
Organizational Citizenship Behavior
Analysis of Dominant Influencing Factors to OCB at Education Personnel of
FKIP Universitas Kuningan
Rani Tania Pratiwi and Iyan Setiawan
Lecture of Faculty of Teacher Training and Education (FKIP) Universitas Kuningan
tania_pratiwi17@yahoo.com
Keywords: Organizational Citizenship Behavior, Organizational Culture, Job Satisfaction, Commitment, Leadership.
Abstract: Campus is an educational institution where students seek knowledge. Colleges can be classified as service
provider organizations that also rely on the quality of services provided to students and the community.
Competence, ability, expertise, hospitality and compassion as well as providing a sense of comfort it will be
a success factor in managing and achieving organizational goals. On campus, lecturers as educators and staff
as educational staff have a very important role in achieving goals in education. The purpose of this study is to
describe "The influence of Organizational Culture, Job Satisfaction, Commitment, Transformational
Leadership, and Servant Leadership to Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB) on the Education
Personnel Faculty of Teacher Training and Education Universitas Kuningan. The method used in this research
is descriptive method, and correlation Population in this research is all educational staff of Faculty of Teacher
Training and Education (FKIP) Universitas Kuningan, amounting to 26 people. Data collection techniques
use questionnaires, and data analysis techniques use correlation analysis, supported by software SPSS for
windows. Based on the results of research conducted by multiple regression analysis, showing that
Organizational Culture (X1), Job Satisfaction (X2), Organizational Commitment (X3), Transformational
Leadership (X4) and Servant Leadership (X5) Against Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB).
1 INTRODUCTION
To achieve organizational goals, the behavior of
members is in concern, the behavior here is not just
the behavior in role or behavior that related to what
has been set by the organization but extra role
behavior is also necessary because the extra role
behavior itself has a positive impact for the
organization. This extra-role behavior is also referred
as Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB).
According to Organ (1988: 4) "Organizational
Citizenship Behavior (OCB) is an extra individual
behavior that is not directly or explicitly known in a
formal work system, in aggregate can improve the
effectiveness of organizational functions ".
Organizational Citizenship Behavior contributes
positively to the organization, OCB Behavior is
exemplified as helping colleagues to solve their
problem, showing respect for fellow workers and
leaders, getting to work early and coming home late,
being concerned about the property and wealth of the
organization and still more the behaviors of
Organizational Citizenship Behavior that can
improve the effectiveness and efficiency for the
organization.
Wirawan (2013: 723) argues that "OCB
employees are part of corporate social responsibility.
OCB also appears in an organization that has a
friendly and familial organizational condition. If the
perceptions of the members of the organization are
friendly to each other and consider a family, OCB
will happen a lot. However, if the organizational
situation is conflict and idealistic, it will be difficult
to present OCB. OCB is more likely to be performed
by employees who are satisfied with their work than
employees who are not satisfied with their work ".
Some studies that examine the OCB include:
The Effect of Servant Leadership on
Organizational Commitment and Organizational
Citizenship Behavior. By: Wike Santa Mira Alumni
Faculty of Economics Management Department
Maranatha Christian University. Meily Margaretha
Faculty of Economics Faculty of Management
Department of Maranatha Christian University.
Discussion. In this study, all hypothesis proposed
answered or it can be proved its correctness that is
Pratiwi, R. and Setiawan, I.
Organizational Citizenship Behavior - Analysis of Dominant Influencing Factors to OCB at Education Personnel of FKIP Universitas Kuningan .
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship (ICEEE 2017), pages 559-565
ISBN: 978-989-758-308-7
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
559

hypothesis servant leadership have positive effect to
organizational commitment and organization
citizenship behavior. It is evident that if a servant
leadership has a close or tied influence with the
company, the employee will be committed to his
organization and will be willing to do a job that is not
his responsibility voluntarily and voluntarily as
quoted by Schake (1991) in Erturk, Et al., 2004).
Effect of Servant Leadership and Organizational
Commitment of Employees on Organizational
Citizenship Behavior (OCB) to Blue Bird Group
Surabaya. Vania Claresta Prabowo and Roy Setiawan
Business Management Program, Management
Studies Program, Petra Christian University Jl.
Siwalankerto 121-131, Surabaya E-mail:
vania_09246@yahoo.com; Roy@petra.ac.id. The
purpose of this study is to test and describe the effect
of servant leadership and organizational commitment
of employees to organizational citizenship behavior
in Blue Bird Group Surabaya. The population of the
study was non-driver Blue Bird Group Surabaya
employees, which amounted to 224 people with a
sample of 60 employees. Data analysis technique in
this study using SPSS program version 16.0.Hasil
research indicates that: (1) Servant Leadership does
not significantly affect the Organizational Citizenship
Behavior. (2) Organizational commitment has
significant effect on Organizational Citizenship
Behavior. (3) Servant Leadership and organizational
commitment have a significant effect on
Organizational Citizenship Behavior.
The Influence of Organizational Culture on
Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB) Case
Study at Pt. Mirina Nusantara. Risna ananda putri¹,
tarcisius t. Sipayung², drs.³. Management (Business
Management Telecommunications & Informatics),
Faculty of Business Economics, Telkom University.
2013. The result of data analysis in this research
shows that organizational culture of PT. Mirina
Nusantara is included in the strong category of
69.32% and the behavior of organizational citizenship
behavior (OCB) of PT. Mirina Nusantara is included
in the high category of 75.38%. In addition, there is a
non-significant influence between organizational
culture on organizational citizenship behavior (OCB)
at PT. Mirina Nusantara is 18.1%.
The Influence of Organizational Culture
Variables, Commitment and Job Satisfaction of
Employee to Organizational Citizenship Behavior
Employee. Ida Ayu Brahmasari. University of 17
August 1945 Surabaya. 2008. Based on the results of
research and discussion that was described previously
can be summarized as follows: (1) Organizational
values, Organizational Climate, Attention to Detail,
Organizational Structure, Commitment of employees
and Employee Satisfaction simultaneously have a
significant influence on Organizational Citizenship
Behavior (OCB); (2) Organizational values have no
significant effect on Organizational Citizenship
Behavior (OCB); (3) Organizational situation has a
significant influence on Organizational Citizenship
Behavior (OCB); (4) Attention to Detail has no
significant effect on Organizational Citizenship
Behavior (OCB); (5) The organizational structure has
no significant effect on Organizational Citizenship
Behavior (OCB); (6) Employee commitment has no
significant effect on Organizational Citizenship
Behavior (OCB); (7) Employee satisfaction has a
significant influence on Organizational Citizenship
Behavior (OCB). In general it can be concluded that
of the four organizational culture variables, only
organizational situation variables have a significant
effect on Organizational Citizenship Behavior
(OCB). In addition, employee satisfaction variables
are also shown to have a significant effect on
Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB).
The Influence of Transformational Leadership on
Organizational Citizenship Behavior and
Organizational Commitment with Mediation of Job
Satisfaction (Study to Fixed Teachers SMA Negeri in
East Lombok). B. Maptuhah Rahmi. Faculty of
Economics Udayana University (Unud), Bali,
Indonesia. The results showed that transformational
leadership had positive and significant effect on
organizational citizenship behavior, transformational
leadership had positive but not significant effect on
job satisfaction, transformational leadership had
positive and significant effect on organizational
commitment, job satisfaction had positive and
significant effect on organizational citizenship
behavior, Positive but insignificant to organizational
commitment. The purpose of this study is to describe
the contribution of dominant factors that influence
OCB. Based on the above description, about the
importance of Organizational Citizenship Behavior in
an organization that can improve productivity,
effectiveness, and organizational efficiency, thus, the
authors are interested in conducting research entitled
"Organizational Citizenship Behavior (Analysis of
Dominant Influencing Factors to OCB at Education
Personnel of FKIP Unversitas Kuningan)".
1.1 Statement of the Problem
How is Organizational Culture, Job Satisfaction,
Commitment, Transformational Leadership, and
Servant Leadership toward Organizational
Citizenship Behavior (OCB) on Teaching Staff of
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
560

Teacher Training and Education Faculty of
Universitas Kuningan?
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
In 1977 for the first time the term Organizational
Citizenship Behavior (OCB) was introduced by the
Organ, and defined Organizational Citizenship
Behavior (OCB) as a discretionary individual
behavior, which was not directly and explicitly
awarded from the formal reward system, Overall
encourages the effectiveness of organizational
functions (Murphy, 2002: 288). Free in the sense that
the behavior is not a requirement to be performed in
a particular role or job description, or behavior that is
personal choice (Podsakoff et al, 2000: 513).
According to Alppebaum (quoted in Quzwini
2013: 134), "Organizational Citizenship Behavior
(OCB) is a voluntary and optional behavior that is not
part of the formal duties of employees, but what they
do affects the effectiveness of the task and the role of
the organization. Meanwhile, according to Teleghani
(2013: 911) states that "Organizational Citizenship
Behavior is a positive behavior of employees that can
improve organizational effectiveness, is voluntary,
and is not formally described (extra role) and not
included in the organization's reward system."
Wirawan (2013: 722) Suggests that "OCB is
voluntary workplace behavior undertaken by an
employee freely which is beyond a person's job
requirements and organizational requirements so that
it does not exist in an organizational reward system
which, if implemented by an employee, will improve
the functioning of the organization". OCB is a
voluntary behavior of members of the organization
rather than the required or enforced behavior of the
organization. The employee's duty at work is to carry
out his work specified in his job description and the
OCB is not in the job description of the employee but
he carries out this behavior because he / she feels
compelled to be a member of the organization.
Because of voluntary behavior, OCB employees do
not expect rewards because it does not exist in the
organization's rewards system. If the employees do it
consistently, it will improve the functioning of the
organization.
Based on the explanation above the author can
conclude that Organizational Citizenship Behavior is
a behavior that does need to exist in an organization.
Although these behaviors are not formally written but
are indispensable, they will have a positive impact on
the organization. When associated with educational
platforms as well as teachers' schools and staff must
have Organizational Citizenship Behavior as this
behavior will bring the organization to its goals well.
Aspects of Organizational Citizenship Behavior
used in research May-Chiun Lo and Rumayah (2009:
41) proposed by Organ and Podsakoff, five aspects
are:
The virtue of citizenship (Civic virtue) is the
participation of subordinates in the life of the
organization, refers to the responsibilities of
subordinates to participate in organizational
political life such as attending meetings that are
not compulsory and following organizational
changes even though cannot attend the meeting
Listening to consciousness is defined as
dedication in performing work that goes beyond
formal requirements such as working beyond
predetermined standards and volunteering to
perform work outside of its formal role
Altriusme (altruism) is defined as a behavior
that cares for and prioritizes the interests of
others such as helping to volunteerly solve
problems co-workers' problems related to work
Courtesy is a behavior that focuses on
preventing problems and taking the necessary
steps to minimize the impact of future problems
Sportsmanship is any behavior that shows
tolerance to the ideal state without complaint.
The sportsmanship of the employees is to
tolerate unexpected or less favorable
circumstances without complaint.
According to Podsakoff, et al., Organizational
Citizenship Behavior has seven dimensions.
Although different, but there are two aspects that
Podsakoff, et al., Have in common with the Big Five
Dimension proposed by the organ namely the
dimensions of sportsmanship and civic virtue. Seven
dimensions of Organizational Citizenship Behavior
according to Podsakoff, et al. (2000: 514), namely:
Helping Behavior conceptually is the behavior
of helping others to prevent work-related
problems
Sportsmanship
is willing to tolerate unavoidable
inconvenience, not complain of work when it
comes to overtime, maintaining a positive
attitude even when organizational matters do not
go as expected, and willing to sacrifice personal
interests for the benefit of the work team, and
not to reject the ideas of the team work
personally
Organizational loyalty is the attitude of
supporting and sustaining organizational goals,
building the organization's image in the external
environment, protecting and defending the
organization against external threats, and
Organizational Citizenship Behavior - Analysis of Dominant Influencing Factors to OCB at Education Personnel of FKIP Universitas
Kuningan
561

staying committed to the organization even
under difficult conditions
Individual initiative is an employee initiative to
communicate with communicative with the aim
of improving individual performance in team
work
Organizational compliance is the acceptance
and adherence to rules and procedures
applicable within the organization even when no
one observes or monitors
Civic virtue is a positive attitude and
commitment to the organization as a whole,
such as a willingness to participate actively in
organizational governance, for example, attend
meetings, engage in policy debates, and respond
to organizational strategies. This attitude
reflects someone's recognition that he or she
becomes a big part of the organization that
shelters it has a great responsibility and
commitment to the organization
Self-development is the employee's voluntary
behavior to be actively involved in the
development and training of human resources
with the aim of increasing knowledge, skills and
abilities thus increasing the contribution of
employees to the organization.
Unlike Organ and Podsakoff, et al., Graham and
Bolino, et al., It is perceived that the
conceptualization of Organizational Citizenship
Behavior is based on modern philosophical concepts
and theories of philosophy. Graham (2002: 508)
suggests that there are three aspects in Organizational
Citizenship Behavior:
Obedience is the willingness of employees to
accept and comply with all organizational rules
and procedures
Loyalty is to describe the attitude or
commitment of employees in overriding
personal interests and prioritizing the interests
of the organization
Participation is describing all aspects of
employees' willingness to participate actively in
all organizational activities.
Organizational Citizenship Behavior-OCB
behavior occurs because there are a number of
preceding factors that cause an employee to do OCB.
The main factor is the personality of the employees
doing OCB. This behavior is mostly done by certain
employees who are happy to help others-employees
are altruism. This personality is also often associated
with employees who are old, have long worked with
enough experience to help colleagues. Young
employees are generally busy understanding and
implementing their job targets by carrying out their
job descriptions.
OCB appears in a particular organizational
culture. Here the OCB of employees is part of the
social responsibility of the organization. OCB also
appears in an organization that has a friendly and
familial organizational condition. If the perceptions
of the members of the organization are friendly and
consider a family, OCB will happen a lot. OCB is
more likely to be performed by employees who are
satisfied with their work than employees who are not
satisfied with their work.
Figure 1: Organizational citizenship behavior model.
Based on the picture1 we can see there are 12
factors that can affect OCB, as well as ten behaviors
Organizational Citizenship Behavior in the
organization and more important is the influence
Organizational Citizenship Behavior against the
organization very high benefits, because it can:
Increase the quantity and quality of productivity
of individual employees and organizations
Effectiveness and efficiency of the organization
Cohesive team
Moril clerks
Espirit de corps
Ethical behavior
Benefits in a company and organization that can
be described as follows:
Improve the work of the company, because it
will move the social machine of the
organization.
Reduce fiction and improve efficiency.
Specifically reduces the need to link resources.
To maintain corporate function.
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
562
Improve productivity of managers and co-
workers.
Increase job satisfaction.
2.1 Hypothesis
Hypothesis in this research is "There is influence of
Organization Culture, Job Satisfaction, Commitment,
Transformational Leadership, and Servant
Leadership to Organizational Citizenship Behavior
(OCB)".
3 METHODS
The method used in this research is correlation
method.
3.1 Operationale Variable
Table 1: Operational variables.
Variable Indicator Measurement
OCB
J.P Mayer &
J.J Allen
(991) in
wirawan
(2013:715)
• Helps
interpersonal
Likert scale 5
option =
Positive
statement
(SS) = 5
(S) = 4
(KS) = 3
(TS) = 2
(STS) = 1
Likert scale 5
option =
negative
statement
(SS) = 1
(S) = 2
(KS) = 3
(TS) = 4
(STS) = 5
• Individual
initiative
• Personalized
crafts
• Loyal boosterism
Cultural
Organization
(Hof stede:
1993) in
Wirawan
(
2013:182
)
• Distance
Management
• Believe In
Co-Workers
• Integration
Job
satisfaction
Luthans
(1995) in
Sopiah (2008 :
173)
• The work itself
• Type and
workload
• Work
p
lacement
• Wages / salaries
• Provision of
salary
• Commissions
• Promotion
• Supervision
• Briefing
• Attention and
supervision
• Working groups /
co-workers
• Caution among
colleagues
• Work
environment /
working
Variable Indicator Measurement
conditions
support
Organization
Commitment
Wirawan
(2013:715)
• Affective
Commitment
• Bind themselves
to the values and
norms of the
organization
• Love the
organization's
goals
• Loyal to the
organization
• Organizational
norms and values
are equal to the
individual values
of employees
• Sustainable
Commitment
• More profitable if
you remain an
organization
member
• Feeling afraid of
losing something
if leaving the
or
g
anization
• Normative
Commitment
• The organization
has contributed to
the lives of
employees.
• Organizations
work better than
other
organizations.
• Experience
working in a fun
and happy
or
g
anization.
• Commitment
Between
• Becoming a
member of the
organization is
just a stepping
stone to becoming
a member of other
or
g
anizations...
Transformati
onal
Leadership
(Bass and
Avolio:1990)
in Wirawan
(2013:182)
• Charisma
• Inspirational
motivation
• Intellectual
Stimulation
• Individual
Consideration
Organizational Citizenship Behavior - Analysis of Dominant Influencing Factors to OCB at Education Personnel of FKIP Universitas
Kuningan
563
Variable Indicator Measurement
Servant
Leadership
Vondey
(2010) in
Wirawan
(2013:182)
• A
g
a
p
ao love
• Helps growers
g
row and succee
d
• Prefer the
subordinates
• Be ethical
• Create value for
the Communit
y
3.2 Population and Sample
Population in this research is all educational staff of
Faculty of Teacher Training and Education (FKIP)
Universitas Kuningan, amounting to 26 people.
Because the population is less than 100, so the
researcher took the entire population to be the
research sample. The sampling technique used is
saturated sampling.
3.3 Data Collection
Data collection techniques that the authors use in this
study is a questionnaire. Data analysis using multiple
regression analysis.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Based on the results of data processing obtained
picture of research variables as follows:
Transformational leadership (X1) at FKIP
University of Kuningan according to the
perception of educational staff is high.
Servant leadership (X2) at FKIP University of
Kuningan according to the perception of
educational staff is high.
Organizational culture (X3) at FKIP University
of Kuningan according to the perception of
educational staff is high.
Job satisfaction (X4) at FKIP University of
Kuningan according to the perception of
educational staff is high.
Organizational Commitment (X5) on FKIP
Universitas Kuningan according to the
perception of educational staff is high.
OCB (variable Y) at FKIP Universitas
Kuningan according to the perception of
educational staff is high
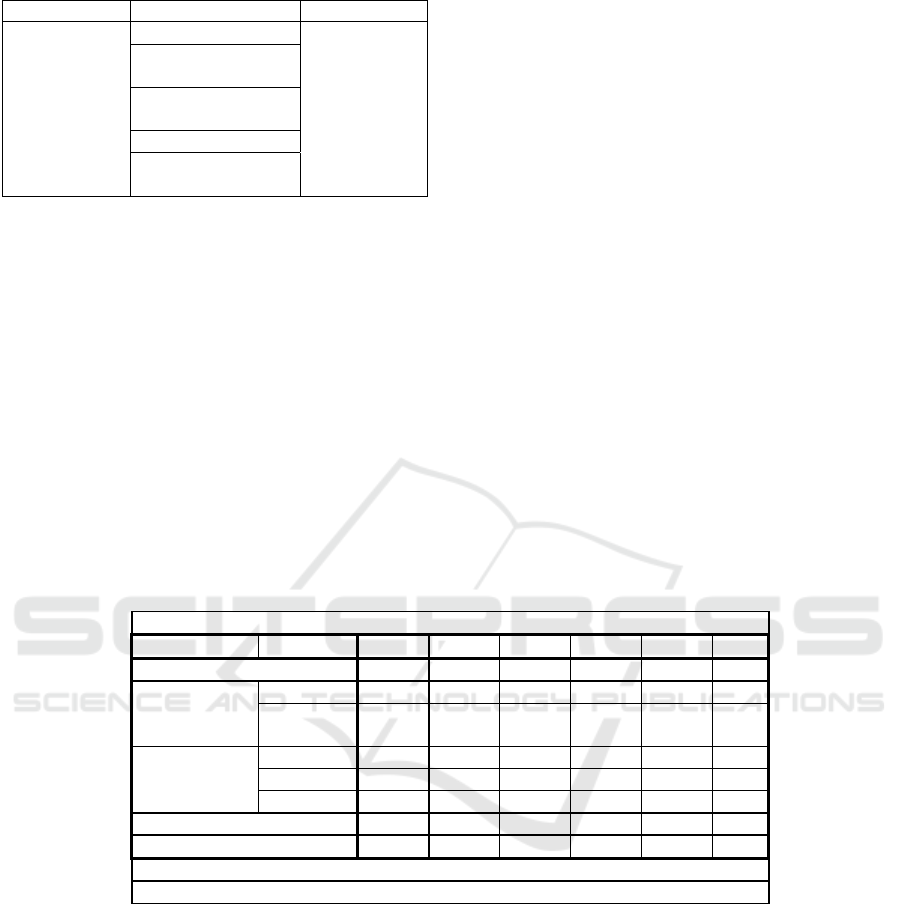
Table 2: Result of data normality test calculation.
One-Sam
p
le Kolmo
g
orov-Smirnov Test
X1 X2 X3 X4 X5 Y
N 26 26 26 26 26 26
Normal
Parameters
a,,b
Mean 27.62 38.46 26.23 39.42 37.65 32.12
Std.
Deviation
3.721 5.501 3.076 5.209 4.399 3.953
Most Extreme
Differences
Absolute .129 .149 .140 .127 .111 .133
Positive .129 .149 .117 .122 .111 .133
Negative -.124 -.110 -.140 -.127 -.088 -.106
Kolmogorov-Smirnov Z .660 .761 .716 .648 .568 .678
Asymp. Sig. (2-tailed) .776 .609 .684 .795 .903 .748
a. Test distribution is Normal.
b
. Calculated from data.
Based on table 2 it is known that all data in the
research variables are declared normal distribution,
where the value of sig> 0,05. The influence of
Organizational Culture (X1), Job Satisfaction (X2),
Organizational Commitment (X3), Transformational
Leadership (X4) and Servant Leadership (X5) on
Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB) based on
calculation coefficient of determination obtained
value 98,7% , 3% influenced by other factors. This
means that OCB is influenced by Organizational
Culture (X1), Job Satisfaction (X2), Organizational
Commitment (X3), Transformational Leadership
(X4) and Servant Leadership (X5) jointly by 98.7%
the remaining 1.3% Influenced by other factors. To
find out whether this research has significant or not,
F test is done. Based on the calculation results
obtained Fcount value of 296,365 with a significance
value of 0.000. Because the sig value. <0,05 i.e. 0,000
<0,05, it is stated significant. So there is a significant
influence between Organization Culture (X1), Job
Satisfaction (X2), Organizational Commitment (X3),
Transformational Leadership (X4) and Servant
Leadership (X5) on Organizational Citizenship
Behavior (OCB).
In addition, based on the F test obtained Fcount
value of 296,365 with a significance value of 0.000.
Because the sig value. <0,05 i.e. 0,000 <0,05 hence it
is stated significant. So that there is a positive
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
564

influence Organizational Culture (X1), Job
Satisfaction (X2), Organizational Commitment (X3),
Transformational Leadership (X4) and Servant
Leadership (X5) Against Organizational Citizenship
Behavior (OCB).
Several previous researches presented by the
researchers at the beginning strengthen the results of
this study that Organizational Culture (X1), Job
Satisfaction (X2), Organizational Commitment (X3),
Transformational Leadership (X4) and Servant
Leadership (X5) influence Organizational
Citizenship Behavior (OCB).
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of research conducted by
multiple regression analysis, showed that
Organizational Culture (X1), Job Satisfaction (X2),
Organizational Commitment (X3), Transformational
Leadership (X4) and Servant Leadership (X5)
influence Organizational Citizenship Behavior
(OCB). Based on the conclusions of the study and as
a consideration in terms of management, especially to
increase Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB)
employees, the authors suggest things as follows:
leaders can pay special attention to the individual
needs for achievement and development, by way of
coaches, advisors, facilitator teachers, trusted people
and counsellors, fellow colleagues or relationships
with superiors should be more tightened by mutual
help and respect for others, leaders can give attention
and supervision to subordinates, so that employees
feel closer and have job satisfaction to the boss.
REFERENCES
Clarista, Vania. dan Roy Setiawan. 2013. Pengaruh Servant
Leadership dan Komitmen Organisasi Karyawan
Terhadap Organizational Citizenship Behavior Pada
Blue Bird Grup Surabaya. Jurnal Manajemen.
Margaretha, M. A., Wike, S.M. 2012. Pengaruh Servant
Leadership Terhadap Organizational Citizenship
Behavior. Jurnal Manajemen Vol. 11. No. 2.
May-Chiun Lo dan Ramayah. 2009. Dimensionality of
Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB) In a
Multicultural Society: The Casa of Malaysia.
International Business Research, Vol. 2:1.
Organ. D.W, 1988. Organizational Citizenship Behavior.
Lexington, MA: Lexington Books.
Podsakoff. P.M., Mackenzie. S.B., et. Al. 2000.
Organizational Citizenship Behavior. A Critical
Review of Theoretical Empirical Literature and
Suggestions for Future Research. Journal of
Management. 26 (3): 513-563.
Putri, Risna Ananda dan Tarcisius T. Sipayung. 2013.
Pengaruh Budaya Organisasi Terhadap Organizational
Citizenship Behavior (Ocb) Studi Kasus Pada Pt.
Mirina Nusantara. Universitas Telkom.
Rahmi, B. Maptuhah. Pengaruh Kepemimpinan
Transformasional Terhadap Organizational Citizenship
Behavior Dan Komitmen Organisasional Dengan
Mediasi Kepuasan Kerja. Bali: Universitas Udayana
Taleghani, M., dan Reyhaneh Rezaee Mehr. 2013. The
Relationship between Servant Leadership and
Organizational Citizenship Behavior in Executive
Organizations of Guilan Province. Journal of Basic and
Applied Scientific Research, Vol. 3:1.
Quzwini, M. 2013. Organizational Citizenship Behavior
pada Pegawai Lapas Kelas 1 Lowokwaru Malang.
Jurnal Psikologi. Vol. 1:1.
Wirawan. 2013. Kepemimpinan Teori, Psikologi, Perilaku
Organisasi, Aplikasi dan Penelitian. Depok: Rajawali
pers.
Organizational Citizenship Behavior - Analysis of Dominant Influencing Factors to OCB at Education Personnel of FKIP Universitas
Kuningan
565
