
Rule-based System Enriched with a Folksonomy-based Matcher for
Generating Information Integration Alignments
Alexandre Gouveia
1
, Nuno Silva
1
and Paulo Martins
2,3
1
School of Engineering, Polytechnic of Porto, 4249-015 Porto, Portugal
2
University of Trás-os-Montes e Alto Douro, 5000-801Vila Real, Portugal
3
INESC TEC, 4200-465 Porto, Portugal
Keywords: Ontology Alignment, Information Integration, Rule-based System.
Abstract: Ontology matchers establish correspondences between ontologies to enable knowledge from different
sources and domains to be used in ontology mediation tasks (e.g. data transformation and information/
knowledge integration) in many ways. While these processes demand great quality alignments, even the
best-performing alignment needs to be corrected and completed before application. In this paper, we
propose a rule-based system that improves and completes the automatically-generated alignments into fully-
fledged alignments. For that, the rules capture the pre-conditions (existing facts) and the actions to solve
each (ambiguous) scenario, in which automatic decisions supported by a folksonomy-based matcher are
adopted. The evaluation of the proposed system shows the increasing accuracy of the alignments.
1 INTRODUCTION
Ontology (or schema) alignment is the process
whereby correspondences between entities of two
different ontologies with common or overlapping
domains are established (Euzenat and Shvaiko,
2007) and is particularly relevant in many areas of
application of ontologies (Otero-Cerdeira et al.,
2015; Shvaiko and Euzenat, 2013).
Automatic alignment systems make use of
automatic matching algorithms (ontology matchers)
which evaluate the similarities between pairs of
source and target ontologies’ entities, exploring
different dimensions of ontologies (Euzenat and
Shvaiko, 2007).
Yet, automatically-generated alignments are
often not information-integration-ready alignments.
Analysis of automatically-generated alignments
shows that ambiguous situations are quite common
and prevent direct application of these alignments in
Ontology Mediation tasks (e.g. data transformation,
integration and migration). Moreover, most of the
existing ontology matchers generate incomplete,
incorrect and mutually contradictory alignments,
preventing their application in scenarios demanding
high quality and completeness, such ontology
mediation (de Bruijn et al., 2006). The results
obtained with the automatic alignment systems are
in fact below the required for ontology mediation,
demanding the user/expert intervention, by
correcting and completing the automatic alignments
into data integration suitable alignments.
The manual alignment systems use complex,
time-consuming and yet error prone mapping
processes that require extensive and profound
(human/expert) knowledge of the domain. Also,
other approaches propose solving alignment
problems or defects by removing correspondences
(Meilicke et al., 2007; Xu and Xu, 2010), or by
detecting the existence of semantic inconsistencies
(Jean-Mary et al., 2009; Wang and Xu, 2007), but
none of them is focused on improving and
completing the automatically-generated alignments
into information integration alignments.
Furthermore, instead of correspondences between
just concepts, we make use of correspondences
between properties.
The next section describes the foundational
concepts adopted in this paper. Section 3 describes
our proposal of a rule-based system and its
conceptual operation. Section 4 describes the
ambiguity scenarios and the design of rules to solve
the ambiguities. Section 5 describes the performed
experiments and, finally, section 6 draws some
conclusions and outlooks future research directions.
Gouveia A., Silva N. and Martins P.
Rule-based System Enriched with a Folksonomy-based Matcher for Generating Information Integration Alignments.
DOI: 10.5220/0006505302110218
In Proceedings of the 9th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (KEOD 2017), pages 211-218
ISBN: 978-989-758-272-1
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 FOUNDATIONAL CONCEPTS
Ontology can be defined as follows.
Definition 1 (Ontology). An Ontology (also
known as knowledge base) is a tuple
where is the terminological axioms and is the
assertional axioms. Both are defined based on a
structured vocabulary
comprised of
concepts (or classes) and properties (or roles) .
Concepts (and properties) axioms are of the form
( ) or ( ) such that
( ) respectively. Properties are used to
establish relations between concepts. For a set of
individuals , concepts and properties assertions are
of form
or
such that ,
and (Baader et al., 2003).
Ontology mediation is a generic term that gathers
a set of techniques needed to achieve interoperability
in semantically enabled systems. Some of these
techniques are query rewriting and instance
translation (data transformation). Conceptually,
ontology mediation includes a process named
Matching that is carried out by Matcher(s) to
identify correspondences between ontology entities.
Definition 2 (Matcher). The matcher is a function
which, from a pair of ontologies to match,
and
, returns an alignment between these ontologies,
i.e.
.
Definition 3 (Alignment). An alignment is a tuple
such that and are sets of
correspondences. is the set of all concept-
correspondences and is the set of all property-
correspondences, both generated by the matcher.
Definition 4 (Concept-correspondence). Let
and
be the source and target ontologies and let
and
be its concepts, respectively. A concept-
correspondence is a quadruple
, where:
is the set of all concept-correspondences;
and
are ontology concepts of the source
and target ontologies respectively, such that
and
;
is the relation holding between the concepts;
is the confidence value in the relation.
Definition 5 (Property-correspondence). Let
and
be the source and target ontologies and let
and
be its properties, respectively. A property-
correspondence is a quadruple
, where:
is the set of all property-correspondences;
and
are ontology properties of the source
and target ontologies respectively, such that
and
;
is the relation holding between properties;
is the confidence value in the relation.
Notice that most of the existing matchers only
generate equivalence () correspondences and that
there is a lack of any widely-accepted benchmark
involving more than 1-to-1 equivalence
correspondences (Amini et al., 2016). The
confidence value is normalized to the interval ]0, 1].
Properties have their own domain and range and
are differentiated according to its range as (i)
datatype property, if the range is Literal and (ii)
object property, if the range is a concept.
Additionally, the same property can have multiple
domain and range concepts, allowing certain
instances to use the same ontology property to relate
two distinct types of property instances. Due to this
central role that properties play in the modeling
process, and besides the object-oriented modeling
capabilities, ontologies of this kind are (also)
categorized as property-centric ontologies.
Due to distinct ontological decisions made when
modeling ontologies, semantically equivalent
properties are often located in different levels of the
ontologies structure. Addressing properties in
distinct levels of the ontology is necessary to
overcome semantic heterogeneity.
In the ontology mapping scenario of Figure 1,
O1:Worker.hasAddress.ContactAddress.address.Lit-
eral is semantically related to O2:Person.postalAd-
dress.Literal. This relation means that the attributes
address and postalAddress are semantically related,
but only when address is accessed through the fully
qualified Path (O1:Worker.hasAddress.ContactAd-
dress.address.Literal). In fact, O1:ContactAddress.
address.Literal is not directly semantically related to
O2:Person.postalAddress.Literal because, without
the hasAddress relation, no semantic correspondence
exists between ContactAddress and Person.
Figure 1: Two structurally different ontologies.

To address these limitations, the Path and Step
concepts are necessary.
Definition 6 (Step). A step is a 3-tuple in the form
of
where:
is the set of all steps;
is the domain of ;
is the ontology property;
is the range of the
ontology property, which can be either an
ontology concept or Literal;
is a function that defines the
ontology concept playing the role of subject in
the step;
is a function that defines
the ontology property playing the role of
predicate in the step;
is a function that
returns the ontology concept or Literal playing
the role of object in the step.
Definition 7 (Path). A path represents a set of valid
relations between multiple concepts. A path is a non-
empty list of steps
where:
is the set of all paths;
;
is a function that returns the
(positive integer) number of steps of the path;
,
,
i.e. the subject of certain step in the path
should be the object of the previous step of the
path;
is a function that returns the first
step of the path;
is a function that returns the
last step of the path.
An information-integration-ready (ii-ready)
scenario is formally described next.
Definition 8 (Information-integration-ready
scenario). An information-integration-ready (ii-
ready) scenario is a tuple
where:
is the set of all ii-ready scenarios;
;
;
;
;
;
.
If and
are object properties, the following
conditions are also satisfied:
;
;
.
Definition 9 (Information-integration-ready
alignment). An information-integration-ready
alignment is a set of all established/accepted ii-
ready scenarios between two ontologies.
Manifestly, the automatically-generated
correspondences, i.e. property-correspondences
(Definition 5) and concept-correspondences
(Definition 4), do not respect Definition 8.
Transforming the automatically-generated
correspondences into ii-ready scenarios is not
univocal, being subject to time-consuming and error-
prone decisions.
3 PROPOSAL
The proposed rule-based system is captured in the
BPMN diagram depicted in Figure 2.
The rules are fired when an ambiguous scenario
is detected, i.e. a scenario-to-resolve, as no existing
facts allows decision. In such cases, the automatic
folksonomy-based matcher is triggered. This
matcher exploits the RhymeZone (http://www.
rhymezone.com) folksonomy via the Datamuse API
(http://www.datamuse.com/api/) and applies the
matching conditions as described next:
foreach 0≤i<se.words.length()
ws=readFolksonomy(se.words[i],t)
if( !ws.includesOneOf(te.words) )
return false
return true
The attribute of source and target entities
( and ) is the set of words comprising their
syntactic representation (e.g. order_items syntax
gives rise to the {order, items} set of words). The
function evaluates the existence of
at least a common word in two sets of words. The
argument is the number of folksonomy-related
words read from the folksonomy.
When no more rules are found to fire, i.e. when
no more ambiguous scenarios are found, the filtering
process prepares an information-integration-ready
alignment. This process typically consists of
eliminating unnecessary facts for the application of
the alignment in ontology mediation.
Drools (http://www.drools.org) was adopted as
the rule engine coupled to the rest of the system with
a service bridge that allows updating and querying
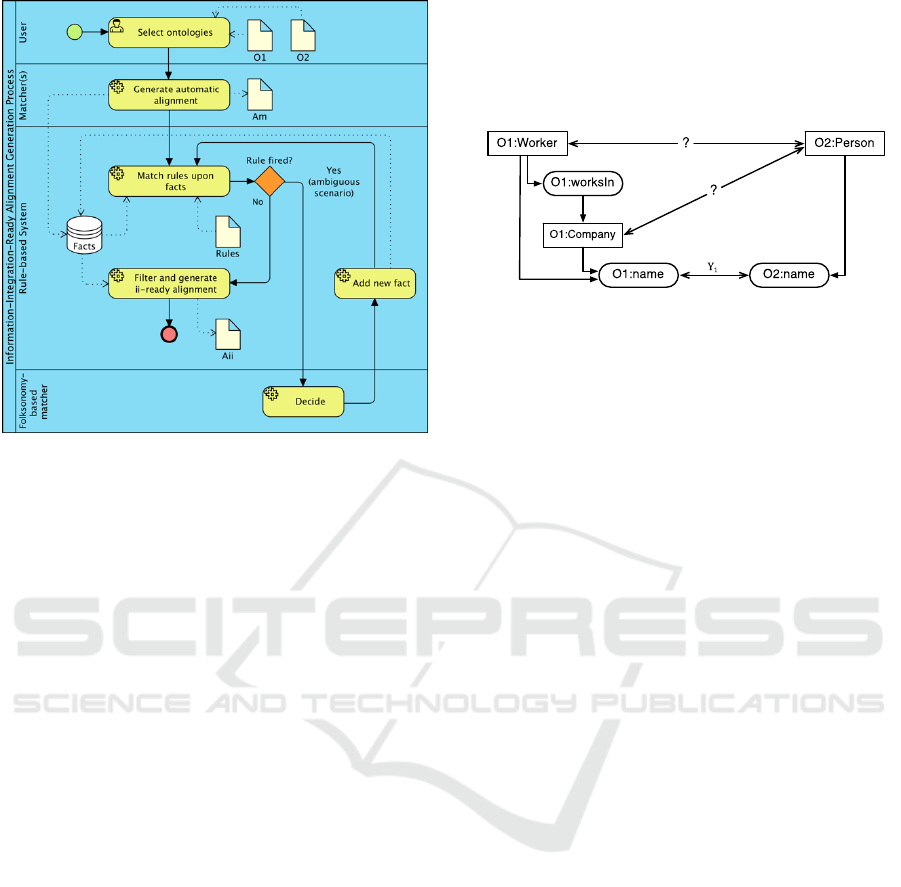
Figure 2: Information-integration-ready alignment genera-
tion process.
the knowledge/facts base, thus allowing a non-
monotonic reasoning. Yet, due to the negation as
failure, the closed-world assumption is affordable
and guaranteed.
4 RULES
The goal is to transform the automatically-generated
property-correspondences into ii-ready scenarios as
defined in Definition 8. Yet, for that, several
possibilities may exist, some of them semantically
correct and other incorrect. The folksonomy-based
matcher will support the system in selecting the
correct and will consider the decisions for further
automatic decisions.
The expert-defined rules capture the pre-
conditions (existing facts) and the actions (i.e. facts
to be asserted) to solve each (ambiguous) alignment
scenario. The rules aim to determine at least one
path for the source and target properties of a
property-correspondence, i.e. Source Path + Target
Path. Notice that determining the source and target
path follows the same process. Based on Definition
7, a path can be defined by the combination of
associations between concepts, either directly
(single-step path) or indirectly (multi-step path).
Consider the alignment scenario of Figure 3 in
which the property-correspondence between
O1:name and O2:name
) is defined. Notice that
although a property can have multiple domain and
range concepts, they are not specified in the
automatically-generated property-correspondences,
allowing multiple interpretations that give rise to
ambiguities during the transformation process (e.g.
which property’s domain concept, or path, should be
considered?).
Figure 3: Ambiguity in a property-correspondence.
Because O1:name has two domain concepts
(O1:Worker and O1:Company) it can be accessed by
the paths:
O1:Worker.name, which is a single-step path;
O1:Company.name, which is also a single-
step path;
O1:Worker.worksIn.Company.name, through
a Property-related Concept, since O1:Worker
and O1:Company are related by O1:worksIn.
The goal is to determine which of these
possibilities should be considered to transform
(copy) the value of O1:name into O2:Person.name.
4.1 Disambiguation Assertions
Because all, some and none of the theoretical
contextualization paths may be valid, an ambiguous
situation arises. For resolving such ambiguous
scenarios, several decisions must be taken, which
will give rise to 4 types of assertions:
Acceptance of a new concept-correspondence
assertion (cf. Definition 4);
Acceptance of an ii-ready scenario assertion
(cf. Definition 8);
Rejection of a concept-correspondence, thus
giving rise to a not-concept-correspondence
assertion (cf. next Definition 10);
Rejection of an ii-ready-scenario, thus giving
rise to a not-ii-ready scenario assertion (cf.
next Definition 11).
Definition 10 (Not-concept-correspondence). Let
and
be the source and target ontologies and let
and
be its concepts, respectively. A not-
concept-correspondence is a tuple
which establishes that and
are explicitly not
related, such that:
is the set of all not-concept-
correspondences;

and
are ontology concepts of the source
and target ontologies respectively, such that
and
;
;
.
Definition 11 (Not-ii-ready scenario). A not-ii-
ready scenario is a ii-ready-scenario that
was stated as not valid, such that:
is the set of all not-ii-ready scenarios;
;
.
The adoption of these two definitions aims to
close the world in a MKNF-similar approach
(Lifschitz, 1991; Motik and Rosati, 2010), i.e. in a
way that negation facts are explicitly asserted in the
knowledge base.
4.2 Formal Definition of Ambiguous
Scenarios
Ambiguous scenarios are defined as follows.
Definition 12 (Concept-ambiguous scenario). Let
be a property-correspondence
such that and
. We are in the presence
of a concept-ambiguous scenario if and only if the
following conditions are simultaneously satisfied:
;
;
;
.
Definition 13 (Path-ambiguous scenario). Let
be a property-correspondence
such that and
. We are in the presence
of a path-ambiguous scenario if and only if the
following conditions are simultaneously satisfied:
;
;
;
(i.e.
);
(i.e. ).
4.3 Concept-Ambiguous Rule in a
Single-Step Path
From the property-correspondence, the search for
paths starts by considering the direct-domain
concepts and then proceeds to indirect-domain
concepts (two-step path, three-step path, etc.).
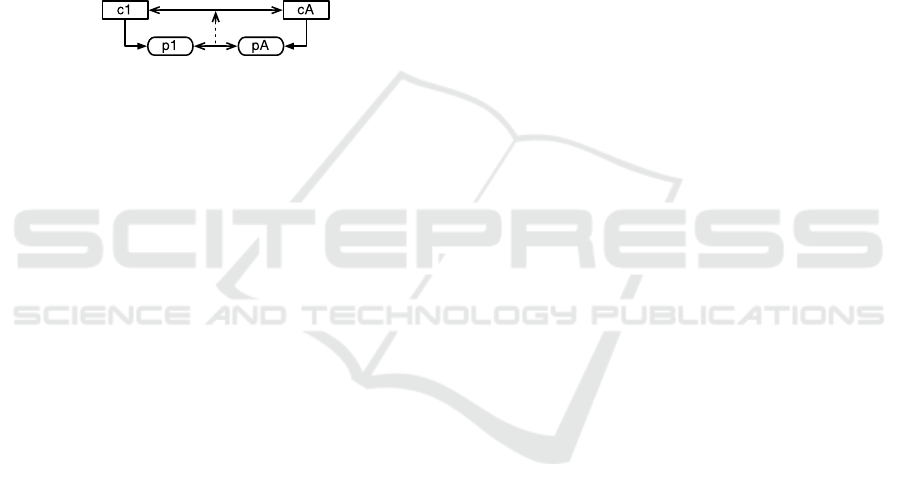
Please consider the scenario depicted in Figure 4
in which there are three possible situations that may
occur between the concepts c1 and cA: (i) the
existence of a concept-correspondence, (ii) the
existence of a not-concept-correspondence and (iii)
neither the existence of a concept-correspondence
nor the existence of a not-concept-correspondence.
Figure 4: Concept-ambiguous in a single-step path.
The inexistence of a concept-correspondence and
of a not-concept-correspondence between the
concepts c1 and cA results in an ambiguous situation
previously identified as a concept-ambiguous
scenario (cf. Definition 12). This is captured by the
pre-conditions (i.e. the LHS) as follows:
, i.e. there is a
property-correspondence between the
properties O1:p1 and O2:pA;
,
i.e. there is a single-step source path where the
predicate of the step is O1:p1;
i.e. there is a single-step target path where the
predicate of the step is O2:pA;
, i.e. there is
not a concept-correspondence between the
domain concepts;
, i.e. there is
not a not-concept-correspondence between the
domain concepts.
If these pre-conditions hold, an ambiguous
situation exists and a decision must be made, either
accepting or rejecting the concept-correspondence
between c1 and cA. Depending on the decision from
the folksonomy-based matcher this will give rise to
one of the following assertions (i.e. the RHS):
The acceptance of the concept-
correspondence, i.e. the fact
is asserted;
The rejection of the concept-correspondence,
i.e. the fact
is
asserted.
4.4 Path-Ambiguous Rule in a Single-
Step Path
If a concept-correspondence exists between c1 and
cA this is an ii-ready scenario (cf. Definition 8). In
this case, there are three new possible situations that
may occur:
The system has already accepted the ii-ready
scenario, which will be part of the ii-ready
alignment (Figure 5);
The system has already rejected the ii-ready
scenario, which gave rise to a not-ii-ready
scenario assertion and therefore will not be
part of the ii-ready alignment;
The system has not yet accepted or rejected
the ii-ready scenario.
Figure 5: Accepted ii-ready scenario.
If the ii-ready scenario has not yet been accepted
or rejected then we are in the presence of a path-
ambiguous scenario (cf. Definition 13). This is
captured by the following pre-conditions (LHS):
, i.e. there is a
property-correspondence between the
properties O1:p1 and O2:pA;
,
i.e. there is a single-step source path with the
predicate O1:p1;
, i.e. there is a
single-step target path with the predicate
O2:pA;
, i.e. there is a
concept-correspondence between the domain
concepts;
, i.e. the ii-ready scenario
has not yet been accepted;
, i.e. the ii-ready
scenario has not yet been rejected.
If these pre-conditions hold, an ambiguous
situation exists and a decision must be made, either
accepting or rejecting the path. Depending on the
decision from the folksonomy-based matcher this
will give rise to one of the following assertions (i.e.
the RHS):
The acceptance of the ii-ready scenario
(Figure 5), asserting the fact
;
The rejection of the ii-ready scenario, thus
asserting the fact
.
4.5 Further Rules
In the previous sections, the rules to prepare ii-ready
scenarios based on one-step paths were designed.
Nevertheless, one-step path may not be correct, thus
suggesting the adoption of paths with more than one
step. Rules for each of those scenarios are
exhaustively defined as necessary. In our
experiments (cf. section 5), only one, two and three-
step path rules were defined. Also, only property-
correspondences between datatype properties or
between object properties were processed, i.e. no
property-correspondence between datatype and
object property (or vice-versa) were considered.
Finally, the range of datatype properties are
processed as literal (string) only.
5 EVALUATION
The evaluation seeks to determine how accurate are
the results of the rule-based system when comparing
to the automatically-generated alignments and to the
best alignments. For that, three elements are
necessary: (i) ontologies, (ii) reference alignments
and (iii) automatically-generated alignments.
The ontologies used in the respected Ontology
Alignment Evaluation Initiative (http://oaei.
ontologymatching.org) Conference track were first
considered. This is the only test set of the initiative
that has reference alignments containing matches
between properties as well as concepts (Cheatham
and Hitzler, 2014). Also, for the automatically-
generated alignments between these pairs of
ontologies, we decided to use the alignments
submitted to OAEI by the automated ontology
matching system AgreementMakerLight – AML
(http://somer.fc.ul.pt/aml.php). In the last years,
AML has been the top performing system in several
tracks of OAEI, including the Conference track
(Achichi et al., 2016; Faria et al., 2016).
However, the execution of the system on these
pairs of ontologies, using the mentioned alignments
resulted in few ambiguous scenarios. These results
conducted us to the conclusion that the OAEI
Conference track ontologies are not appropriate to
thoroughly evaluate the current proposed rule-based
system. Despite the ability of the system to solve the
existing ambiguities found in these ontologies, they
do not allow the demonstration of the system’s
capabilities. In fact, due to the simplicity of the
ontologies, the ambiguities are practically
nonexistent because at least one of the following
situations occurs:
the alignments have few property-
correspondences;
when searching for paths to contextualize the
automatically-generated property-correspond-
ences, only single-step paths are found;
the properties’ domains concepts in the
property-correspondences are already related
in concept-correspondences derived from the
alignment.
Therefore, we decided to use other ontologies
(and alignments). Some were based on data models
obtained from the Database Answers (http://www.
databaseanswers.org). The others were developed by
the authors in previous contexts and are available at
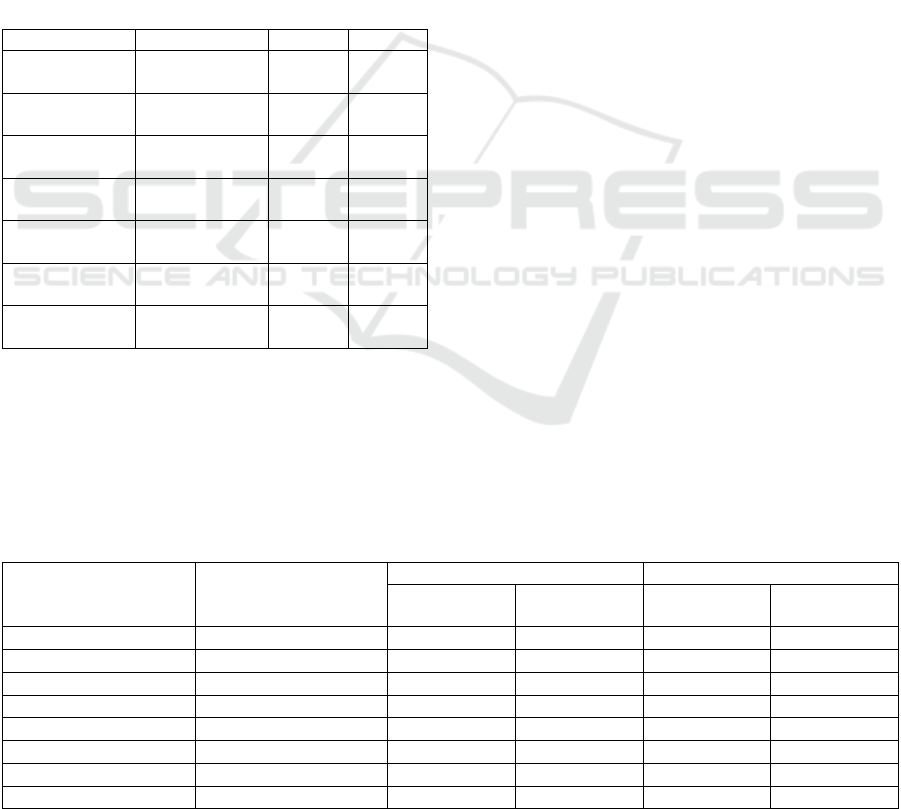
https://goo.gl/CsDVhz. Table 1 characterizes these
ontologies.
Table 1: Characterization of the ontologies used in
experiments.
Ontology
Domain
Concepts
Properties
Workers
Company
employees
2
3
Persons
People
2
3
WorkerPersons
Company
employees
2
4
Customers and
Addresses
Customer
addresses
4
17
Clients and Fees
Customer
addresses
3
16
Customers and
Invoices
Customer orders
5
33
Customers and
Products
Customer orders
10
35
To evaluate the proposed system we had to
manually create reference alignments consisting of
1-to-1 equivalence correspondences for all pairs of
ontologies. Furthermore, AML was used as the
matcher to generate the automatic alignments (cf.
Figure 2). The GUI version of AML was used and
its configuration was based on predefined
parameters, which included a threshold of 0.6, i.e.
only correspondences with a confidence value ()
above 0.6 were kept. Table 2 describes the pairs of
ontologies and the alignments used in the evaluation.
5.1 Experiments
The proposed system was used to solve the
ambiguities of each pair of ontologies presented in
Table 2. In these experiments, the threshold of the
system was set to match the following targets:
Shortest paths are preferred to longer paths;
Only one contextualization must be tried for
each property-correspondence, even if more
can exist.
To adequately measure the results obtained by
the system and thus try to determine how accurate
the results are, we compare 3 different resulting
alignments for each pair of ontologies used in the
experiments, namely:
1. The non-ii-ready initial alignment, i.e. the
alignment automatically-generated by AML;
2. The ii-ready alignment generated by the system;
3. The best possible ii-ready alignment, i.e. the ii-
ready alignment with the best precision and
recall, considering the initial alignment. This
alignment is possibly different from the
previous, because based on the folksonomy-
based matcher decisions, the system’s decisions
may be wrong.
5.2 Analysis of Results
Precision, recall and f-measure are computed with
respect to the reference alignment, as presented in
Table 2. The chart depicted in Figure 6 considers all
the pairs of ontologies used in the experiments and
shows an increase of accuracy of the system
alignments over the initial alignments.
Table 2: Characterization of the pairs of ontologies and the alignments used in the experiments.
Source
Ontology
Target
Ontology
Reference alignment
AML alignment
Concept
correspondences
Property
correspondences
Concept
correspondences
Property
correspondences
Workers
Persons
1
2
0
2
Persons
Workers
1
2
0
2
Workers
WorkerPersons
1
3
0
2
WorkerPersons
Workers
1
3
0
2
Customers and Addresses
Clients and Fees
3
13
2
7
Clients and Fees
Customers and Addresses
3
13
2
7
Customers and Invoices
Customers and Products
5
22
4
19
Customers and Products
Customers and Invoices
5
22
4
19
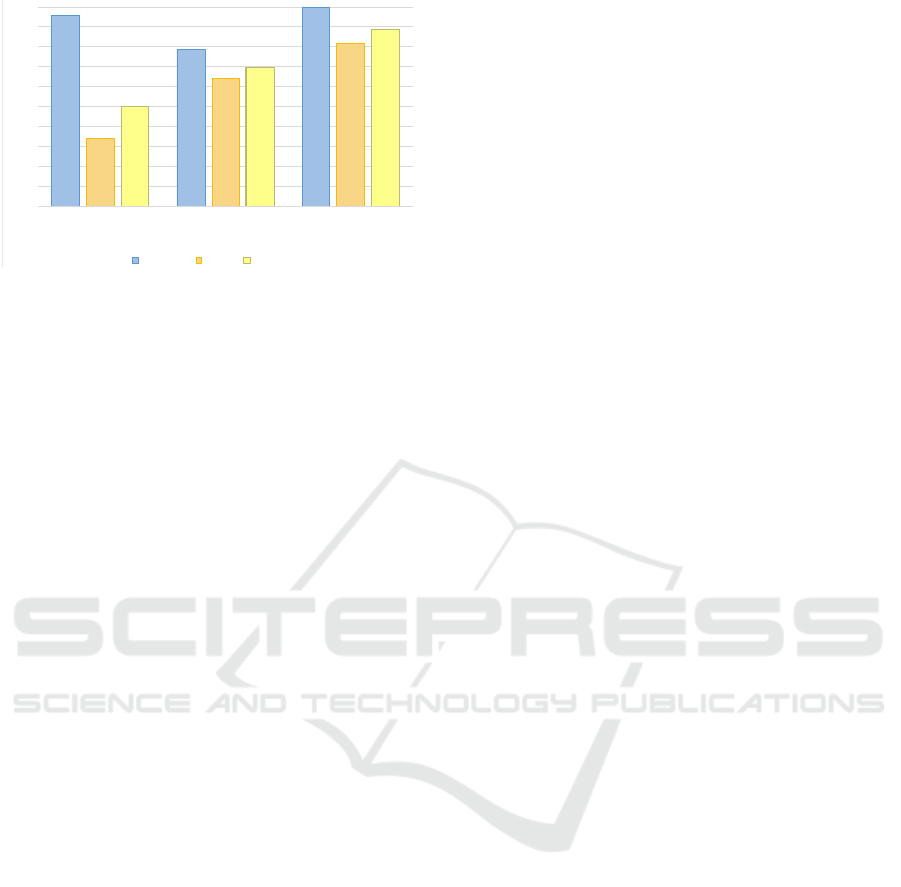
Figure 6: Overall results.
As expected, the precision of the ii-ready
alignments generated by the system is lower than of
the automatic alignments. Instead, the results show a
significant increase of accuracy obtained with the
proposed system: recall increased from 34.1% to
63.7% and f-measure increased from 49.9% to
69.5%. Also, the results obtained by the system are
still below the best possible alignments.
6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
This paper addresses the resolution of the problems
found when transforming the automatically-
generated correspondences into information-
integration suitable alignments, by proposing a
system based in a general-purpose rule engine that
improves and completes the automatically-generated
alignments into fully-fledged alignments.
The rules at the core of the system are designed
according to the formal and multi-dimensional
analysis of the ontologies (section 2) and of the ii-
ready alignment presented (section 4), yielding a
strong formal rational to the system.
A prototype of the system was developed and
evaluated, showing an increase of accuracy of ii-
ready alignments over non-ii-ready initial
alignments (cf. Figure 6).
As future work, the authors are focusing in four
complementary concerns: (i) designing the rules to
address other dimensions of the alignment space
(e.g. concept subsumption, property subsumption);
(ii) evaluating the rule-based system with larger and
more complex ontologies and data models; (iii)
designing of meta-rules that adaptively control the
firing of rules; and (iv) involving the user in the
decision process.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is financed by FEDER funds through the
Competitive Factors Operational Program
(COMPETE), POCI-01-0247-FEDER-017803
(dySMS - Dynamic Standards Management System).
REFERENCES
Achichi, M., Cheatham, M., Dragisic, Z., Euzenat, J.,
Faria, D., Ferrara, A., Flouris, G., Fundulaki, I.,
Harrow, I., Ivanova, V., 2016. Results of the Ontology
Alignment Evaluation Initiative 2016, in: 11th ISWC
Workshop on Ontology Matching (OM). pp. 73–129.
Amini, R., Cheatham, M., Grzebala, P., McCurdy, H.B.,
2016. Towards best practices for crowdsourcing
ontology alignment benchmarks, in: 11th Int. Works. on
Ont. Matching-Vol. 1766. CEUR-WS, pp. 1–12.
Baader, F., Calvanese, D., McGuinness, D.L., Nardi, D.,
Patel-Schneider, P.F., 2003. The description logic
handbook: Theory, implementation and applications.
Cambridge University Press, New York, NY, USA.
Cheatham, M., Hitzler, P., 2014. The properties of
property alignment, in: 9th Int. Workshop on Ontology
Matching-Volume 1317. CEUR-WS, pp. 13–24.
de Bruijn, J., Ehrig, M., Feier, C., Martíns-Recuerda, F.,
Scharffe, F., Weiten, M., 2006. Ontology mediation,
merging and aligning, in: Sem. Web Technologies.
Euzenat, J., Shvaiko, P., 2007. Ontology matching, 1st ed.
Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, Germany.
Faria, D., Pesquita, C., Balasubramani, B.S., Martins, C.,
Cardoso, J., Curado, H., Couto, F.M., Cruz, I.F., 2016.
OAEI 2016 Results of AML. Ontology Matching.
Jean-Mary, Y.R., Shironoshita, E.P., Kabuka, M.R., 2009.
Ont. matching w/ semantic verification. Web Sem.:
Science, Serv. & Agents on the WWW 7, 235–251.
Lifschitz, V., 1991. Nonmonotonic databases and
epistemic queries, in: 12th Int. Joint Conf. on Artif.
Intell. John Mylopoulos and Ray Reiter, pp. 381–386.
Meilicke, C., Stuckenschmidt, H., Tamilin, A., 2007.
Repairing ontology mappings, in: 22nd National Conf.
on Artificial Intelligence. AAAI Press, pp. 1408–1413.
Motik, B., Rosati, R., 2010. Reconciling description logics
and rules. Journal of the ACM 57, 1–62.
Otero-Cerdeira, L., Rodríguez-Martínez, F.J., Gómez-
Rodríguez, A., 2015. Ontology matching: A literature
review. Expert Systems w/ Applications 42, 949–971.
Shvaiko, P., Euzenat, J., 2013. Ontology matching: State
of the art and future challenges. IEEE Transactions on
Knowledge and Data Engineering 25, 158–176.
Wang, P., Xu, B., 2007. Debugging ontology mappings: A
static approach. Computing & Informatics 27, 21–36.
Xu, T., Xu, T., 2010. An approach for ontology mapping
based on semantic and structural information in
ontologies, in: 2010 International Conference on
Information Management, Innovation Management
and Industrial Engineering (ICIII). IEEE, pp. 636–
639.
95.5
78.8
100
34.1
63.7
81.5
49.9
69.5
88.6
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
Non-ii-readyinitial
alignments
ii-readyalignments Bestpossibleii-ready
alignments
Precision Recall F-measure
