
Technological Factor and Social Media Marketing Adoption Among
SMEs in Kelantan
Muhammad Faizal Samat
1
, Mohd Nor Hakimin Yusoff
2
, Mohamad Ismail
2
, Norazlan Annual
1
and
Mazlina Mamat
1
1
Faculty of Business Management, Universiti Teknologi Mara (UiTM) Kelantan, Malaysia
2
Faculty of Entrepreneurship and Business, Universiti Malaysia Kelantan, Malaysia
faizal951@kelantan.uitm.edu.my
Keywords: Social Media Marketing, Technological Factors, Compatibility, Cost Effectiveness, Interactivity.
Abstract: Social media becomes popular among Internet applications due to increasing numbers of users’ presence
online. However, past studies showed the use of social media as marketing tool in SMEs is still in its infancy
due to their lack of knowledge and technical skills about technology adoption. This study was conducted
Social media becomes popular among Internet applications due to increasing numbers of users’ presence to
identify the technological factors (compatibility, cost effectiveness and interactivity) that lead to the adoption
of social media marketing among SMEs. Theoretical framework of this study was derived from Unified
Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) that figure out whether the user were able to adopt
the new technologies. The study was carried out in Kelantan using 134 respondents and analysed using SPSS
version 22.0. Overall, the study provides supportive evidence on the factors influencing social media
marketing adoption and the results could help businesses to formulate better strategy in order to implement
the social media marketing.
1 INTRODUCTION
Social media differs from traditional/industrial media
in many aspects such as quality, reach, frequency,
usability, immediacy and permanence. Consumers
not only obtain information about the product by
clicking within the Internet advertisement but they
can also place an order and download some products
such as e-books to their computer (Haque, Al
Mahmud, Tarofder, & Ismail, 2007). In regards to
internet usage of social media as of 2012, Cheong,
Fischer-Nielsen, Gelfgren, and Ess (2012), internet
users continue to spend more time in social media
than any other sites. In addition, there has been an
increase in mobile social media which has created
new opportunities, in particular, for businesses, which
are able to utilize social media for marketing research,
sales promotions, and customer relationship
development among other activities.
Mangold and Faulds (2009) stated that the 21st
century is witnessing the explosion of internet-based
messages transmitted through social media. They
have become a major factor in influencing various
aspects of consumer behavior including awareness,
information acquisition, opinions, attitudes, purchase
behavior, and post-purchase communication,
satisfaction, and evaluation.
1.1 Problem Statement
Social media ranks among the most popular Internet
applications and these include Facebook and Twitter
among many others, which offer users the
opportunity to get connected with each other to share
their activities of common interest (O'Keeffe &
Clarke-Pearson, 2011). Surveys done by the Stats
(2016) showed that 21,090,777 Malaysians have
become active users of social media, which has also
become the medium for businesses to advertise
products and services since it plays a significant role
in Malaysia's advertising market. SMEs are expected
to improve business performance and
competitiveness through the use of Internet-based
applications (Shang, 2014). Overall, SMEs are
expected to be significant users of the Internet and
social media. Although access to social media has
456
Samat, M., Yusoff, M., Ismail, M., Annual, N. and Mamat, M.
Technological Factor and Social Media Marketing Adoption Among SMEs in Kelantan.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship (ICEEE 2017), pages 456-461
ISBN: 978-989-758-308-7
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

improved, engagement and use of the Internet is still
at low levels within small firms (Shang, 2014).
1.2 Objectives
The objective that guided this study was to explore
the potential relationship between technological
factors and social media marketing adoption among
SMEs.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Social Media Marketing
We strongly encourage authors to use this document
for the preparation of the camera-ready. Please follow
the instructions closely in order to make the volume
look as uniform as possible (Moore and Lopes, 1999).
Please remember that all the papers must be in
English and without orthographic errors.
Do not add any text to the headers (do not set
running heads) and footers, not even page numbers,
because text will be added electronically.
For a best viewing experience the used font must
be Times New Roman, on a Macintosh use the font
named times, except on special occasions, such as
program code (Section 2.3.7).
2.2 Technological Factor
Advances in technology make it possible for many
businesses to operate either completely online or
partially online. Creating an online business is done
by building a website and combining it with a
business system. The costs for conducting business
online from a website are minimal compared to costs
incurred with a physical business location. However,
brick-and-mortar businesses also find it convenient to
conduct some of their operations on the Internet.
Technology also plays a role in helping companies
create closer working relationships.
Today’s business world has been deeply
influenced by social media and the application of
social media in business is widespread. According to
El-Gohary (2012), recent research into social media
adoption and use has been motivated by the desire to
predict factors which can lead to better business
performance. Alam and Noor (2009) in their study
found that SMEs nowadays are increasingly using
and adopting social media in their business.
There are many factors that associated to
technology. For this study, interactivity, cost
effectiveness and compatibility have been chosen as
to measure technological factors. Past studies have
found that the planning and usage of data frameworks
considers the fruitful connection between humans and
innovation as a key element (Lee & Kozar, 2004;
Shillair et al., 2015). Among the different planning
qualities, interactivity emerges as a key and
recognized variable that affects clients' reaction to
new innovations including sites (Agarwal &
Venkatesh, 2002; Ainin, Parveen, Moghavvemi,
Jaafar, & Mohd Shuib, 2015; Jiang & Benbasat,
2007). Handayani and Lisdianingrum (2011)
explored appropriation and utilization of Facebook in
two Indonesian SMEs, and found that Facebook can
be utilized as an effective free Internet promotional
platform to reach a wide segment of the market.
Therefore, it can be hypothesized as:
H1: The greater the interactivity of social media,
the more likely social media marketing will be
adopted by SMEs.
Rigby and Bilodeau (2015) had discovered
critical relationship between cost and adoption of
technology. In addition, Genç and Öksüz (2015)
observed that cost effectiveness is a vital variable in
the selection of new technology. Therefore, it can be
hypothesized as:
H2: The greater the cost effectiveness of social
media, the more likely social media marketing will
be adopted by SMEs.
According to Gutierrez, Boukrami, and Lumsden
(2015), compatibility is important factor in adopting
of technology. However, according to Dwivedi,
Papazafeiropoulo, Ramdani, Kawalek, and Lorenzo
(2009), compatibility is irrelevant in calculating the
reception of business frameworks. From these
arguments, it can be hypothesized as:
H3: The greater the compatibility of social media,
the more likely social media marketing will be
adopted by SMEs.
2.3 Linking the Technological Factor
and Social Media Marketing
Adoption among SMEs
The research framework for the study at hand was
derived from Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use
Technological Factor and Social Media Marketing Adoption Among SMEs in Kelantan
457
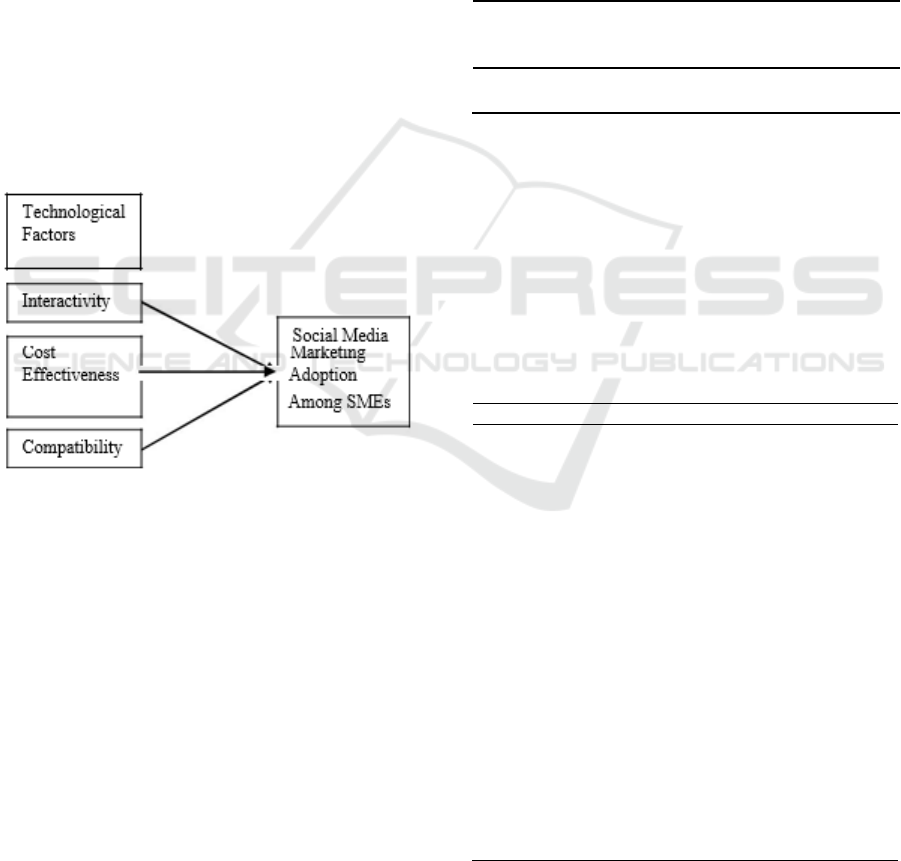
of Technology (UTAUT). UTAUT is a technology
acceptance model introduced by Venkatesh, Morris,
Davis, and Davis (2003) that try to explain the degree
of acceptance of the use of information technology.
This theory figure out whether the user will be able to
adopt the new technologies. UTAUT consists four
main factors which are performance expectancy,
effort expectancy, social influence and facilitating
conditions that will influence the dependent variables
which are behaviorals and usage, however, for this
study, only a part of the theory being used which are
facilitating conditions (technological factors) that
will influence the behaviors which are adoption of
social media marketing.
Each column must be 7,5-centimeter wide with a
column spacing of 0,8-centimeter.
The section text must be set to 10-point, justified
and line space single.
Section, subsection and sub subsection first
paragraph should not have the first line indent, other
paragraphs should have a first line indent of 0,5-
centimeter.
Figure 1: Theoretical framework.
3 METHODS
This study used quantitative approach to test the
hypothesis in order to get reliable results. The study
was conducted in the East Coast Region of Peninsular
Malaysia which is Kelantan. The main tool to collect
the data was questionnaires and 150 respondents were
selected to answer the questions. The study used non-
probability sampling, which is judgemental sampling.
The basic criterion to be become the respondents of
this study was they must own a business in Kelantan
and applied social media as part of their operation.
After the major data collection, 134 completed
questionnaires were returned and the raw data was
manually keyed in through SPSS version 22.0 and
analysed. The hypotheses were tested using the linear
regression analysis.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Normality
Normality test was conducted and measured using
skewness and kurtosis. Normality test was used to
determine if a data significantly deviate from a
normal distribution.
Table 1: Normality result.
SMM
Interactivity
Cost
Compatibility
Adoption
Effectiveness
Skewness
-0.885
-0.763
-0.576
-0.740
Kurtosis
0.422
0.977
0.019
0.685
Based on the above table, the result of normality
test range from -0.576 to 0.977, considered that all
value is acceptable. According to George and Mallery
(2016) the value between - 2 and +2 are acceptable
and consider as a normal. It means that all variables
that were used in this study are normal. Hence, the
researcher can proceed for further analysis.
4.2 Demographic Profiles
Table 2: Frequency and percentage distribution.
Demographic
N
%
Type of Industry
Manufacturing
32
23.9
Service
82
61.2
Others
20
14.9
Total
134
100.0
Type of Company Internet
Connection
UniFi
26
19.4
Streamyx
54
40.3
TMNet
29
21.6
Jaring
24
17.9
Leased Line (ISDN)
1
0.7
Total
134
100.0
Years of Using Internet for
Business Purposes
Less than 5 years
96
71.6
6-10 years
3
2.2
11-15 years
34
25.4
16-20 years
0
0.0
Above 20 years
1
0.7
Total
134
100.0
Source: Survey
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
458

A total of 134 respondents completed the
questionnaire and summarized in Table 2 as above.
For the type of industry category, 61.2 percent of the
total numbers of respondents were in service, 23.9
percent were in manufacturing and 14.9 percent were
others. In terms of type of company ownership
category, majority of the respondents were sole
proprietors which indicated the percentage of 68.7
percent, 24.6 percent were partnership business and
6.7 percent were limited company. When respondents
were asked about their age of business, 41.0 percent
reported to be operating for 4-8 years, followed by
39.6 percent were less than three years of operation,
while 14.2 percent were 9 to 15 years in business.
Only 4.5 percent were above 20 years while 0.7
percent are above 16 to 20 years. In terms of type of
company internet connection, 40.3 percent of the total
number of respondents used Streamyx, TMNet (21.6
percent), UniFi (19.4 percent), Jaring (17.9 percent)
and Leased Line (0.7 percent). Finally, when the
respondents were asked about how many years they
has been using Internet for business purposes, 71.6
percent reported they had used less than 5 years. The
respondents had used 6 to 10 years of Internet has
25.4 percent, followed by 11 to 15 years (2.2 percent)
and lastly, only 0.7 percent of the total number of
respondents reported that they have been using
internet for more than 20 years for business purposes.
4.3 Reliability Analysis
Generally, Cronbach's alpha was used to measure the
reliability and value of less than 0.60 are considered
to be poor, whereas those close to 0.70 are considered
good and those over 0.80 are considered to be high
(Amiri et al., 2010). The average alpha values for
variables for every section are shown in Table 3
below.
For social media marketing adoption, the overall
Cronbach's Alpha is 0.930 or 93.0 percent, with the
highest value of was 0.923 while the lowest was
0.906. For interactivity, the Cronbach's Alpha value
was 0.835 or 83.5 percent, and the Cronbach's Alpha
for every item ranged between 0.758 to 0.811. For
cost effectiveness, the overall Cronbach's Alpha is
0.819 or 81.9 percent, with the highest value of was
0.791 while the lowest was 0.710. For compatibility,
the Cronbach's Alpha value was 0.834 or 83.4
percent, and the Cronbach's Alpha for every item
ranged between 0.760 to 0.819. As a conclusion, in
general, the Cronbach's Alpha values were higher for
all sections with the Cronbach's Alpha value 0.899 or
89.9 percent.
Table 3: Reliability test.
Variable
Cronbach's Alpha
Social Media
Marketing
Adoption
0.930
Interactivity
0.835
Cost Effectiveness
0.819
Compatibility
0.834
Source: Survey
4.4 Pearson Correlation Analysis
Pearson Correlation analysis is a statistical analysis
that summarizing the strength of association between
two metric variables (Malhotra, 2011). The
correlation is a technique on how strongly pairs of
variables are correlated.
Table 4: Correlation coefficient.
SMM
Adoption
Interactivity
Cost
Effectiveness
Compatibility
SMM
1
Adoption
Interactivity
0.563**
1
Cost
0.630**
0.805**
1
Effectiveness
Compatibility
0.663**
0.713**
0.821**
1
** Correlation is significant at the level 0.01 level
(2 tailed)
The relationship between interactivity, cost
effectiveness and compatibility with social media
marketing adoption by SME has been tested.
Interactivity (r value = 0.563, p-value < 0.01)
indicated that positive relationship between
interactivity with social media marketing adoption
and have a moderate strength of association with
social media marketing adoption. In addition, cost
effectiveness (r value = 0.630, p-value < 0.01)
showed that there is a positive relationship and have
a moderate strength of association between cost
effectiveness with social media marketing adoption.
Lastly, compatibility (r value = 0.663, p-value < 0.01)
indicated that positive relationship between
compatibility with social media marketing adoption
and have a moderate strength of association with
social media marketing adoption.
4.5 Hypotheses Testing
The study hypothesized that interactivity have a
significant relationship with social media marketing
adoption (t-value = 7.817, p-value = 0.000). Thus, the
result H1 is supported. Besides that, the study
revealed cost effectiveness have a significant
relationship with social media marketing adoption (t-
Technological Factor and Social Media Marketing Adoption Among SMEs in Kelantan
459

value= 9.327, p-value = 0.000) hence, the result H2 is
supported. And finally, compatibility have a
significant relationship with social media marketing
adoption (t-value = 10.179, p-value = 0.000). Thus,
the result H3 is supported. As for conclusion, all the
variables has a significant relationship with social
media marketing adoption by SME.
Table 5: Hypotheses testing.
Hypotheses
t-value
Sig
Result
H1: The greater the
interactivity of social
media, the more
likely social media
marketing will be
adopted by SMEs
7.817
0.000
Supported
H2: The greater the
cost effectiveness of
social media, the
more likely social
media marketing will
be adopted by SMEs.
9.327
0.000
Supported
H3: The greater the
compatibility of
social media, the
more likely social
media marketing will
be adopted by SMEs.
10.179
0.000
Supported
5 CONCLUSIONS
The study was to identify the relationship between
technological factors and social media marketing
adoption among SME in Kelantan. For hypothesis
testing, linear regression was used as statistical tools.
Technological factors that hold three dimensions
which are interactivity, cost effectiveness and
compatibility, is found and concluded to be
significantly linked to social media marketing
adoption by SME in this study. The impact of these
factors is high as these factors employed high R
squared value, thus, it can be concluded that in order
for firm to adopt social media marketing, they need to
look into these three indicators which are
interactivity, cost effectiveness and compatibility.
As a conclusion, it is recommended that
businesses especially small medium enterprises to
consider the technological factors that has been
determined in this study such as interactivity, cost
effectiveness and compatibility in order for them to
adopt social media marketing in their firm.
REFERENCES
Agarwal, R., Venkatesh, V., 2002. Assessing a firm's Web
presence: A heuristic evaluation procedure for the
measurement of usability. Information Systems
Research, 13(2), 168-186.
Ainin, S., Parveen, F., Moghavvemi, S., Jaafar, N. I., Mohd
Shuib, N. L., 2015. Factors influencing the use of social
media by SMEs and its performance outcomes.
Industrial Management & Data Systems, 115(3), 570-
588.
Alam, S. S., Noor, M. K. M., 2009. ICT adoption in small
and medium enterprises: An empirical evidence of
service sectors in Malaysia. International Journal of
Business and Management, 4(2), 112.
Amiri, P., Ardekani, E. M., Jalali-
Farahani, S., Hosseinpanah, F., Varni, J. W.,
Ghofranipour, F., . . . Azizi, F., 2010. Reliability and
validity of the Iranian version of the Pediatric Quality
of Life Inventory™ 4.0 Generic Core Scales in
adolescents. Quality of Life Research, 19(10), 1501-
1508.
Blackshaw, P., Nazzaro, M., 2004. Consumer-Generated
Media (CGM) 101: Word-of-mouth in the age of the
Web-fortified consumer. Retrieved July 25, 2008.
Cheong, P. H., Fischer-Nielsen, P., Gelfgren, S., Ess, C.,
2012. Digital religion, social media and culture:
perspectives, practices and futures: Peter Lang
Publishing Group.
Cruz, D., Fill, C., 2008. Evaluating viral marketing:
isolating the key criteria. Marketing Intelligence &
Planning, 26(7), 743-758.
Dubihlela, J., Rundora, R., 2015. Role of Social Media, Its
Adoption and Usage Patterns within Accounting Firms.
Studia Universitatis Babes-Bolyai, 60(1), 23.
Dwivedi, Y. K., Papazafeiropoulo, A., Ramdani, B.,
Kawalek, P., Lorenzo, O., 2009. Predicting SMEs'
adoption of enterprise systems. Journal of Enterprise
Information Management, 22(1/2), 10-24.
El-Gohary, H., 2012. Factors affecting E-Marketing
adoption and implementation in tourism firms: An
empirical investigation of Egyptian small tourism
organisations. Tourism Management, 33(5), 1256-
1269.
Genç, M., Öksüz, B., 2015. A Fact or an Illusion: Effective
Social Media usage of Female Entrepreneurs.
Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 195, 293-
300.
George, D., Mallery, P., 2016. IBM SPSS Statistics 23 step
by step: A simple guide. Reference:
Routledge.
Gutierrez, A., Boukrami, E., Lumsden, R., 2015.
Technological, Organisational and Environmental
factors influencing managers’ decision to adopt cloud
computing in the UK. Journal of Enterprise
Information Management, 28(6), 788-807.
Handayani, P. W., Lisdianingrum, W., 2011) Impact
analysis on free online marketing using social network
Facebook: Case study SMEs in Indonesia. Paper
presented at the Advanced Computer Science and
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
460

Information System (ICACSIS), 2011 International
Conference on.
Haque, A., Al Mahmud, S., Tarofder, A. K., Ismail, A. Z.
H., 2007. Internet advertisement in Malaysia: A study
of attitudinal differences. The Electronic Journal of
Information Systems in Developing Countries, 31.
Jiang, Z., Benbasat, I., 2007. Research note-investigating
the influence of the functional mechanisms of online
product presentations. Information Systems Research,
18(4), 454-470.
Kaplan, A. M., Haenlein, M., 2010. Users of the world,
unite! The challenges and opportunities of Social
Media. Business horizons, 53(1), 59-68.
Lee, Y., Kozar, K., 2004. Developing a theory of website
usability: an exploratory study to identify constructs
and nomological networks. ICIS 2004 Proceedings, 51.
Malhotra, N. K., 2011. Review of Marketing
Research: Special Issue–Marketing Legends: Emerald
Group Publishing Limited.
Mangold, W. G., Faulds, D. J., 2009. Social media: The new
hybrid element of the promotion mix. Business
horizons, 52(4), 357-365.
O'Keeffe, G. S., Clarke-Pearson, K., 2011. The impact of
social media on children, adolescents, and families.
Pediatrics, 127(4), 800-804.
Osterrieder, A., 2013. The value and use of social media as
communication tool in the plant sciences. Plant
methods, 9(1), 1.
Rigby, D., Bilodeau, B. 2015. Management tools & trends
2015. London, Bain & Company.
Shang, Y., 2014. Adoption of social media by SMTEs in
China.
Shillair, R., Cotten, S. R., Tsai, H.-Y. S., Alhabash, S.,
LaRose, R., Rifon, N. J., 2015. Online safety begins
with you and me: Convincing Internet users to
protect themselves. Computers in Human Behavior,
48, 199-207.
Stats, I. W. (2016). Asia Marketing Research, Internet
Usage, Population Statistics and Facebook
Information. Retrieved from
http://www.internetworldstats.com/asia.htm#my
Treadaway, C., Smith, M., 2012. Facebook
marketing: An hour a day: John Wiley & Sons.
Venkatesh, V., Morris, M. G., Davis, G. B., Davis, F. D.,
2003. User acceptance of information technology:
Toward a unified view. MIS quarterly, 425-
478.
Technological Factor and Social Media Marketing Adoption Among SMEs in Kelantan
461
