
The Implementation of the Standard of Process in Social Studies
Teaching and Learning in State Junior High Schools
Adam Firdaus, Hayatin Nisa, Emi Minarni, Hanisa Sismaya Lestari and Rosita Rosita
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Jalan Setiabudhi 229 Bandung, Jawa Barat, Indonesia
{hayatinnisa, hanisasismayalestari} @student.upi.edu
Keywords: Standard of Process, Social Studies Teaching and Learning.
Abstract: One of the problems frequently encountered in education is the weak teaching and learning process. The
researchers would like to know whether the teaching and learning process of social studies in junior high
schools in Palembang-South Sumatera has been implemented based on the standard of process set by the
government. The aim of the research is to find about the implementation of the standard of process in terms
of planning, implementation, and evaluation of learning outcomes. The method employed was descriptive.
The subjects were four civil servant teachers of Palembang-South Sumatera who taught social studies in junior
high schools. The data collection techniques consisted of: observation, interview, and documentation. The
results show that the implementation of the standard of process in social studies teaching and learning process
in terms of assessment is categorized as Very Good (82.66%).The implementation of the standard of process
in the aspect of instructional planning is Very Good (100%); in terms of social studies teaching and learning
process is Good (66.74%), and in terms of assessment of learning outcomes is Very Good (81.25%).
1 INTRODUCTION
The learning process is the spearhead of improving
the quality of education both in the educational unit
scale and on the scale of national education (Yani,
2016). But, one of the problems frequently
encountered in education today is the weak teaching
and learning process. Meanwhile, teaching and
learning process is an important part of measuring
learners’ learning outcomes (Linand Wu, 2016;
Yazici, 2016). In reality, today’s classroom teaching
and learning is directed towards making learners able
to memorize information, in which their brain is
forced to remember and store information without
being required to understand what they can recall and
relate it to their daily life.
Teaching and learning process cannot be
separated from teachers and learners (Ayeni and
Olasunkanmi, 2015:2). However, in reality,
classroom teaching and learning is implemented
according to the ability and desire of the teachers.
Meanwhile, teachers have varying abilities in the
management of teaching and learning, depending on
their academic background and their motivation and
love of the profession. There are teachers who
seriously carry out the management of teaching and
learning through careful planning, utilizing all the
existing learning resources, and taking into account
the level of learners’ intellectual and psychological
development.
Such teachers will produce higher quality of
graduates compared to teachers who manage the
teaching and learning without serious efforts and
without considering the various factors that can affect
the success of the teaching and learning process.
Given the diversity of cultures, other
backgrounds, and characteristics of learners, and the
demand to produce qualified graduates, the teaching
and learning process for each subject must be flexible,
varied, and meet the standards. The teaching and
learning process in each unit of elementary and
secondary education must be interactive,
inspirational, fun, challenging, and motivating
learners to participate actively, and must provide
sufficient space for initiative, creativity, and
independence according to the learners’ talents,
interests, physical and psychological development.
Priority order in improving the competency of
graduates is done by improving the quality of labor
standards, contents, facilities and infrastructure,
management, assessment, process and financing. In
accordance with the mandate of the Government
Regulation No. 19 of 2005 concerning National
24
Firdaus, A., Nisa, H., Minarni, E., Lestari, H. and Rosita, R.
The Implementation of The Standard of Process in Social Studies Teaching and Learning in State Junior High Schools.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship (ICEEE 2017), pages 24-29
ISBN: 978-989-758-308-7
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Standards of Education, one of the standards to be
developed is the standard of process. The
Government has set a standard of education that
regulates teaching and learning process, namely in the
Regulation of the Minister of Education and Culture
(Permendikbud) No. 41 of 2007 on the Standard of
Process. The Standard of Process is the criteria of the
implementation of teaching and learning in one unit
of education to achieve the Graduate Competency
Standard (Permendikbud No. 41 of 2007 on
(Mukarramah, Juanda, and Fitriah, 2015)). From this
definition, there are several things that need to be
underlined, namely: (1) the standard of education
process applies to every formal educational
institution at a certain level of education. This means
that all schools must carry out the teaching and
learning process in accordance with the standards
formulated in the standard of education process; (2)
the standard of education process is related to the
procedure of the implementation of teaching and
learning. This means that the standard of process can
be used as a guideline for teachers in making
instructional planning for a certain period of time or
on a daily basis in executing the planning in the real
activities in the field; and (3) the standard of process
is directed towards achieving Graduate Competency
Standard. Graduate Competency Standards the
primary source or reference in determining a standard
of process (Wina Sanjaya, 2007). This means that the
standard of process can be applied if the graduate
competency standardis already in place (Raharjo,
2012).
The standard of process includes the planning of
teaching and learning process or instructional
planning, the implementation of teaching and
learning process, the assessment of learning
outcomes, and the supervision of teaching and
learning process for an effective and efficient
teaching and learning process (Rahmawati and
Soeharto, 2013). Through the standard of education
pr process, every teacher can develop the teaching
and learning process in accordance with the specified
rules. Instructional planning becomes mandatory for
teachers before conducting a teaching and learning
activity. Planning can be interpreted as the process of
preparing instructional materials, instructional media,
approaches and methods of learning and assessment
for a certain allocated time implemented at a certain
time to achieve the set goals (Abdul Majid, 2008).
Instructional planning includes syllabi and lesson
plans that both refer to the content standard
(Rahmawati and Soeharto, 2013).
Syllabus is a reference for the framework of
teaching and learning for each subject matter of study
(Permendikbud No. 41 Year 2007). Lesson plan is
defined as a plan of face-to-face teaching and learning
activities for one or more meetings. The educator
must prepare a complete and systematic lesson plan
so that teaching and learning will take place
interactively, inspiringly, efficiently, and will
motivate students to actively participate in the
teaching and learning activities. The components of a
lesson plan include the subject identity, competency
standard (CS), basic competence (BC), competency
achievement indicators, learning objectives, teaching
materials, time allocation, learning methods, learning
activities, assessment of learning outcomes, and
learning resources. Therefore, every teacher should
not ignore the instructional planning when carrying
out the teaching and learning activities so as to keep
the learning activities in control.
The Implementation teaching and learning
process is the implementation of the instructional
planning prepared by educators. The Implementation
teaching and learning process consists of requirement
of implementation teaching and learning process and
implementation of learning. Requirement of
implementation teaching and learning process
include study groups, minimal teacher workload,
textbooks, and classroom management.
Implementation of learning it includes preliminary
activities, core activities, and closing activities
(Permendikbud No. 41 of 2007).
Assessment is a systematic process which
involves collecting, analyzing, and interpreting
information to determine the extent to which a student
or a group of students has achieved the set learning
objectives, both in the aspects of knowledge and
attitudes (Kusaeri, 2014). Assessment is done by
teachers to the learning outcomes to measure the
levels of attainment of learners’ competences, and the
result is used to make progress report of learning
outcomes, and a basis to improve teaching and
learning process (Permendikbud No. 41 Year 2007).
Assessment is carried out consistently,
systematically, and programmatically by using test
and non-test activities, in written or oral form;
performance observation; attitude measurement; and
assessment of work in the forms of tasks, projects
and/or products, portfolios, and self-assessment.
Assessment of learning outcomes references the
Standard of Educational Assessment and the
Guidelines for Subject Group Assessment.
The role of teachers is crucial in an attempt of
improving the quality of education. Therefore,
teacher as a learning agent is required to be able to
organize the teaching and learning process as well as
possible to support the development of education. A
The Implementation of The Standard of Process in Social Studies Teaching and Learning in State Junior High Schools
25

teacher should not only be skilled in delivering
materials, but also in planning, implementing, and
evaluating the teaching and learning (Mukarramah,
Juanda, and Fitriah, 2015). An example of the skill in
planning an instruction is making instructional media.
A teacher should especially be skilled in making
lesson plan and syllabus, because these two serve to
help a teacher in implementing teaching and learning
in the classroom. In developing lesson plans and
syllabi, the government has set the standard of
process that contains rules to be referenced by
teachers.
Research on the implementation of the standard of
process has previously been done by Syarifudin
(2014) under the title of “A Study on the
Implementation of the Standard of Process by Physics
Teachers in Several Senior High Schools in Medan
City”. The result of this research reveals that the
standard of education process in several senior high
schools in Medan City has not been fully
implemented in accordance with the Regulation of the
Minister of National Education (Permendiknas) No.
65 Year 2013. The present research is different from
Syarifudin’s (2014) in that the senior high schools
under his study applied the 2013 Curriculum,
referencing the standard of process based on
Permendiknas No. 65 Year 2013. Meanwhile, the
present study took junior high schools as its subjects
and the schools applied the school-based curriculum
which references the standard of process in
accordance with the Regulation of the Minister of
National Education of the Republic of Indonesia No.
41 of 2007.
To find about the implementation of the standard
of process in the subject of social studies at secondary
school level, the authors conducted research in three
state junior high schools implementing the school-
based curriculum in Palembang-South Sumatera,
each of which accredited A, B, and C.
Based on the results of a survey conducted to four
civil servant teachers teaching the subject of social
studies in three junior high schools, it is found that the
teachers have been aware of the Regulation of the
Minister of Education and Culture of the Republic of
Indonesia No. 41 of 2007 on the Standard of Process.
The teachers always make instructional media, such
as syllabi and lesson plans which are in accordance
with the provisions that apply to the school-based
curriculum; however, whether the teaching and
learning process has been in accordance with the
Standard of Process has to be further investigated.
The purpose of this research is to find about the
Implementation of the Standard of Processing terms
of the planning of teaching and learning process,
implementation of teaching and learning process, and
assessment of teaching and learning outcomes in the
subject of social studies in the junior high schools in
Palembang-South Sumatera.
2 METHODS
The research employed the descriptive-qualitative
method. The research variables the Standard of
Process. The subjects of this research consisted of
four teachers of social studies subject with a civil
servant status from three state junior high schools in
Palembang-South Sumatera
In this research, observation is the main
instrument of data collection. Observation was
conducted two times to each teacher by seeing first-
hand how the social studies teachers implemented the
standard of process, starting from the beginning of the
teaching and learning process in the classroom to the
end of the process. The observation sheet consists of
39 items.
Interview to the research subjects is the technique
of collecting data to support data from observations
to find about the implementation of the standard of
process in the teaching and learning process. The type
of interview carried out by the researchers was the
semi-structured interview. Initially, there were 10
items in the interview sheet.
The researchers also documented some
complementary data to the research, which are
written data, in the forms of syllabus, lesson plans
made by the social studies teachers, data of the
number of students in one class, the teaching load,
and learners' learning outcomes for social studies
subject. There were eight items of written documents
in total.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The variable of standard of process in this study is
measured using three indicators, namely instructional
planning, teaching and learning implementation, and
assessment of learning outcomes by using
observation, interview, and documentation. The
results were then analyzed using the Guttmann scale
with the following steps:
1. Check-listing each descriptor on the observation
sheet
2. Calculating the score for each indicator, which
is as follow:
0 = if the descriptor is NOT OBSERVED
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
26
1 = if the descriptor is OBSERVED
3. Calculating the maximum score for all items
4. Comparing the total score obtained to the total
maximal score
The obtained score was calculated with the
following formula
P =
ி
ே
X 100 (1)
The results of observations, interviews, and
documentation that were originally in the form of
quantitative data were then processed into qualitative
data by matching the percent value with the criteria of
assessment in Table 1 as follows:
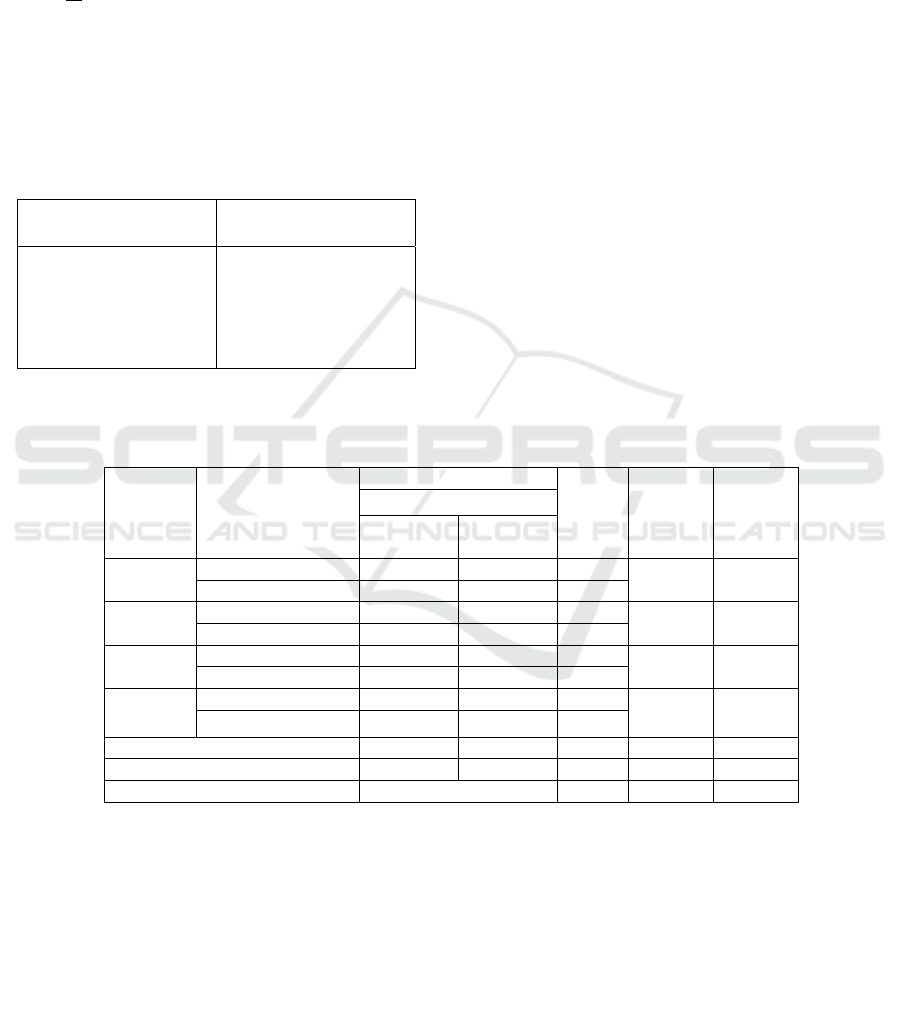
Table 1: Criteria of Assessment
(Modified from Arikunto, 2013)
Based on the results of data calculation, it is found
that the implementation of the standard of process in
the teaching and learning of social studies in state
junior high schools in Palembang-South Sumatera is
included under the category of very good, with a
score of 82.66%. This result is described and
discussed as follows:
Analysis of the Standard of Process in Terms of
Instructional Planning
The results of the documentation of the
implementation of the standard of process in terms of
instructional planning in SMP Negeri (State Junior
High School) Palembang-South Sumatera can be seen
in Table 2:
Table 2: Documentation planning the learning process
Teacher’s
Name
Documentation of
the n-meeting
Indicato
r
Total Average Criteria
1
Syllabus Lesson
Plan
A 1 1 1 2 100% Very
Good
2 1 1 2
B 1 1 1 2 100% Very
Good
2 1 1 2
C 1 1 1 2 100% Very
Good
2 1 1 2
D 1 1 1 2 100% Very
Good
2 1 1 2
Total 8 8
Maximal Score 8 8
Avera
g
e 100%
Based on table 2 Documentation Planning The
learning process that instructional planning is
categorized as very good.
3.1 Analysis of the Standard of Process in
terms of Teaching and Learning
Implementation
The observation results of the application of the
standard of process in terms of the implementation of
the teaching and learning process of social studies in
the state junior high schools in Palembang-South
Sumatera can be seen in table 3:
Percent Value Criteria of
Assessmen
t
76% <value ≤ 100%
51% <value ≤ 75%
26% < value ≤ 50%
0% < value ≤ 25%
0%
Very Good
Good
Average
Fair
Poor
The Implementation of The Standard of Process in Social Studies Teaching and Learning in State Junior High Schools
27

Table 3: The Implementation of Teaching and Learning Process
Techniques of Data Collection
Observation Interview Documentation
81.47% 62.50% 56.25%
Total 200.22%
Average 66.74%
Based on table 3 that the implementation of teaching
and learning process in social studies is categorized
as good.
3.2 Analysis of the Standard of Processin
Terms of Assessment of Learning
Outcomes
Documentation data for the assessment of learning
outcomes obtained from teacher A, B, C, and D from
three state junior high schools in Palembang-South
Sumatera are presented in Table 4.
Table 4: Documentation of Assessment of Learning Outcomes
Teacher’s
Name
Documentation of
the n-meeting
Indicato
r
Total Average Criteria
3
Written Exam Work-Based
Assessment
A
1 1 1 2
100% Very good
2 1 1 2
B
1 0 1
Fair
2 0 1 1
C
1 1 1 2
100% Very good
2 1 1 2
D
1 1 0 1
75% Good
2 1 1 2
Total 6 7
Maximal Score 8 8
Average 81.25%
Based on table 4 that documentation of assessment of
learning outcomes in social studies is categorized as
very good.
Furthermore, based on the recapitulation of data
analysis results, it can be concluded that the
implementation of the standard of process in social
studies teaching and learning is categorized as very
good, or with a score of 82.66%, as can be seen in
Table 5:
Table 5: Recapitulation of Data Analysis Results of
the Standard of Process
Indicator of the Standard
of Process
Average
%
1 2 3
A
verage
%
100% 66.74% 81.25% 82.66%
4 CONCLUSIONS
The implementation of the standard of process in the
teaching and learning of social studies in the state
junior high schools in Palembang-South Sumatera is
overall included under the category of Very Good.
Individually, in terms of instructional planning, the
implementation is also included under the category of
Very Good; meanwhile, in terms of the teaching and
learning process and assessment of learning
outcomes, the implementation of the standard of
process in the teaching and learning of social studies
are included under the categories of Good and Very
Good, respectively. In this research, several aspects
are found to be not in accordance with the standard of
process. First, the number of learners in a class
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
28

exceeds the maximum limit of 32 students. In
addition, as regards the ratio of textbooks to students,
there are learners who do not have a textbook. Finally,
the teachers still very rarely use instructional media
in the teaching and learning process.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was made possible because of the
contribution in the forms of thoughts, advice, and
information from the lecturers of the Economics
Education Program of the School of Post-Graduate
Studies of UPI and lecturers of Sriwijaya University
as well as the participation of social studies teachers
at SMPN (State Junior High School) 1 Mesuji, SMPN
2 Mesuji, and SMPN 3 Mesuji.
REFERENCES
Amri, S. 2013. Pengembangan dan Model Pembelajaran
dalam Kurikulum 2013. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara.
Arikunto. (2013). Manajemen Penelitian. Jakarta: Rineka
Cipta.
Ayeni, A., and Olasunkanmi, O. 2015. Relationship
Between Student Learning Factors and Their Learning
Outcome in Senior Secondary School Economics in
Osun State Public Secondary Schools , Nigeria. Journal
of Emerging Trends in Educational Research and
Policy Studies (JETERAPS), 6(2), 159–168.
Depdiknas. 2007. Permendiknas No 41 tahun 2007 tentang
Standar Proses untuk Satuan Pendidikan Dasar dan
Menengah. Jakarta: Depdiknas.
Kusaeri. 2014. Acuan dan Teknik Penelitian Proses dan
Hasil Belajar. Yogyakarta: ar-Ruzz Media
Lin, C. S., and Wu, R. Y. W. 2016. Effects of Web-Based
creative thinking teaching on students’ creativity and
learning outcome. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics,
Science and Technology Education, 12(6), 1675–1684.
https://doi.org/10.12973/eurasia.2016.1558a
Majid, Abdul. 2008. Perencanaan Pembelajaran
Mengembangkan Standar Kompetensi Guru. Bandung:
PT. Remaja Rosdakarya
Mukarramah, U., Juanda, A., and Fitriah, E. 2015. Analisis
Standar Proses Pembelajaran Biologi Kelas XI di SMA
Negeri 1 Majalengka Tahun Pelajaran 2014/2015.
Science Education, 5.
Raharjo, S. B., 2012. Evaluasi Trend Kualitas Pendidikan
di Indonesia. Jurnal Penelitian dan Evaluasi
Pendidikan Tahun 16, Nomor 2, 2012.
Rahmawati, N. A., and Soeharto. 2013. Implementasi
Standar Proses Pembelajaran Paket Keahlian Teknik
Instalasi Pemanfaatan Tenaga Listrik Di Yogyakarta.
E-Journal Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta, 25(2), 82–
89.
Sanjaya, Wina. 2007. Strategi Pembelajaran Berorientasi
Standar Proses Pendidikan. Jakarta: Kencana Prenada
Media Group
Yani. A., 2016, Standar Proses Pembelajaran Geografi pada
Kurikulum 2013. Jurnal Pendidikan Geografi. Volume
16, Nomor 1, hlm 1-12.
Yazici, H. 2016. Role of learning style preferences and
interactive response systems on student learning
outcomes. International Journal of Information and,
6(2), 109–134. Retrieved from
http://www.inderscienceonline.com/doi/abs/10.1504/IJ
IOME.2016.076046
The Implementation of The Standard of Process in Social Studies Teaching and Learning in State Junior High Schools
29
