
Internship Course Design
Ex-Post Facto on Curriculum Development of Educational Technology Study
Program
Riche Cynthia Johan, Rudi Susilana, M. Ridwan Sutisna and Didi Supriadie
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia
{riche, rudi_susilana, m.ridwan.sutisna}@upi.edu, cintadidi@gmail.com
Keywords: Internship Course Design, Ex-post Facto, Educational Technology Competences.
Abstract: Professional practice training program, known also as internship course, is the field application of
knowledge and skills that educational technology students have obtained on campus. Educational
technology experts must be able to perform their role as professional educational technologists who have
several competences. However, the professional practice training program is not in line with the expected
competences as professional educational technologist. The objective of this research is to produce relevant
structured program and competences formula which are appropriate for students of educational technology
program based on their outcome competences. An ex-post facto method was used in this research and the
data was collected from last year of finished professional practice training program. This research used
Association for Educational Communication and Technology (AECT) standard as a guideline and
framework, especially the 2012 AECT standard consisting of five aspects: content knowledge, content
pedagogy, learning environments, professional knowledge and skills, and research. Each aspect is explained
within the framework of creating, using, assessing/evaluating, and managing ethics. The results of this
research are: 1) Matrix of educational technology competences; 2) Course design of professional practice
training program; 3) Model of practice that can be used to improve the existing program.
1 INTRODUCTION
Indonesian people today and in the future, are
technology-cultural society. In other words,
technological developments have occurred in such a
way that is widespread and have affected all aspects,
especially education.
Responding to these facts, educational
technology program needs to develop more
meaningful curriculum, more useful in order to
develop student competencies which is relevant to
competences of educational technology graduates
both theoretically and practically. For educational
technology students, professional practice training
program is an application of the knowledge and
skills that have been obtained on campus.
Therefore, professional practice training program
in the Educational Technology program is intended
to train students in real situations, and the field
experience is also suggested to give some feedback
for curriculum adjustment and development. It is
also to be used as an early analysis for developing
the design of work practices in the field of
educational technology.
There are symptoms that lead to the lack of
accordance between the training program and
expectation of gained competences. The existing
program tends to be various and is only based on the
need of institution and gained ability of student.
Generally, "Professional practice training
program can be described as an attempt to increase
the mastery of professional competence through
practicum in the real environment" (Miarso, 2004).
Narayanan et al. (2010) view internships as a
knowledge transfer process, and distinguish between
internship antecedents, processes, and outputs.
Strengthen the opinion, Tovey (2001) has
investigated what makes the internship experience
valuable for the student, supervisor, or faculty
member. It can be concluded that these three
opinions completed each other. To make a good
internship program which can increase the mastery
256
Cynthia Johan, R., Susilana, R., Sutisna, M. and Supriadie, D.
Internship Course Design - Ex-Post Facto on Curriculum Development of Educational Technology Study Program.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences (ICES 2017) - Volume 2, pages 256-261
ISBN: 978-989-758-314-8
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
of professional competence, it needs support from
every person involved, starts from antecedent’s
phase. One of most the most crucial part of
antecedent’s phase is the program formation.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Educational Technology Profession
Practice
Practice of Professional Educational Technology in
Indonesia is increasing after the existence of
Functional Position of Instructional Technology
Developers which have six main tasks: (1) Analysis
and assessment instructional technology
model/system, (2) Instructional technology
model/system design, 3) Instructional media
production, (4) application of instructional
system/model and utilization of instructional media,
(5) Control of instructional system/model and (6)
evaluation of implementation system/model and
utilization of instructional media (Ministerial
Regulation of the Utilization of the State Apparatus,
2009). Instructional technology is the theory and
practice of design, development, management,
utilization, and evaluation of instructional process
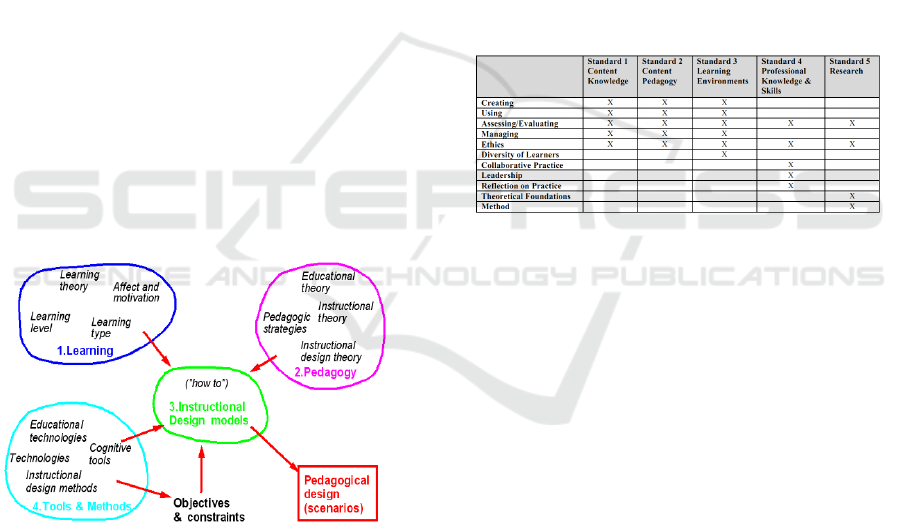
and resources (see in figure 1).
Figure 1: Competence of education technology according
to AECT, 2008.
Along with the rapid development of science and
technology, especially in the field of educational,
communication and computer science, the definition
of educational technology according to Association
for Educational Communication and Technology
(AECT) also shifted. “Educational technology is the
study and ethical practice of facilitating learning and
improving performance by creating, using, and
managing appropriate technological processes and
resources” (AECT, 2012). All of these new changes
and developments have influenced the development
of the field of educational technology competence
and the environment as illustrated in Figure 1.
Based on Figure 1, it can be seen that education,
especially learning and learning, has been
transformed recently, especially at the turn of the
millennium beginning of the 21st century. The
paradigm in learning now leads to changes in school
services and teacher’s role. Responding to this fact,
students of educational technology must be able to
master their professional competences in order to
keep up with the changes. Therefore, to facilitate the
fulfilment of these competences, in 2012 AECT has
been made further action. The Association made
formulation of the standardized competences for a
professional educational technologist. According to
the AECT formulation, in the table 1 is the map of
education technology standardized competences.
Table 1: Competences of educational technologist
profession according to 2012 AECT standard.
2.2 Professional Practice Training
Program
Educational Technology Study Program has
developed Professional Practice Training Program.
This program is an Intra-curricular activity which
held in eighth semester that must be followed by all
students. The activities are more practical-applicable
in applying concepts and principles gained from
lectures. The allocation of time required for the
practice is equivalent to sixteen (16) meetings and
equal to 4 credit hours for each meeting. Activities
of professional practice training program must
include: theoretical discussion activities, preparation
and program planning, review and panel discussion,
implementation of the program activities and will be
ended with a seminar of program results and activity
report.
Clark (2003) stated that the educational value of
internships can be enhanced through academic
assignments, in which the internship can offer some
enhancement for student competences development.
Therefore, the professional practice training program
should be academically supportive.
Internship Course Design - Ex-Post Facto on Curriculum Development of Educational Technology Study Program
257
The implementation of professional practice
training program for students of educational
technology is intended for the professional forming
in the field of educational technology. Therefore, the
implementation of a well-programmed training is
very important. It is also aimed to anticipate the
student perception of the value that they will receive
after the internship program. Cook et al. (2004) said
that students perceived the value of internships
largely in the social and people skills, and only
weakly related to improved academic skills.
Thus, in the implementation of professional
practice training program it is necessary to have a
plan or design in order to achieve the expected
objectives. So that, we offer a design that can be
implemented in an integrated, directed, and guided
way. These designs include patterns of briefing,
orientation, real practice and report preparation.
These activities must involve two instances: the
campus and the institution coordinated by the
program organizing unit and implemented
sustainably.
3 RESEARCH METHODS
This study used ex-post facto method because the
variable is not manipulated nor treated by the
researcher and it used the data that already existed as
suggested by Kerlinger (1964) that in ex-post facto
research the variables have already occurred and the
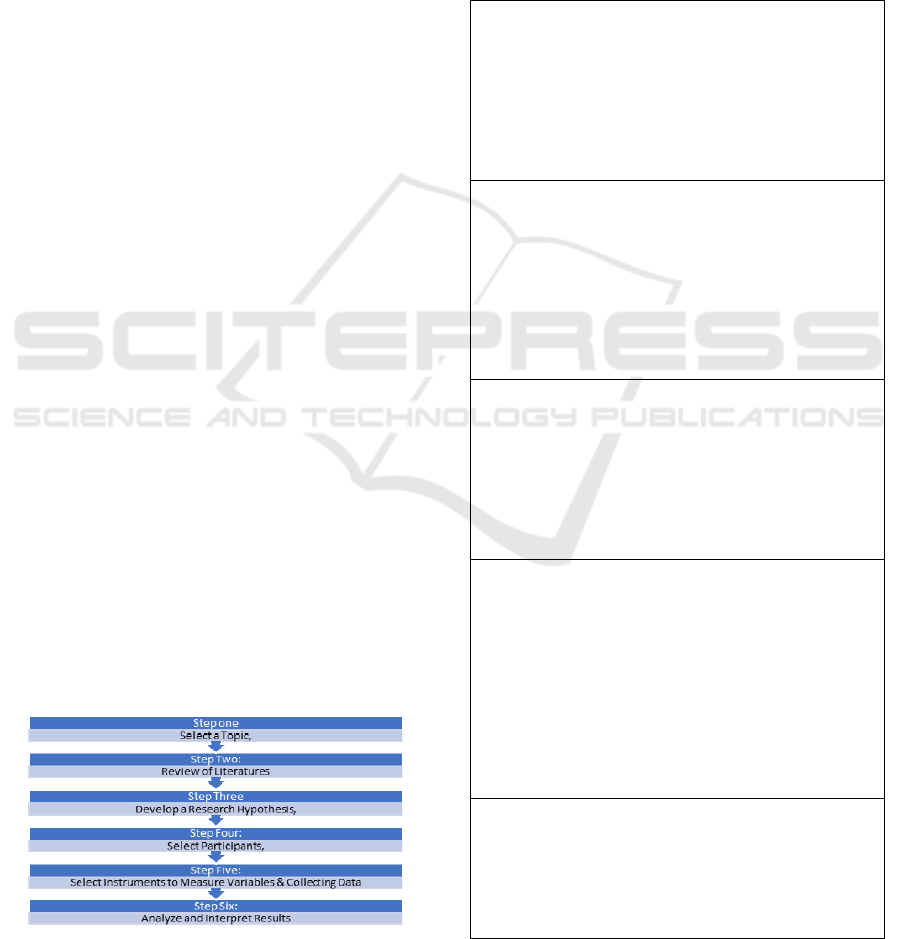
researcher only use the existed data. The design of
this research will be using six step Lodico et al.’s
way (2006) of ex-post facto implementation.
The data collected for this research was taken
from 2017 period and the proposals analyzed were
picked up randomly for this research. The proposals
were analyzed and interpreted comparing to 2012
AECT Standards. Based on the data analysis and
then use the 2012 AECT Standard as comparison,
we mapped the internship design that has been done
and draw the whole figure 2 about the design of
internship program.
Figure 2: Lodico steps of research (2006).
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Matrix of Educational Technology
Competences
According to Association for Educational
Communications and Technology (AECT) in 2012,
in more detail suggests the following competency
standards for educational technology (see in table 2).
Table 2: Matrix of educational technology competence
according to AECT standard, 2012.
1. Content Knowledge
Candidates demonstrate the knowledge necessary to create,
use, assess, and manage theoretical and practical applications
of educational technologies and processes.
1.1 Creating Content Knowledge
1.2 Using Content Knowledge
1.3 Assessing/Evaluating Content Knowledge
1.4 Managing Content Knowledge
1.5 Ethics of Content Knowledge
2. Content Pedagogy
Candidates develop as reflective practitioners able to
demonstrate effective implementation of educational
technologies and processes based on contemporary content
and pedagogy
2.1 Creating Content Pedagogy
2.2 Using Content Pedagogy
2.3 Assessing/Evaluating Content Pedagogy
2.4 Managing Content Pedagogy
2.5 Ethics of Content Pedagogy
3. Learning Environments
Candidates facilitate learning by creating, using, evaluating,
and managing effective learning environments.
3.1 Creating Learning Environments
3.2 Using Learning Environments
3.3 Assessing/Evaluating Learning Environments
3.4 Managing Learning Environments
3.5 Ethics Learning Environments
3.6 Diversity of Learners
4. Professional Knowledge and Skills
Candidates design, develop, implement, and evaluate
technology-rich learning environments within a supportive
community of practice.
4.1 Collaborative Practice of Professional Knowledge
and Skills
4.2 Professional Leadership Knowledge and Skills
4.3 Reflection on Practice of Professional Knowledge and
Skills
4.4 Assessing/Evaluating Professional Knowledge and
Skills
4.5 Professional Knowledge and Skills Ethics
5. Research
Candidates explore, evaluate, synthesize, and apply methods
of inquiry to enhance learning and improve performance.
5.1 Research Theoretical Foundations
5.2 Research Method
5.3 Assessing/Evaluating Research
5.4 Research Ethics
ICES 2017 - 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences
258

4.2 Field Experience Practice Program
(Internship)
The 2012 AECT standards has been analyzed and
then combined with four aspect of systematic design
that is input, process, output and outcome. This
combination can be elaborated by this illustration in
figure 3.
Figure 3: Design of educational technology work practice
The input of the internship program is the
students with their attained competences from
lectures in campus. Their skills and knowledge are
the input. While the process implementation of
internship stages consists of three main stages:
campus orientation, off campus orientation and real
practice stage.
The above pictures are the ideal procedure
retrieved from expected situation and competences
of 2012 AECT Standard. Its achievement has not
been measured yet. The recent professional practice
training program runs with the following activities:
4.2.1 On Campus Briefing (1 Week)
This briefing activity is the first part of PLP
activities which held on campus organized by
faculty of education technology program. Focused
on the refreshment of knowledge and professional
skills, as well as developing values and attitudes
suitable with the conditions and situations in the real
field.
The briefing activities are divided into two
sessions. The first is a 4-day briefing that all the
students get the same lectures on general
professional practice training program which invite
the institution representative (1 of 4 day). The
second session is 2 days of briefing for each group
of the training student, discussing the program that
they proposed.
4.2.2 Field Orientation (1 Week)
This is an introduction activity about the institution
where the internship will take place. This orientation
includes the following activities: a) Collecting
information on organizational and personnel
management of the institution, b) Subject matter
orientation, c) Collecting and analyzing information
of problems related to educational technology field,
d) Discussing alternative solution of the problem, e)
Arrangement and discussion of professional practice
training program that will be implemented during
the internship period.
4.2.3 Real Practice (8 Weeks)
Practical activities in this field provide hands-on
experience for participants to implement the
program that has been planned in the first stage. This
professional practice covers the integration of
educational technology competencies such as
Content Knowledge, Content Pedagogy, Learning
Environment, Professional Knowledge and Skills
and Research with the work tasks of the institution.
Students’ achievement of the program is mostly
evaluated from this real practice stage. The
evaluation is not only about the program but also
about the personality such as discipline and
socialization.
4.2.4 Internship Report (2 Weeks)
Report preparation activity is an individual activity
of student participants that describe and discuss the
activity during orientation stage and real practice.
This activity is held for 2 weeks until signed by the
supervisor and the head of the institution where the
actual practice, the format of the report in outline
adjusted to the pattern offered for its contents,
covering the discussion of the briefing activities,
orientation and field practice that has been
implemented by students of the participants
4.3 Best Practice in Professional
Practice Training Program
The following programs presented in Table 3 are
reviewed product design of the programs of 30
professional practice training program of educational
technology in 2017.
Internship Course Design - Ex-Post Facto on Curriculum Development of Educational Technology Study Program
259

Table 3: Programs of 2017 educational technology
professional practice training (PLP).
NO PROGRAM INFORMATION
1 Program/ Training
Need Analysis
Need analysis to be able to decide form
and type of training / program needed
by institution.
2 Content Analysis Content compatibility analysis with the
delivery form used and the suitability
of existing needs in the field. Includes
adequate material coverage and
material sequence accuracy.
3 Development of
training
curriculum
Development of training curriculum in
the form of curriculum development of
existing training programs.
4 Training Design Create a new training program design.
Or as a form of improvement to
existing designs.
5 Media Design Create a media product design. From
start making GBPM, storyboard script
to its usage guide.
6 Development of
Learning
Materials
Development of teaching materials is
mainly done in module form.
Specifically, not touching content
development but rather on the
development of structure and delivery
and providing advice to content
providers.
7 Media
Development
Conducting the process of developing
media learning from the existing
content theme. Media development is
mostly done in the form of digitized
content and video-making or
presentation of computer-based
presentation.
8 Observation of
Learning
Activities
Observing the learning process in the
implementation of the training system
at the institution.
9 Development of
Online Learning
Activities
Development of online activities by
changing the atmosphere of learning
from conventional to online. They
include providing learning content that
was previously copied and pasted into
a download system, or by creating an
online-based evaluation instrument.
10 Testing Learning
Resources
Implementation
Testing the various types of learning
resources that already exist.
Compatibility, attractiveness to
effectiveness.
11 Management of
Training
Training Administering and managing
the implementation of the training.
12 Training
Evaluation
Evaluate the implementation of the
training. Make a problem or evaluation
instrument to process the result of
evaluation and analysis and report on
the implementation of the training
13 Information
System-based
evaluation
database
Management
The values and attainment of existing
training participants in management
through an internet-based information
system with centralized database
systems and automation of analysis
and reporting.
14 Others It was varying according to the
institution specific instruction. Various
institution orientation and requirement,
made it possible that student will be
given other task irrelevant directly to
the subject of educational technology.
The programs above are proposed in the first
week during on-campus briefing and fixed in second
week as field orientation ended. Most of the
programs are good and relevant with educational
technology. However, there are some programs
which are irrelevant directly with educational
technology and which occur during discussion in the
field orientation stage. So far, this is uncontrolled
due to institution requirement of work. Programs
such as administration, public relation, or any
general office works in specific case become major
and dominant at internship program despite the more
educational technology relevant programs has been
arranged. Besides, the perception of student
mentioned by Cook et al. (2004) must be countered.
Meanwhile other opinion by Clark (2003) must be
supported.
That is why it is important to have the same idea
between faculty member, students and the internship
institution. That is how the first day meeting was
conducted in which all three representatives
participated in the first session of on campus
orientation, which becomes very important. That is
one of the best practices which should be noted and
simply as an example to follow.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Professional practice training program is an intra-
curricular activity which held in the eighth semester
that must be followed by all students. The process of
the activities is more practical in applying applicable
concepts and principles derived from lectures. The
effectiveness of the program implementation
requires guidelines that can direct the
implementation of activities in a structured and
systematic way, through the fulfilment of the
following points: 1) Matrix of education technology
competence, 2) Course design of professional
practice training program, and 3) Model of practice
that can be used to improve the existing program.
REFERENCES
AECT Standards, 2012. Standards. In adopted AECT
Board of directors July 16, 2012. Bloomington,
IN•47404-3745
Clark, S. C., 2003. Enhancing the educational value of
business internships. Journal of Management
Education, 27(4): 472–484.
Cook, S., Parker, R. S., Pettijohn, C. E., 2004. The
perceptions of interns: A longitudinal case study.
Journal of Education for Business, 79: 179–185.
ICES 2017 - 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences
260

Kerlinger, F. M., 1964. Foundations of behavioral
research, Holt, Rinehart, & Winstron. New York.
Lodico, M., Spaulding, D., Voegtle, K., 2006. Methods in
educational research: From theory to practice,
Jossey-Bass. San Francisco.
Miarso, Y., 2004. Menyemai Benih Teknologi Pendidikan,
Kencana. Jakarta.
Narayanan, N., Olk, O., Futami, F., 2010. Determinants of
Internship Effectiveness: An Exploratory Model.
Academy of Management Learning & Education, Vol.
9, No. 1, pp.61–80.
Ministerial Regulation of the Utilization of the State
Apparatus, 2009. Functional Position of Technology
Learning Developer and Credit Score.
Seels, B. B., Richey, R. C., 1994. Instructional
technology: The definition and domains of the field.
Washington, DC. Association for Educational
Communications and Technology
Tovey, J., 2001. Building connections between industry
and university: Implementing an internship program at
a regional university. Technical Communication
Quarterly, 10 (2): pp.225–239.
Internship Course Design - Ex-Post Facto on Curriculum Development of Educational Technology Study Program
261
