assignment mechanism is planned
for the next version of the PALAS, which would
lessen the teacher workload. The review assignments
are shown to the students as soon as the review start
date is passed, which is configured in the review set-
tings.
5.5 Review Phase
After the assignment phase, students are able to see
the solutions assigned to them and can submit their
reviews for the peer solution. The anonymity in the
review settings plays an important role here as the so-
lutions and reviews are anonymized according to the
preference of the teacher. The teacher could allow re-
viewers and authors to both see each other’s names or
he/she could enforce a double blind mechanism where
no one is aware of each other’s identity to minimize
bias in the review process.
The review submission form shows the submitted
solution on the top and the students could add their
review in the bottom part of the page as shown in Fig-
ure 7. The students are required to answer the rubric
questions added by the teacher via review settings and
could additionally add their own comments and some
files to support their review.
In a multi-loop scenario, the reviews are made
available to the peers after the completion of first re-
view phase. The students could then work on their
A Multi-dimensional Peer Assessment System
691
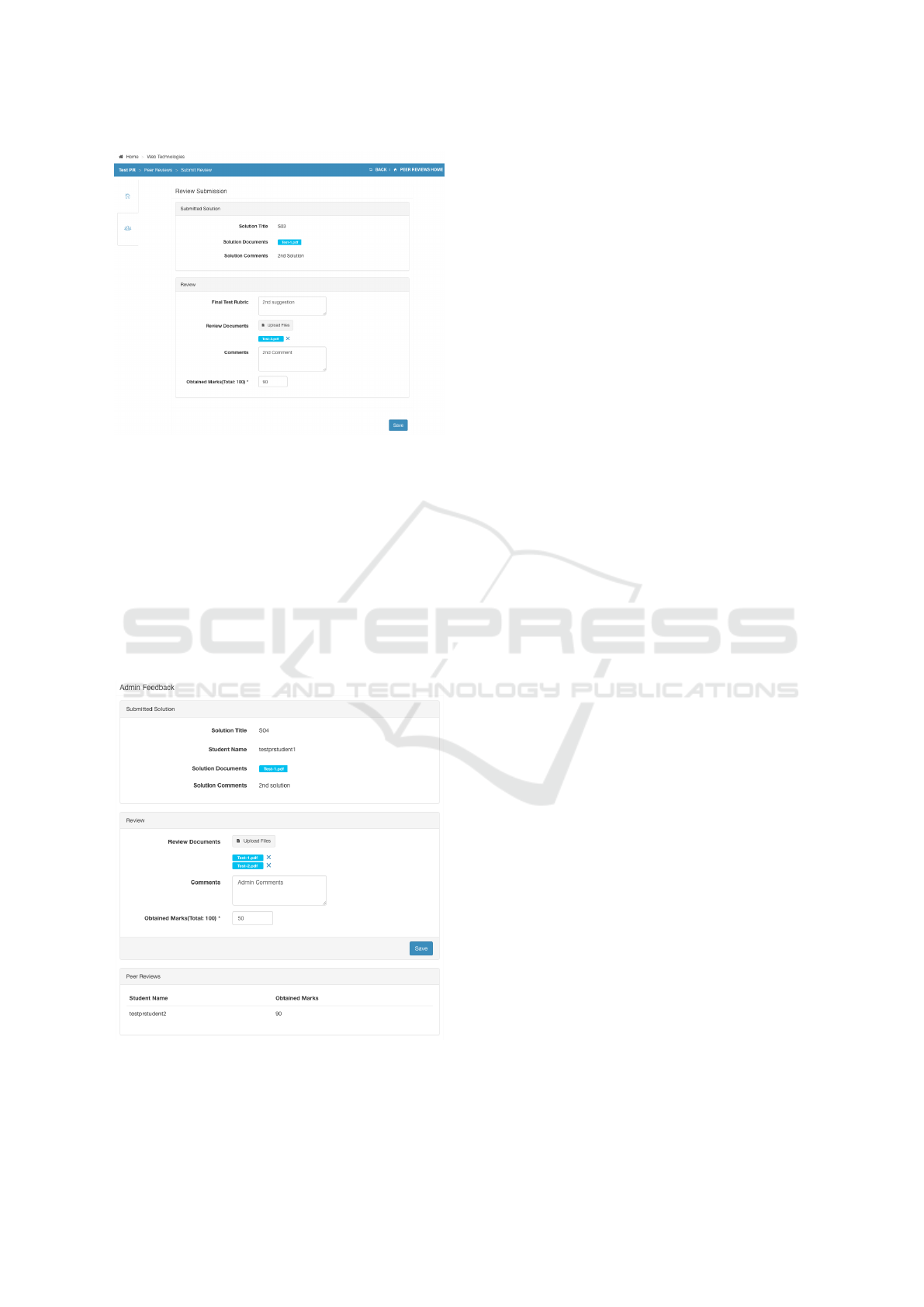
Figure 7: Submit peer reviews.
solutions again, incorporating the ideas from the in-
termediate reviews. The solution management mod-
ule allows the students to work on their solutions until
the second submission deadline defined in the review
settings. Once the deadline is over, the second re-
view phase starts in which the teacher could add new
review assignments as well or just keep the old as-
signments and let the students review the peer sub-
missions again.
5.6 Teacher Assessment
Figure 8: Submit teacher reviews.
The peer review phase is followed by a review from
the teacher, where the teacher can see the original sub-
mission from the student and the reviews from the
peers in a single screen as shown in Figure 8. The
teacher has the option to add marks for the review
along with their comments and upload related files for
the review.
5.7 Publish Results
As soon as the teacher review phase is over, the stu-
dents are able to see the review for their submissions.
The final review sheet consists of the teacher review
and the reviews from the peers. The peer reviews for
multiple loops are categorized separately.
6 EVALUATION
We conducted a thorough evaluation of the new peer
assessment component in PALAS, with the aim of
evaluating the usability and effectiveness of the sys-
tem with respect to the provided dimensions.
6.1 Usability
Building a software system without actually evaluat-
ing usability of the system, carries a risk of the end
user not finding the tool user friendly or even worth
using. As a result, the implemented system becomes
less appealing to users and not a worthy competitor
to its adversaries. One way to quickly measure the
system usability is by using the system usability scale
(SUS). We choose to use SUS to measure the usabil-
ity of peer assessment component in PALAS because
even though it uses a simple scaling system, the re-
sults of SUS are able to cover three important aspects
that must be defined relative to the context of system
usage (Brooke, 2013):
• Effectiveness (determine if people can complete
the tasks and achieve goals)
• Efficiency (the extent to which they expend re-
sources in achieving their goals)
• Satisfaction (satisfaction of user in achieving
those goals)
The SUS assessment score for peer assessment
component in PALAS is 78.3, which according to
SUS guidelines is a relatively good score. The SUS
guidelines state that any score above 68 considered as
above average, hence, the implemented system does
well in achieving its intended goals.
Despite a good usability score, there were a few
common issues identified by multiple respondents of
the survey. The main issue was the lack of an ad-
equate help regarding the implemented dimensions.
LLL 2017 - Special Session on Lifelong Learning
692

Some ideas were confusing to respondents, e.g., users
were unclear of the meaning of ”Review Channel”
and what implications this setting will have on the re-
view process. Another common request was to pre-fill
the date fields in review settings as there are a lot of
date fields and the users suggested to fill them with
suitable dates in the future.
6.2 Effectiveness of Dimensions
The respondents were asked to indicate whether the
peer assessment component allows them to flexibly
configure the implemented dimensions. As can be
seen from Table 2, the overall response to the eval-
uation items 1-7 was very positive with mean val-
ues ranging in strongly agree region with a minimum
value of 4.25 with acceptable standard deviation val-
ues.
Table 2: Effectiveness of Dimensions.
Dimension No. Evaluation Items M SD
Anonymity 1 By selecting anonymity while creating the
assignment, I am able to hide students
identity in the process.
4.37 0.91
Grading Weightage 2 While creating the assignment, I am able
to add peer grading weightage which will
then contribute to the final grade.
4.25 0.88
Channel 3 While creating the assignment, I am able to
assign one assignment to single or multiple
reviewers.
4.5 0.75
Review Loop
4 I am able to create a multi-review loop set-
ting for my assignment task.
4.87 0.35
5 The multiple reviews from peers are easily
available at evaluation/feedback time.
4.75 0.46
Rubrics
6 I am able to configure rubrics for my
course room.
4.5 0.75
7 While creating the assignment, I am able
to select rubrics for my assignment.
4.25 1.16
1. Strongly disagree ... 5. Strongly agree
Table 2 clearly indicates the fact that the peer as-
sessment component in PALAS implements the ad-
vertised features/dimensions in an efficient and effec-
tive way. This leads to teachers having greater control
over the peer assessment process, as they can easily
configure the review settings on a task by task basis
allowing the tool to be used across different domains
and contexts.
7 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
Peer assessment has established itself as a rich and
powerful assessment method in technology-enhanced
learning (TEL). This paper presents the conceptual
framework and implementation details of a core peer
assessment module in Peer Assessment & Learning
Analytics System (PALAS). The module presents a
flexible, customizable and multi-dimensional peer as-
sessment module which allows the teachers to tai-
lor fit the peer assessment process to their own
needs. The system implements a number of dimen-
sions including anonymity, delivery, grading weigh-
tage, channel, review loop and rubrics. The initial
evaluation results show promising results in terms of
system usability and flexibility of customizing the re-
view process.
The proposed peer assessment module in PALAS
also successfully overcomes a number of peer assess-
ment challenges. The module handles transparency
and diversity by making use of assessment rubrics
which allow the students to take an inside look at the
assessment process and brings uniformity to peer as-
sessments. The system also handles the credibility
challenge to some extent by making use of anonymity
settings to remove obvious bias from the review pro-
cess but more measures have to be taken to fully over-
come this challenge. And last but not the least, the
peer assessment module in PALAS tackles the chal-
lenge of flexibility in peer assessment by introduc-
ing the customizable peer assessment properties to the
teaching staff to adapt the peer review process to their
own liking.
The later versions of the system will provide a
customizable implementation for further dimensions,
namely: collaboration, efficient feedback and reverse
reviews. The other dimensions like validity, reviewer
calibration and scalability will be achieved by inves-
tigating and using learning analytics techniques. The
learning analytics techniques like classification, text
mining, machine learning, prediction, dashboards,
and visualization will be used to enhance PALAS and
improve user experience.
REFERENCES
Astels, D. (2003). Test driven development: A practical
guide. Prentice Hall Professional Technical Refer-
ence.
Brooke, J. (2013). Sus: a retrospective. Journal of usability
studies, 8(2):29–40.
Chatti, M. A., Lukarov, V., Th
¨
us, H., Muslim, A., Yousef,
A. M., Wahid, U., Greven, C., Chakrabarti, A., and
Schroeder, U. (2014). Learning analytics: Challenges
and future research directions. eleed, 10(1).
Costello, J. and Crane, D. (2013). Technologies for learner-
centered feedback. Open Praxis, 5(3):217–225.
Draaijer, S. and van Boxel, P. (2006). Summative peer as-
sessment using ’turnitin’ and a large cohort of stu-
dents: A case study.
Falchikov, N. and Goldfinch, J. (2000). Student peer as-
sessment in higher education: A meta-analysis com-
paring peer and teacher marks. Review of educational
research, 70(3):287–322.
Frederiksen, J. R. and Collins, A. (1989). A systems ap-
A Multi-dimensional Peer Assessment System
693

proach to educational testing. Educational researcher,
18(9):27–32.
Gehringer, E. F. (2001). Electronic peer review and peer
grading in computer-science courses. ACM SIGCSE
Bulletin, 33(1):139–143.
Gielen, S., Dochy, F., Onghena, P., Struyven, K., and
Smeets, S. (2011). Goals of peer assessment and their
associated quality concepts. Studies in Higher Educa-
tion, 36(6):719–735.
Goh, G., Lai, X., and Rajapakse, D. C. (2011). Teammates:
A cloud-based peer evaluation tool for student team
projects.
Hamer, J., Kell, C., and Spence, F. (2007). Peer assess-
ment using arop
¨
a. In Proceedings of the ninth Aus-
tralasian conference on Computing education-Volume
66, pages 43–54. Australian Computer Society, Inc.
Joordens, S., Desa, S., and Par
´
e, D. (2009). The pedagogical
anatomy of peer-assessment: Dissecting a peerscholar
assignment. Journal of Systemics, Cybernetics & In-
formatics, 7(5).
Kaufman, J. H. and Schunn, C. D. (2011). Students percep-
tions about peer assessment for writing: their origin
and impact on revision work. Instructional Science,
39(3):387–406.
Komarov, S. and Gajos, K. Z. (2014). Organic peer assess-
ment. In Proceedings of the CHI 2014 Learning Inno-
vation at Scale workshop.
Kulkarni, C., Bernstein, M. S., and Klemmer, S. (2015).
Peerstudio: Rapid peer feedback emphasizes revision
and improves performance. In Proceedings from The
Second (2015) ACM Conference on Learning@ Scale,
pages 75–84.
Kulkarni, C. E., Socher, R., Bernstein, M. S., and Klem-
mer, S. R. (2014). Scaling short-answer grading by
combining peer assessment with algorithmic scoring.
In Proceedings of the first ACM conference on Learn-
ing@ scale conference, pages 99–108. ACM.
Lehmann, K. and Leimeister, J. M. (2015). Theory-driven
design of an it-based peer assessment to assess high
cognitive levels of educational objectives in large-
scale learning services. In 23rd European Conference
on Information Systems (ECIS 2015), Mnster, Ger-
many.
Luo, H., Robinson, A. C., and Park, J.-Y. (2014). Peer grad-
ing in a mooc: Reliability, validity, and perceived ef-
fects. Online Learning: Official Journal of the Online
Learning Consortium, 18(2).
Luxton-Reilly, A. (2009). A systematic review of tools that
support peer assessment. Computer Science Educa-
tion, 19(4):209–232.
McCrea, B. and Weil, M. (2011). On cloud nine: Cloud-
based tools are giving k-12 collaboration efforts a
boost. THE Journal (Technological Horizons In Edu-
cation), 38(6):46.
McGarr, O. and Clifford, A. M. (2013). ’just enough to
make you take it seriously’: exploring students’ at-
titudes towards peer assessment. Higher education,
65(6):677–693.
Osmani, A. (2012). Learning JavaScript design patterns. ”
O’Reilly Media, Inc.”.
O’Toole, R. (2013). Pedagogical strategies and technolo-
gies for peer assessment in massively open online
courses (moocs).
Planas Llad
´
o, A., Soley, L. F., Fraguell Sansbell
´
o, R. M.,
Pujolras, G. A., Planella, J. P., Roura-Pascual, N.,
Su
˜
nol Mart
´
ınez, J. J., and Moreno, L. M. (2014). Stu-
dent perceptions of peer assessment: an interdisci-
plinary study. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Ed-
ucation, 39(5):592–610.
Suen, H. (2014). Peer assessment for massive open on-
line courses (moocs). The International Review of Re-
search in Open and Distributed Learning, 15(3).
Sung, Y.-T., Chang, K.-E., Chiou, S.-K., and Hou, H.-T.
(2005). The design and application of a web-based
self-and peer-assessment system. Computers & Edu-
cation, 45(2):187–202.
Topping, K. J. (2005). Trends in peer learning. Educational
psychology, 25(6):631–645.
Vogelsang, T. and Ruppertz, L. (2015). On the validity of
peer grading and a cloud teaching assistant system.
In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference
on Learning Analytics And Knowledge, pages 41–50.
ACM.
Vozniuk, A., Holzer, A., and Gillet, D. (2014). Peer assess-
ment based on ratings in a social media course. In Pro-
ceedings of the Fourth International Conference on
Learning Analytics And Knowledge, pages 133–137.
ACM.
Wahid, U., Chatti, M. A., and Schroeder, U. (2016a). Im-
proving Peer Assessment by using Learning Analyt-
ics. In GI Edition Proceedings Band 262 DeLFI
2016 Die 14. E-Learning Fachtagung Informatik
: 11.-14. September 2016 Potsdam / Ulrike Lucke,
Andreas Schwill, Raphael Zender ; Gesellschaft fr
Informatik (GI), Bonn, Herausgeber, pages 52–55.
14. e-Learning Fachtagung Informatik, Potsdam (Ger-
many), 11 Sep 2016 - 14 Sep 2016, Kllen.
Wahid, U., Chatti, M. A., and Schroeder, U. (2016b). A
systematic analysis of peer assessment in the mooc era
and future perspectives. In Proceedings of the Eighth
International Conference on Mobile, Hybrid, and On-
line Learning, elml 2016. IARIA XPS Press.
Walvoord, M. E., Hoefnagels, M. H., Gaffin, D. D., Chum-
chal, M. M., and Long, D. A. (2008). An analysis of
calibrated peer review (cpr) in a science lecture class-
room. Journal of College Science Teaching, 37(4):66.
Wang, Y., Liang, Y., Liu, L., and Liu, Y. (2014). A moti-
vation model of peer assessment in programming lan-
guage learning. CoRR, abs/1401.6113.
Willmot, P. and Pond, K. (2012). Multi-disciplinary peer-
mark moderation of group work. International Jour-
nal of Higher Education, 1(1):p2.
Yousef, A. M. F., Wahid, U., Chatti, M. A., Schroeder, U.,
and Wosnitza, M. (2015). The effect of peer assess-
ment rubrics on learners’ satisfaction and performance
within a blended mooc environment. In Proc. CSEDU
2015 conference, volume 2, pages 148–159.
LLL 2017 - Special Session on Lifelong Learning
694
