
Method for Training of Long Distance Runners Taking into Account
Bioenergetic Types of Energy Provision for Muscular Activity
Alexander Bolotin and Vladislav Bakayev
Institute of Physical Education, Sports and Tourism, Peter the Great St. Petersburg Polytechnic University,
29, Polytechnicheskaya Str, St. Petersburg, Russia
Keywords: Long-distance Runners, Peculiarities of Energy Provision for the Muscular Activity, Bioenergetics Types,
Training Method.
Abstract: The paper shows that the improved training process quality can be achieved by the use of different methods
for training of long-distance runners taking into account peculiarities of energy provision for their muscular
activity. The essence of these methods consists in the following: for sportsmen with “aerobic type” of
provision for their muscular activity, tempo endurance should be developed, mainly, by the method of
standard continuous exercise and speed endurance should be developed by the repetition method; for
sportsmen with “anaerobic type” of provision for their muscular activity, tempo endurance should be
developed, mainly, by the method of standard interval exercise and speed endurance should be developed by
the submaximal effort method with standardized number of repetitions of sections covered; for sportsmen
with “mixed type” of provision for their muscular activity, tempo endurance should be developed, mainly, by
the method of variable continuous exercise and speed endurance should be developed by the combination of
the repetition method and submaximal effort method with standardized number of repetitions of sections
covered.
1 INTRODUCTION
The competitive activity of long-distance runners
makes high requirements to their physical fitness
level (Bakaev et al., 2015; Bolotin and Bakayev,
2017; Bolotin et al., 2017; Kuznetsova et al., 2015).
Training of long-distance runners is based on the
development of physical qualities among which
different endurance types are the most important
(Ammann and Wyss, 2015; Bolotin and Bakaev,
2015). The development of these qualities is possible
only in case of the targeted influence on their
physiologic systems and, in particular, mechanisms
of energy provision for the muscular activity (Bakaev
et al., 2016; Osipov et al., 2016).
The literature analysis shows that most papers
concerning training of long-distance runners do not
contain well-grounded scientific information
characterizing peculiarities of the energy provision
for their muscular activity. This limits significantly
the possibilities to differentiate means and methods
for development of different endurance types in the
training process. The problems concerning the use of
the methods for development the endurance in long-
distance runners, in which different bioenergetic
types of energy provision for the muscular activity
would serve as a differentiation criterion are also
insufficiently investigated.
2 ORGANIZATION AND
METHODS
Objective of the study is to assess the method
efficiency for training long-distance runners taking
into account peculiarities of energy provision for their
muscular activity.
Research Design. We examined 28 Russian long-
distance runners aged 19 – 27 years. The runners
specialized in the race for the distance of 5000 meters.
Training for the competitions took place in 4 groups
with 7 sportsmen in each: “aerobic type”, “mixed
type”, “anaerobic type” and a group without
consideration of the energy provision type for the
muscular activity. The experiment lasted for 6
months. The training means and methods were
selected taking into account the bioenergetic types of
energy provision for sportsmen’ muscular activity. In
Bolotin A. and Bakayev V.
Method for Training of Long Distance Runners Taking into Account Bioenergetic Types of Energy Provision for Muscular Activity.
DOI: 10.5220/0006516101260131
In Proceedings of the 5th International Congress on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support (icSPORTS 2017), pages 126-131
ISBN: 978-989-758-269-1
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

order to substantiate the sportsmen training methods
taking into account the bioenergetic types, we:
- determined sportsmen’ bioenergetic types;
- performed the comparative analysis of the
parameters of the functional condition and reserve
possibilities of the sportsmen’s organism in different
bioenergetic groups.
A method for rapid diagnostics of the functional
condition and reserve possibilities of the sportsmen’s
organism with the help of the “D&K Test” program
developed by V. Karlenko was used (Karlenko et. al.,
2008). This method for rapid diagnostics of the
organism functional condition and reserve
possibilities was used in order to determine the
bioenergetic type of sportsmen. The program
analyzed the R and S wave height in the
electrocardiogram recorded in the standard and
pectoral leads. As a result we calculated the parameter
values characterizing the power, capacity, efficiency
of the anaerobic and aerobic energy provision
systems for the muscular activity. The following
parameters were assessed during the study:
1. ANMC is anaerobic metabolic capacity. It
characterizes the ability to perform the stress in
the third, fourth and fifth intensity zones.
2. АNMC (%) is anaerobic utilization capacity. It
characterizes runners’ predisposition to anaerobic
work in percentage.
3. AMC is aerobic metabolic capacity. It
characterizes the ability to perform the stress in
the first and second intensity zones.
4. АМC (%) is aerobic utilization capacity. It
characterizes runners’ predisposition to aerobic
work in percentage.
5. TMC is total metabolic capacity. It characterized
the organism’s total capacity for work.
6. CPMP is creatine phosphate metabolic power. It
characterizes runners’ speed abilities.
7. GLMP is glycolytic metabolic power. It
characterizes runners’ speed endurance.
8. AMP is aerobic metabolic power. It characterizes
the abilities to general endurance and also to
recovery after the anaerobic work.
The improved training process quality was achieved
by the use of different methods for training of long-
distance runners (Bolotin and Bakayev, 2016; Bolotin
and Bakayev, 2017; Zakharova and Mekhdieva,
2016). The peculiarities of energy provision for their
muscular activity were taken into account:
- for sportsmen with “aerobic type” of provision for
their muscular activity, tempo endurance was
developed, mainly, by the method of standard
continuous exercise and speed endurance was
developed by the repetition method;
- for sportsmen with “anaerobic type” of provision
for their muscular activity, tempo endurance was
developed, mainly, by the method of standard
interval exercise and speed endurance was
developed by the submaximal effort method with
standardized number of repetitions of sections
covered;
- for sportsmen with “mixed type” of provision for
their muscular activity, tempo endurance was
developed, mainly, by the method of variable
continuous exercise and speed endurance was
developed by the combination of the repetition
method and submaximal effort method with
standardized number of repetitions of sections
covered;
- for the sportsmen group without taking into
account the bioenergetic type, the wider range of
means and methods for development of the tempo
and speed endurance was used.
All athletes had a different level of preparedness,
therefore the tempo training load for runners was
selected based on the current result in the 800 meters
(Table 1) and in the 5000 meters (Table 2). The
number of repetitions of the runs and the weekly
amount of running training load were selected
depending on the preparedness of the runners. The
weekly volume of running training load ranged from
100 to 140 km. To manage the training process, the
"Adidas Coach" and "Garmin Forerunner 60 Men
Black HRM + Foot Pod" systems were used to record
statistics during the training period. These systems
were used to plan a training program for runners,
taking into account the heart rate and the type of
energy supply for muscle activity.
Table 1: Approximate training tempo loads for runners at
800 m (min, sec).
Current
result
(min, sec)
Tempo for repetitions
(sec)
Interval tempo (sec)
800 m 200 m 400 m 200 m 400 m
1.50 0.26 0.54 0.27 0.58
1.55 0.27 0.55 0.28 0.59
2.00 0.28 0.57 0.29 0.61
2.05 0.29 0.60 0.30 0.64
2.10 0.30 0.62 0.32 0.68
2.15 0.31 0.64 0.33 0.71
2.20 0.32 0.67 0.34 0.74
2.25 0.33 0.71 0.35 0.78
2.30 0.34 0.75 0.36 0.82
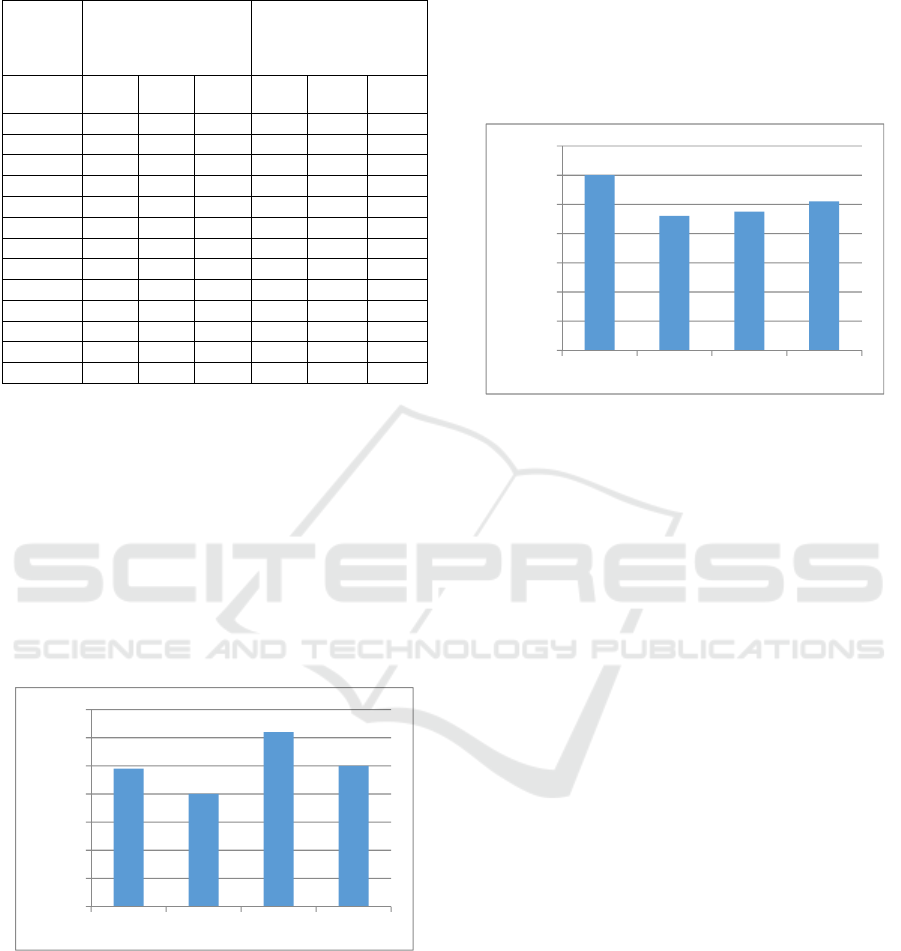
Table 2: Approximate training tempo loads for runners at
5000 m (min, sec).
Current
result
(min,
sec)
Tempo for repetitions
(min, sec)
Interval tempo (min,
sec)
5000 m
200
m
400
m
800
m
400
m
1000
m
1200
m
13.50 0.30 0.61 2.02 0.67 2.48 3.21
14.10 0.31 0.62 2.05 0.68 2.50 3.24
14.30 0.32 0.64 2.08 0.70 2.55 3.30
14.50 0.32 0.65 2.11 0.71 2.58 3.33
15.10 0.33 0.66 2.14 0.72 3.00 3.36
15.30 0.34 0.68 2.16 0.74 3.05 3.42
15.50 0.35 0.70 2.20 0.77 3.13 3.51
16.10 0.36 0.72 2.24 0.78 3.15 3.54
16.30 0.37 0.74 2.28 0.80 3.20 4.00
16.50 0.37 0.75 2.30 0.81 3.22 4.03
17.10 0.38 0.76 2.32 0.82 3.25 4.06
17.30 0.39 0.78 2.36 0.84 3.30 4.12
17.50 0.39 0.79 2.38 0.85 3.33 4.15
Note: weekly volume 100-140 km
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The study shows that runners with different type of
energy provision for the muscular activity need
different training methods (Kuznetsova et al., 2015).
The prevalence of different regulatory mechanisms
for recovery after the stress was revealed depending
on the types of energy provision for the muscular
activity.
Figure 1: Changes in result increase during the race for a
distance of 800 meters (%). TG1 - aerobic type, TG2 -
mixed type, TG3 - anaerobic type, TG4 - without
considering their bioenergetic type.
In the race of a distance of 800 meters (Figure 1),
the sportsmen of the “aerobic type” group showed the
time reduction by 10.7 s, i.e. the increase of results
was 4.86% (P <0.05), the sportsmen of the “mixed
type” group showed time reduction by 8.8 s, i.e. the
increase was 4.06% (Р <0.05), the sportsmen of the
“anaerobic type” group showed time reduction by
13.2 s, i.e. the increase was 6.24% (Р <0.05).The
mean time reduction in this test in sportsmen from the
group without considering their bioenergetic type was
10.9 s what corresponded to the increase by 5.05% (Р
<0.01).
Figure 2: Changes in result increase during the race for a
distance of 5000 meters (%). TG1 - aerobic type, TG2 -
mixed type, TG3 - anaerobic type, TG4 - without
considering their bioenergetic type.
In the race of a distance of 5000 meters (Figure 2),
the sportsmen of the “aerobic type” group showed the
time reduction by 43.3 s, i.e. the increase of results
was 6.07% (P <0.05), the sportsmen of the “mixed
type” group showed time reduction by 32.8 s, i.e. the
increase was 4.58% (Р <0.05), the sportsmen of the
“anaerobic type” group showed time reduction by
33.6 s, i.e. the increase was 4.75%. The mean time
reduction in this test in sportsmen from the test group
without considering their bioenergetic type was 36.57
s what corresponded to the increase by 5.13% (Р
<0.01).
Table 3 and Figure 3 show the assessment results
of the functional reserve possibilities of sportsmen's
organism before and after the experiment. The
increase of ANMC value in the sportsmen of “aerobic
type” was 3.54 conditional units (7.8%), the
sportsmen of the “mixed type” group showed the
increase by 5.83 conditional units or by 8.2% (Р
<0.05), the sportsmen of the “anaerobic type” group
had the increase by 11.45 conditional units or by 9.2%
(Р <0.05). The mean increase of ANMC value in the
sportsmen of the test group without consideration of
their bioenergetic type was 6.4 conditional units
(8.4%).
4,9
4
6,2
5
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
TG1 TG2 TG3 TG4
%
6
4,6
4,75
5,1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
TG1 TG2 TG3 TG4
%
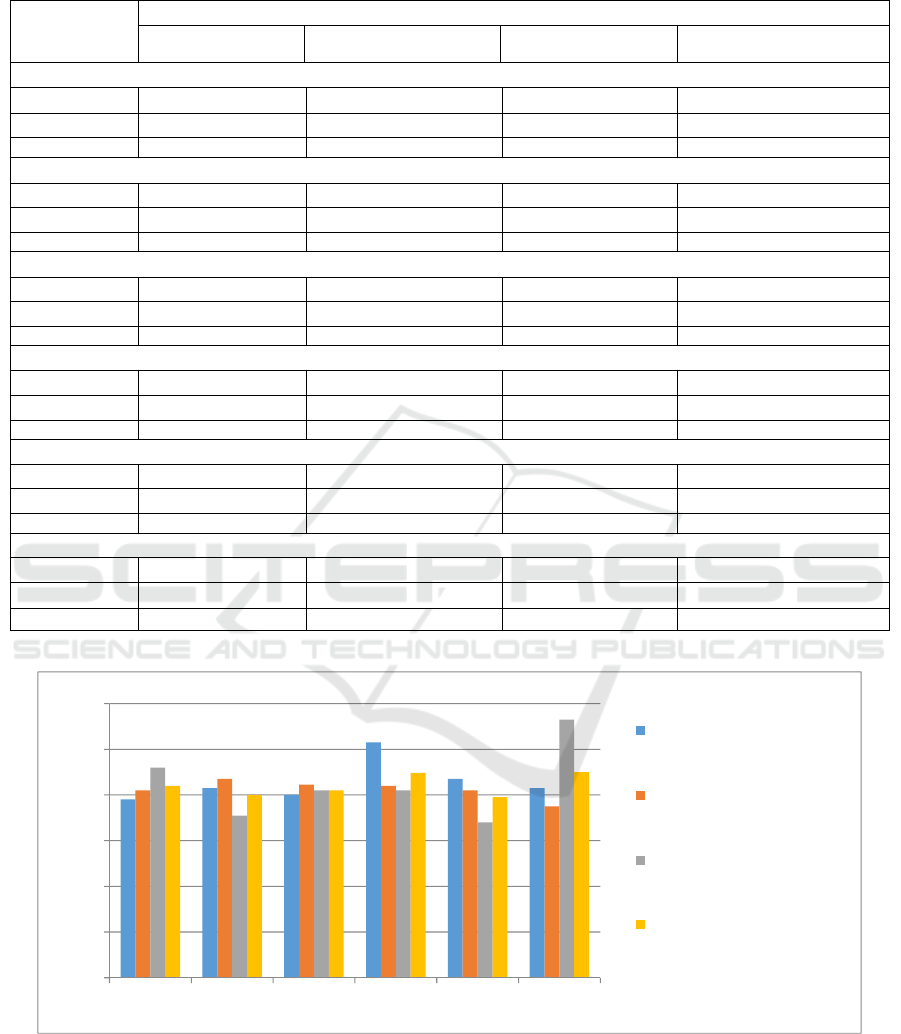
Table 3: Assessment results of the parameters characterizing the functional and reserve possibilities of sportsmen’s organism
in the experiment (conditional units).
Test group (TG)
Aerobic type (TG1) Mixed type (TG2) Anaerobic type (TG3)
Without consideration of
b
ioenergetic type (TG4)
Anaerobic metabolic capacity (ANMC), conditional units
before 45.42±13.68 71.07±6.9 124.65±8.96 76.12±34.63
after 48.96±11.23 76.9±4.89 136.1±11.32 82.52±9.15
t
0.62 2.19* 2.44* 0.84
Aerobic metabolic capacity (AMC), conditional units
before 240.1±21.36 229.5±17.63 204.41±21.69 226.65±29.49
after 260±18.13 249.5±13.68 218.92±18.67 244.85±16.83
t
2.22* 2.89* 1.38 2.50*
Total metabolic capacity (TMC), conditional units
before 285.5±12.3 300.6±21.42 329.06±22.18 302.78±34.07
after 308.52±14.38 326.4±19.22 355±23.01 327.65±18.87
t
4.10** 2.98** 2.34* 2.98**
Creatine phosphate metabolic power (CPMP), conditional units
before 31.54±2.35 29.55±1.95 38.75±2.26 32.64±5.93
after 34.79±2.167 32.03±2.19 41.93±2.12 35.57±2.16
t
3.23** 2.96** 2.86* 2.17*
Glycolytic metabolic power (GLMP), conditional units
before 31.60±2.65 29.52±2.47 33.5±2.03 31.28±3.19
after 34.35±2.76 31.94±2.03 35.77±1.58 33.75±2.12
t 2.35* 2.47* 2.35* 3.00**
Aerobic metabolic power (AMP), conditional units
before 57.48±4.43 52.12±5.80 46.39±4.03 51.62±10.60
after 62.25±3.22 56.03±6.13 51.63±4.34 56.28±8.96
t 2.63* 1.60 2.57* 1.56
Note: **-Р <0.01; *-Р <0.05
Figure 3: Increase dynamics of the parameters characterizing the functional and reserve possibilities of sportsmen’ organism
in different groups (%). ANMC - anaerobic metabolic capacity, AMC - aerobic metabolic capacity, TMC - total metabolic
capacity, CPMP - creatine phosphate metabolic power, GLMP - glycolytic metabolic power, AMP - aerobic metabolic power.
The increase of AMC value in the sportsmen of
“aerobic type” was 19.9 conditional units or 8.3% (P
<0.05), the sportsmen of the “mixed type” group
showed the increase by 20 conditional units or by
8.7% (Р <0.05), the sportsmen of the “anaerobic type”
group had the increase by 14.51 conditional units or
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
ANMC AMC TMC CPMP GLMP AMP
%
Test group “Aerobic type”
Test group “Mixed type”
Test group “Anaerobic
type”
Test group “Without
consideration of
bioenergetic type”

by 7.1%. The mean increase of AMC value in the
sportsmen of the test group without consideration of
their bioenergetic type was 18.2 conditional units or
8.03% (P <0.05).
The assessment of TMC value changes in the
sportsmen of “aerobic type” group showed the
increase by 23.02 conditional units or 8.05% (P
<0.01), the sportsmen of the “mixed type” group
showed the increase by 25.8 conditional units or by
8.45% (Р <0.01), the sportsmen of the “anaerobic
type” group had the increase by 25.94 conditional
units or by 8.2% (P <0.05). The mean increase of
TMC value in the sportsmen of the test group without
consideration of their bioenergetic type was 24.87
conditional units or 8.22% (P <0.01).
The increase of CPMP value in the sportsmen of
“aerobic type” was 3.25 conditional units or 10.3% (P
<0.01), the sportsmen of the “mixed type” group
showed the increase by 2.48 conditional units or by
8.4% (Р <0.01), the sportsmen of the “anaerobic type”
group had the increase by 3.18 conditional units or by
8.2% (P <0.05). The mean increase of CPMP value in
the sportsmen of the test group without consideration
of their bioenergetic type was 2.93 conditional units
or 8.97% (P <0.05).
The assessment of GLMP value changes basing
on the test results in the sportsmen of “aerobic type”
group showed the increase by 2.75 conditional units
or 8.7% (P <0.05), the sportsmen of the “mixed type”
group showed the increase by 2.42 conditional units
or by 8.2% (Р <0.05), the sportsmen of the “anaerobic
type” group had the increase by 2.27 conditional units
or by 6.8% (P <0.05). The mean increase of GLMP
value in the sportsmen of the test group without
consideration of their bioenergetic type was 2.47
conditional units or 7.9% (P <0.01).
The increase of AMP value in the sportsmen of
“aerobic type” was 4.77 conditional units or 8.3% (P
<0.05), the sportsmen of the “mixed type” group
showed the increase by 3.91 conditional units or by
7.5%, the sportsmen of the “anaerobic type” group
had the increase by 5.24 conditional units or by 11.3%
(P <0.05). The mean increase of AMP value in the
sportsmen of the test group without consideration of
their bioenergetic type was 4.66 conditional units or
9.03%.
Thus, the use of the experimental training method
in the sportsmen resulted in revealing the confident
increase of the parameter values characterizing the
functional and reserve possibilities of the organism,
namely, AMC, TMC, CPMP and GLMP. It should be
mentioned also that although there was no confident
increase of ANMC and AMP values in the sportsmen
group without consideration of the organism
bioenergetic type, we observed confident increase of
these parameters in the groups of “mixed” and
“anaerobic” types. The obtained data allows to make
a conclusion of the efficiency of the experimental
training method for long-distance runners taking into
account the peculiarities of energy provision for their
muscular activity.
4 CONCLUSIONS
1) The different organism’s response to the training
stress was observed during preparation for the
competitions in the sportsmen with different type
of energy provision for muscular activity. The
sportsmen of the test groups recovered after the
training stress more rapidly.
2) Studies have shown that athletes with "anaerobic"
and "mixed" type of muscular activity quickly
adapt to speed-strength work, and runners
"aerobic" type to the long work on endurance.
Further research in this direction can provide a
more accurate prediction of the efficiency of the
training process when you use an individual
approach to the planning of the running activity of
varying intensity.
3) This is evidence of the fact that consideration of
bioenergetic types of energy provision for
muscular activity in long-distance runners may
underlie the determination of training means and
methods for sportsmen.
REFERENCES
Ammann R. and Wyss T. (2015). Running Asymmetries
during a 5-Km Time Trial and their Changes over Time.
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Congress on
Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support,
pp.161-164.
Bakaev, V.V.,Bolotin, A.E.,Vasil'eva, V.S. (2015). Factors
determining sports specialization of cross country
skiers. Teoriya i Praktika Fizicheskoy Kultury, (2),
pp.40-41.
Bakaev, V.V.,Bolotin, A.E.,Aganov, S.S. (2016). Physical
training complex application technology to prepare
rescuers for highland operations. Teoriya i Praktika
Fizicheskoy Kultury, (6), pp.6-8.
Bolotin, А. Е. Bakaev V. V. (2015). Structure and content
of the educational technology of managing students'
healthy lifestyle. Journal of Physical Education and
Sport, 15(3), pp.362-364.
Bolotin, A., & Bakayev, V. (2017). Pedagogical conditions
necessary for effective speed-strength training of young
football players (15-17 years old). Journal of Human

Sport and Exercise, 12(2), pp. 405-413.
Bolotin A, Bakayev V. (2017). Peripheral circulation
indicators in veteran trail runners. J Phys Ther Sci, 29,
pp. 1092–1094.
Bolotin A., Bakayev V., Orlova N., Kozulko A. (2017).
Peculiarities of time structure and of biomechanical
organization of a construction of motor actions in the
hammer throw. Proceedings of Faculty of Kinesiology,
University of Zagreb (8th International Scientific
Conference on Kinesiology), pp. 137-141.
Bolotin A., Bakayev V. (2016). Factors that determine high
efficiency in developing speed and strength abilities of
female hurdlers. Journal of Physical Education and
Sport, 16(3), pp.910-913.
Karlenko V., Karlenko N. and Pshenichnova A. (2008).
Cardiomonitoring "D & K-TEST" as a diagnostic
method for determining the functional state and reserve
capabilities of the athlete's body. Journal of Actual
Problems of Physical Culture and Sports, 15, pp.39-50.
Kuznetsova Z., Kuznetsov A., Mutaeva I., Khalikov G. and
Zakharova A. (2015). Athletes Preparation based on a
Complex Assessment of Functional State. In
Proceedings of the 3rd International Congress on Sport
Sciences Research and Technology Support, pp. 156-
160.
Osipov, A., Kudryavtsev, M., Kuzmin, V., Salyamova, P.,
Gavrilyuk, O., Struchkov, V., Galimov, G., Zakharova
L. (2016). Methods of operative and informative
control of the muscle loading level used during the
training of sambo wrestlers. Journal of Physical
Education and Sport, 4. 1247-1252.
Zakharova A. and Mekhdieva K. (2016). Technologies of
Effective Training Control in Amateur Triathlon - Non-
Invasive Hemodynamic Measurements and Exercise
Testing for Accurate Training Prescription. In
Proceedings of the 4th International Congress on Sport
Sciences Research and Technology Support, pp. 83-88.
