
Risk Management, Bank Profitability and Non Performing Loan
Handiani Suciati and Mochamad Dzikri
Universitas Padjadjaran, Bandung, Indonesia
Keywords: Credit risk management, bank profitability, non-performing loan.
Abstract: Risk management has an important role for supporting good corporate governance and for any business going
concern, moreover under the rapid changes of business complexity and economic condition. Bank,
specifically, as a business whose rely heavily on public trust, need to have a reliable risk management. The
purpose of this study was to analyze the impact of credit risk management on bank profitability, with non-
performing loan as an intervening variable in banking industry. This research use descriptive analysis method,
with cross sectional and time series analysis. 20 bank was selected as the sample of this research, based on
the purposive sampling method. We found evidence that credit risk management and non-performing loan
has a significant impact on bank profitability. Bank management need to have a good credit risk management
as it will improve non-performing loan, which eventually will improve bank profitability.
1 INTRODUCTION
Globalization has a significant impact on business
activities, with free transfer of capital, goods, and
services across national frontiers. It has increased the
number and the complexity of transactions, which
made banking industry always developed their
business activities, to meet the business needs.
However this brought additional cost for banking
industry, as it will increase the banking industry risk.
Banking industry activities closely related with many
risks, such as market risk, operational risk, reputation
risk, liquidity risk, credit risk and so on.
Banking is an industry whose business rely
heavily on public trust. Bank need to raise fund from
public, in order to be able to distribute fund to the
debtor, as a loan, which eventually will provide a
profit for the bank. Bank is an industry which quit
heavily regulated by government authority, as bank
rising a fund from public, so government need to
protect the public interest. Therefor bank need to have
a proper and reliable risk management, so it could
manage risk effectively, specifically credit risk, it
could comply with regulations and could maintain
public trust. Bank will prone to many risks that it need
to have an effective risk management. The failure in
detecting and managing bank risk will cause a
contraction on bank activities, decrease the output
and will impact state economic condition (Joseph et
al., 2012)
In the other hand, the awareness of how important
it is, for a business not to pursue profit merely, but to
prioritize the business going concern itself, has risen
the need for every entity to apply good corporate
governance in conducting their business activities.
The implementation of good corporate governance is
influenced by many factors, such as having a sound
risk management, as an example.
Patricio (2005) study proved that the increasing of
bankruptcy cases around the world has induced the
urgency of improving the credit risk management,
which is related with the asset’s variability of cash
flow as an important indicator of bank financial
failure. Ghozali (2007) study proved that the
implementation of bank risk management increase
the shareholder value, providing management with
information regarding the loss possibility which
allow them to improve the decision making method
and process. It is also used to measure bank’s
performance more accurately and also to develop a
sound risk management infrastructure thus improve
bank competitiveness.
The US subprime mortgage crisis, in 2008 started
with default payment of property credit with
subprime mortgage scheme, which could not been
paid by the debtor due to the high interest rate and the
downfall of property price itself. It boost the number
of non-performing loan with worldwide pervasive
impact including Indonesia.
The implementation of bank risk management in
Indonesia is stipulated in Peraturan Bank Indonesia
286
Suciati, H. and Dzikri, M.
Risk Management, Bank Profitability and Non Performing Loan.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship (ICEEE 2017), pages 286-290
ISBN: 978-989-758-308-7
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
Nomor 5/8/PBI/2003. Bank conducting their
operational activities based on prudence principles,
specifically in deciding credit approval so it could
minimize the non-performing loan. Bank will
evaluate the potential debtor based on several
criterions, which is known as 6 C; debtor’s character,
capital, collateral, condition, capacity and constraint
(Veithzal, 2006).
Non-performing loan is the debtor failureness to
repay its debt at the specific period, based on the
agreement. The existence of non-performing loan will
influence the bank’s profitability and bank credit risk.
Lower non-performing loan, implies less bank credit
risk. In Indonesia, Bank Indonesia regulation Nomor
15/2/PBI/2013, stated the ratio of bank’s non-
performing loan is 5%. Bank’s profitability reflects
bank ability to obtain profit, it is also as a
measurement of management effectiveness
(Wiagustini, 2010:76). Profitability could be
measured by return on asset (ROA), which emphasize
the company’s ability to generate earning from its
operational activity. Higher ROA, implies higher
Banks’s profitability thus better asset utilization by
management (Lukman, 2009:118).
Previous study regarding bank’s credit risk
management, non-performing loan and profitability
shown various result. Nawaz et al (2012) study
proved that credit risk management impact bank’s
performance significantly; Li (2014) study proved
that credit risk management has a positive influence
on bank’s profitability. However, Kithinji (2010)
found that bank profitability is not influence by bank
credit risk management.
Study on non-performing loan and profitability
conducted by George et al. (2012); Han & Young
(2012) shown that non-performing loan has a
negative impact on ROA, significantly. On the
contrary with the result of study conducted by Zha &
Hui (2012).
2 METHODS
The purpose of this research is to study the influence
credit risk management on bank’s profitability with
non-performing loan as an intervening variable.
To achieve that, we use descriptive analysis
method, with cross sectional and time series analysis.
The variables involved in this study are:
credit risk management (as independent
variable),
bank’s profitability (as dependent variable) and
Non-performing loan (as an intervening
variable).
The measurement of each variable, is provided in
table 1, below.
Table 1: Operational variable and measurement
Variable
Definition
Indicator
Measur
ement
scale
X, Credit
risk
manageme
nt
implementa
tion (SEBI
No
13/24/DPN
P)
Credit risk
management in
providing loan
Self-assessment
matrix of the
implementation
quality of credit
risk
management.
Grade 1: Strong
Grade 2:
Satisfactory
Grade 3: Fair
Grade 4:
Marginal
Grade 5:
Unsatisfactory
ordinal
Z, Non
performing
loan
(Nawaz et
al., 2012)
Credit which
collectability
included in
trouble
criterion:
special mention,
substandard,
doubtful and
bad
NPL Ratio =
(The amount of
credit under
trouble criterion
: the credit total
amount) x
100%
Ratio
Y,
profitability
rate (Gizaw
et al., 2014)
Ratio to
measure
management
ability to
generate profit
Return On
Asset =
(Net income :
total asset) x
100%
Ratio
Conventional bank (non-Sariah bank) are used as
the subject in this research. Sample selection
conducted based on non-probability sampling-
purposive sampling, which selected based on several
criterion (Sekaran, 2011).
Table 2: Purposive sampling criterion
Number
Criteria
Amount
1
Conventional bank issued annual
report 2012-2014
119
2
Conventional bank which are not
listed in Indonesia Stock Exchanges
during 2012-2014
(77)
3
Conventional bank did not provide
risk profile and risk management
report related with the assessment
of the quality of risk management
implementation in 2012 -2014
annual report.
(37)
4
Conventional bank fulfil the
criterions
20
5
Conventional Bank data used as the
sample for 2012-2014
60
Risk Management, Bank Profitability and Non Performing Loan
287
At the end this research use 60 samples, as an
observation. These samples are taken from 20
selected conventional bank which then being
observed for 3 years (2012 – 2014).
Hypotheses being tested in this study are:
Ho
1 :
β
1
> 0 “there is no negative influence
between credit risk management and
non-performing loan”
Ha
1 :
β
1
< 0 "there is negative influence between
credit risk management and non-
performing loan”
Ho
2 :
β
2
> 0 “there is no negative influence
between non-performing loan and
bank profitability”
Ha
2
: β
2
< 0 “there is negative influence between
non-performing loan and bank
profitability”
Ho
3 :
β
3
< 0 “there is no positive influence
between credit risk management and
bank profitability”
Ha
3 :
β
3
> 0 “there is no positive influence
between credit risk management and
bank profitability”
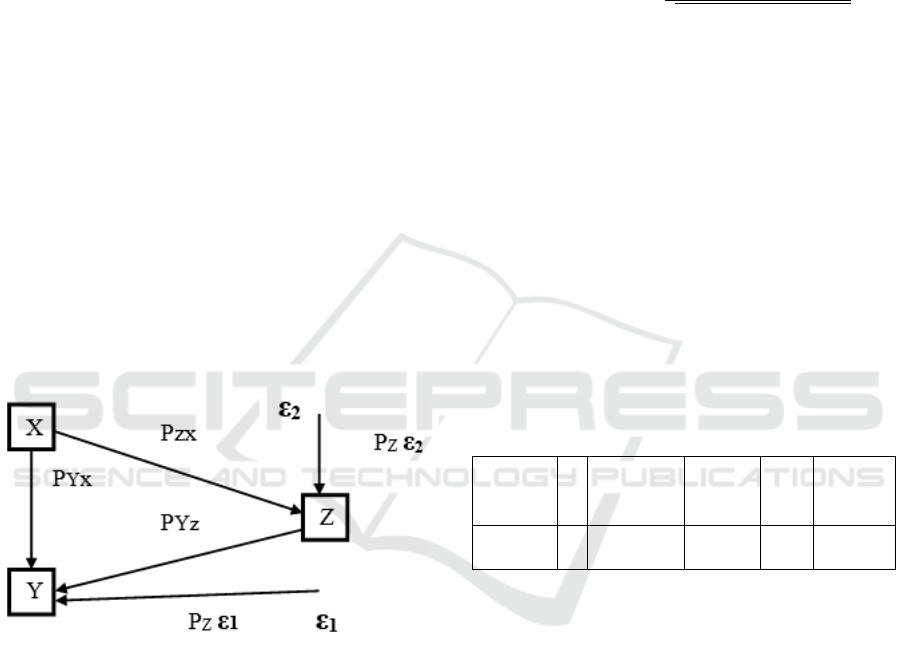
This research is using path analysis to analyze the
data, as described in figure 2.
Figure 1: Path analysis diagram
The structural equation for the figure above are:
Z = P
ZX
+
ε
2
Y = P
YX
+ P
YZ
+ ε
1
Where as:
X = credit risk management
Y = profitability
Z = non-performing loan
ε
1
= other variable influencing Y
ε
2
= other variable influencing Z
P
YX
= Path coefficient, X influence on Y
P
ZX
= Path coefficient, X influence on Z
P
YZ
= Path coefficient, Z influence on Y
P
Y
ε
1
= Path coefficient, ε
1
influence on Y
P
Z
ε
2
= Path coefficient, ε
2
influence on Z
We conducted several test including normality,
multicollinearity, heteroscedasticity and
autocorrelation test, followed by the F and t test.
In conducting the path analysis, we applied
several steps, as described below:
1. Correlation analysis, to analyze the
dependencies between variables, which
determine using this model :
R
xy
=
nΣxy−(Σx)(Σy)
√
(nΣx
2
−
(
Σx
)
2
)(nΣy
2
− Σ
(
y
)
²
R
2
/ KP = r² x 100%
Where as:
R
xy
= correlation coefficient
N = sample size
x = independent variable value
y = dependent variable value
KP = determination coefficient
2. Regression analysis
3. Influence calculation
We conducted one side test, using α 5 %.
3 RESULTS
Table 3 displays the descriptive statistic of credit risk
management qualities.
Table 3: Credit risk management descriptive statistic
N
Minimum
Maximum
Mean
Std.
Deviation
X
60
1.00
3.00
2.1167
.55515
Valid N
(listwise)
60
The average score for the quality of credit risk
management from the sample in this research is
2.1667, which shown adequate level. The maximum
score 3 shown that the worst self-assessment on the
quality of credit risk management is in fair level. The
minimum score 1 shown that the best self-assessment
on the quality of credit risk management is in strong
level. With 0.55515 standard deviation, it shown the
deviation and score variability of the quality of credit
risk management is quite low.
The descriptive statistic for profitability shown
average score 2.1558 %, which implies the average
profitability of conventional bank during the research
period is 2.1558 %, with 5.15 % as a maximum score
and -1.58 % as the minimum score. Standard
deviation score 1.20474, shown the deviation and
score variability of the profitability is quite low.
The non-performing loan descriptive statistic
shown average score 2,2642 %, which is quite below
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
288

the maximum score 5%. The maximum NPL in this
research is 9,95 %, with 0,21% as the minimum score.
With 1.71488 standard deviation, it shown the
deviation and score variability of non-performing
loan is quite low.
3.1 Path Analysis Substructure 1
Path analysis on substructure 1, analyze the influence
of credit risk management on NPL. Using SPSS we
found the value of coefficient correlation or R 0.495,
which shown quite strong correlation between
variable based on Guildford criterion. The coefficient
determination is 24.5 %, which implies that credit risk
management contribute 24,5 % influence on NPL.
The rest 75,5 % shown the contribution of other factor
on NPL.
Table 4: Test result on path coefficient simulant regression
Model
Sum of
squares
df
Mean
square
F
Sig
1 Regression
42.557
1
42.557
18.849
0,000
a
Residual
130.952
58
2.258
Total
173.509
59
a. Predictors (constant), X
b. Dependent variable: Z
From table 4, we can see that F-stat (18,849) >
F.table (2.769431), which implies reject Ho. It means
that credit risk management has a significant
influence on non-performing loan.
Table 5: Test result on path coefficient partial regression
Unstandardized
Coefficients
Standardi
zed
Coefficie
nts
T
Sig
Model
B
Std. Error
Beta
1 (Constant)
4.591
0.570
8.054
0.000
X
-0.988
0.228
-.0495
-4.342
0.000
a. dependent variable: Z
From table 5, we can see credit risk management
t score is -4.342 which is lower than t table -2.002465,
therefor we reject Ho, and so we conclude that credit
risk management has significant negative influence
on non-performing loan.
3.2 Path Analysis Substructure 2
Path analysis on substructure 2, analyze the influence
of credit risk management (X), non-performing loan
(Z) on profitability (Z).
Table 6: Coefficient Correlation
Model Summary
Model
R
R Square
Adjusted
R
Standard Error of The
Estimate
1
0.735
a
0.539
0.523
0.83176
a. Predictors: (constant), Z, X
From table 6, we know the coefficient correlation
(R) is 0,735, which based on Guildford criterion
indicating there is strong correlation between
independent and dependent variables,
simultaneously.
Based on calculation, the determination
coefficient is 53,9%, which shown credit risk
management and non-performing loan together, have
53,9% influence on profitability, while the rest 46,1%
is influenced by other factors which not being study
in this research. The simulant test on substructure 2
found that F-stat is 33,388 which is higher than
F.tabel, 2.769431. It mean the Ho is being rejected,
which implies credit risk management and non-
performing loan, together, have significant influence
on profitability.
As for the next test, we did the partial test to
analyze which variable has an influence on
profitability.
Table 7: Regression on partial path coefficient
Unstandardized
Coefficients
Standardized
Coefficients
t
Sig
Model
B
Std. Error
Beta
1 (Constant)
1.208
0.459
2.630
0.011
X
0.658
0.145
0.469
4.538
0.000
Z
-0.266
0.073
-0.378
-3.657
0.001
a. dependent variable: Y
From table 7, we know that the path coefficient is
0.469 for credit risk management and for non-
performing loan is -0.378. The NPL partially has
negative significant influence on profitability, as the t
count (-3.657) is less than t table (-2.002465). In
means we reject Ho for the second hypothesis.
The test on third hypothesis shown that t count is
4.538 > t table 2.002465, therefor Ho is being
rejected, with conclusion that partially credit risk
management has positive, significant influence on
profitability.
From calculation we also found that the direct
effect between X and Y (P
yx)
is 0,469, the indirect
effect of X on Y through Z is 0,187. Therefor the total
effect is 0.656.
Risk Management, Bank Profitability and Non Performing Loan
289

4 CONCLUSIONS
The research shown that credit risk management and
NPL has significant influence on profitability, both
contributes 53,9 % influence on profitability.
Therefor bank management need to implement a
sound and effective credit risk management in order
to improve bank’s performance, to be able to protect
investor interest and the most important one is to
prevent the banking crisis, which will have a
pervasive impact.
Bank need to be equipped with comprehensive
credit risk management which allow management to
identify, measure, supervise and control the credit
risk.
We found that credit risk management has a
negative significant influence on non-performing
loan. Applying a sound credit risk management is a
must for banking industry, as it will decrease the non-
performing loan.
This study also show that nonperforming loan has
a negative significant influence on profitability. It
means that the increased in nonperforming loan, due
the poor bank credit quality, will resulted in a loss
from bank’s operational activity.
The research shown that credit risk management
has a positive, significant influence on profitability.
An effective credit risk management will support the
achievement of bank profit, thus will increase its
profitability.
REFERENCES
Bank Indonesia. 2011. Lampiran Surat Edaran Bank
Indonesia Nomor 13/24/DPNP Tentang Pedoman
Standar Penerapan Manajemen Risiko, 25 Ok-tober
2011.
____- Peraturan Bank Indonesia Nomor 11/25/PBI/2009
tentang Perubahan atas Peraturan Bank Indonesia
5/8/pbi/2003 tentang Penerapan Manajemen Risiko
bagi Bank Umum.
____2013. Peraturan Bank Indonesia Nomor
15/2/PBI/2013 tentang Penetapan Status dan Tindak
Lanjut Pengawasan Bank Umum Kon-vensional, 20
Mei 2013
George, G., Enock, Barrack Otieno Ouma, and Jane
Nasimiyu Were. 2012. "Effect of Financial Risk on
Profitability of Sugar Firm in Kenya." European
Journal of Business and Management ISSN 2222-1905
(paper) ISSN 2222-2839 (online) Vol. No.5, No.3.
Gizaw, Milion, Matewos Kebede, and Sujata Selvaraj. "The
Impact of Credit Risk on Profitability Performance of
Commercial Banks in Ethiopia." African Journal of
Business Manajemen ISSN 1993-8233 (ISSN 1993-
8233) vol 9(2) (2014): 59-66.
Li, Fan, and Yizun Zou. 2014. The Impact of Credit Risk
Management on Profitability of Commercial Banks.
Han, Xiaoxiao, and Ji-Young Seo. "Influential Factors in
Lending and Profitability in Commercial Chinese
Banks." African Journal of Business Management
ISSN 1993-8233 Vol.6 (32) (2012): Pp. 10041-10049.
Imam, Ghozali. 2007. Manajemen Risiko Perbankan.
Semarang: BPUNDIP.
Joseph, Mabvure Tendai. 2012. "Non Performing Loans in
Commercial Banks: A Case of CBZ Bank Limited in
Zimbabwe." Interdiciplinary Journal of Contemporary
Research in Business Vol.4(7).
Kithinji, A. M. Credit risk management and profita-bility of
commercial banks in Kenya, 2010. School of Business,
University of Nairobi, Nairobi.
Lukman, Dendawijaya. 2009. Manajemen Perbankan.
Jakarta: PT Raja Ghalia Indonesia.
Nawaz, Muhammad. 2012. "Credit Risk and The
Performance of Nigerian Banks." Interdiciplinary
Journal of Contemporary Research in Business. Vol. 4.
Patricio, A. P., and A. P. I. Vong. "Credit Risk Assessment
in The Macau Banking Sector." Euro Asian Journal of
Management Vol 15 (2005): 113-124.
Sekaran, U., 2011. Research Method for Business:
Metodologi Penelitian untuk Bisnis Jilid 2. Jakarta:
Salemba Empat.
Veithzal, Rivai. 2006. Credit Management Handbook.
Jakarta: PT Raja Grafindo Persada.
Wiagustini, Ni Luh Putu. 2010. Dasar-Dasar Manajemen
Keuangan. Denpasar: Universitas Udayana.
www.bi.go.id
www.idx.com
Zha, Suvita, and Xiaofeng Hui. 2012. "A Comparison of
Financial Performance of Commercial Banks: A Case
Study of Nepal." African Journal of Business
Management ISSN 1993-8233 Vol. 6(25) (2012):
Pp.7601-7611.
Sistem Pendidikan Nasional 2003
Slameto. 2003. Belajar dan Faktorfaktor yang
Mempengaruhinya. Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Sudarmanto,Y,B. 2003. Tuntutan Metodologi Belajar.
Jakarta: PT.Gramedia Widiasaran Indonesia
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
290
