
Student’s Self Development in Higher Education
Nunu Heryanto, Purnomo Purnomo and Viena R. Hasanah
Department of Society Education, Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Jl. Dr. Setiabudhi No. 229, Bandung, Indonesia
nu2_heryanto@yahoo.co.id, purnomo@upi.edu, vienarusmiati@gmail.com
Keywords: Students, Self-Development, Seven Habits.
Abstract: Students as generation of hope of the nation, young people who have great potential in applying scientific, of
course, tend to be motivated by the young age, in the age of transition from juvenile stage to the adult stage.
Thus, students are also thick with dynamism and attitudes that objective, systematic and rational. This research
done for 6 months (1 semester) to students in the 1st semester in the Department of Society Education in
Faculty of Science Education in Indonesia University of Education, the approach of this research is
quantitative descriptive. This research aim to reveal behavior or habits that enrich the student’s academic
climate with seven habits indicators and efforts that is needed to be done in the context of self-development.
The number of respondents is 64 students. The results shows that the lowest score is in “be proactive” indicator
with the attitude that shows “commitment and responsibility”, and other indicators of the seven habits is in
good category. This aspect influenced by the group climate and the role of the leader in the group that was
too democratic, so the group was uncontrolled. As a new college student (first semester), they not find yet
about the pattern of the good communication in the group, they are still looking for the click (small groups)
that separates themselves. Besides that, there are students that still on adaptation process in the groups.
Implication from this research is the necessity of knowing college student’s behavior in the first semester, in
order to be able to mapping, addressing potential self-college student and self-concept should be built well.
1 INTRODUCTION
The individual personality of the student is a group of
individuals who experience the process as adults,
prepared by the University in accordance with its
expertise. Coupled with the development era of social
situations constantly changing, affecting the
individual personalities or groups. Building character
of students in University need to be supported by
learning environment situation. Setting learning for
adolescents, has differences with the setting of
learning for children. Students included the late teens
to the age range of 17 to 21 years, so the transition
maturation process also needs to be directed in the
learning process. In contrast to adults over the age of
30-55 years (mid adult) and age over 55 years is
called (late adulthood), preferring the principles
Andragogy in the learning process (Brooks, Gunn, J.,
1993); (Rice, PF, 1996); (Benson, PL, 2002);
(Zaidatun Tasir et al., 2008); (Norah Md Noor, et al.,
2012); (Paramitasari, R., 2012); (Coal, JR, 2016).
Students have a strategic role as a change agent
(agent of change) in establishing, revitalizing, revise,
and criticized the order of life of the nation,
realistically and logically accepted by society.
Students as part of society, it is expected and a hope
of the community to provide their contributions on
development. The learning experience (learning
experiences) obtained by the students consists of two
forms, namely: 1) experience in involvement in the
study, called the learning process; and 2) experience
learning in the form of the ability of learning
outcomes, in the form of knowledge, attitudes and
skills. Activities occurs in adult learning undertaken
to produce a learning experience. However, in order
to gain the maximum experience and consistently
takes other factors that can support learning activities
in a sustainable manner as motivation, environmental
conditions, and support educators in solving
problems that arise in the activities of the learning
process (Romiszowski, A., 1981); (Kelly, C., 1997);
(Healey, M.,andJenkins, A., 2000); (Kolb, D.A et
al.,2001); (Moon, JA, 2004); (Kolb, LM,and Kolb,
DA, 2005); (Roberts, TG, 2006).
Some way view affect achievement and behavior
student, determined by internal factors (individual
student) and external (environment), so influence way
thinking ambition forward after they pass
40
Heryanto, N., Purnomo, P. and Hasanah, V.
Student’s Self Development in Higher Education.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences (ICES 2017) - Volume 2, pages 40-45
ISBN: 978-989-758-314-8
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

(Ariwibowo, MS, 2013); (Agusta, YN,2015); (Tanis,
H., 2013); (Kulsum TM, 2016). For knowing
character achievement, several institution in
education has apply seven habits indicators (7Habits)
as standard to knowing behavior learner participants.
There are: 1) Be proactive, 2) Begin with the end in
mind, 3) Put first things first, 4) Think win-win, 5)
Seek first to understand and then to be understood, 6)
Synergize, 7) Sharpen the saw, (Covey, SR, 2014);
(Kamphoff, CS, et al., 2007); (Wright, WA, et al.,
199); (Labby, S., et al., 2012); (Goff, DG 2002). This
research aim to reveal behavior or habits that enrich
the student’s academic climate with seven habits
indicators and efforts that is needed to be done in self-
development.
2 RESEARCH METHOD
This research done in the Department Society
Education in Indonesia University of Education. This
research used quantitative descriptive approach, this
approach was used to obtain the data on the behavior
of student assessment results. Measurement of
behavior through observation directly (performance
test) to 64 respondents with 1 semester period, with
the dominant activity appear when lectures activities
and practice activities using seven habits indicators,
namely: 1) Be proactive, 2) Begin with the end in
mind, 3) Put first thing first, 4) Think win-win, 5)
Seek first to understand and then to be understood, 6)
Synergize, 7) Sharpen the saw (Covey, SR, 2014)
following the conversion standard scores are
interpreted as follows:
Table 1: Conversion of Performance Test Scores.
Value Range Score Information
A 3.5 - 4.0 Very goo
d
B 2.8 - 3.4 Goo
d
C 2.0 - 2.7 Enough
D 1.0 - 1.9 Less
E 0.0 - 0.9 Very less
For measuring the performance test, data
processing used including:
1. Determining amount of scores, determine the
average score.
2. Determining general trend based on range score.
3 RESULTS OF THE STUDY
Or climatic conditions which facilitate the activities
of college students, of course, provide a snapshot of
the behavior or habit that enrich students' academic
climate. There are several categories of students when
viewed from habit or common in the academic
community colleges, such as: first, the diligent
student in college, but following the organizational
activities of excessive so called "activist campus,"
social life (associate in organizations) tend to be high
, that sometimes his job to learn forgotten. The type
of student like this, tend to be clever in associating,
communicating, even regarded as the most senior
student with the nickname "Timeless Student",
graduation tends to be slow as comfortable as
possible by activities outside campus, but when
graduating, students with this type more survive in the
society. Second, students who have the notion that
college is just as routine activities as course, it is
characterized by habit to come to campus, coming to
the class has the designation in "3D concept, (seated,
silent, listen)" then come back (to the boarding house
or home), with no activity. The type of student, to the
orientation of the most important is the gain value
only, lecture made as formality of obtaining a
diploma, and when it passed, the type of the students
like this, will be difficult to survive, because the
ability of organization skill and the ability of social
relationships is bad, so it tends to be a "handyman
work" instead of as a leader or manager in their work
environment. Third, the student with the criteria of
balance between college with activities outside the
campus (association), they tend to have the ability to
set the time and activities, this practice is carried out
systematically as schedule pressed board on her wall,
good at designing, planning, and tend to be the type
of students upon graduation will eventually sought
and needed by the work environment, even his career
a lot to be a leader or a manager.
The concept of establishing their own potential
and understand the concept of self, is inseparable
from the concept of empowerment. Man's
relationship with others and the environment
(external), is a social creature behavior that indicates
its ability to adapt to the environment or
environmental change as he wishes. While Habit is
defined as a mix between knowledge, skills, and
someone’s desire. Awareness and willingness to
renew it self will shortly cause effective habits. On
this research, the student’s habits obtained from the
relevant faculty ratings of seven indicators.
Based on results observation through performance
test seven habits that shows the average value of all
Student’s Self Development in Higher Education
41
students in the category of "good". Each indicator
also shows a number that is not much different. The
lowest scores are on be proactive indicator with an
average value of 3.09. However, each component is
in a good category. Students have shown initiative,
enthusiasm to take steps, quick response, and have
made group commitment well. Meanwhile, for
component shows commitment or responsibility still
in enough category. There are still students who can’t
understand a commitments. For the highest score, was
in the synergize indicator with a value of 3.22.
Students have been trying to synergize themselves to
the group. It is seen from the component recognizing
the achievement of the organization as a common
property, appreciating the work together, contribute
to the achievement of group goals, and ready to
combine personal power to the group. Students
appreciate every difference that exists. The
limitations of his understanding are realized to
develop while interacting with others. Following
table 2 which illustrates the average results of the
assessment of student’s performance, as follows:
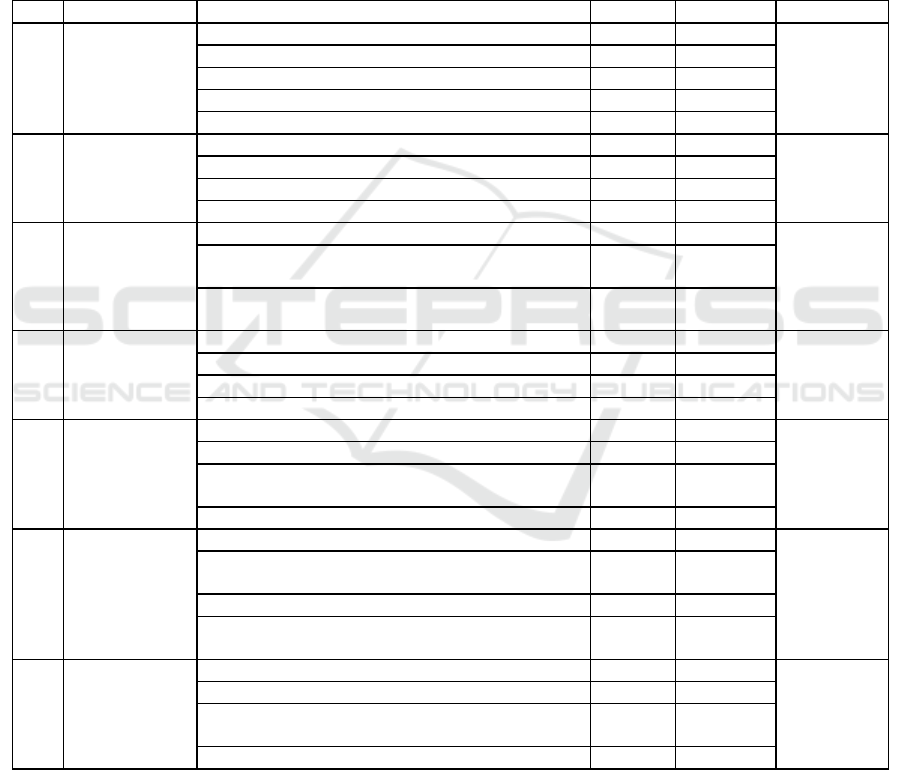
Table 2: Performance Test Results in Seven Habits.
4 DISCUSSION
Before heading to the ability to empower others, of
course, self-empowerment (personal empowerment)
will be more important. As a creature that has
creativity and initiative, humans are known as a
civilized creature and have a higher degree among
other creatures of God. In determining the direction
of his steps, human beings are required to establish
the principle of himself as a form of maturity or
No Indicato
r
Com
p
onent Score Cate
g
or
y
Note
1 Be Proactive
Show initiative
(
not alwa
y
s waitin
g
for orders
)
3.11 Goo
d
3.09
Good
Enthusiasticall
y
take ste
p
s3.17Goo
d
Make commitments with the
g
rou
p
3.2 Goo
d
Shows commitment or res
p
onsibilit
y
2.67 Enou
g
h
Quick res
p
onse 3.3 Goo
d
2
Begin With
The End in
Mind
Show the final destination clearl
y
3.2 Goo
d
3.20
Good
Have the motivation to reach the final
g
oal 3.16 Goo
d
Started the action with the
p
lan 3.22 Goo
d
Shows actions based on clear objectives 3.23 Goo
d
3
First Things
First
Determining priorities in action 3.17 Goo
d
3.21
Good
Breaking down complex issues becomes easy to
solve
3.17 Good
Announce the unimportant and start the most
important
3.3 Good
4
Think Win-
Win
Not selfish 3.13 Goo
d
3.19
Good
Mentoring goodness for others and himself 3.22 Goo
d
Identify solutions for everyone to enjoy 3.22 Goo
d
Ready to work with the tea
m
3.17 Goo
d
5
Seek First To
Understand
and Then To
Be Understood
Empathy (feel what others feel) 3.2 Goo
d
3.19
Good
Listening to others gives an opinion 3.2 Goo
d
Trying to understand what other people's thoughts
p
atientl
y
3.2 Good
Skilfull
y
communicates o
p
inions / ideas / ideas 3.17 Goo
d
6 Synergize
Read
y
to combine
p
ersonal
p
ower with the
g
rou
p
3.16 Goo
d
3.22
Good
Contributing to the achievement of group goals
(organization)
3.2 Good
Appreciate the work togethe
r
3.22 Goo
d
Recognize the achievements of the organization as
a common
p
ro
p
ert
y
3.28 Good
7
Sharpen the
Saw
Want to learn from mistakes 3.31 Goo
d
3.14
Good
Read
y
for criticism 2.91 Goo
d
Improving capability (ability / skill / knowledge)
self
3.09 Good
Maintain intellectual values 3.23 Goo
d
ICES 2017 - 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences
42

maturity to himself. According to Hopson and Scally
in Anwar (2007:78) states that More empowered
individuals show open attitudes to change,
assertiveness, proactivity, responsibility, direction,
sensitivity, likes to learn from mistakes, courage to
advance, contemporary, realistic, looking for an
alternative, developing commitment, respect
themselves, evaluating people, being sensitive to the
needs of society, enjoying the crowds, referring to
harmonious, harmonious and balanced lifestyles.
According to Stewart (1994) empowerment is an
internal power quality individual person's personality
or organization to realize and adapt to the
environment to gain an edge for the promotion and
preservation of the future. Whereby empowerment is
conditioned in eight "E" such as, educate (increase
themselves through education), Eliminate (ability to
overcome obstacles), express (express ideas
correctly), enthuse (vitality of life), equip (complete
lack of self), Evaluate (evaluating the work to work),
and expect (hope for the future clear).
Listening to these views, that power or empowerment
is an internal potential. The problem, potential is not
realized by students before stepping on college,
therefore from the initial stage before entering the
campus gate at least students are given mental
provisions in preparing themselves for the potential
they have. At this stage, it is introduced to students in
the form of a "healthy" campus orientation without
any violence or seniority, but rather to prepare
prospective students to receive academic climate.
That is, the external side also gives impact to the
internal changes (individual) itself.
The principle of building this empowerment is
inseparable from the help of others, whether it is a
fellow friend or from the campus itself that needs to
accommodate their potential (students). The concept
of this collectivity, will be more effective when the
principle of help and mutual reminder occurs in the
student learning environment. According to Walgito
(1994), the relationship between the individual and
his environment, especially the social environment is
not only going in the same direction that only the
environment has an influence on the individual, but
between the individual and the environment there is a
reciprocal relationship, such as the environment
influences the individual, and otherwise individuals
also have an influence on the environment.
Furthermore Walgito (1994) explains that the pattern
of relationships or attitudes of individuals to their
environment can be categorized into three forms,
namely:
1. Individual reject environment, that is, if the
individual is not in accordance with the state of
the environment. In such circumstances, the
individual can give shape (change) to the
environment in accordance with what is
expected by the individual concerned.
2. Individual receive environment, such as when
the environmental conditions appropriate or
suitable to individual circumstances. With
thereby individual will receive circumstances
environment.
3. Individual behave neutral or the status quo, for
example, if the individual is not in accordance
with the state of the environment, but people do
not take steps to change the environment. In
such circumstances, the individual is passive
towards the environment.
Thus, in both cases, establishing values oriented
to life and empower themselves (self-empowerment)
is to be aware of the position values of internal and
external. Self-effort in identifying, exploring, and
absorbing information is the first step before building
the environment (the community).
Success someone, never out of effort and effort
made during his life. The profiles of great and
successful people in this country as evidence that
building his potential is not solely obtained from the
recognition alone, but built by the achievement and
able to donate his opinion to the nation and state. In
fact, students are empowered students who are able to
actualize his potential on the positive, able to open
themselves to positive things, clever to evaluate
themselves to what he has done, sociable or
socializing with others and have a high readiness in
the face of the future.
Empower yourself is a step in choosing
perspective (choice) there is a belief that the
individual self, as the analysis is whether we are
(people) are not helpless or be trapped against the
wrong choice. For example, when an individual has a
perception of the belief itself not so talented, it will
encounter a point where it must make an effort to
improve his life or will always afraid to try.
Not separated from the conception of perception
and belief, there are several ways to help individuals
move from the perspective of helplessness, including:
1. Change the situation and conditions
Environment take big effect to development
themselves. Effort for change environment, of
course, is not easy thing and is a struggle which
is considered difficult. Thus, requiring time and
effort for go through everything. For example
one of the students wanted to change the
learning climate in the classroom to be more
proactive and creative, of course need an
agreement that will affect the crowd.
Student’s Self Development in Higher Education
43

2. Willingness to change oneself
Each individual has their own identity, thus
providing the characteristics or perceptions of
different people. The individual's ability to
evaluate oneself is the most important thing,
because there will be many known deficiencies
or weaknesses in his or her identity. At that
stage, it is necessary that they (students) to
throw away and change themselves from things
that would be considered a weakness for him.
For example: a student is often nicknamed by
his "sleeping" friends in class, this being an
indication that the environment has a negative
perception of him and strives to change himself
to be more diligent, never sleep in class, always
pay attention to lecturers' explanations and be
active in class discussion.
3. Life is creativity
Creative origin of the word creative which
means creativity or have the ability to create. In
this criterion, creativity is not only physical in
nature, but the creativity here is a way to solve
the problems of life, to produce something
useful. Creativity is integrated in everyday life
such as the ability of individuals in managing or
managing the time and activities arranged in
such a way so as not to harm yourself. Many
students are active in the organization but forget
the learning task (active but not productive). For
example: A student who has a habit of doing his
job "Kebut Semalam" to stay up is a bad habit,
in this case the student needs to design time
doing the task so no need to stay up and harm
the health.
4. Face the problem
As social beings who are given the ability to
think, it should not be surrendered and avoided
when experiencing a difficulty or a problem.
Face the problem of life, because with the
problem someone will be more mature and
mature in managing life, responsible for the
actions and actions that do. Example: The
economic problems of students to meet the cost
of living, but embarrassed to entrepreneurship
because of prestige with the title of students.
This prestige factor will hinder the development
itself, but a lot some figures success started with
entrepreneurial success in college.
If the ability of empowerment owned by students
can be managed well, then it will form habit (habit)
to learn, productive, always critical thinking, rich of
idea / idea, ability of socialize and communicate
good, accompanied by soul honest, and able to
account for all his actions. Characteristics of
empowerment owned by students, accompanying the
characteristics of society, because the students are the
smallest part of society who have interests in putting
the ideals and great expectations of family, nation and
religion as the priorities.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The strategic position of Higher Education in
community life is very big, the students as a
component of the campus academic community have
hope that is always eagerly awaited by the society.
The strategic role of youth and students is very
important, in the framework of regional development,
nation and state, as agents of social, economic and
political change. Behind professional academic
ability there is a great responsibility too, so this
becomes the basis in empowering yourself (students).
On the basis of this, the student must be empowered
in making breakthroughs of critical, progressive,
productive attitude of a very expected young man.
It is a duty for Students in the struggle for nation
building. From the beginning until now, students have
always been an integral part of the elements of change
actors in this country.
The most important thing in empowering the
potential of self (students) is to instill the vision of
self-mission as a principle in life. The categories of
students who are considered to have grown up, have
strategic position and potential in empowering
themselves with the principle of divinity and
humanity.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to express our deepest gratitude to
LPPM UPI (Institute of Research and Community
Service of Indonesia University of Education) for the
research grant.
REFERENCES
Anwar, 2007. Management of Women. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Ariwibowo, M. S., 2013. Effect of Learning Environment
on Student Achievement of PPKn Force 2008/2009
Universitas Ahmad Dahlan Odd Semester Academic
Year 2010/2011. Journal of Citizenship, 1 (2).
Agusta, Y. N., 2015. Relationship between Future
Orientation And Power Juang Readiness To Work On
Final Level Students of the Faculty of Social and
ICES 2017 - 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences
44

Political Sciences at the University of Mulawarman.
eJournal Psychology. Vol. 3 No. 1 (369-381).
Coal, J. R, 2016. Adolescent development. Sari
Paediatrics, 12 (1), 21-9.
Benson, P. L., 2002. Adolescent development in social and
community context: A program of research. New
Directions for Student Leadership, 2002 (95), 123-
148.
Brooks-Gunn, J., Duncan, G. J., Klebanov, P. K., Sealand,
N., 1993. Do neighborhoods influence child and
adolescent development?. American journal of
sociology, 99 (2), 353-395.
Covey, S. R., 2014. The 7 habits of highly effective
families. St. Martin's Press.
Healey, M., Jenkins, A., 2000. Kolb's experiential learning
theory and its application in geography in higher
education. Journal of geography, 99 (5), 185-195.
Kamphoff, C. S., Hutson, B. L., Amundsen, S. A., Atwood,
J. A., 2007. A motivational / empowerment model
applied to students on academic probation. Journal of
College Student Retention: Research, Theory &
Practice, 8 (4), 397-412.
Kulsum, T. M., 2016. Relationship Between Independence
With Job Readiness At Final Year Students (Doctoral
dissertation, UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya).
Kolb, D. A., Boyatzis, R. E., Mainemelis, C., 2001.
Experiential learning theory: Previous research and
new directions. Perspectives on thinking, learning, and
cognitive styles, 1 (8), 227-247.
Kolb, A. Y., Kolb, D. A., 2005. Learning styles and learning
spaces: Enhancing experiential learning in higher
education. Academy of Management learning &
education, 4 (2), 193-212.
Goff, D. G., 2002. Community College Presidency: What
Are The Challenges To Be Encountered and Traits To
Be Successful?.
Kelly, C., 1997. David Kolb, the theory of experiential
learning and ESL. The Internet TESL Journal, 3 (9),
1-5.
Labby, S., Lunenburg, F. C., Slate, J. R., 2012. Emotional
Intelligence and Academic Success: A Conceptual
Analysis for Educational Leaders. International
Journal of educational leadership preparation, 7 (1),
n1.
Noor, N. M., Aaron, J., Aris, B., 2012. Andragogy and
pedagogy learning model preference among
undergraduate students. Procedia-Social and
Behavioral Sciences, 56, 673-678.
Moon, J. A., 2004. A handbook of reflective and
experiential learning: Theory and practice. Psychology
Press.
Paramitasari, R., Alfian, I. N., 2012. The relationship
between emotional maturity and the tendency to forgive
the late teenager. Journal of Educational Psychology
and Development, 1 (02), 1-7.
Rice, P. F., 1996. The adolescent: Development,
relationships and culture. Adolescence, 31 (121),
250.
Roberts, T. G., 2006. A philosophical examination of
experiential learning theory for agricultural education.
Journal of Agricultural Education, 47 (1), 17.
Romiszowski, A., 1981. Designing Instructional System.
London: Kogan Page.
Suharto, E., 2006. Building People Empowering
Communities. Bandung: Refika Aditama.
Stewart, Mitchell Allen. 1994. Empowering People.
London: Pitman Publishing.
Tanis, H., 2013. The Importance of Building Character
Education in Shaping Personality of Students.
Humanities, 4 (2), 1212-1219.
Tilaar, H. A. R., 1994. National Education Management.
Bandung: Rosdakarya.
Walgito, Ben. 1994. Social Psychology. Yogyakarta: Andi
Offset.
Wright, W. A., Knight, P. T., Pomerleau, N., 1999.
Portfolio people: Teaching and learning dossiers and
innovation in higher education. Innovative Higher
Education, 24 (2), 89-103.
Student’s Self Development in Higher Education
45
