
Toward Testing Security Attacks and Defense Mechanisms for P2PSIP in
MANETs with a Simulator
Alexandre Cormier
1
, Franc¸ois Gagnon
2
, Babak Esfandiari
1
and Thomas Kunz
1
1
Department of Systems and Computer Engineering, Carleton University, Ottawa, Canada
2
Cybersecurity Research Lab, C
´
egep Sainte-Foy, Qu
´
ebec, Canada
Keywords:
P2P, SIP, MANET, Security, Attacks, Simulation Experiments.
Abstract:
Mobile Ad hoc NETworks (MANETs) are comprised of mobile devices communicating with each other over
multi-hop wireless links. Because they do not require any fixed infrastructure, these networks are appropriate
for communication in military operations, for example. The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is a standard for
session establishment in Voice over IP context, notably, but is not adapted to MANETs and peer-to-peer (P2P)
networks. Though solutions have been proposed, their security properties are not addressed in depth. We thus
analyze the different threats affecting a military MANET used for P2PSIP, propose a security solution, based
in large part on cryptographic challenges, to counter the identified threats and present some simulation-based
experiment results for our proposed solution.
1 INTRODUCTION
Peer-To-Peer (P2P) networks are used in many dif-
ferent contexts and for many different reasons. For
instance, P2P is interesting for file sharing systems
(Androutsellis-Theotokis, 2002) since it provides en-
hanced robustness compared to the traditional client-
server mode (where the server becomes a single point
of failure). In other contexts, using P2P allows to pre-
vent giving too much trust to a single controlling en-
tity (the server); instead, putting a small amount of
trust in many other peers (Wendlandt et al., 2008).
The security aspects of P2P systems have been
studied in the literature (e.g., (Urdaneta et al., 2011)
and (Levine et al., 2006)). However, security studies
and solutions are usually general to P2P and not spe-
cific to the various contexts (e.g., who are the peers)
and applications (e.g., file sharing) for which a P2P
system will be deployed. We believe that consider-
ing both the context and the application underlying
the P2P system is important when building a threat
model to consider which security solutions to adopt.
In this paper, we present our work toward securing
a P2P network used for a Voice over IP (VoIP) appli-
cation (with SIP
1
) in the context of military missions
relying on Mobile Ad hoc NETworks (MANETs)
(Giordano et al., 2002). The contributions of this pa-
1
Session Initiation Protocol
per are:
• Presenting a threat model for the specific situation
of P2P SIP over MANETs.
• Proposing the first layers of a defense mechanism
to protect the network.
• Providing experimental results in OverSim
2
, a
P2P simulation environment built on top of OM-
NeT++
3
.
The rest of the paper is structured as follows. First,
Section 2 provides some background information re-
garding P2P, SIP and MANET. Then, Section 3 dis-
cusses related work from the literature. Sections 4
and 5 respectively present the threat model and the
defense mechanisms for our context (P2P for VoIP in
a military MANET). Section 6 then presents security-
related experiments performed in a network simula-
tor. Finally, Section 7 concludes with a discussion
regarding the lessons learned and pointers towards fu-
ture work.
2 BACKGROUND
This section provides a short background on the key
elements used throughout this paper: MANET, SIP,
2
http://www.oversim.org (Baumgart et al., 2007)
3
https://omnetpp.org/ (Varga and Hornig, 2008)
Cormier, A., Gagnon, F., Esfandiari, B. and Kunz, T.
Toward Testing Security Attacks and Defense Mechanisms for P2PSIP in MANETs with a Simulator.
DOI: 10.5220/0006478300430054
In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on e-Business and Telecommunications (ICETE 2017) - Volume 1: DCNET, pages 43-54
ISBN: 978-989-758-256-1
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
43

and P2P.
2.1 Mobile Ad Hoc Networks
MANETs (Giordano et al., 2002), being
infrastructure-less wireless networks, do not re-
quire any kind of central administration. Every node
in such a network acts both as an end device and
as a router. When a node wants to send a packet to
another one that is not within communication range,
the packet will follow a multi-hop path and will be
routed wirelessly through intermediate nodes until it
reaches its destination.
This kind of network thus allows for constantly-
changing topology, and nodes can be devices carried
by people or vehicles. This makes MANETs ideal for
a number of scenarios, such as emergency response
and, more specifically for this paper, military net-
works. Soldiers and military vehicles can carry mo-
bile devices and form a network to communicate even
in the most hostile of environments.
2.2 Session Initiation Protocol
SIP (Rosenberg et al., 2002) is a protocol standard-
ized by the IETF that, as the name indicates, is used
to initiate a session between two users’ devices, which
are identified by an ID (SIP URI) similar to an email
address (sip:alice@example.com). A key part of the
protocol is thus a registrar,
`
a la DNS, to map SIP
URIs to a contact address, which is the current net-
work location (IP address) where the SIP client can
be reached. A SIP URI mapping to a contact address
in such a way is called an Address-of-Record (AOR).
SIP is based on a client-server architecture. The
role of the registrar is assumed by a number of SIP
servers, that are generally managed by larger orga-
nizations or Internet service providers. When a SIP
client needs to establish a connection with another
one, it contacts its SIP server which, using DNS, will
locate the recipient’s SIP server, which knows the sta-
tus and location of the recipient itself.
2.3 P2P
Because SIP is based on a client-server architecture, it
is not appropriate for use in MANETs. A solution to
this is to use a P2P overlay network such as a dis-
tributed hash table (DHT) to store and retrieve the
registrations associated with SIP URIs. Such an ap-
proach was standardized by the IETF as the RELOAD
protocol (Jennings et al., 2014).
A P2P (Schollmeier, 2001) network is a dis-
tributed network in which participants share a part of
their hardware resources to provide, together, a cer-
tain service and content. Peers are accessible to one
another directly, eliminating the need for central in-
termediary entities to pass through. In the case of a
pure P2P network, any node can come and go without
affecting the overall service, meaning that no central
entity is needed at all to offer the service. The fact
that no central entity is needed and that nodes can
leave and rejoin at will makes P2P an ideal choice
for MANETs.
One way to structure a P2P network is to use a dis-
tributed hash table (DHT). A DHT stores (key, value)
pairs and peers can easily and efficiently retrieve the
value associated with a given key. The way this works
is by having keys and node identifiers be values in the
same identifier space. This is often achieved by using
a hash of the node’s IP address as its ID. The same
hashing function is then used to calculate keys from a
meaningful name related to their values. The value as-
sociated with key k is stored on the node whose iden-
tifier is closest to k, for some definition of closeness.
3 RELATED WORK
A few solutions have been proposed to address the
implementation of SIP over MANETs. TacMAN
(Li and Lamont, 2005) and an approach identified
as “Loosely Coupled” (LCA) by (Banerjee et al.,
2004) do so by replacing the central registrars with lo-
cal storage and broadcast lookups. AdSIP (Yahiaoui
et al., 2012), MANETSip (Fudickar et al., 2009) and
another approach identified as “Tightly Coupled” by
(Banerjee et al., 2005), on the other hand, select
a subset of the network’s peers to act as registrars,
more akin to the standard, centralized version of SIP.
Finally, two unnamed proposals (Wongsaardsakul,
2010; O’Driscoll et al., 2007) and SIPHoc (Stuedi
et al., 2007) implement a DHT to replace registrars.
This last approach was also proposed in early P2PSIP
literature, is used in the standardized RELOAD pro-
tocol (Jennings et al., 2014) and is also used for the
purposes of this paper.
However, these solutions do not, for the most part,
focus on security. RELOAD does have a three-level
security model, based on a central certificate author-
ity (CA). Connections between nodes use TLS or
an equivalent protocol, all messages are signed, and
stored objects are signed as well by the creating node.
Other proposed solutions for securing P2PSIP in-
clude P2PNS (Baumgart, 2008) and unnamed pro-
posals by (Bryan et al., 2008) and (Seedorf, 2006).
Both P2PNS and (Bryan et al., 2008) use public-key
cryptography to sign overlay messages. Additionally,
DCNET 2017 - 8th International Conference on Data Communication Networking
44

the former signs registration messages while the lat-
ter signs the registrations themselves. Also, neither
relies on a central CA but rather make it harder for an
attacker to get a valid key pair using a rate limiting
mechanism (crypto-puzzles in the case of P2PNS).
(Seedorf, 2006) proposes the use of self-certifying
SIP URIs to protect the integrity of registrations. This
is achieved by using a hash of a node’s self-generated
public key as the user part of its SIP URI and signing
its registrations with the corresponding private key.
In short, most security solutions for P2PSIP make
little assumptions about the context in which the net-
work will be used. For example, they do not assume
that a central entity can manage the network, which
is possible in our context. This means they are not
tailored to the context under focus for this paper (de-
scribed in Section 4.1), and thus they often lack some
security properties that we consider important like re-
sistance to DHT poisoning.
4 THREAT MODEL
Before discussing the threat model per se, we provide
a description of the context underlying our P2P sys-
tem and then discuss the security objectives that are
important in that context.
4.1 Context
This paper considers a P2P network built over a mil-
itary MANET used to run SIP (to initiate VoIP ses-
sions). In such a setting, the P2P layer will be used
to store and retrieve the mapping between a SIP URI
(the id of the user we want to contact) and his current
contact address (the IP address where to locate this
user). This mapping will be stored in a distributed
hash table (DHT), common in P2P systems. The fo-
cus of our work is to protect this DHT.
Furthermore, we are making the following as-
sumptions/observations regarding the context in
which P2P will be used:
• The P2P network is “Private”. Or more accu-
rately, it is owned/operated/controlled by a given
entity. Indeed, being a military network, random
users should not be part of the core network unless
they are part of the military team. This is differ-
ent from the usual P2P context which are usually
designed to be as open as possible.
• The application level IDs (SIP URI) can be au-
thorized by the central authority when a node
is granted access to the network (we assume
this is done offline, before the military deploy-
ment). Thus, there is no need to worry about
ID generation and potential collisions. Those
IDs will be something human readable (e.g., first-
Name.LastNameNumber).
• The DHT acts as a DNS-like service. The role of
the DHT is to store the mapping [AOR → contact
address]. In that sense, it acts as a service that
allows users to resolve a SIP URI and update their
own record.
• The DHT will be dynamic, which is not
something usually considered for DHT security.
MANETs provide mobility which means that
nodes will join and leave the network causing re-
addressing to occur.
• The DHT does not need to be fully persistent.
Once a user y leaves the network, it is not mean-
ingful to keep the entry mapping y to its network
address up-to-date.
• For simplicity reasons, we assume that each de-
vice (each P2P node) is associated with a single
user. This is reasonable for personal devices (e.g.,
smartphone-like gear) but would not be for larger
devices (e.g., vehicles).
4.2 Security Properties
Several security objectives can be defined for P2P sys-
tems:
• Data integrity (security): the content delivered by
DHT in the underlying P2P network has not been
tampered with.
• Service availability (resilience): whenever two
available (and reachable) nodes want to commu-
nicate together, they should be able to do so.
• Confidentiality: Information extracted from the
DHT should not be exposed to intermediary nodes
(only the querying node should access the con-
tent).
• Anonymity: when a node queries the DHT, the
node providing the information should not be able
to trace back where the query originated from.
Data integrity (security) and service availability
(resilience) are the primary security objectives in our
context. Confidentiality and anonymity are not con-
sidered in this paper, but they have been studied in
the P2P literature (e.g., Tarzan (Freedman and Mor-
ris, 2002), MorphMix (Rennhard and Plattner, 2002),
and Octopus (Wang and Borisov, 2012) for Confiden-
tiality and (Fonville, 2010) for Anonymity).
Toward Testing Security Attacks and Defense Mechanisms for P2PSIP in MANETs with a Simulator
45

4.3 Attacker
We consider malicious nodes to have the following
capabilities:
• They can collaborate together to achieve their
goal.
• They can communicate together via a dedicated
channel to coordinate their attack.
• They control one legitimate device with one valid
SIP URI and the associated certificate. This al-
lows them to impersonate this ID, but should not
allow them to impersonate others.
The objectives of the malicious nodes are twofold.
On the one hand, they aim to manipulate the DHT
service in order to fool honest nodes regarding the lo-
cation of their peers. On the other hand, failing to
compromise the content of the DHT, they will try to
deny DHT service to legitimate nodes. We focus on
DHT-level attacks, also known as storage-retrieval at-
tacks.
To achieve their objectives, they can rely on vari-
ous attacks. Below, Section 4.3.2 describes some pos-
sible storage-retrieval attack scenarios. Other attacks,
although not directly compromising the DHT, could
help mount a storage-retrieval attack. In Section 4.3.3
we briefly discuss two types of impersonation attacks
that may be used for such a purpose and are widely
discussed in the P2P literature.
4.3.1 Notation
The following notation is used throughout this paper:
• Q and R stand for legitimate nodes.
• x and y stand for legitimate users.
• Q and x are used to denote an entity querying the
DHT.
• R and y are used to denote an entity to communi-
cate with.
• M stands for a malicious node (and user).
• S stands for a generic node (and user).
• A stands for a contact address.
4.3.2 Storage-Retrieval Attacks
This section presents attack scenarios relevant to the
storage-retrieval operation in a DHT. In a VoIP con-
text, the DHT is used to store/retrieve a mapping be-
tween the SIP URI of a user and the address at which
that user can be reached in the network.
In this section, we often refer to attacks available
in OverSim since this is the environment used for the
experiments in Section 6.
For the attack scenarios, assume node Q queries
the DHT to get the location of user y. There is a
node (or multiple if storage is redundant) which is re-
sponsible for storing the mapping for y, we call this
node P(y). The query from Q must be routed to P(y)
through the underlying P2P network.
Routing-based Attacks. A simple routing attack
consists of dropping requests seeking the next hop
to reach P(y). This attack can take place whenever
a malicious node happens to be on the request path
and poses resilience issues. This attack is called Drop
Find Node Attack in OverSim. A similar attack in
OverSim is the Drop Route Message Attack. It is also
a simple attack that only consists of dropping packets.
The difference resides in the type of message that is
dropped: the Drop Route Message Attack applies to
messages sent using key-based routing.
A more sophisticated version of a routing attack
is for an intermediate node to provide a wrong an-
swer (as to which node should be the next hop toward
P(y)) sending the querier on a false trail. The goal is
to end up fooling the querier by providing a false (and
malicious) node as P(y). This then sets up the table
for a Query-Based attack (see below). This is imple-
mented as two attacks scenarios in OverSim: Invalid
Nodes Attack and Is Sibling Attack. The former is
rather superficial as the answer (next hop) is just ran-
domly generated (a malicious, legitimate, or nonex-
istent node), while the latter will indicate that P(y)
is the malicious node itself (which can later mount a
query-based attack).
Query-based Attacks. The easiest query attack is
for a malicious node posing as P(y) to refuse to serve
the data by not replying to the query: a Denial of Ser-
vice (DoS) attack.
A more interesting scenario is for a malicious P(y)
node to answer a query with bogus data. If the querier
is unable to detect the attack, the data integrity will be
compromised leading to potentially serious problems.
If the querier detects the attack, a DoS is likely to oc-
cur unless strong mechanisms are implemented to re-
cover from such a situation. This scenario is called
Invalid Data Attack in OverSim, where a malicious
node would answer with random data which would
not be adequate in a DNS-like DHT.
Because the attack scenarios implemented in
OverSim are general and not specific to P2PSIP, we
implemented our own attack scenario refining the In-
valid Data Attack, we call it Resolve to Self Attack. In
this new scenario, a malicious node M which happens
to be responsible for storing y’s information (i.e., M
DCNET 2017 - 8th International Conference on Data Communication Networking
46

is also P(y)) will answer that y is located at M instead
of answering random data.
Resource Exhaustion Attack. RELOAD (Jennings
et al., 2014), an RFC for P2PSIP with security con-
siderations, mentions a type of resource exhaustion
attack where a node is asked to store an abnormally
large amount of data by malicious nodes. As a conse-
quence, the attacked node might be unable to store le-
gitimate data for which it should be responsible, lead-
ing to resilience problems.
DHT Poisoning Attack. In a P2PSIP application
where the DHT acts as a naming service (mapping
each SIP URI to a contact address), poisoning attacks
become a real threat. In this attack, a malicious node
inserts/overwrites data in the DHT instead of focus-
ing on attacking the query mechanism. Hence, when
Q queries the DHT, a legitimate P(y) will unknow-
ingly serve wrong data after being poisoned by a ma-
licious node. Unless strong security mechanisms are
in place to validate updates to the DHT, poisoning at-
tacks would be problematic as they are quite easy to
perform (compared to query-based attacks).
Replay Attack. If the address of a peer changes
over time, then a replay attack becomes possible: an
attacker currently located at address A could reuse an
old DHT entry saying SIP URI of node y is located at
A (y was located at A in the past) to fool a querier into
thinking y is still at A while a malicious node is there.
Even tough not as powerful as a poisoning attack, a
replay attack is difficult to counter.
4.3.3 Impersonation Attacks
Sybil Attack. The Sybil attack (Douceur, 2002)
comes from the inherent openness of P2P systems
and consists of one malicious peer being able to act
as multiple different logical nodes in the system (i.e.,
controlling multiple IDs in the DHT). By itself, this
kind of attack does not compromise the resilience nor
the integrity of the network. However, the ability for
a malicious entity to easily control a large number of
nodes greatly enhances its ability to perform attacks.
For instance, if an entity can setup several malicious
nodes in a network, its chances of disrupting the net-
work through a DoS attack are vastly superior than if
it controls a single one.
Eclipse Attack. An extreme case of the Sybil attack
is the Eclipse attack (Ismail et al., 2015) where a ma-
licious entity controls all the nodes “surrounding” its
target. Hence, every query from the target peer passes
through a malicious node which can then manipulate
the data as it sees fit since the target has a compro-
mised view of the logical network.
5 SECURING DHT FOR P2PSIP
We propose a multilayer approach to securing a DHT.
The proposed approach is centered around an offline
public key infrastructure (PKI). We start by tackling
the data integrity problem and then work toward in-
creasing resilience.
5.1 Data Integrity
The main security objective is to prevent manipula-
tion of the DHT; that is, for P2PSIP, malicious nodes
(possibly colluding together) should not be able to
convince node Q that user y is located at node R when
this is not the case. When malicious nodes try fool-
ing Q in such a way, Q should be able to detect the
problem and abort the attempt to communicate with
y. Q should be able to detect this before sending any
meaningful data to R.
We identify two attack vectors for malicious nodes
to try and fool Q:
• At query time. When Q queries the DHT, mali-
cious nodes will attempt to redirect the query to
a malicious node M (the goal is to let Q believe
that the node responsible for handling its query is
one of the malicious nodes). Then, M can answer
the query from Q with false information. This is
a combination of Routing-based and Query-based
attacks mentioned in Section 4.3.2.
• At insertion time. Before Q even queries the
DHT, a malicious node could insert a mapping
in the DHT (possibly overwriting the previous le-
gitimate entry) with bogus information. This is
the DHT poisoning attack discussed in Section
4.3.2. This attack is particularly important when-
ever the DHT acts as a registrar (like it is the case
of P2PSIP) as poisoning the DHT is much simpler
and efficient then building attacks at query time.
5.1.1 End-User Validation
In our specific context (P2PSIP), where the DHT
stores the mapping between a user ID and the node
where that user is located, the easiest way to prevent
impersonation is to allow the querier to validate the
result of its DHT query by challenging the returned
node to prove it is indeed occupied by the right user.
So if Q wants to know where y is, it asks the DHT
and gets a node R. Now Q will challenge R and ask
Toward Testing Security Attacks and Defense Mechanisms for P2PSIP in MANETs with a Simulator
47

for a proof that user y is indeed at R. This can be done
with an offline PKI in the following way.
5.1.2 Details
We use an offline CA to give, to each node, a root
certificate (rootCert with public key only) and a user
certificate (userCert with private key). userCert is is-
sued for the SIP URI (user) associated to the node and
is signed by rootCert. This is not a major overhead
as each device will have to be prepared for missions
beforehand anyway and we have a central authority
owning the P2P network.
So now, a node R can prove its real identity by us-
ing the private key associated with its userCert to sign
a challenge. The challenge protocol should be such
that the answer will not be re-playable nor transfer-
able.
Back to our above example, Q will issue a chal-
lenge to R asking to sign a random value with y’s
public key. The random value makes past answers
non re-playable. So, only a node with access to y’s
private key can answer the challenge correctly. Once
the answer from the challenge comes back to Q, Q can
validate it using y’s public key which should be sent
in a certificate alongside the answer. Q will first vali-
date the certificate (it should be for y and be properly
signed by rootCert).
To avoid a malicious node M posing as y to simply
transfer the challenge to the real node hosting y and
forwarding y’s answer back to Q, the response should
be specific to y’s location. For instance, Q will send
a random number Rand as the challenge for y to node
R. The answer should be < Rand, y, R > signed with
y’s private key.
If the node R successfully passes the challenge, Q
can go along with the communication. If the node R is
malicious, it can’t answer the challenge. As a result,
Q stops its communication attempts with y.
The PKI provides good security trough end-user
validation. But, the network needs to be more resilient
to DoS because it is currently easy for a malicious
node to DoS the system (making sure a communica-
tion fails because of invalid challenge-response).
5.2 Resilience
The approach discussed above, end-user validation
with a PKI, will solve the data integrity problem.
However, the system will not be very resilient (DHT
poisoning will easily lead to DoS). Resilience can be
increased with a three-step approach. Note that 100%
resilience is unattainable because if an attacker con-
trols a “strategic” part of the P2P network (enough
nodes or the right nodes), he can generate DoS below
the DHT (e.g., at the network level).
5.2.1 Step 1 - Preventing DHT Poisoning
To prevent malicious nodes from inserting false en-
tries in the DHT, nodes are required to sign their in-
sertion requests, and nodes responsible for storing the
information are required to validate signatures before
storing the information. So, whenever node y wants to
store/update its address A in the DHT, it will sign the
new mapping with its private key. The node respon-
sible for storing that information, P(y), will validate
that any insertion for the SIP URI of y are properly
signed by y’s private key.
This signature validation upon storing in the DHT
will prevent poisoning attacks. And since the end-
user validation presented in Section 5.1.1 above turns
retrieval attacks into DoS attacks, the attacker is left
with less attack surface. However, a replay attack is
still possible.
5.2.2 Step 2 - Limiting Replay Attacks
In a replay attack, a malicious node reuses an old
DHT entry that should not be valid anymore to fool
honest nodes. Assume user y was previously at ad-
dress A and has stored this in the DHT at some point.
Now, assume y is at another address and a malicious
node M is able to obtain address A. M could now in-
ject the old information saying that y is at A in the
DHT. This will lead to a DoS (not a data integrity
problem) since legitimate nodes will challenge y at
A and M (located at A) will not be able to resolve the
challenge. Still, this allows for easy DoS under the
right conditions.
To limit replay attacks, information stored in the
DHT should be timestamped. Then either those en-
tries older than the most recent one or those expired
(for some given threshold) are not valid. The problem
with the first approach is the need of a relative point of
view (the most recent one is needed to make sure all
the old ones are considered invalid). The second ap-
proach on the other hand, requires some form of clock
synchronization for various nodes. It also requires
that legitimate nodes periodically update their info,
even if it did not change, before it expires. Moreover,
the second approach is not entirely local: one entry
that is not expired might still be invalid if a newer en-
try exists. Nevertheless, the second approach is kept
as it is more flexible.
At insertion time, P(y) will reject insertion re-
quests that are older than the currently stored entry,
to prevent replay-based DHT poisoning.
DCNET 2017 - 8th International Conference on Data Communication Networking
48

Figure 1: Limiting the attack surface with Store Everywhere
- Retrieve Locally.
Replay attacks are hard to completely circumvent,
especially in a decentralized context. But, since the
end-user validation will prevent replay attacks from
compromising data integrity and instead turn them
into resilience problems (DoS), limiting those attacks
to corner cases will make them highly unattractive.
5.2.3 Step 3 - Adding Redundancy
Now that DHT entries are timestamped to limit re-
play attacks, it is possible to further limit the oppor-
tunities of replay attacks by adding redundancy in the
storage-retrieval procedure. Indeed, the more nodes
are responsible for y’s entry in the DHT, the harder it
becomes for a malicious node to reuse an old entry.
To do so, a malicious node has to prevent all the le-
gitimate nodes responsible for y from answering the
initial query. Just one legitimate answer is enough to
prevent a replay attack, indeed, if the querier receives
multiple answers, only the most recent one will be
considered valid.
To illustrate the effectiveness of redundancy, let’s
consider an extreme case where the information is
stored everywhere and retrieved locally. In this con-
text, an attack is successful if the malicious node is
able to push an old entry into the DHT (which every
node stores locally) and prevent any newer entry from
reaching the targeted node (the eventual “querier” Q).
However, to prevent the new entry from reaching Q,
the attacker must eclipse Q from y (y is assumed to
broadcast his entry info). To achieve this, the attacker
must control every path from y to Q. The gain for the
attack is only a denial of service because the attacker
will fail end-user validation anyway. Figure 1 illus-
trates such a possible scenario. However, it is possi-
ble for the malicious node (M) to achieve the same
DoS without manipulating the DHT entries because it
controls the traffic flow between Q and y.
6 EXPERIMENTS
We describe our experiments in 6.1, show the results
obtained from these experiments in Section 6.2 and
discuss them in Section 6.3.
6.1 Methodology
As previously mentioned, we implemented simula-
tions in OMNeT++ using the OverSim framework.
The simulated network has 25 nodes placed in such
a way that, if they are all honest and cooperate, any
node can reach any other node. Nodes are static and
form a Chord DHT (Stoica et al., 2001) over an OLSR
network (Clausen and Jacquet, 2003).
Upon joining the DHT, nodes try registering their
AOR in the DHT with the P2PSIP service and keep
trying until they succeed. After 100 seconds of sim-
ulation time, nodes that have successfully registered
start issuing random resolve requests for SIP URIs
that have also been successfully registered. They do
so periodically, every 30 seconds.
The defense mechanism against attacks on data in-
tegrity described in Section 5.1 has been implemented
with a simulated PKI. The Resolve to Self Attack, de-
scribed in Section 4.3.2, has also been implemented
in order to test the effectiveness of the PKI.
We simulated 600 seconds per simulation and
each scenario was run 20 times in order to account
for randomness and get representative results.
6.2 Results
This section shows the results of our simulations eval-
uating the effect of different attacks on the ability of
nodes to join the DHT and, most importantly, the suc-
cess rate of resolve calls. They all show these statis-
tics for different proportions of malicious nodes, rang-
ing from none to half of the nodes, as indicated on the
horizontal axis. The margin of error displayed on all
graphs is for 95% confidence intervals.
Graphs for the resolve call statistics show four
relevant statistics. A solid green line indicates the
percentage of resolve requests that were successful
with the defense mechanism in place, meaning that
a response was received, it was determined with the
cryptographic challenge that it was valid and commu-
nication could be established with the correct node.
An orange line shows the percentage of resolve calls
that yielded a valid response in the sense that it was
in the correct format (i.e. an IP address), but the
cryptographic challenge determined that the response
had been tampered with and the correct node could
not be reached at the received address. A dashed
Toward Testing Security Attacks and Defense Mechanisms for P2PSIP in MANETs with a Simulator
49

green line (sometimes over the solid green line), com-
bine both of these last statistics to show the percent-
age of requests that would have been considered suc-
cessful had there not been a defense mechanism in
place, including connections established with mali-
cious nodes. Finally, the red line indicates the per-
centage of requests that failed to yield a valid re-
sponse, because of a network error or wrongly for-
matted data (i.e. not an IP address) for example.
Section 6.2.1 shows results for attacks that are in-
cluded in OverSim, and for which the simulated PKI
that we have implemented is not expected to make a
difference — because they are DoS attacks
4
or are de-
tectable without the PKI
5
. Section 6.2.2 shows results
for the attack scenario that we have implemented, the
Resolve to Self Attack, as well as a combination of this
one with the Is Sibling Attack, which is expected to be
more powerful. These last two scenarios are expected
to demonstrate the effectiveness of the PKI.
6.2.1 Attacks in OverSim
These attacks are part of the OverSim framework and
reside at the overlay layer, meaning they do not have
knowledge nor account for the P2PSIP context. They
are thus either DoS attacks or data integrity attacks
that are easily detectable by the P2PSIP application,
effectively turning them into DoS attacks. The de-
fense mechanism that we have implemented for data
integrity is not expected to show any improvement in
results in this context.
Drop Find Node Attack. Figures 2 and 3 show the
effect of the Drop Find Node Attack on the ability of
peers to join the DHT and on the success rate of re-
solve calls, respectively. We notice that the number
of nodes able to join the DHT and the resolve success
rate both drop as the number of malicious nodes in-
crease, because more nodes drop messages intended
to locate nodes. Our defense mechanism does not
have any impact as this is a DoS attack.
Invalid Data Attack. This attack does not affect
nodes joining the DHT, but it does, of course, af-
fect resolve calls. The success rate drops as the num-
ber of malicious nodes increases, as shown in Fig-
ure 4, as more resolves result in invalid data being re-
ceived. Cryptographic challenges are not needed be-
cause having data in the wrong format is enough to
4
Drop Find Node Attack, Invalid Nodes Attack and Is
Sibling Attack, when performed by themselves.
5
Invalid Data Attack, because a random value is re-
turned and an IP address is expected.
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
0.5
0
5
10
15
20
25
Probability of any node to be malicious
Number of Peers
Figure 2: Drop Find Node Attack — Peers that Successfully
Join the DHT.
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
0.5
0
20
40
60
80
100
Probability of any node to be malicious
Percentage of total resolve calls [%]
Failed resolves Failed challenges
Successful challenges Successul w/o challenge
Figure 3: Drop Find Node Attack — Resolve Calls Statis-
tics.
detect attacks. This shows that generic attack scenar-
ios are not always sufficient.
Invalid Nodes Attack. This attack affects both
nodes trying to join the DHT and resolve attempts, as
shown in Figures 5 and 6. Nodes have more trouble
joining the DHT in the presence of more malicious
nodes and the success rate of resolve calls drop in
the same cirumstances as a result of malicious nodes
sending queriers on false trails. This is a DoS attack,
so cryptographic challenges are of no help.
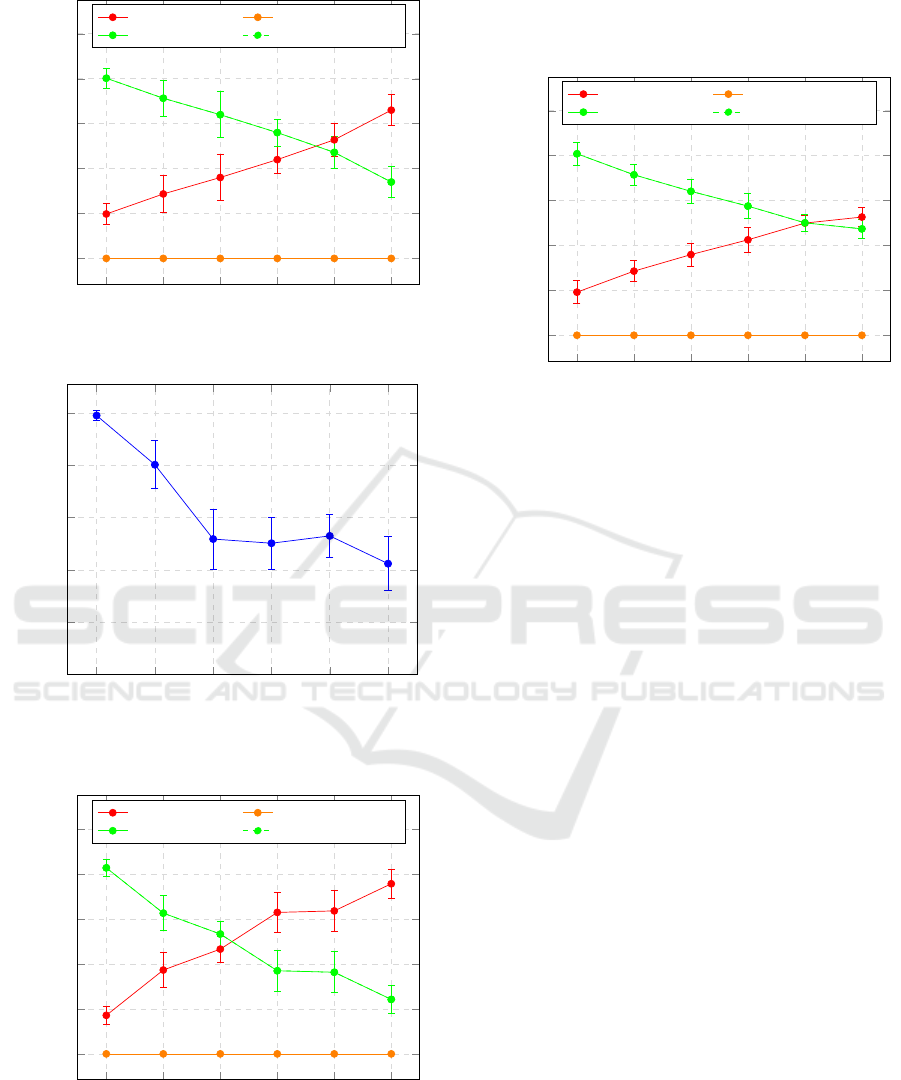
Is Sibling Attack. Resolve success rate drops in the
presence of an attacker performing an Is Sibling At-
tack, as shown in Figure 7. This is because, in this
scenario, resolve calls are ultimately replied to by the
first malicious node reached when trying to find the
node responsible for the desired AOR, whether it is
DCNET 2017 - 8th International Conference on Data Communication Networking
50
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
0.5
0
20
40
60
80
100
Probability of any node to be malicious
Percentage of total resolve calls [%]
Failed resolves Failed challenges
Successful challenges Successul w/o challenge
Figure 4: Invalid Data Attack — Resolve Calls Statistics.
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
0.5
0
5
10
15
20
25
Probability of any node to be malicious
Number of Peers
Figure 5: Invalid Nodes Attack — Peers that Successfully
Join the DHT.
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
0.5
0
20
40
60
80
100
Probability of any node to be malicious
Percentage of total resolve calls [%]
Failed resolves Failed challenges
Successful challenges Successul w/o challenge
Figure 6: Invalid Nodes Attack — Resolve Calls Statistics.
responsible for the queried data or not. The ability of
nodes to join the DHT is unaffected, however, as this
attack specifically targets DHT-level GET operations,
used for resolves. Cryptographic challenges have no
impact as resolves are either answered truthfully or
not at all.
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
0.5
0
20
40
60
80
100
Probability of any node to be malicious
Percentage of total resolve calls [%]
Failed resolves Failed challenges
Successful challenges Successul w/o challenge
Figure 7: Is Sibling Attack — Resolve Calls Statistics.
6.2.2 Attacks Demonstrating the Effectiveness of
the PKI
The following attacks target data integrity, with
knowledge of the P2PSIP application, thus making
them effective and impossible to detect without some
security mechanism in place. The cryptographic chal-
lenge mechanism that we have implemented is ex-
pected to prove useful in this context.
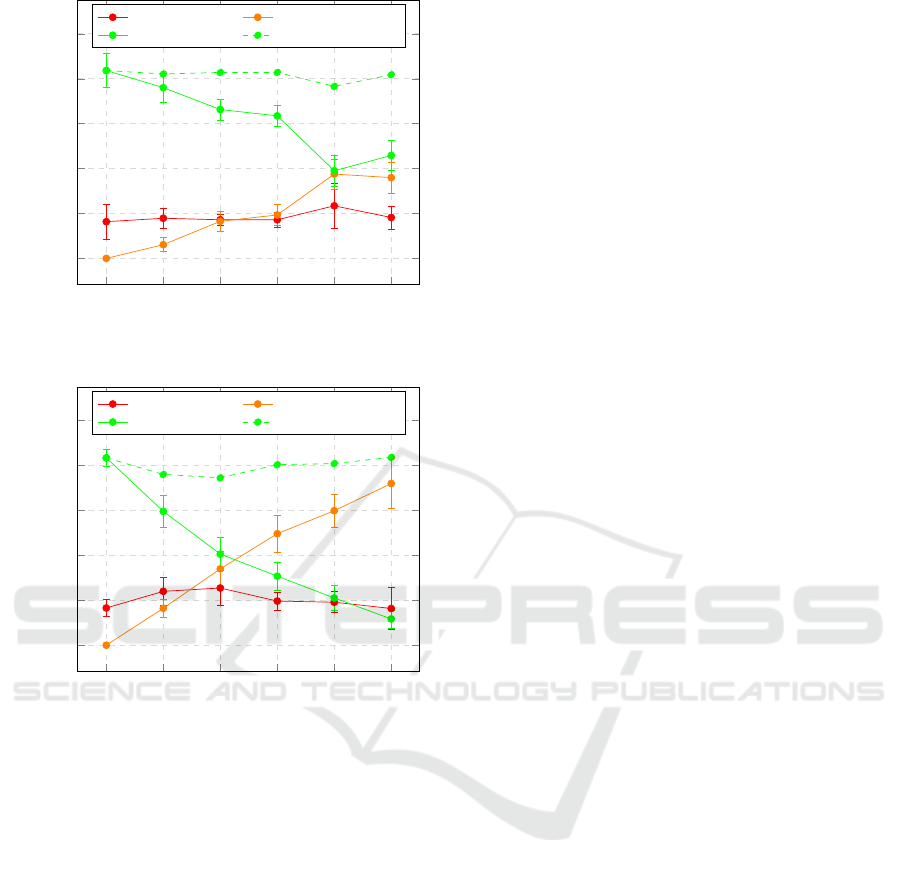
Resolve to Self Attack. This attack does not affect
nodes joining the DHT, but it does affect resolve calls,
as they are the target of the attack. It is also unde-
tectable without a security mechanism in place, as
shown in Figure 8, because responses are valid IP ad-
dress of a (malicious) node in the network.
Resolve to Self and Is Sibling Attacks Combined.
This attack has the same kind of impact as the Re-
solve to Self Attack alone, only the Is Sibling Attack
worsens the situation. When trying to find the node
responsible for the queried AOR, the first malicious
node reached will resolve the call to itself. This is
shown in Figure 9.
6.3 Discussion
As expected, the simulation of attacks presented in
Section 6.2.1 had the effect of denying service to hon-
est nodes. The Drop Find Node Attack and Invalid
Nodes Attack both prevented some peers from join-
ing the DHT by preventing them from locating peers
that had already joined. All of these attacks made the
Toward Testing Security Attacks and Defense Mechanisms for P2PSIP in MANETs with a Simulator
51
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
0.5
0
20
40
60
80
100
Probability of any node to be malicious
Percentage of total resolve calls [%]
Failed resolves Failed challenges
Successful challenges Successul w/o challenge
Figure 8: Resolve to Self Attack — Resolve Calls Statistics.
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
0.5
0
20
40
60
80
100
Probability of any node to be malicious
Percentage of total resolve calls [%]
Failed resolves Failed challenges
Successful challenges Successul w/o challenge
Figure 9: Is Sibling and Resolve to Self Attack — Resolve
Calls Statistics.
success rate of resolve requests drop as the number of
malicious nodes increased. This is either because they
prevented the requests from reaching the node respon-
sible for the queried data (Drop Find Node Attack, In-
valid Nodes Attack and Is Sibling Attack) or because
malicious nodes did tamper with the data they were
responsible for (Invalid Data Attack), but in a way
that is easily detected by the P2PSIP application —
i.e. by replying to requests with data that is not a con-
tact address.
Results for the attack scenario that we have im-
plemented ourselves, the Resolve to Self Attack, are
also as we expected them to be. With any node in
the network having probability Pr of being malicious
and performing this attack, any resolve request should
succeed with a little more than probability Pr (ac-
counting for the case where a malicious node is re-
sponsible for its own AOR and replies with the cor-
rect address when resolving it). Figure 8 shows that
our results generally follow that rule. This figure
also shows the effectiveness and usefulness of the de-
fense mechanism presented in Section 5.1 to protect
data integrity. All the failed challenges shown would
have been considered successful resolves without this
mechanism, meaning the node performing the request
would have initiated communication with the mali-
cious node that responded. Instead, these failed chal-
lenge only mean that the SIP URI could not be re-
solved, effectively turning the attack into a DoS.
Also expected was the fact that combining the Is
Sibling Attack with the Resolve to Self Attack would
amplify the negative effect on resolve success rate. By
comparing orange lines in Figures 8 and 9, we can
see that with our simulation parameters (i.e. 25 nodes
with probability of being malicious from 0.1 to 0.5),
the addition of the Is Sibling Attack roughly doubled
the attack rate. This is explained by the fact that, in
this scenario, all resolve requests going through a ma-
licious node, while trying to find a path to the node
responsible for the queried AOR, will be replied to by
this node with its own address, rather than just the re-
quests it is actually responsible for. Again, the crypto-
graphic challenge mechanism proved useful by turn-
ing these data integrity attacks into DoS attacks.
7 CONCLUSION
Security in P2P networks has already been studied.
However, proposed solutions are usually very generic
and do not address challenges specific to a given
context and application. By focusing on the threat
model for VoIP applications (through SIP) in military
MANETs, we were able to identify threats that are not
usually part of the P2P security literature such as DHT
poisoning and replay attacks. When experimenting in
the OverSim P2P simulator, we quickly found that ex-
isting attack scenarios are too generic to be applicable
in a specific context. Hence, we conclude that efforts
regarding the security of specific P2P systems is im-
portant and should be further explored.
In this paper, we detailed the threat model affect-
ing our military MANET used for P2PSIP. We then
presented a security solution both to protect data in-
tegrity and make the network more resilient to DoS
attacks. We simulated the data integrity protection
mechanism, based on a cryptographic challenge, in
OverSim and showed its effectiveness and importance
through experimentation.
As future work, we plan to implement the re-
silience part of our security solution. For instance,
we will work on having signed and timestamped in-
sertion requests and using storage redundancy. We
will also integrate other meaningful attack scenarios
DCNET 2017 - 8th International Conference on Data Communication Networking
52

(e.g., DHT poisoning and replay attacks). Further-
more, we will include node mobility in the experiment
to provide a simulation more representative of the ac-
tual context. Finally, performing experimental com-
parison between our solution and existing ones would
provide a clearer picture regarding the differences and
their impacts.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Research was sponsored by the Army Research Lab-
oratory/US Army RDECOM-Americas and was ac-
complished under Cooperative Agreement Number
W911NF-16-1-0345. The views and conclusions con-
tained in this document are those of the authors and
should not be interpreted as representing the official
policies, either expressed or implied, of the Army Re-
search Laboratory/US Army RDECOM-Americas or
the U.S. Government. The U.S. Government is au-
thorized to reproduce and distribute reprints for Gov-
ernment purposes notwithstanding any copyright no-
tation herein.
REFERENCES
Androutsellis-Theotokis, S. (2002). A survey of peer-to-
peer file sharing technologies. White paper - athens
university of economics and business.
Banerjee, N., Acharya, A., and Das, S. K. (2004). Peer-
to-peer SIP-based services over wireless ad hoc net-
works. In BROADWIM: Broadband Wireless Multi-
media Workshop.
Banerjee, N., Acharya, A., and Das, S. K. (2005). Enabling
SIP-based session setup in ad hoc networks. In Pro-
ceedings of INFOCOM.
Baumgart, I. (2008). P2pns: A secure distributed name ser-
vice for p2psip. In Pervasive Computing and Com-
munications, 2008. PerCom 2008. Sixth Annual IEEE
International Conference on, pages 480–485. IEEE.
Baumgart, I., Heep, B., and Krause, S. (2007). OverSim:
A flexible overlay network simulation framework. In
Proceedings of 10th IEEE Global Internet Symposium
(GI ’07) in conjunction with IEEE INFOCOM 2007,
Anchorage, AK, USA, pages 79–84.
Bryan, D. A., Lowekamp, B. B., and Zangrilli, M. (2008).
The design of a versatile, secure p2psip communica-
tions architecture for the public internet. In Parallel
and Distributed Processing, 2008. IPDPS 2008. IEEE
International Symposium on, pages 1–8. IEEE.
Clausen, T. and Jacquet, P. (2003). Optimized link state
routing protocol (olsr). RFC 3626.
Douceur, J. R. (2002). The sybil attack. In Peer-to-Peer
Systems, First International Workshop, IPTPS 2002,
Cambridge, MA, USA, March 7-8, 2002, Revised Pa-
pers, pages 251–260.
Fonville, M. (2010). Confidential peer-to-peer file-sharing
using social-network sites. In 13th Twente Student
Conference on IT, Jun, volume 21, page 10.
Freedman, M. J. and Morris, R. (2002). Tarzan: a peer-to-
peer anonymizing network layer. In Proceedings of
the 9th ACM Conference on Computer and Commu-
nications Security, CCS 2002, Washington, DC, USA,
November 18-22, 2002, pages 193–206.
Fudickar, S., Rebensburg, K., and Schnor, B. (2009).
MANETSip - a dependable SIP overlay network for
MANET including presentity service. In Network-
ing and Services, 2009. ICNS ’09. Fifth International
Conference on, pages 314–319.
Giordano, S. et al. (2002). Mobile ad hoc networks.
Handbook of wireless networks and mobile comput-
ing, pages 325–346.
Ismail, H., Germanus, D., and Suri, N. (2015). Detecting
and mitigating P2P eclipse attacks. In 21st IEEE Inter-
national Conference on Parallel and Distributed Sys-
tems, ICPADS 2015, Melbourne, Australia, December
14-17, 2015, pages 224–231.
Jennings, C., Lowekamp, B., Rescorla, E., S.Baset, and
Schulzrinne, H. (2014). REsource LOcation And Dis-
covery (RELOAD) Base Protocol. RFC 6940.
Levine, B. N., Shields, C., and Margolin, N. B. (2006). A
survey of solutions to the sybil attack. Technical Re-
port - University of Massachusetts Amherst.
Li, L. and Lamont, L. (2005). Support real-time interactive
session applications over a tactical mobile ad hoc net-
work. In Military Communications Conference, 2005.
MILCOM 2005. IEEE, pages 2910–2916. IEEE.
O’Driscoll, A., Rea, S., and Pesch, D. (2007). Hierarchi-
cal clustering as an approach for supporting P2P SIP
sessions in ubiquitous environments. In 9th IFIP In-
ternational Conference on Mobile Wireless Communi-
cations Networks, MWCN 2007, Cork, Ireland, 19-21
September, 2007, pages 76–80. IEEE.
Rennhard, M. and Plattner, B. (2002). Introducing mor-
phmix: peer-to-peer based anonymous internet usage
with collusion detection. In Proceedings of the 2002
ACM Workshop on Privacy in the Electronic Society,
WPES 2002, Washington, DC, USA, November 21,
2002, pages 91–102.
Rosenberg, J., Schulzrinne, H., Camarillo, G., Johnston, A.,
Peterson, J., Sparks, R., Handley, M., and Schooler, E.
(2002). Sip: session initiation protocol. RFC 3261.
Schollmeier, R. (2001). A definition of peer-to-peer net-
working for the classification of peer-to-peer architec-
tures and applications. In Peer-to-Peer Computing,
2001. Proceedings. First International Conference on,
pages 101–102. IEEE.
Seedorf, J. (2006). Using cryptographically generated sip-
uris to protect the integrity of content in p2p-sip. In
Third Annual VoIP Security Workshop.
Stoica, I., Morris, R., Karger, D., Kaashoek, M. F.,
and Balakrishnan, H. (2001). Chord: A scalable
peer-to-peer lookup service for internet applications.
ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review,
31(4):149–160.
Stuedi, P., Bihr, M., Remund, A., and Alonso, G. (2007).
SIPHoc: Efficient SIP middleware for ad hoc net-
Toward Testing Security Attacks and Defense Mechanisms for P2PSIP in MANETs with a Simulator
53

works. In Cerqueira, R. and Campbell, R. H., editors,
Middleware 2007, ACM/IFIP/USENIX 8th Interna-
tional Middleware Conference, Newport Beach, CA,
USA, November 26-30, 2007, Proceedings, volume
4834 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages
60–79. Springer.
Urdaneta, G., Pierre, G., and van Steen, M. (2011). A sur-
vey of DHT security techniques. ACM Comput. Surv.,
43(2):8:1–8:49.
Varga, A. and Hornig, R. (2008). An overview of the om-
net++ simulation environment. In Proceedings of the
1st international conference on Simulation tools and
techniques for communications, networks and sys-
tems & workshops, page 60. ICST (Institute for Com-
puter Sciences, Social-Informatics and Telecommuni-
cations Engineering).
Wang, Q. and Borisov, N. (2012). Octopus: A secure
and anonymous dht lookup. In Distributed Comput-
ing Systems (ICDCS), 2012 IEEE 32nd International
Conference on, pages 325–334. IEEE.
Wendlandt, D., Andersen, D. G., and Perrig, A. (2008).
Perspectives: improving ssh-style host authentica-
tion with multi-path probing. In 2008 USENIX Annual
Technical Conference, Boston, MA, USA, June 22-27,
2008. Proceedings, pages 321–334.
Wongsaardsakul, T. (2010). P2P SIP over mobile ad hoc
networks. PhD thesis, Evry, Institut national des
t
´
el
´
ecommunications.
Yahiaoui, S., Belhoul, Y., Nouali-Taboudjemat, N., and
Kheddouci, H. (2012). AdSIP: Decentralized SIP for
mobile ad hoc networks. In Advanced Information
Networking and Applications Workshops (WAINA),
2012 26th International Conference on, pages 490–
495.
DCNET 2017 - 8th International Conference on Data Communication Networking
54
