
A Fuzzy Logic Approach to Improve Phone Segmentation
A Case Study of the Dutch Language
Victor Milewski
1
, Aysenur Bilgin
1
and Tufan Kumbasar
2
1
Institute for Logic, Language and Computation, University of Amsterdam, Science Park 107, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
2
Control and Automation Engineering Department, Istanbul Technical University, Istanbul, Turkey
Keywords:
Fuzzy Logic Systems, Phone Segmentation, IFA Corpus, Automatic Speech Recognition.
Abstract:
Phone segmentation is an essential task for Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems, which still lack
in performance when compared to the ability of humans’ speech recognition. In this paper, we propose novel
Fuzzy Logic (FL) based approaches for the prediction of phone durations using linguistic features. To the
best of our knowledge, this is the first development and deployment of FL based approaches in the area of
phone segmentation. In this study, we perform a case study on the Dutch IFA corpus, which consists of
50000 words. Different experiments are conducted on tuned FL Systems (FLSs) and Neural Networks (NNs).
The experimental results show that FLSs are more efficient in phone duration prediction in comparison to
their Neural Network counterparts. Furthermore, we observe that differentiating between the vowels and the
consonants improves the performance of predictions, which can facilitate enhanced ASR systems. The FLS
with the differentiation between vowels and consonants had an average Mean Average Precision Error of
43.3396% on a k=3 fold. We believe that this first attempt of the employment of FL based approaches will be
an important step for a wider deployment of FL in the area of ASR systems.
1 INTRODUCTION
Speech is naturally the most basic and efficient way
of communication between human beings. In order to
mimic this form of communication and interact with
computers via speech, Automatic Speech Recognition
(ASR) systems have been under development for over
five decades (Yu and Deng, 2014). With the recent ad-
vancements in the field, ASR systems have been en-
tering our daily lives through commercialised systems
that offer voice activation for intelligent personal as-
sistants. Examples of such systems are Google Assis-
tant
1
, Apple’s Siri
2
, Microsoft’s Cortana
3
and Ama-
zon’s Alexa
4
. Despite the impressive embarking of
ASR systems in real life, these systems still suffer
from significant performance gaps when compared
to human speech recognition, and therefore are re-
strained from being widely accepted in real-world sit-
uations (Garg and Sharma, 2016).
The primary goal of an ASR system is to automat-
ically transcribe the speech from an audio fragment
1
https://assistant.google.com/
2
http://www.apple.com/uk/ios/siri/
3
https://www.microsoft.com/en/mobile/experiences/cortana/
4
https://developer.amazon.com/alexa-voice-service
(Jurafsky and Martin, 2014). Typical architecture of
ASR systems has four main components: signal pro-
cessing and feature extraction, acoustic model, lan-
guage model and hypothesis search (Yu and Deng,
2014). Essential to the successful behaviour of
ASR systems is training the system on large speech
databases. These databases need to be annotated with
the words and phones. For several databases, the
annotation is constructed manually (Garofolo et al.,
1993; Son et al., 2001). However, manual segmenta-
tion is not only a very time consuming and expensive
task but also exposed to inconsistencies as multiple
people working on the task may use different styles
of annotation. Therefore, there is a need for automatic
phone segmentation that will facilitate annotating the
data to be used in the training of ASR systems. A
challenge of the automatic phone segmentation, how-
ever, is that phone transitions are not very clear and
may differ extensively according to a number of fac-
tors (Yu and Deng, 2014). These factors include,
for example, different speech rates and different pro-
nunciations of various speakers, environment noise as
well as connected utterances of separate words and
phones. A successful ASR system must take into ac-
count these factors, which may be referred to be the
Milewski V., Bilgin A. and Kumbasar T.
A Fuzzy Logic Approach to Improve Phone Segmentation - A Case Study of the Dutch Language.
DOI: 10.5220/0006499800640072
In Proceedings of the 9th International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence (IJCCI 2017), pages 64-72
ISBN: 978-989-758-274-5
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

major causes of uncertainty.
In this paper, we use Fuzzy Logic (FL), which is a
powerful tool to handle real-world uncertainties, and
present pioneering FL based approaches to improve
the phone segmentations in ASR systems. Specifi-
cally, this study focuses on building upon the feature
extraction component in ASR systems using FL and
investigates the impact of phone durations, which in-
herently bear uncertainty due to the aforementioned
factors. Predicting the actual durations of the phones
can be used to enhance the quality of the annotations
by improving the boundaries of the annotated phones,
and hence facilitate advanced ASR systems. In this
context, we propose two methods for constructing
FL based systems that will improve the phone seg-
mentations by using phone durations. For evaluation
purposes, the efficiency of the developed FL based
methods are compared to their Neural Network (NN)
counterparts on the Dutch language data set. The FL
system (FLS) is fitted to the data using the adaptive-
network-based fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) tool-
box (Jang et al., 1991)(Jang, 1993) of MATLAB
5
. To
the best of our knowledge, this is a pioneering system
that uses the distinct features of vowels and conso-
nants (non-vowels) in combination with ANFIS.
The rest of the paper is organised as follows: Sec-
tion 2 presents an overview of the previous work on
phone segmentation. In Section 3, the Dutch dataset
is presented. The proposed FL based approaches are
presented in Section 4. The experiments and results
are discussed in Section 5. Finally, Section 6 presents
the conclusions and future work.
2 PREVIOUS WORK
The most widely used technique for phone segmen-
tation is the Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) with
embedded training (Jurafsky and Martin, 2014). An
HMM is a chain of states, where each transition de-
fines a probability of going from one state to the next.
In an ASR system, the states represent phones, and
a chain represents a word in the language (Rabiner,
1989; Yu and Deng, 2014). With the use of HMMs,
the waveform can be aligned to the states by sampling
it into frames where each frame is matched to the most
corresponding phone. A disadvantage of this method
is that the frames are of fixed size. However, the dura-
tion of the annotated phones may require being longer
or shorter and therefore, the phone boundaries using
fixed frames are not very accurate (Zi, 2009). In or-
der to tackle this shortcoming, the predicted durations
5
https://nl.mathworks.com/products/matlab.html
can be utilised as an additional probability measure in
HMMs that will facilitate determining the likelihood
of the phones in a more accurate and robust way.
Due to the potential improvements allowed by
utilising phone durations, various studies have been
conducted in different languages. In a recent work,
which focussed on speaker recognition, Igras et al.
(Igras et al., 2014) investigated the use of phone dura-
tions in the Polish language. Their findings suggested
that the average durations of the phones are charac-
teristic for speakers, and that phone durations can be
applied on speech recognition and synthesis. In a
later study, Igras and Ziolko (Igras and Zi
´
ołko, 2016)
showed that phone durations are useful for sentence
boundary detection in the spoken Polish language.
Phone duration modelling has been shown to be im-
portant for speech synthesis also in the Lithuanian
language by Kasparaitis et al. (Kasparaitis and Be-
niu
ˇ
s
˙
e, 2016). Another study conducted by Goubanova
et al. (Goubanova and King, 2008) used linguis-
tic factors for predicting phone durations. Consider-
ing different features for vowels and consonants, they
trained Bayesian Networks for the English language.
One of the areas FL has often been used
in, is speech based emotion recognition (Lee
and Narayanan, 2003)(Grimm and Kroschel,
2005)(Giripunje and Bawane, 2007). In order to
achieve emotion recognition a lot of speech features
are used, with some of them similar to the features
used in the current study (which are described in
Section 4.1). Although for a different goal, these
studies show that features like the formants are well
suited for the use in speech based predictive FLSs.
However, FL has not been widely applied in the
prediction of phone durations although it is a pow-
erful tool to deal with real-world uncertainties. Zi-
olko (Zi
´
ołko, 2015) used FL for evaluating the seg-
mented phones based on their durations in the Polish
language. Unlike Ziolko (Zi
´
ołko, 2015), we use FL
for predicting phone durations in this study.
As a case study, we use Dutch language, which
has nine types of phones: short vowels, long vowels,
diphthongs, schwa, plosives, fricatives, nasals, liq-
uids, and glides (Pols, 1983). The vowels in the Dutch
language have been shown to be easily recognised by
using the first and second formant from the audio sig-
nal (Pols et al., 1973). This classification is visualised
in Figure 1, which displays a potential clustering pat-
tern for this data. We present the details of the Dutch
dataset in the following section.

Figure 1: The logarithm of the first two formants for the 12
vowels in Dutch language (Pols et al., 1973).
3 DUTCH LANGUAGE
DATABASE
In order to show the efficiency of the proposed FL
based methods, we will use the data provided by the
IFA Spoken Language Corpus v1.0 (Son et al., 2001).
This is a free (GPL) database of hand-segmented
Dutch speech
6
and is distributed by The Dutch Lan-
guage Organization (Nederlandse Taalunie)
7
. The
Ducth Language was chosen, since it is well known
by the authors, which made it easier to understand cer-
tain features and duration occurrences in the speech.
The IFA corpus has been used in research on Artic-
ulatory Features (Ten Bosch et al., 2006), Prosodic
Features (Schuller et al., 2008), diphthong analysis
(Jacobi et al., 2005), conversation detection (Harma
and Pham, 2009) and more. The IFA corpus consists
of a total of 50000 words spoken by eight different
speakers where four are male, and the other four are
female. The ages of the speakers range between 20
and 70.
In this case study, each of the spoken phones in the
IFA corpus is represented as a data structure
8
com-
posed of the duration of the phone and several dis-
tinct features, which are presented in Section 4. Af-
ter pre-processing
9
the dataset, which leads to a total
6
http://www.fon.hum.uva.nl/IFA-
SpokenLanguageCorpora/IFAcorpus/
7
http://taalunie.org/
8
We will refer to this data structure as data point in the rest
of the paper and in the figures.
9
The IFA corpus comes in files formatted for the program
Praat. This textgrid format was transformed to a mlf for-
mat which has on one line the start time of a phone, the
end time of a phone, which phone was uttered, and if it is
the first phone of a word, which word begins at this time.
of 175184 phones, the data is split into three subsets
for training, validation, and testing to be used by the
first approach (see Section 4.2). Each of the subsets
uses 70%, 15%, and 15% of the entire data, respec-
tively. Splitting the data is carried out randomly by
using a random generator with a fixed random seed.
Due to the random generation of the subsets, an unfair
separation can be created which might give skewed
results in the experiments. Therefore, we employ a
k-fold cross-validation strategy, where k=3, and per-
form three different splits using the same percentages.
For the second approach (see Section 4.3), the data
is first separated into the vowels and the consonants
(non-vowels). This results in two datasets: a dataset
consisting of 110012 consonants (non-vowels) and
a dataset consisting of 65172 vowels. These two
datasets are also further split into k=3 folds for train-
ing, validation, and testing using the same random
seed and the same percentages as stated above.
4 FL APPROACHES FOR PHONE
SEGMENTATION
FL, which was introduced by Zadeh in 1965 (Zadeh,
1965), is referred to be an extension to classical
crisp logic. The building blocks of FL, which are
fuzzy sets, are characterized by a membership func-
tion (MF). The MF associates each point in the uni-
verse of discourse with a real number in the interval
[0,1], which is called a membership degree. The ob-
jective of a FLS, as depicted in Figure 2, is to map the
inputs to the outputs by the help of fuzzy reasoning
that is encoded in the rules. The generic rule struc-
ture of a FLS composed of N rules (n = 1, . . . , N) is
formalised as follows (Mendel, 2001):
R
n
:IF x
1
is X
n
1
and . . . and x
I
is X
n
I
THEN y is Y
n
1
(1)
where X
n
i
(i = 1, . . . , I) are the antecedent MFs and Y
n
are the consequent MFs. A complete rule base incor-
porates all the combinations of the antecedents, which
are the variables used in the system design. In the
proposed FLSs, we use product implication and the
weighted average defuzzification method.
In this study, we used ANFIS toolbox of MAT-
LAB to employ the following techniques in the con-
struction of a rule base: Grid Partitioning (GP) (Jang,
1993), Subtractive Clustering (SC) (Chiu, 1996), and
Fuzzy C-Means (FCM) Clustering (Bezdek et al.,
1984). For the system using the GP approach, a com-
plete rule base needs to be generated. On the other
hand, the system using FCM clustering generates one
rule for a given number of clusters. And, the system
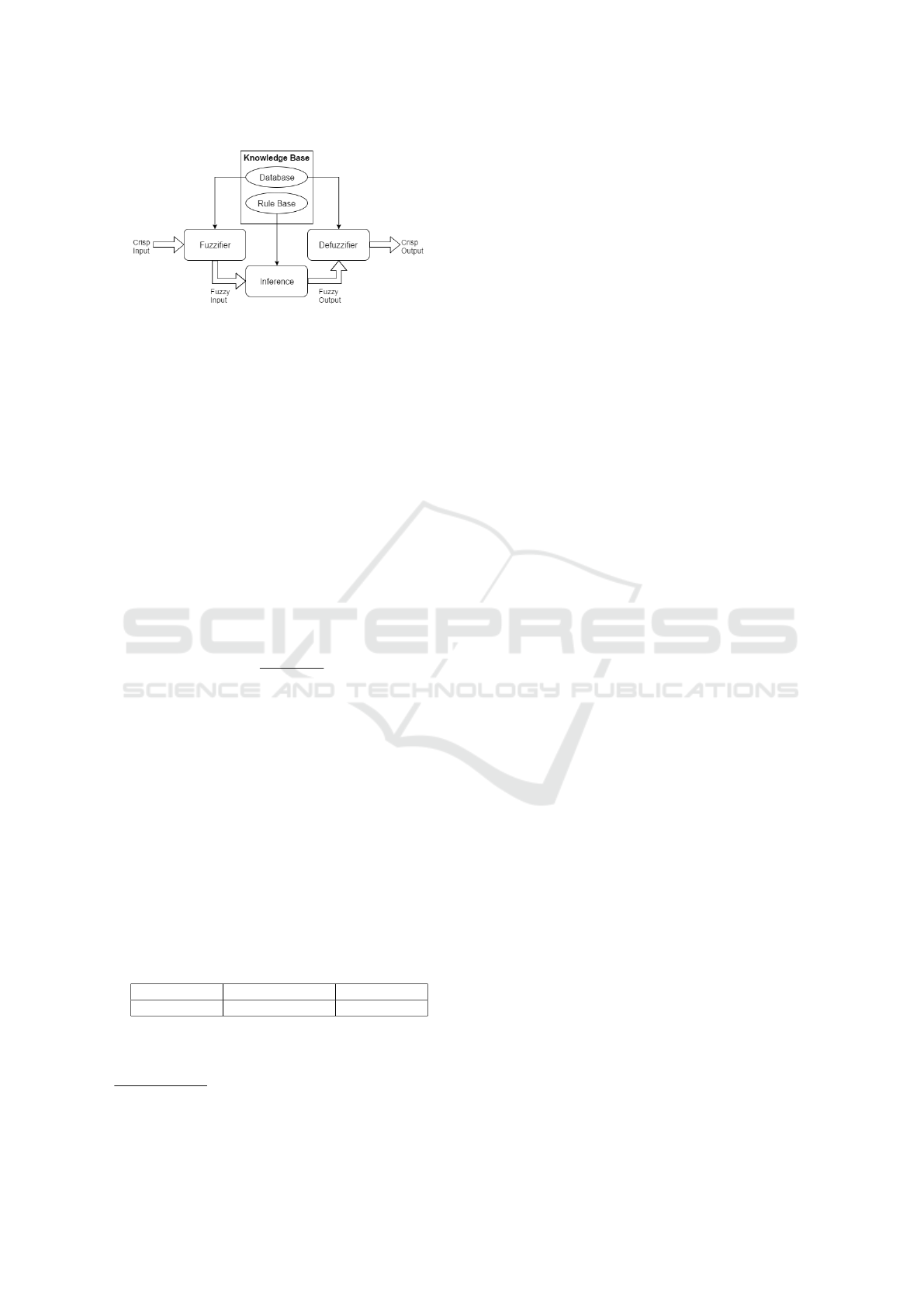
Figure 2: Schematic overview of a FLS.
using SC decides on the number of clusters (equal to
the number of rules) depending on the data and a de-
fined radii. The radii specifies how important each
of the variables is
10
. The ANFIS toolbox generates
Sugeno type Inference Systems
11
. During the infer-
ence of the FLS, the first step is to determine the fir-
ing strength for each of the rules. Each of the an-
tecedents (IF part of the rule) has a membership de-
gree, and with the combination method, the strength
for the rule is determined. For combining the an-
tecedents in a rule to calculate the firing strength, the
product method is used. The firing strength of the rule
is applied to the consequent (THEN part of the rule).
The consequents of all the fired rules are combined
to calculate a crisp output with the following equa-
tion(Mendel, 2001):
z =
∑
N
n=1
y
n
w
n
∑
N
n=1
w
n
(2)
where z is the defuzzified output, y
n
is the output for
rule n, and w
n
is the firing strength of rule n.
In this study, we propose two FL based systems
that utilise distinct sets of features, some of which
are introduced for the first time in the literature. The
features are discussed in Section 4.1. The first FLS,
referred to as S-FLS is explained in further detail in
Section 4.2. The second system, referred to as P-FLS,
consists of two FL based subsystems that are designed
separately for vowels and consonants (non-vowels).
P-FLS is presented in Section 4.3.
4.1 Feature Sets
Table 1: The distinct feature sets employed by the FLSs.
Feature Set 1 Feature Set 2 Feature Set 3
f
1
, f
2
, f
3
, f
4
f
1a
, f
1b
, f
2
, f
3
, f
4
f
2
, f
3
, f
4
, f
5
We compiled three different feature sets to be used
by the FLSs. It should be noted that the formants
10
https://nl.mathworks.com/help/fuzzy/genfis2.html
11
https://nl.mathworks.com/help/fuzzy/anfis.html
are used for recognizing vowels in the literature, how-
ever, we introduce a novel use for the formants where
we exploit them for phone duration prediction. An
overview of the feature sets is given in Table 1. The
descriptions of the features are as follows:
f
1
: In the Dutch language, all phones can be cat-
egorised into nine types (Pols, 1983). In this
study, we use 6 phone types as follows: vow-
els, diphthongs, vowel-likes, plosives, frica-
tives, and nasals. Feature f
1
is a constant for
the phone type that takes on the integer val-
ues {0,1,2,3,4,5}, with each value representing
a particular phone type.
f
2
: This feature represents the location of the phone
in the word. Its value is normalised to the unit
interval [0,1].
f
3
: This feature represents the location of the word
in the sentence (for the phone that is being ut-
tered). Its value is normalised to the unit inter-
val [0,1].
f
4
: This feature is the speech rate, which represents
how fast the speaker is talking. Its value is nor-
malised to the unit interval [0,1]. The under-
lying idea is that the number of words spoken
per second has an impact on the duration of the
phones. For example, if more words per sec-
ond are spoken, the durations of the phones will
decrease accordingly.
f
5
: Similar to feature f
1
. However, the phone type
vowel is excluded, which results in five classes
that are used.
f
1a
: The logarithm of the first formant from the time
fragment the vowel is in.
f
1b
: The logarithm of the second formant from the
time fragment the vowel is in.
The features f
1
, f
2
, f
3
, and f
4
were also employed by
Pols et al. (Pols et al., 1996). However, we introduce
the use of the features f
5
, f
1a
and f
1b
for the first time
in the literature.
4.2 S-FLS: The Simple FLS
The first proposed system, namely the Simple FLS(S-
FLS), is built on the assumption that all phones within
a single category behave the same. An overview of
this system is depicted in Figure 3. S-FLS employs
the default configuration wich uses the GP technique
for the construction of the rule base and has a linear
output MF. Furthermore, S-FLS makes use of Feature
Set 1 in Table 1.

Figure 3: Overview of phone duration prediction in S-FLS.
4.3 P-FLS: The Parallel Structured FLS
The assumption employed for S-FLS, which states
that all phones within a single phone type behave sim-
ilarly, works reasonably well for a couple of types.
However, the vowels are used more often in the Dutch
language, and they can show different behaviour in
comparison with the other types of phones. There-
fore, in order to handle such uncertainties, we pro-
pose a hierarchical FLS that is composed of two
sub-FLSs; one for representing the consonants (non-
vowels) (SubFLS C) and one for representing the
vowels (SubFLS V), separately. The overview of the
Parallel FLS(P-FLS) is given in Figure 4.
4.3.1 SubFLS C
SubFLS C, which is trained on consonants (non-
vowels), makes use of Feature Set 3 in Table 1. Sim-
ilar to S-FLS, default configuration that employs the
GP technique is used for the construction of the rule
base for SubFLS C.
4.3.2 SubFLS V
SubFLS V, which is trained on vowels only, employs
Feature Set 2 in Table 1. In this feature set, the phone
type feature ( f
1
) is replaced with two new features. As
mentioned in Section 2, using the first two formants
(see Figure 1), the vowels can be recognised with suf-
ficiently high accuracy (Pols et al., 1973). Therefore,
in SubFLS V, we use features f
1a
and f
1b
, as inputs
for the purpose that the system can learn vowel spe-
cific characteristics with respect to the phone dura-
tion. It can be observed from Figure 1 that recognis-
ing the vowels using the first two formants require a
clustering approach. Hence, we employ SC and FCM
clustering techniques for the construction of the rule
base for SubFLS V.
5 EXPERIMENTS, RESULTS &
DISCUSSION
This section presents the experiments and results,
which were obtained using a personal computer with
an Intel Core i7 3630QM processor, running Win 10
64-bit and MATLAB R2016b. ANFIS was set to train
for ten epochs with an initial step size of 0.01, a step
size decrease rate of 0.9 and it was optimized on the
Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE). The FLS after the
epoch with the lowest validation RMSE was used for
evaluating the performance.
We begin by presenting the results of the tun-
ing processes of S-FLS and P-FLS in Section 5.1.
We then continue our discussions with further ex-
periments that compare the FL approaches to their
Neural Network (NN) counterparts. The Neural Net-
work Toolbox
12
from MATLAB was used. The
NNs all have a single hidden layer of ten nodes, they
were initialised with all ones and were trained for
100 epochs using the Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm
(Mor
´
e, 1978). Again, the NN after the epoch with the
lowest validation error was used as optimal trained
network.
We analyse and compare the performances of the
developed approaches by defining the error value as
the difference between the predicted phone duration
and the actual phone duration. In specific, we use the
performance measures RMSE, and the Mean Average
Percentage Error (MAPE) to make a fair comparison.
It should be noted that the presented performance val-
ues in this section are the averages of the k=3 folds.
5.1 The Design of FLSs
In the design of each FLS for phone segmentation,
there are several parameters that require tuning. For
both FLSs that use GP (S-FLS and SubFLS C within
P-FLS), the number of membership functions (MFs),
as well as the type of MFs, need to be determined. It
12
https://nl.mathworks.com/products/neural-network.html

should be noted that the phone type features ( f
1
and
f
5
) do not need to be tuned, as the values are constants
and represented using singleton fuzzy sets. Initially,
we conducted experiments using two Gaussian MFs
and two Triangular MFs for each of the features f
2
,
f
3
, and f
4
. We then increased the number of MFs
to observe the performance changes. The results for
tuning experiments are displayed in Table 2 for both
S-FLS and SubFLS C.
By comparing the results from the training set
with the results from the test set, it can be observed
from Table 2 that these values are close to each other.
This ensures that the FLSs are not over-fitting. It can
also be deduced that increasing the number of MFs
reduces both RMSE and MAPE results, and there-
fore has a positive impact on the performance. Fur-
thermore, we examined the effect of changing the
type of MFs from Gaussian to Triangular. Since the
change causes a negligible difference in performance,
we decided to continue with Gaussian MFs. Finally,
we opted for three Gaussian MFs per feature ( f
2
, f
3
,
and f
4
) for both S-FLS and SubFLS C. Even though
the errors may be further decreased by increasing the
number of MFs per feature, we have decided not to
increase the number of MFs as our aim is to provide
a proof of concept in this paper.
In the design of SubFLS V within P-FLS, the
number of clusters needs to be determined. Although
there are twelve vowels in the Dutch language, there
are only nine clusters as shown in Figure 1. There-
fore, in FCM clustering approach, we employed nine
and twelve clusters to find the optimal number of clus-
ters. Furthermore, the number of clusters has been in-
creased to thirty-six clusters to increase the number of
rules. In SC method, we used three different settings
for the radii values. The first setting is configured to
use the same radii value of 0.5 for all the features.
However, considering the fact that the formants play
an important role in recognition of the vowels, we de-
creased the radii values to 0.2 for both formant fea-
tures and used 0.5 for the rest of the features. In order
to identify the trends in the performance, we increased
the number of clusters, and the radii values were de-
creased to 0.1 for the formant features and to 0.2 for
the rest of the features. The results are presented in
Table 3.
Regarding the comparison between SC and FCM
clustering techniques, Table 3 shows that SC method
outperforms FCM clustering. It should be noted that
a one to one comparison cannot be made, since both
systems are not tuned with the same number of clus-
ters. A logical reason for SC outperforming FCM is
the rapidly increasing of the number of clusters with
decreasing radii values. However, FCM demonstrates
similar increase in performance when the number of
clusters is increased. In the future, a better compari-
son with an equal number of clusters should be made.
5.2 Comparison between FLSs and
Neural Network
We have compared the performance of the FLSs,
which are designed to predict phone durations, with
their NN counterparts. The systems are named as S-
NN, SubNN C and SubNN V for the counterparts of
S-FLS, SubFLS C and SubFLS V, respectively. For
the NN systems, the same features and settings as
described in Section 4 were used. For each of the
three counterpart NN systems, a single layer neural
network was created with ten nodes. We have opted
for a single hidden layer to maintain a fair comparison
in the complexity of the NN systems and the FLSs.
The results of the counterpart NN systems are demon-
strated in Table 4.
A quick comparison of the RMSE and MAPE re-
sults presented in Table 2 - Table 4 demonstrates that
the FLSs outperform their NN counterparts. Further-
more, we performed paired t-test with 95% confi-
dence interval to determine whether the improvement
in error measures between the FLSs and their NN
counterparts are statistically significant. For the sta-
tistical tests, we used both the absolute errors (AE)
(i.e. the absolute difference between the prediction
errors of FLS and counterpart NN) and the MAPE re-
sults for all the k=3 folds from the training, validation,
and test runs. The results are demonstrated in Table
5.
Most of the results presented in Table 5 show that
FLSs have, according to the paired t-test, significant
improvements over their NN counterparts as the p-
values are lower than 0.05. However, in the AE
row for Feature Set 3, it can be observed that there
is no significant difference between SubFLS V and
SubNN V. This is due to the fact that it is quite diffi-
cult to predict the phone durations for the vowels. As
shown in the Table 3 and Table 4, SubFLS V records
the lowest results.
In order to demonstrate the robustness of the per-
formances of both approaches using FL and NN, we
performed another paired t-test with 95% confidence
interval between the predicted and the actual phone
durations. We took the AE between the predicted
and the actual values of phone durations for both ap-
proaches individually. The results are presented in Ta-
ble 6.
As can be observed from Table 6, the differences
in the actual and predicted phone durations are not
significant (p > 0.05). In other words, the predictions

Figure 4: Overview of phone duration prediction in P-FLS.
Table 2: Tuning of the MF parameters for S-FLS and SubFLS C, which employs the GP method.
MF settings RMSE MAPE
System Number Type Training Validation Test Training Validation Test
2 Gaussian 0.0500 0.0467 0.0463 47.1785 46.9859 46.5857
S-FLS 2 Triangular 0.0499 0.0467 0.0462 46.9898 46.7845 46.4768
3 Gaussian 0.0491 0.0461 0.0456 45.9654 45.9271 45.6425
2 Gaussian 0.0407 0.0368 0.0447 41.3006 41.6663 41.2696
SubFLS C 2 Triangular 0.0406 0.0367 0.0446 41.1766 41.5156 41.0681
3 Gaussian 0.0399 0.0362 0.0441 40.3368 40.8010 40.4366
Table 3: Tuning of the clustering parameters for SubFLS V within P-FLS, which employs SC or FCM clustering methods.
Clustering Radii Number of RMSE MAPE
Algorithm f
1a
, f
1b
f
2
, f
3
, f
4
Clusters Training Validation Test Training Validation Test
Fuzzy
C-Means
9 0.0565 0.0576 0.0592 51.1408 51.3355 51.0067
12 0.0561 0.0573 0.0586 50.1382 50.5860 50.0325
36 0.0550 0.0564 0.0580 48.8078 49.4466 49.1826
Subtractive
Clustering
0.5 0.5 6 0.0587 0.0597 0.0610 55,1802 55,7577 54,9291
0.2 0.5 11 0.0566 0.0577 0.0591 50.2379 50.2936 50.4446
0.1 0.2 258 0.0525 0.0557 0.0574 46.0806 47.9864 48.2402
Table 4: Results of counterpart NN systems, S-NN for S-FLS, SubNN C for SubFLS C, and SubNN V for SubFLS V.
RMSE MAPE
System Training Validation Test Training Validation Test
S-NN 0.0498 0.0464 0.0460 46.9563 46.7046 46.4153
SubNN C 0.0406 0.0367 0.0446 40.9604 41.3023 40.9007
SubNN V 0.0578 0.0564 0.0578 48.2689 48.4094 48.3892
for the phone durations given by both the FL and NN
approaches are close enough to the real-world values.
This means that the proposed FLSs can predict phone
durations quite accurately.

Table 7: Comparison results of S-FLS and P-FLS where the results from SubFLS C and SubFLS V are merged for P-FLS.
RMSE MAPE
Training Validation Test Training Validation Test
S-FLS 0.0491 0.0461 0.0456 45.9654 45.9271 45.6425
P-FLS 0.0450 0.0445 0.0497 42.4736 43.4741 43.3396
Table 5: Results of the paired t-test between the FLSs and
their NN counterparts for the AE and MAPE (p-values are
shown in parentheses).
Feature Set 1 Feature Set 2 Feature Set 3
AE
significant
(1.3183e-21)
significant
(1.0331e-04)
not significant
(0.1278)
MAPE
significant
(4.5072e-07)
significant
(2.2122e-07)
significant
(0.0258)
Table 6: Results of the paired t-test between the actual and
the predicted phone durations for both the FLSs and their
NN counterparts (p-values are shown in parentheses).
FLS NN
Feature Set 1
not significant
(0.4812)
not significant
(0.4246)
Feature Set 2
not significant
(0.9956)
not significant
(0.9719)
Feature Set 3
not significant
(0.7928)
not significant
(0.4427)
5.3 Comparison between S-FLS and
P-FLS
In this subsection, we present the results of the com-
parison performed between the simple approach (S-
FLS) and the parallel structured approach (P-FLS).
To reiterate, S-FLS is trained on the entire dataset
whereas P-FLS, composed of two subsystems, is
trained on separate vowels and consonants dataset.
Therefore, the errors from both subsystems of P-FLS
(i.e., SubFLS V and SubFLS C) are merged into a sin-
gle set of errors for each of k=3 folds and the corre-
sponding training, validation, and test set. RMSE and
MAPE results for S-FLS and P-FLS are reported in
Table 7. It can be observed that in all of the results
except the RMSE obtained from the test set, P-FLS
outperforms S-FLS. We performed statistical tests in
order to determine whether the difference in these re-
sults are significant. While using a paired t-test for
MAPE, we used a two-sampled t-test for the AE due
to the separation of the system and a potentially dif-
ferent order of errors recorded. The results for these
t-tests are shown in Table 8.
As can be observed from Table 8, the differences
are indeed significant, according to the paired t-test.
For the MAPE, P-FLS is significantly better than S-
FLS as also shown in Table 7. Since S-FLS performed
Table 8: Results of the paired t-test between the MAPE
scores and the two-sampled t-test of the AE for S-FLS and
P-FLS.
Significant P-value Confidence Interval
MAPE Yes 0.0057 (1.1409, 4.3576)
AE Yes 0.0180 (0.0005, 0.0018)
better on the RMSE results obtained from the test set,
we also checked the consistency of the results by ex-
amining the confidence intervals, which are reported
in Table 8. If both values are above or below zero,
then the two systems are determined to be signifi-
cantly different. As all the values for the confidence
interval of AE in Table 8 are above zero, it can be con-
cluded that, overall, the P-FLS is significantly better
than the S-FLS.
6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper, we proposed two FL based approaches
that predict phone durations for improving phone seg-
mentation. We have shown that the proposed FLSs
can accurately predict phone durations, which inher-
ently bear real-world uncertainties. We presented the
results of our tuning and comparison experiments and
inferred that the FLSs outperform their NN counter-
parts in predicting phone durations considering the
Dutch IFA corpus. Furthermore, we observed that us-
ing a parallel structured approach, which differenti-
ates between the vowels and the consonants, for de-
signing the FLS improves the performance of phone
duration predictions. We also confirmed that the dif-
ferences in the comparison experiments are statisti-
cally significant.
As part of future work, the systems need to be fur-
ther optimised. For the FLSs, this involves that Type-
2 FL can be employed to better handle the real-world
uncertainties and improve the performance. For the
NN counterparts, more layers and nodes per layer can
be added to obtain a deep NN matching the state of the
art. Furthermore, the proposed systems require to be
compared against the state of the art baseline systems
like the results from HMMs. Finally, the FLSs should
be able to handle multiple languages, which means
experiments on i.e. the TIMIT corpus (Garofolo et al.,

1993). In the case where all these experiments result
in high accuracy phone duration prediction, the de-
veloped system can be applied and tested in an ASR
system and employed in a real-world application for
phone segmentation. We believe that this first imple-
mentation of FL based approaches for phone segmen-
tation will be an important step for a wider deploy-
ment and development of FL approaches in the re-
search area of ASR.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This work is partially supported by the Marie Curie
Initial Training Network (ITN) ESSENCE, grant
agreement no. 607062.
REFERENCES
Bezdek, J. C., Ehrlich, R., and Full, W. (1984). Fcm: The
fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. Computers &
Geosciences, 10(2):191–203.
Chiu, S. (1996). Method and software for extracting fuzzy
classification rules by subtractive clustering. In Fuzzy
Information Processing Society, 1996. NAFIPS., 1996
Biennial Conference of the North American, pages
461–465. IEEE.
Garg, A. and Sharma, P. (2016). Survey on acoustic mod-
eling and feature extraction for speech recognition.
In Computing for Sustainable Global Development
(INDIACom), 2016 3rd International Conference on,
pages 2291–2295. IEEE.
Garofolo, J. S., Lamel, L. F., Fisher, W. M., Fiscus, J. G.,
and Pallett, D. S. (1993). Darpa timit acoustic-
phonetic continous speech corpus cd-rom. nist speech
disc 1-1.1. NASA STI/Recon Technical Report N, 93.
Giripunje, S. and Bawane, N. (2007). Anfis based emo-
tions recognision in speech. In Knowledge-based In-
telligent Information and Engineering Systems, pages
77–84. Springer.
Goubanova, O. and King, S. (2008). Bayesian networks
for phone duration prediction. Speech communication,
50(4):301–311.
Grimm, M. and Kroschel, K. (2005). Rule-based emotion
classification using acoustic features. In in Proc. Int.
Conf. on Telemedicine and Multimedia Communica-
tion. Citeseer.
Harma, A. and Pham, K. (2009). Conversation detection in
ambient telephony. In Acoustics, Speech and Signal
Processing, 2009. ICASSP 2009. IEEE International
Conference on, pages 4641–4644. IEEE.
Igras, M. and Zi
´
ołko, B. (2016). Detection of sentence
boundaries in polish based on acoustic cues. Archives
of Acoustics, 41(2):233–243.
Igras, M., Ziolko, B., and Ziolko, M. (2014). Is
phoneme length and phoneme energy useful in auto-
matic speaker recognition? In Pacific Voice Confer-
ence (PVC), 2014 XXII Annual, pages 1–5. IEEE.
Jacobi, I., Pols, L. C., Stroop, J., et al. (2005). Polder dutch:
Aspects of the/ei/-lowering in standard dutch. In In-
terspeech, number 6, pages 2877–2880. ISCA.
Jang, J.-S. (1993). Anfis: adaptive-network-based fuzzy in-
ference system. IEEE transactions on systems, man,
and cybernetics, 23(3):665–685.
Jang, J.-S. R. et al. (1991). Fuzzy modeling using general-
ized neural networks and kalman filter algorithm. In
AAAI, volume 91, pages 762–767.
Jurafsky, D. and Martin, J. H. (2014). Speech and language
processing. Pearson.
Kasparaitis, P. and Beniu
ˇ
s
˙
e, M. (2016). Automatic parame-
ters estimation of the d. klatt phoneme duration model.
Informatica, 27(3):573–586.
Lee, C. M. and Narayanan, S. (2003). Emotion recognition
using a data-driven fuzzy inference system. In Eighth
European Conference on Speech Communication and
Technology.
Mendel, J. M. (2001). Uncertain rule-based fuzzy logic sys-
tems: introduction and new directions. Prentice Hall
PTR Upper Saddle River.
Mor
´
e, J. J. (1978). The levenberg-marquardt algorithm: im-
plementation and theory. In Numerical analysis, pages
105–116. Springer.
Pols, L. C. (1983). Three-mode principal component anal-
ysis of confusion matrices, based on the identification
of dutch consonants, under various conditions of noise
and reverberation. Speech Communication, 2(4):275–
293.
Pols, L. C., Tromp, H. R., and Plomp, R. (1973). Fre-
quency analysis of dutch vowels from 50 male speak-
ers. The journal of the Acoustical Society of America,
53(4):1093–1101.
Pols, L. C., Wang, X., and ten Bosch, L. F. (1996). Mod-
elling of phone duration (using the timit database) and
its potential benefit for asr. Speech Communication,
19(2):161–176.
Rabiner, L. R. (1989). A tutorial on hidden markov models
and selected applications in speech recognition. Pro-
ceedings of the IEEE, 77(2):257–286.
Schuller, B. W., Zhang, X., and Rigoll, G. (2008). Prosodic
and spectral features within segment-based acoustic
modeling. In INTERSPEECH, pages 2370–2373.
Son, R. J. v., Binnenpoorte, D., Heuvel, H. v. d., Pols, L. C.,
et al. (2001). The ifa corpus: a phonemically seg-
mented dutch” open source” speech database.
Ten Bosch, L., Baayen, R. H., and Ernestus, M. (2006). On
speech variation and word type differentiation by ar-
ticulatory feature representations. In INTERSPEECH.
Yu, D. and Deng, L. (2014). Automatic speech recognition:
A deep learning approach. Springer.
Zadeh, L. A. (1965). Fuzzy sets. Information and control,
8(3):338–353.
Zi, B. (2009). Speech recognition of highly inflective lan-
guages.
Zi
´
ołko, B. (2015). Fuzzy precision and recall measures for
audio signals segmentation. Fuzzy Sets and Systems,
279:101–111.
