
A Practical Approach for the Auto-tuning of PD Controllers for Robotic
Manipulators using Particle Swarm Optimization
Ahmed Zidan, Jens Kotlarski and Tobias Ortmaier
Institute of Mechatronic Systems, Leibniz Universit
¨
at Hannover, 30167 Hanover, Germany
Keywords:
Robotic Manipulators, Particle Swarm Optimization, PD Control, Automatic Tuning.
Abstract:
An auto-tuning method of PD controllers for robotic manipulators is proposed. This method suggests a practi-
cal implementation of the particle swarm optimization technique in order to find optimal gain values achieving
the best tracking of a predefined position trajectory. For this purpose, The integral of the absolute error IAE is
used as a cost function for the optimization algorithm. The optimization is achieved by performing the desired
movement of the robot iteratively and evaluating the cost function for every iteration. Therefor, the necessary
constraints that guarantee a safe and stable movement of the robot are defined, which are: a maximum joint
torque constraint, a maximum position error constraint and an oscillation constraint. A constraint handling
approach is suggested for the optimization algorithm in order to adapt it to the problem in hand. Finally, the
efficiency of the proposed method is verified through a practical experiment on a real robot.
1 INTRODUCTION
PID control schemes provide simple and effective so-
lutions for most applications of control engineering.
However, the effectiveness of PID controllers is con-
ditioned by accurate tuning of the controller gains.
Robotic manipulators are highly non linear, highly
coupled, Multi-Input Multi-Output (MIMO) dynamic
systems. Using PID controller to control robotic ma-
nipulators can be a desired choice because of its sim-
plicity and effectiveness. However, the conventional
tuning methods of the gains depending on manual or
experimental approaches do not necessarily give sat-
isfactory results for such complex systems (Johnson
and Moradi, 2005).
The difficulty of using experimental and manual tun-
ing methods rises in the application fields, where the
assigned task of a robot might constantly change or
where a robot is of variable configuration or geome-
try (e. g. modular robots). In such cases, the need for
an auto-tuning method is urgent.
Recently, after the rapid increase of computing power,
auto-tuning methods based on optimization tech-
niques has been applied to non linear systems in or-
der to obtain an increased performance with respect
to predefined fitness functions.
In the field of robotic manipulators, a number of op-
timization methods (e. g. Genetic Algorithms (GA)
(Kim et al., 2012), Particle Swarm Optimization
(PSO) (Kapoor and Ohri, 2015)) has been used to
automatically tune the PID controllers of robot ma-
nipulators. Also, comparative studies between differ-
ent algorithms have been done in (Ouyang and Pano,
2015) and (Kwok and Sheng, 1994) in order to find
the most effective tuning method.
In (Ayala and dos Santos Coelho, 2012), more than
one single objective were considered within the con-
troller design. The proposed optimization method
was based on a multi-objective evolutionary algo-
rithm (MOEA), which aimed to tune the PID con-
troller gains by taking two conflicting objective func-
tions into consideration: minimization of position er-
rors and minimization of the control signal variation
(joint torques). In (Pierezan et al., 2014), a com-
parative study between different multi-objective opti-
mization techniques has been introduced and an im-
proved multi-objective particle swarm optimization
(I-MOPSO) has been proposed.
Artificial intelligence techniques like fuzzy logic and
neural networks have also been implemented to build
PID tuning systems for robotic manipulators. Exam-
ples for those systems can be found in (Bekit et al.,
1998), (Llama et al., 2001), and (Melek and Golden-
berg, 2003). Those systems gave the PID gains vari-
able values depending on the online measurements of
the robot joint positions and, therefore, turned the tra-
ditional controller into an adaptive controller.
Another approach has been proposed in (Nahapetian
34
Zidan, A., Kotlarski, J. and Ortmaier, T.
A Practical Approach for the Auto-tuning of PD Controllers for Robotic Manipulators using Particle Swarm Optimization.
DOI: 10.5220/0006419700340040
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO 2017) - Volume 2, pages 34-40
ISBN: Not Available
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

et al., 2009). Here a combination of both the GA tech-
nique and the fuzzy logic was used to form a hybrid
tuning method for a PID regulator.
Regarding the optimization methods, the known and
previously mentioned research focuses on analyzing
and testing the optimization algorithm itself. For this
purpose, the validation of the proposed methods has
only be tested on simple simulations of the robots.
However, from a practical point of view, more at-
tention needs to be diverted to the problem in hand,
i. e. the necessary constraints, which guarantee a safe
movement of the robot during the search for optimal
controller parameters. Otherwise, these optimization
algorithms will not be practicable.
2 ROBOT CONTROLLER
OPTIMIZATION
This work considers a robot manipulator controlled
by an independent PD controller for every joint of the
robot. The controller gains are usually tuned by using
manual tuning methods which are unable to obtain
critical damping behavior (Craig, 2005) and , there-
fore, settle for an overdamped one. Recently, it be-
came possible to use heuristic optimization methods
to solve the practical problems of complicated mecha-
tronics systems such as robotic manipulators. The
principle of these optimization methods is based on
defining a search algorithm aiming at finding the op-
timal solution of the problem after a number of itera-
tions. To do an auto-tuning of PD controllers using an
optimization method, it is required to define the opti-
mization problem and its parameters. In the consid-
ered problem, it is desired to fined the control param-
eters that lead to the best trajectory tracking accuracy
of the robot. The optimization parameters are the PD
gains K
p
and K
d
. The cost function is the integral of
the absolute error IAE:
IAE =
Z
T
0
|e(t)|dt =
Z
T
0
|(q
d
(t) − q(t))|dt . (1)
the aim of this work is to produce a practical
application of an optimization method for a robotic
manipulator, i. e. the evaluation of the cost function
will be depending on a real movement of the robot
along the desired trajectory. Therefore, it is inevitable
to define necessary constraints that guarantee a safe
and stable movement of the robot while searching for
the optimal gain values.
2.1 The Optimization Problem
Constraints
Usually by the tuning procedure of the controller’s
gains in robotic manipulators, one pays attention to
three possible dangerous situations. The gains should
not be too high and result in high torques from the
actuators, they should also be high enough to make
the tracking error lower than a maximum limit, and
finally, one should be careful not to excite high oscil-
lations by the chosen gains. These oscillations occur
mostly as a result of the potential flexibilities in the
joints and/or the links of the robot.
The proposed approach in this work considers these
same conditions without assuming any knowledge of
the robot dynamics. That is why the problem will be
addressed only from a practical viewpoint by combin-
ing the evaluation of the cost function with an obser-
vation system, which will stop the movement imme-
diately if one of the constraints is violated and inform
the optimization algorithm about the occurred situa-
tion. After that, the optimization algorithm must gen-
erate new parameter values based on these informa-
tion.
Detecting the violations of the error and the torque
constraints can be done simply by comparing the ab-
solute values of the positions and the motor torques
to the maximum limits e
max
and τ
max
respectively. A
bigger challenge by choosing the controller parame-
ters, however, is to detect any excited oscillations in
the robot movement. This can not be done analyti-
cally because no knowledge of the robot dynamics is
assumed. Therefore, the most suitable option here is
to do an on-line detection of the oscillations in real
time. It is important to do the task on-line so the
movement can be stopped as soon as the oscillations
are detected in order to prevent any unsafe movement
of the robot. A simple -but effective- way to detect os-
cillations was suggested in (H
¨
agglund, 1995), where
the integral of the absolute error IAE between suc-
cessive zero-crossings of the error signal was calcu-
lated. This value can distinguish between oscillations
and random signals taking into consideration the fact
that an oscillating signal will have between the zero-
crossings relatively larger IAE values and longer time
periods in comparison to random signal. As a thresh-
old, the IAE of a sinusoidal signal was used, which
has an amplitude equals 1% of the control range and a
frequency equals the ultimate frequency of the closed
loop.
Another approach was introduced in (Forsman and
Stattin, 1999), which also was capable of detect-
ing oscillations on-line in the time domain. In this
method, an index was defined to estimate the similar-
A Practical Approach for the Auto-tuning of PD Controllers for Robotic Manipulators using Particle Swarm Optimization
35

Figure 1: The Oscillation Detection Method from (Forsman
and Stattin, 1999).
ity between every two successive zero-crossing IAEs
of the error signal. However, This method handled the
positive error IAEs and the negative error IAEs sepa-
rately. Accordingly, the similarity was examined be-
tween every tow successive areas which had the same
sign (positive or negative). This separation enabled
the defined criterion to detect asymmetric oscillations.
The proposed index was defined as follows:
h
A
(N
zc
) = #
i <
N
zc
2
;α <
A
i+1
A
i
<
1
α
∧ γ <
δ
i+1
δ
i
<
1
γ
(2)
h
B
(N
zc
) = #
i <
N
zc
2
;α <
B
i+1
B
i
<
1
α
∧ γ <
ε
i+1
ε
i
<
1
γ
(3)
h(N
zc
) =
h
A
(N
zc
) + h
B
(N
zc
)
N
zc
(4)
where #S denotes the number of elements in the
set S. A
i
is the IAE of the positive area i of the error
signal, B
i
is the IAE of the negative area i of the error
signal. δ
i
and ε
i
are the time durations of the posi-
tive and the negative areas i respectively. N
zc
is the
number of the considered successive zero-crossings.
0 < α < 1 and 0 < γ < 1 are tuning parameters define
the degree of similarity. It was suggested in (Fors-
man and Stattin, 1999) to chose α = 0.5 − 0.7 and
γ = 0.7 − 0.8.
In this work, the two previously mentioned in-
dexes will be combined. i. e. both the similarity and
the maximum area of the zero-crossing regions will
be considered to detect oscillation.
This is done simply by adding another condition to the
calculation of the index h of the second method where
the values of h
A
and h
B
increases only if A and B are
bigger than maximum limits A
max
and B
max
respec-
tively. This modification on the second method will
increase its robustness against low amplitude noises,
which might be detected as potential oscillations. The
maximum limits are defined as follows:
A
max
,B
max
=
Z
∆t
zc
0
0.01e
max
sin(
πt
∆t
zc
)dt =
0.02∆t
zc
e
max
π
.
(5)
Figure 2: The Proposed Oscillation Detection Method.
With ∆t
zc
being the time between the two corre-
sponding zero-crossings and e
max
is the previously de-
fined limit of the position error.
Based on the foregoing, the modified index for os-
cillations detection becomes:
h
A
(N
zc
) =#
n
i <
N
zc
2
;A
i
< A
i,max
∧ α <
A
i+1
A
i
<
1
α
∧ γ <
δ
i+1
δ
i
<
1
γ
o
(6)
h
B
(N
zc
) =#
n
i <
N
zc
2
;B
i
< B
i,max
∧ α <
B
i+1
B
i
<
1
α
∧ γ <
ε
i+1
ε
i
<
1
γ
o
(7)
h(N
zc
) =
h
A
(N
zc
) + h
B
(N
zc
)
N
zc
(8)
Because the used controller here is only a PD con-
troller and no integral gain is applied, it is not guaran-
teed that the error signal will oscillate around the zero
value. Therefore, instead of using the error signal, it
is chosen to use the difference between the error sig-
nal and its mean value e(t) − mean(e(t)), which will
rescale the oscillating signal around the zero value.
Finally, the proposed procedure to detect oscillations
is achieved by the following steps:
1. After the beginning of the robot movement, record
the values of the position error through a long
enough period ∆T . A reasonable value of ∆T is
0.1T
tot
− 0.2T
tot
, where T
tot
is the total duration
of the robot movement.
2. Calculate the function e
zc
(t) = e(t) − mean(e(t))
along the period ∆T .
3. Determine and count the zero-crossing points, and
calculate the values A, B, δ, ε between these
points.
4. For every N
zc
successive zero-crossings, calculate
h
A
, h
B
and h.
ICINCO 2017 - 14th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
36

5. If h > h
max
, oscillations exist and the movement
must be stopped immediately. Otherwise, record
the values of the position error for the next period
∆T and repeat the previous steps until reaching
the end position of the robot.
It was suggested in (Forsman and Stattin, 1999) to
choose h
max
∈ [0.4 − 0.8] and N
zc
≥ 20.
3 PARTICLE SWARM
OPTIMIZATION
After defining the optimization problem and the nec-
essary constraints, It is now possible to choose one
of the optimization methods to find the optimal gains.
The chosen method in this work is the particle swarm
optimization (PSO).
The PSO, first introduced in (Eberhart and Kennedy,
1995), is a population-based algorithm simulating the
movement of a swarm of particles in a predefined
space. After a number of iterations, the particles are
attracted towards the optimal location and gathered
around it. This location defines the optimal solution
of the problem.
The PSO has many features that make it efficient in
solving optimization problems, e. g. it has less pa-
rameters to be identified in comparison with other op-
timization methods and has a very high success rate
in finding the global minimum (Rezaee Jordehi and
Jasni, 2013), and it has also a relatively high conver-
gence speed to a near optima (Angeline, 1998).
In our case, each particle position represents a vector
with a number of elements equals to the total num-
ber of gains. The main contribution of this research
is to propose a practical implementation of the PSO
method for robotic manipulators.
3.1 Defining the PSO Parameters
For every iteration of the PSO algorithm, every parti-
cle of the swarm will have a new position and velocity
assigned to it based on the following equations:
V
j
(i + 1) = ω(i)V
j
(i) + c
1
γ
1
(P
j
(i) − X
j
(i))
+ c
2
γ
2
(G(i) − X
j
(i))
(9)
X
j
(i + 1) = X
j
(i) + V
j
(i + 1)
(10)
Where i indicates the current iteration, j indicates
a particle of the swarm, X
j
(i) is the position vector
of the particle j, V
j
(i) is the velocity vector of the
particle j, c1 and c2 are the cognitive and the social
acceleration coefficients respectively, ω(i) is the iner-
tia factor and γ
1
and γ
2
∈ [0 1] are random variables
with uniformly distributed values.
There is no standard way to choose the swarm size
and the maximum number of iterations. However,
both parameters must be high enough in order to guar-
antee a convergence of the objective value toward the
global minimum.
Regarding the inertia weight, a dynamically changing
inertia leads to better results than a constant one, and
defining ω as a linear decreased function is an effec-
tive and reasonable choice as it was proven in (Shi
and Eberhart, 1999) and (Bansal et al., 2011). In this
work, the inertia weight is given as follows:
ω = ω
max
−
(ω
max
− ω
min
)N
i
N
max
. (11)
where N
max
is the maximum number of iterations, N
i
is the current number of iterations, ω
max
and ω
min
are
the maximum and the minimum values of the inertia
weight respectively. The chosen values in this work
are ω
max
= 0.9 and ω
min
= 0.4 as it was suggested in
(Shi and Eberhart, 1998).
Based on the stability conditions that was introduced
in (Perez and Behdinan, 2007), it is possible to define
the parameters c1 and c2 in a way that guaranties a
convergence toward an equilibrium point eventually.
These conditions are:
0 < c1 + c2 < 4 (12)
(c1 + c2)
2
− 1 < ω < 1 (13)
Considering that ω ∈ [0.4 − 0.9], choosing c1 = c2 =
1 is suitable.
3.2 Constraints Handling
After defining the PSO parameters, one step is only
needed before applying the method on the robot,
which is finding a suitable way to handle the con-
straints that were defined in the last section. The
mostly used methods to handle constraints in PSO are
either penalty-based methods, where a penalty value
is added to the cost function if the particle position
violates any constraints, or methods that try to define
the feasible regions in the search space and restrict the
particle positions to be always inside these regions.
Unfortunately, the practical nature of the optimization
problem in this work makes both methods unsuitable.
As it was mentioned before, if one of the constraints is
violated, the movement of the robot must be stopped
immediately, which means that the cost function IAE
cannot be calculated for this movement and, there-
fore, no penalty-based method can be used. Besides,
the feasible region cannot be defined theoretically in
advance and the only way to detect a violation of con-
straints is by performing the movement that results
A Practical Approach for the Auto-tuning of PD Controllers for Robotic Manipulators using Particle Swarm Optimization
37

Figure 3: Constraints Handling Method.
according to the particle position.
The proposed method here to handle the con-
straints was inspired by the work in (Venter and
Sobieszczanski-Sobieski, 2003), where modifications
of the optimization method were suggested. The Han-
dling method is done after considering the following
simplifications:
• Assume that one constraint corresponding to the
link l is violated, if we ignored the coupling ef-
fects between the robot links, one can state that
the gains K
l
p
and K
l
d
of the corresponding con-
troller are only responsible for this violation and
must be modified, i. e. handling the constraints
can be done by modifying the particle position in
only two dimensions.
• There is only one continuous feasible region in-
side the search space, i. e. if a particle moves in a
direction that leads to a constraint violation, con-
tinuing to move the particle in the same direction
will also lead to a constraint violation.
• Most of the initial swarm positions are located in-
side the feasible region.
based on these simplifications, a proper method to
keep the particles inside the feasible region can be
achieved as follows:
If one of the constraints of the link l is violated, the
exploration term (ωV
l
) for the corresponding dimen-
sions are set to zero, which will restrict the next move-
ment in theses two dimensions to be only influenced
by the personal and the global best positions as it is
shown in figure 3. Off course these positions are lo-
cated in the feasible region, therefore, the resulted ve-
locity victor will bring the particle back to the feasible
region.
The Assumption of having only one feasible re-
gion is a reasonable assumption, because it indicates
that if a gain value violated one of the constraints after
it was increased, then continuing to increase it (while
keeping the other gains with the same values) will
keep violating this constraint. The same applies for
when the gain is decreased.
Based on the foregoing, it is now only required to lo-
cate the initial swarm inside the feasible region. A
simple strategy is to define only one suitable position
{K
p,0
,K
d,0
} (e. g. by tuning the controller through
trails and errors). After that, one can define an interval
in the neighborhood of this position, let it be for ex-
ample {[K
p,0
−∆K
p
K
p,0
+∆K
p
],[K
d,0
−∆K
d
K
d,0
+
∆K
d
]}. Finally, random initial positions can be allo-
cated with a unified distribution in this interval. It is
possible that some of the initial positions may violate
one or more of the constraints (if the chosen interval is
too large), however, they will return in the following
iterations to the feasible region thanks to the proposed
method.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
The proposed tuning method has been tested on a 7-
DOF robot, which is built of specially designed mod-
ules called PowerCube from the company “Schunk”.
The experiment was carried on for the joints (3,4,6)
of the robot as it is shown in figure 4. All the joints
are rotational and actuated by brushless dc-motors.
Figure 4: PowerCube Robot.
The trajectory tracking performance of the PD
controllers of the robot is tested according to the de-
sired trajectories shown in figure 5. These trajectories
represent point-to-point movements with sinusoidal
velocity profiles.
To define the constraints for the chosen joints,
the value e
max
=
π
90
≈ 0.035[rad] was chosen as the
maximal position error. The PowerCube modules
provide the user with current measurements for
ICINCO 2017 - 14th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
38
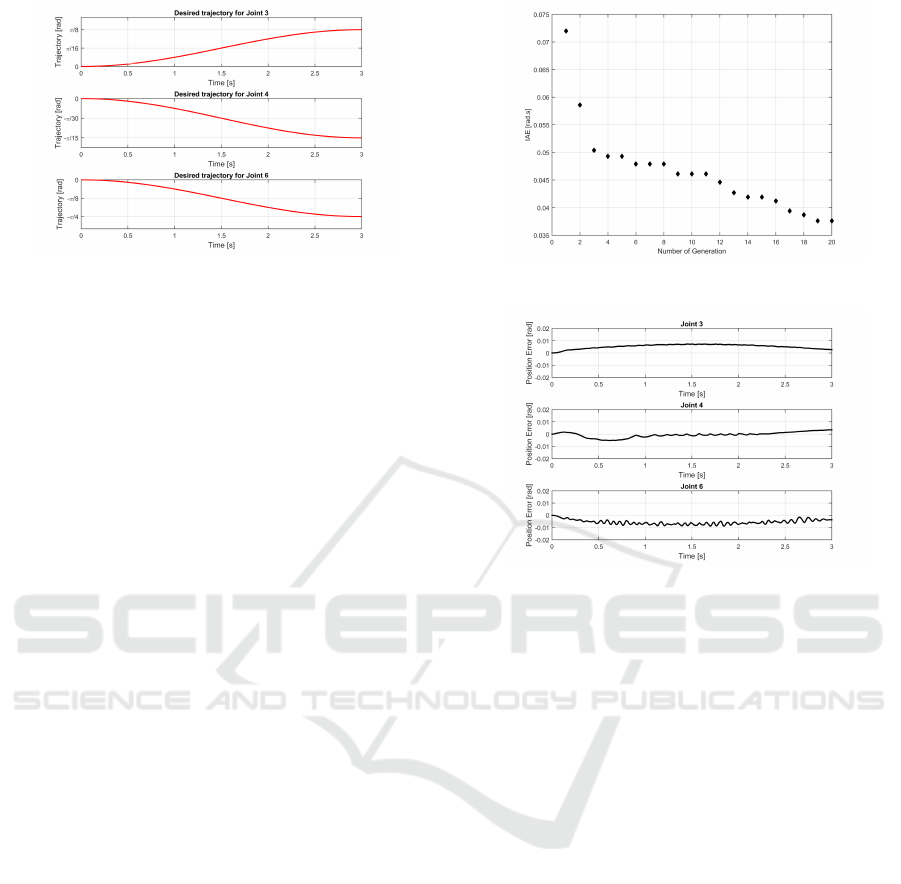
Figure 5: Desired Trajectories in Joint Space.
every motor instead of torque measurements, that
is why a maximum current constraints is used in
the experiment instead of a maximum torque. The
maximum allowed current in all of the modules
equals 15[A], but for the optimization procedure
only the half of this value is defined as the current
limit (I
max
= 7.5[A]). Oscillations detection is carried
on after detecting at least N
zc
= 20 zero-crossings
of the rescaled error signal e
zc
(t). if the condition
h(N
zc
) > 0.5 is met, then oscillations are considered
to be occurred and the movement of the robot must
be stopped.
Regarding the PSO algorithm, a swarm size of 10 par-
ticles is chosen and the maximum number of genera-
tions is set to 20. In addition, a tolerance value of the
cost function is set to 0.03[rad.s]. To define initial po-
sitions for the particle swarm, an acceptable gain set
of values was defined through trials and errors which
are K
p,0
= [90,60,120] and K
d,0
= [5,2,8]. Based
on these values, two intervals for the initial gains are
defined as follows: [K
p,0
− K
p,0
/2 K
p,0
+ K
p,0
/2]
and [K
d,0
− K
d,0
/2 K
d,0
+ K
d,0
/2].
The initial positions were then determined randomly
from inside this interval with a uniform distribution.
The search space for all the K
p
gains is defined to
be [1 − 500] and for the K
d
gains [0 − 50], which
make the maximum gain limits be relatively high
compared to the initial gains. However, the maximum
velocity value V
max
was set to be equal 20% of these
maximum limits in order to avoid big leaps in the
particle movement.
After applying the PSO on the PD-controllers for the
three joints of the robot, the following optimal gain
values was found:
K
p
= {182.20, 107.46,205.8} and K
d
=
{10.29,5.55,17.83}. The optimal objective value is:
IAE = 0.0376[rad.s].
The convergence of the objective value during the
searching procedure is shown in figure 6, while figure
7 shows the position error diagram according to the
optimal gain values.
One may notice that some low amplitude oscillations
Figure 6: Convergence of the Objective Value After 20 Gen-
erations.
Figure 7: Position Error Signals According to the Optimal
Gains.
appear on the error diagram of the joint 6. These
oscillations, however, are not high enough to violate
the oscillation constraint. The fact that the optimal
gains are causing such oscillations indicates that there
is a tradeoff between the tolerated oscillations and
the accuracy of the trajectory tracking movement.
This also means that the PSO technique was able to
direct the particles toward the limits of the feasible
region to the position were the optimal gain values
are expected to be.
5 CONCLUSION
In this paper, an auto-tuning method of PD-controllers
for robotic manipulators has been proposed. The sug-
gested approach uses the particle swarm optimiza-
tion in order to find the optimal control parameters.
The main contribution of this work was to address
the practical challenges that faces such a task and to
propose suitable solutions for it. For this sake, the
necessary constraints that guarantee a stable and safe
movement for the robot while searching for the opti-
mal gains have been defined. Additionally, a suitable
way for the PSO to handle these constraints has been
suggested. Finally, the proposed approach has been
successfully experimented on a real robot.
A Practical Approach for the Auto-tuning of PD Controllers for Robotic Manipulators using Particle Swarm Optimization
39

REFERENCES
Angeline, P. J. (1998). Evolutionary optimization versus
particle swarm optimization: Philosophy and perfor-
mance differences. pages 601–610.
Ayala, H. V. H. and dos Santos Coelho, L. (2012). Tuning of
pid controller based on a multiobjective genetic algo-
rithm applied to a robotic manipulator. Expert Systems
with Applications, 39(10):8968–8974.
Bansal, J. C., Singh, P., Saraswat, M., Verma, A., Jadon,
S. S., and Abraham, A. (2011). Inertia weight strate-
gies in particle swarm optimization. pages 633–640.
Bekit, B., Seneviratne, L., Whidborne, J., and Althoefer, K.
(1998). Fuzzy pid tuning for robot manipulators. In
Industrial Electronics Society, 1998. IECON’98. Pro-
ceedings of the 24th Annual Conference of the IEEE,
volume 4, pages 2452–2457. IEEE.
Craig, J. J. (2005). Introduction to robotics: mechanics and
control, volume 3. Pearson Prentice Hall Upper Sad-
dle River.
Eberhart, R. and Kennedy, J. (1995). A new optimizer using
particle swarm theory. In Micro Machine and Human
Science, 1995. MHS’95., Proceedings of the Sixth In-
ternational Symposium on, pages 39–43. IEEE.
Forsman, K. and Stattin, A. (1999). A new criterion for
detecting oscillations in control loops. pages 2313–
2316.
H
¨
agglund, T. (1995). A control-loop performance monitor.
Control Engineering Practice, 3(11):1543–1551.
Johnson, M. A. and Moradi, M. H. (2005). PID control.
Springer.
Kapoor, N. and Ohri, J. (2015). Improved pso tuned classi-
cal controllers (pid and smc) for robotic manipulator.
International Journal of Modern Education and Com-
puter Science, 7(1):47.
Kim, E.-J., Seki, K., Iwasaki, M., and Lee, S.-H. (2012).
Ga-based practical auto-tuning technique for indus-
trial robot controller with system identification. IEEJ
Journal of Industry Applications, 1(1):62–69.
Kwok, D. and Sheng, F. (1994). Genetic algorithm and
simulated annealing for optimal robot arm pid con-
trol. In Evolutionary Computation, 1994. IEEE World
Congress on Computational Intelligence., Proceed-
ings of the First IEEE Conference on, pages 707–713.
IEEE.
Llama, A. M., Kelly, R., and Santiba
˜
nez, V. (2001). A stable
motion control system for manipulators via fuzzy self-
tuning. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 124.
Melek, W. W. and Goldenberg, A. A. (2003). Neuro-
fuzzy control of modular and reconfigurable robots.
IEEE/ASME transactions on mechatronics, 8(3):381–
389.
Nahapetian, N., Motlagh, M. J., and Analoui, M. (2009).
Pid gain tuning using genetic algorithms and fuzzy
logic for robot manipulator control. pages 346–350.
Ouyang, P. and Pano, V. (2015). Comparative study of de,
pso and ga for position domain pid controller tuning.
Algorithms, 8(3):697–711.
Perez, R. and Behdinan, K. (2007). Particle swarm ap-
proach for structural design optimization. Computers
& Structures, 85(19):1579–1588.
Pierezan, J., Ayala, H. H., da Cruz, L. F., Freire, R. Z., and
Coelho, L. d. S. (2014). Improved multiobjective par-
ticle swarm optimization for designing pid controllers
applied to robotic manipulator. In Computational In-
telligence in Control and Automation (CICA), 2014
IEEE Symposium on, pages 1–8. IEEE.
Rezaee Jordehi, A. and Jasni, J. (2013). Parameter selec-
tion in particle swarm optimisation: a survey. Journal
of Experimental & Theoretical Artificial Intelligence,
25(4):527–542.
Shi, Y. and Eberhart, R. C. (1998). Parameter selection in
particle swarm optimization. pages 591–600.
Shi, Y. and Eberhart, R. C. (1999). Empirical study of par-
ticle swarm optimization. 3:1945–1950.
Venter, G. and Sobieszczanski-Sobieski, J. (2003). Particle
swarm optimization. AIAA journal, 41(8):1583–1589.
ICINCO 2017 - 14th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
40
