The Impact of Entrepreneurship Education to Entrepreneurial
Intention and Motivation
Febrina Iqhyanul Imansari
Postgraduate Universitas Negeri Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: Entrepreneurship Education, Entrepreneurial Intention, Entrepreneurial Motivation.
Abstract: The increasing economic growth of a country cannot be separated from the existence of entrepreneurs that
can increase employment and productivity so that it affects the increased economic growth so that
entrepreneurship education is required early to increase interest and motivation for entrepreneurship,
especially among students. The purpose of this paper is to analyze the influence of entrepreneurship education
on the interest and motivation of entrepreneurship of economic education students. The method of this
research is associative research using quantitative approach. The sample in this research is University of
Surabaya Economic Education Student. Technique of collecting data in this research that is using test to know
entrepreneurship education, and questionnaire to know intention and motivation entrepreneurship student of
economic education. The result of this study showing that Entrepreneurship Education has a positive and
significant influence on entrepreneurship interest and Entrepreneurship education also has a positive and
significant influence on entrepreneurship motivation.
1 INTRODUCTION
Unemployment becomes one of the problems that
occur in some countries is no exception in Indonesia.
Unemployment occurs because the number of
available jobs is not proportional to the number of job
seekers. In Indonesia, the open unemployment rate in
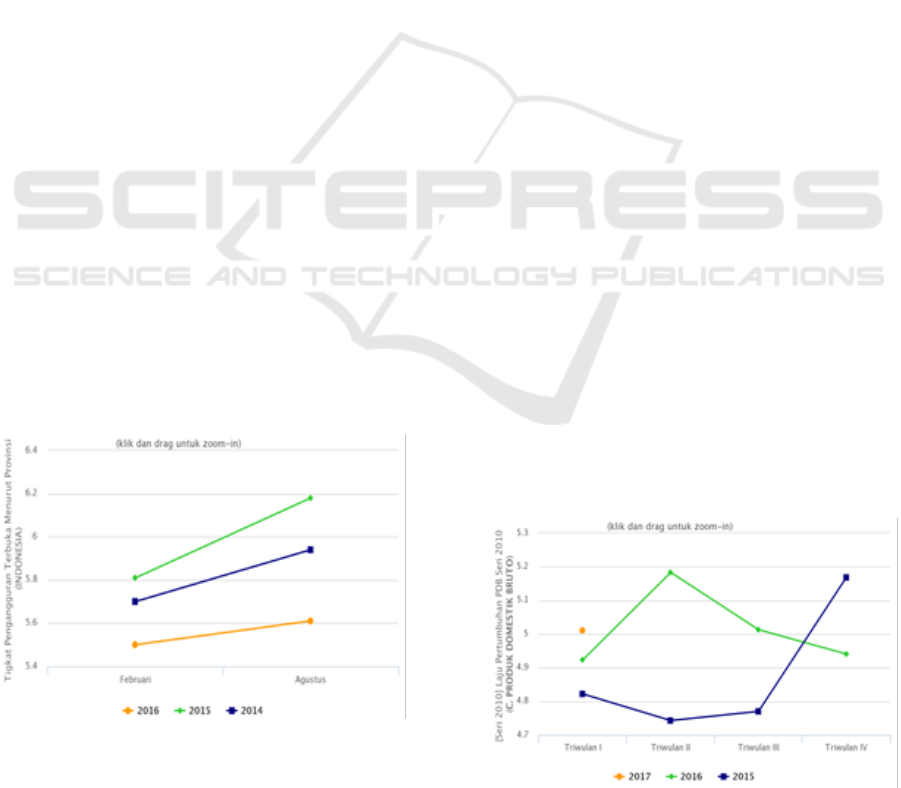
August of 2016 is 5.61% as shown in the following
graph:
Figure 1: Open Unemployment Rate in Indonesia
Source: Badan Pusat Statistik (Bps.go.id)
From the graph above can be seen that the
unemployment rate from 2015 to 2016 decreased,
whereas in 2016 the unemployment rate per month
increased. Nevertheless, unemployment remains a
problem that needs to be resolved and must be
addressed immediately because this unemployment
can affect the economic growth of a country and the
welfare of society itself. Unemployment causes a
decrease in the productivity of a country so that the
output produced by a country will also decrease, it
affects the economic growth rate of a country.
Economic growth in Indonesia can be seen in the
following graph:
Figure 2: Indonesia GDP Growth Rate of Basic Year 2010
Imansari, F.
The Impact of Entrepreneurship Education to Entrepreneurial Intention and Motivation.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship (ICEEE 2017), pages 257-262
ISBN: 978-989-758-308-7
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
257

From the above chart can be seen in 2017 the first
quarter of Indonesia's economic growth of 5.01
percent. The rate of economic growth has increased
from the previous year. This corresponds to the
previous unemployment chart. When the number of
unemployed decreases then economic growth
increases. The relationship between unemployment
and economic growth can also be explained by
Okun's law or "Okun's Law" which explains the
negative relationship between unemployment and
economic growth, where as unemployment rises,
economic growth declines and vice versa if
unemployment declines, economic growth increases.
Therefore, to increase economic growth one of
them by reducing the unemployment rate in
Indonesia. One way to reduce the unemployment rate
is by creating jobs or in other words by growing
entrepreneurship in order to reduce unemployment in
Indonesia. Nowadays it should be more inculcate
thinking to the people of Indonesia for as opening job
field not as job seeker. This should be instilled
especially for high school and college graduates so
that they are not joboriented but how to create jobs
for the community as well as for the welfare of their
lives.
Growing the entrepreneurial spirit is needed from
an early age, that is, since it is still in the educational
institution. This is where the role of educational
institutions to instill entrepreneurial spirit to learners,
to foster motivation and interest of learners to
entrepreneurship after graduation later. The role of
educational institutions is to provide entrepreneurship
education. Entrepreneurship education is expected to
generate entrepreneurial spirit in accordance with the
potential of each learner. Not a lot of unemployment
is from college graduates, this is the reason for
entrepreneurship education as one of the subjects in
universities such as Universitas Negeri Surabaya. The
existence of entrepreneurship education is to instill
entrepreneurship spirit in the students so have interest
and motivation to entrepreneurship both still in
college and after graduation later. Have a thought that
this time what is needed is to open a job field instead
of looking for a job.
In accordance with the results of research
conducted by Michael Lorz (2011) which states that
"entrepreneurial intention will be positively
influenced by the entrepreneurship education
program". In addition, the research conducted by
Remeikiene et al (2013) concluded that "The student
of economics is of the opinion that education has a
positive impact on their intentions to seek for
entrepreneurship." Research conducted by Yunita
(2013) also shows that there is a positive influence
between entrepreneurship education on
entrepreneurship motivation.
Department of Economic Education has a mission
"Developing entrepreneurial spirit" so that
entrepreneurship education becomes a compulsory
course for students majoring in economic education.
It is expected that with this entrepreneurship
education can foster interest and motivation of
students of economic education courses for
entrepreneurship. However, according to researcher
observation, after getting entrepreneurship course,
Economics education student who continue
entrepreneurship is only 5% of the total student of
economic education program class of 2014.
Previously, entrepreneurship students only because of
the demands of the subject of entrepreneurship
practice in order to get value from the eyes
Entrepreneurship lectures. Based on this background,
researchers are interested to examine the effect of
entrepreneurship education to the interest and
motivation of entrepreneurship student of economic
education program class of 2014 at Universitas
Negeri Surabaya.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Entrepreneurship Education
Understanding education according to Law no. 20 of
2003 on National Education System as a conscious
and planned effort to create learning atmosphere and
learning process so that learners actively develop
their potential to have spiritual power of religion, self-
control, personality, intelligence, noble character, as
well as the skill needed by him, Society, nation and
state. While the definition of entrepreneurship
according to Purnomo (2005: 20) is a capability in
thinking creative and innovative behavior that is used
as the basis, resources, driving force, the purpose of
strategy, tips and processes in the face of life
challenges. The science of entrepreneurship
according to Daryanto (2012: 4) is a discipline that
studies about the values, abilities and behavior of a
person in facing the challenges of life to obtain
opportunities with various risks that may be faced.
According to Soeharto Prawirokusumo in
Daryanto (2012: 4), entrepreneurship education needs
to be taught as a separate independent discipline
because: a. Entrepreneurship contains a complete
body of knowledge and the real that there is a theory,
concepts, scientific methods are lengkah; B.
Entrepreneurship has two concepts, namely startup
and venture growth venture; C. Entrepreneurship is a
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
258

discipline that has its own object, the ability to create
something new and different; D. Entrepreneurship is
a tool for creating equitable distribution and revenue
bending.
Here are some ways to instill entrepreneurship
education for students according to Asmani (2011:
124), namely:
a. Increase the practitioner from theory
The educational institution should multiply the
practice rather than the theory. An interactive
applicative learning model should be applied to
encourage students to entrepreneurship learning
spirit. Better if learners practice their business ideas
while still in college and school so as to practice the
theory directly obtained.
b. Develop teaching methodologies
In an educational institution requires an
applicative, motivate, creative and inspirational
teaching strategies that motivate learners in learning
and practicing entrepreneurship.
c. Learning Strategy / Innovation
Learning innovation strategy known as Spices
acronym which is short for student entered, problem
based, integrated aching, community oriented, early
clinical exposure and self-directed learning. This
strategy is most appropriate applied to
entrepreneurship lectures.
d. The role of department managers
Any innovation or change of teaching and
learning method should be designed, implemented,
monitored and evaluated by the manager consistently
and consistently, as well as making vision of the goals
to be achieved. Learning innovation or
entrepreneurship education requires appropriate
strategies or can accommodate the entrepreneurial
character of the entrepreneur.
2.2 Entrepreneurial Intention
Interest according to Purnomo (2005: 66) is an
awareness of the soul that is active to receive
something from the outside. While Interests
according to White and Bernard in Purnomo (2005:
66) is a condition that occurs when a person sees
temporary characteristics or meanings of situations
connected with desires or needs themselves.
Meanwhile, interest in entrepreneurship according to
Purnomo (2005: 67) is defined as a strong desire of a
person, whether conscious or unconscious are
satisfied through certain behaviors. Empathic al that
need to be considered in the interest variable are: 1.
Interest is considered as "catcher" or intermediary
motivational factors that have an impact on the
behavior, 2. Interest shows how strong a person's
effort to dare to try to do something. 3. Interest shows
how much effort a person is planning to do, 4. Interest
is closest to dealing with subsequent behavior.
Interest in entrepreneurship can be seen from two
main indicators are: 1. how strong a person's effort to
dare to try to do entrepreneurial activity; How much
effort a person is planning to engage in
entrepreneurial activity (such as managing time and
finances for entrepreneurial purposes).
2.3 Entrepreneurial Motivation
According to Terry in Purnomo (2005: 59)
Motivation is an intrinsic desire that encourages a
person to act. Meanwhile, according to Donnel,
motivation is defined as the impetus and effort to
meet or satisfy a need or a goal. There are three
aspects related to motivation are: 1) What factors that
drive behavior. 2) Where the behavior is directed. 3)
How the behavior is maintained.
There are several motivations in entrepreneurship
are: a) Financial reasons, namely to earn a living to
get rich, to seek additional income as a guarantee of
financial stability; B) The social reason of obtaining
prestige / status to be known and respected to be an
example for others, in order to meet the crowds; C)
The reason for the service is to provide employment
to the community, to organize the community, to help
the community economy for the future of the family;
D) The reason for self-fulfilment is to be self-
sufficient, to achieve something desirable, to avoid
dependence on others, to be more productive, and to
use personal abilities.
3 METHODS
The type of research used in this study is associative
research because this study aims to determine the
effect of entrepreneurship education on the interest
and motivation entrepreneurial student of economic
education program of Universitas Negeri Surabaya.
While the approach used in this study is a quantitative
approach. According to Sugiyono (2007: 15),
quantitative research emphasizes the testing of
theories through the measurement of variables with
numbers, words, and sentences. The design of this
research are:
The Impact of Entrepreneurship Education to Entrepreneurial Intention and Motivation
259

Information:
= partial impact
Figure 3. Entrepreneur Education Chart
The research was conducted at the Faculty of
Economics, State University of Surabaya, located at
the Campus of Surabaya State University of
Surabaya, East Java. Population in this research is all
student of education program of economy class of
2014 which is counted 81 student. The sampling
technique in this research use saturated sampling
technique with sample number 81 students. The
research instrument used by the researcher is a closed
questionnaire. Questionnaire that the number of items
and alternative answers have been determined,
respondents just choose according to the actual
situation. Questionnaire is used to measure the
variables of entrepreneurship education,
entrepreneurship interest and entrepreneurship
motivation. Researchers develop the instrument using
Likert scale with four alternative answers are
Strongly Agree (SS), Agree (S), No Agree (TS),
Strongly Disagree (STS). In order for the data
obtained in accordance with the actual fact (valid) and
is permanent or reliable (reliable). Then the required
validity test and reliability test on the instrument. The
result of validity test shows that the result of pearson
correlation or rhitung is bigger (>) than rtabel. Rtabel
for n = 81 with 5% significance is equal to 0,213, so
that every item of statement in research instrument in
the form of questionnaire about entrepreneurship
education, entrepreneurship interest, and
entrepreneurship motivation are valid. The results of
the reliability test show that the cronbach's Alpha
(0.846> 0.60) result in the entrepreneurship
educational instrument is considered reliable, while
the entrepreneurship interest instrument produces
cronbach's Alpha of 0.822> 0.60 so it is stated
reliably and the entrepreneurship motivation
instrument cronbach's alpha 0.883> 0.60 The
technique of data collection in this research is using
questionnaire, interview, documentation,
observation, data analysis technique in this research
is by using classical assumption test (normality test,
linearity test, heteroscedasticity test), simple
regression analysis, hypothesis test (t test) And
coefficient of determination.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
In this study to measure the entrepreneurship
education variable using 12 statements, to measure
the entrepreneurship interest variable using 13
statements and to measure entrepreneurship
motivation using 9 statements.
4.1 Normality Test
Table 1: Tests of Normality x
Kolmogorov-Smirnov
a
Shapiro-Wilk
Statistic
Df
Sig.
Statistic
df
Sig.
x
.089
81
.173
.983
81
.376
a. Lilliefors Significance Correction
Table 2: Tests of Normality y
Tests of Normality
Kolmogorov-Smirnov
a
Shapiro-Wilk
Statistic
df
Sig.
Statisti
c
df
Sig.
y1
.098
81
.052
.970
81
.055
y2
.090
81
.161
.982
81
.324
a. Lilliefors Significance Correction
The table above shows that the value of
significance of entrepreneurship education variables
of p = 0.173, so p> α (0,05). Thus the sample comes
from a normally distributed population. For
entrepreneurship interest variable shows a
significance value of 0.052> 0.05 so that the sample
comes from normally distributed populations. The
variable of learning motivation shows a significance
value of 0.161> 0.05 so that the sample comes from a
normally distributed population.
Entrepreneur
Education
Entrepreneurial
Intention
Entrepreneurial
Motivation
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
260
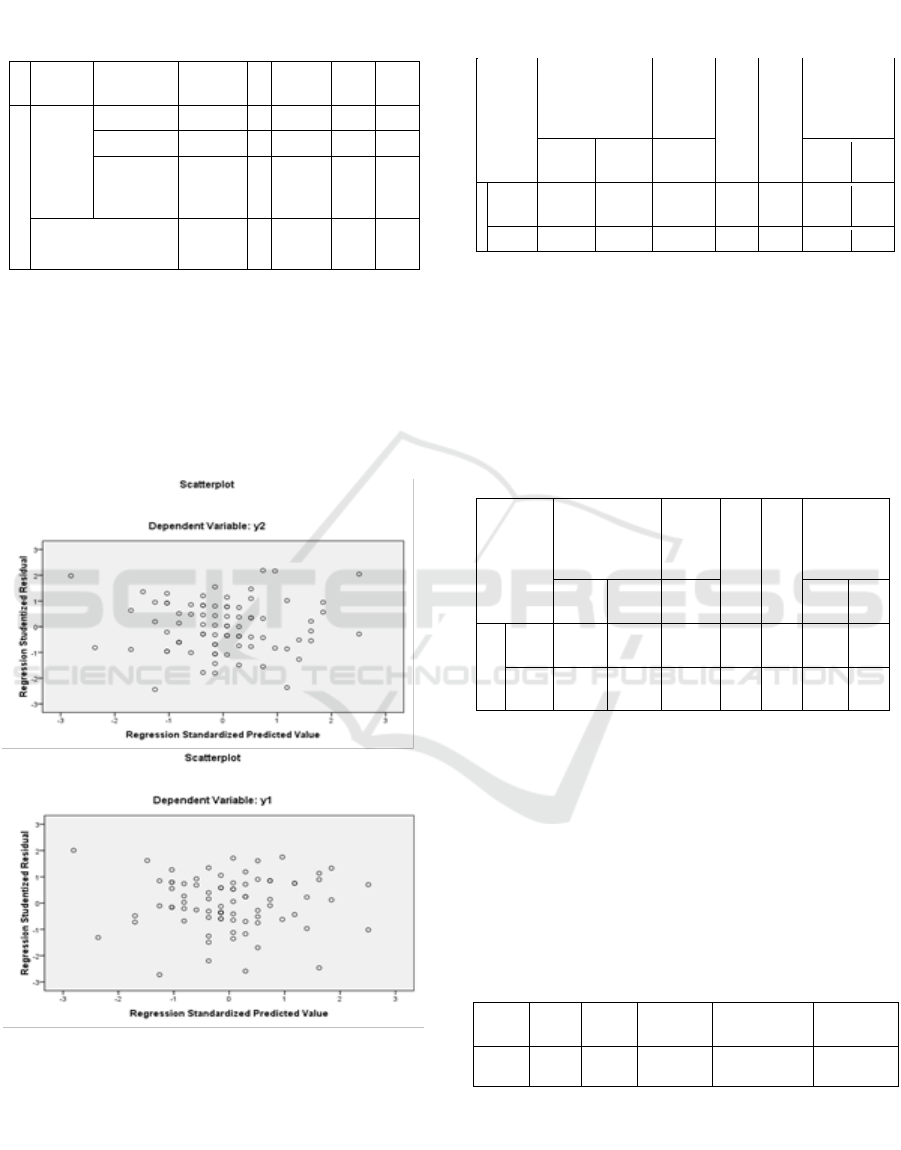
4.2 Test Linearity
Table 3: ANOVA Table
Sum of
Squares
df
Mean
Square
F
Sig.
y
1
*
x
Between
Groups
(Combined)
396.617
19
20.875
1.138
.339
Linearity
77.182
1
77.182
4.207
.045
Deviation
from
Linearity
319.435
18
17.746
.967
.507
Within Groups
1119.037
61
18.345
Total
1515.654
80
From the anova table above shows that the sig
value of 0,507, this means the value of sig> 0,05, so
it can be concluded that between entrepreneurship
education variable with entrepreneurship interest has
a linear relationship.
4.3 Heteroscedasticity Test
Figure 4: The appearance of spreading points and does not
occur a certain pattern
From the picture above can be seen that the
appearance of spreading points and does not occur a
certain pattern. Thus it can be concluded that there is
no heteroscedasticity.
4.4 T Test
Table 4: Coefficients
a
Model
Unstandardized
Coefficients
Standard
ized
Coeffici
ents
t
Sig.
Collinearity
Statistics
B
Std.
Error
Beta
Tolera
nce
VIF
1
(Const
ant)
32.697
3.906
8.371
.000
x
.218
.106
.226
2.059
.043
1.000
1.000
a. Dependent Variable: y1
The table above shows that entrepreneurship
malnutrition variables have a significance value of
0.043 that is less than (<0.05) so it can be concluded
there is a significant influence between
entrepreneurship education on entrepreneurship
interests.
Table 5: Coefficients
a
Model
Unstandardized
Coefficients
Standar
dized
Coeffici
ents
t
Sig.
Collinearity
Statistics
B
Std.
Error
Beta
Toler
ance
VIF
1
(Cons
tant)
22.384
2.299
9.73
7
.000
x
.198
.062
.337
3.18
6
.002
1.000
1.00
0
a. Dependent Variable: y2
The table above shows that the entrepreneurship
education variable has a significance value of 0.002
that is less than (<0.05) so it can be concluded there
is a significant influence between entrepreneurship
education on entrepreneurship motivation.
4.5 Coefficient of Determination
Table 6: Model Summary
b
Model
R
R
Square
Adjusted
R Square
Std. Error of
the Estimate
Durbin-
Watson
1
.226
a
.051
.039
4.267
1.915
a. Predictors: (Constant), x
b. Dependent Variable: y1
The table above shows the coefficient of
determination seen in the column Adjusted R Square
of 0.039 or 3.9% so it can be concluded that the
The Impact of Entrepreneurship Education to Entrepreneurial Intention and Motivation
261

contribution of entrepreneurship education to
entrepreneurship interest of 3.9%, while the rest
influenced by other variables outside the variable that
is not examined.
Table 7: Model Summary
b
Model
R
R Square
Adjusted
R Square
Std. Error of
the Estimate
Durbin-
Watson
1
.337
a
.114
.103
2.511
2.036
a. Predictors: (Constant), x
b. Dependent Variable: y2
The table above shows the coefficient of
determination seen in the Adjusted R Square column
of 0.103 or equal to 10.3% so it can be concluded that
the contribution of entrepreneurship education to the
entrepreneurship motivation of 10.3%, while the rest
is influenced by other variables outside the variable
that is not examined.
5 CONCLUSION
Entrepreneurship Education has a positive and
significant influence on entrepreneurship interest,
meaning that the better entrepreneurship education
that is obtained by the students, the higher the
entrepreneurship interest for the students of the
economic education program of the State University
of Surabaya. Entrepreneurship education also has a
positive and significant influence on entrepreneurship
motivation, which means that the better
entrepreneurship education obtained by students, the
higher the motivation for entrepreneurship of the
students of economics education program of the state
university Surabaya. In this study useful for
entrepreneurship education to entrepreneurship
interest of 3.9%, while the rest due to other variables
that are not examined. While the contribution of
entrepreneurship education to entrepreneurship
motivation of 10.3%, while the rest due to other
variables that are not examined. Because in the results
of this study showed a small effect and largely
influenced by other variables, it is advisable for
researchers to further add other variables beyond this
research variables. From the results of research
obtained although there is a positive and significant
influence but only little effect. Thus, preferably with
the existence of entrepreneurship education that is
obtained by students can be a provision for
entrepreneurship not only as a compulsory course and
to get grades, but it should be a motivation and can
foster an interest to become a young entrepreneur
who can help the economy of the surrounding
community.
REFERENCES
Asmani, Jamal Ma’mur. 2011. Sekolah Entrepreneur.
Yogyakarta: Harmoni
Astiti, Yunita Widyaning. 2014. Pengaruh Pendidikan
Kewirausahaan terhadap Motivasi Berwirausaha dan
Keterampilan Bewirausaha Mahasiswa Pendidikan
Ekonomi Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta, (Online)
Daryanto. 2012. Pendidikan Kewirausahaan. Yogyakarta:
Gaya Media
Lorz, Michael. 2011. The Impact of Entrepreneurship
Education on Entrepreneurial Intentio, Dissertation
(Online).
Purnomo, Bambang Haadi. 2005. Membangun semangat
kewirausahaan. Yogyakarta: LaksBang PRESSindo
Remeikiene, Rita etc. 2013. Explaining Entrepreneurial
Intention of University Students: The Role of
Entrepreneurial Education, (Online)
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
262
