Cognitive-Behavioral Counseling Model to Optimize Cognitive
Potentiality and Adaptive Behavior of Attention Deficite
Hyperactivity Disorders (ADHD) Students
Hidayat Hidayat
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Bandung, Indonesia
hidayatday999@upi.edu
Keywords: Cognitive Behavioral Counselling Model, ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorders) Students.
Abstract: The aim of this research is to find out counselling model (cognitive - behavioral) which optimizing
cognitive ability and adaptive behavior of ADHD students, to find out correlation between cognitive ability
and adaptive behavior of ADHD students, to examine contribution of counselling model (cognitive-
behavioral), both of simultaneous and one by one toward the optimizing cognitive ability and adaptive
behavior of ADHD students, and to find out the contribution of counselling model (cognitive - behavioral)
in optimizing cognitive ability and adaptive behavior of ADHD students. This research uses quantitative and
qualitative methods altogether. This research is conducted in order to analyze the tendentious of learning
difficulties of ADHD students, its causes and teachers’ effort in guiding ADHD students’ learning
difficulties using participative-collaborative in examining the worthiness of hypothetic counselling model
(cognitive - behavioral) to attack learning difficulties of ADHD students. The result of this research showed
that counselling model (cognitive-behavioral) in effect to optimizing cognitive ability and adaptive behavior
of ADHD students and to decrease its causes such as; less of concentration, hyperactive behavior, and
impulsive ADHD students both of SD (Elementary) and SMP (Secondary) level on high or lower lever
showed the effective result. Cognitive-behavioral model effectively decrease almost all of indicator
problems of optimizing cognitive ability and adaptive behavior of ADHD students.
1 INTRODUCTION
Cognitive development is related with adaptive
behavior on ADHD students. Therefore, researchers
are interested to analyze further more about
cognitive ability and adaptive behavior on ADHD
students at the age of 6 to 15 years old. Empirical
data related with cognitive issue and adaptive
behavior of ADHD students (Barkley, 2007) and all
of its implications indicate the need of counselling
cognitive - behavioral sequences in this research
are as follows: (1) identify ADHD students and
their problems; (2) explore various areas related
with lack of concentration, hyperactivity, and
impulsivity; (3) intervention through (cognitive -
behavioral) counselling to change non – adaptive
learning behaviour that cause social interaction
difficulties and decreasing studying performance, by
applying instruction, prompt, reward, generalisation,
and cognitive technique to monitor the achievement
of counselling process; (4) support the student self-
confident to be able to endure and develop adaptive
behavior in accordance with his/her peer and to
increase learning performances and maintain the
conducive condition after counselling; and (5)
testing the counselling effectiveness process and
result.
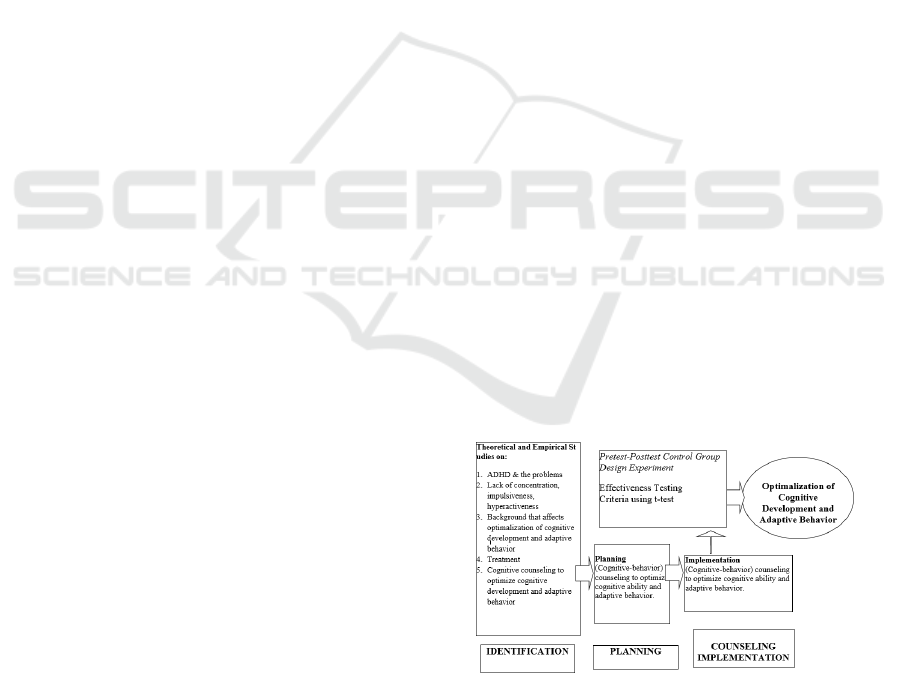
To be clearer, the (cognitive - behavioral)
counselling procedures in this research can be
illustrated as Figure 1:
Figure 1: Cognitive-behavioral counselling
procedure.
It is a challenge for researchers to identify
empirically whether the implementation of
(Cognitive - Behavioral) Counselling Model is
relevant to the ADHD child, as contained in
Hidayat, H.
Cognitive-Behavioral Counseling Model to Optimize Cognitive Potentiality and Adaptive Behavior of Attention Deficite Hyperactivity Disorders (ADHD) Students.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences (ICES 2017) - Volume 2, pages 405-409
ISBN: 978-989-758-314-8
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
405

Individual intervention qualities to stimulate
cognitive ability optimization and adaptive behavior
(Willson and Branch, 2006). If the answer is yes, by
modifying both antecedent, hopefully many ADHD
children can increase their learning performances
and independence in society.
The aim of this research is to find out
counselling model (cognitive - behavioral) Bowers
and Hatch (2002) which optimizing cognitive
ability and adaptive behavior of ADHD students, to
find out correlation between cognitive ability and
adaptive behavior of ADHD students, to examine
contribution of counselling model (cognitive -
behavioral), both of simultaneous and one by one
toward the optimizing cognitive ability and
adaptive behavior of ADHD students, and to find
out the contribution of counselling model
(cognitive - behavioral) in optimizing cognitive
ability and adaptive behavior of ADHD students
(Quill, 2000). This research uses quantitative and
qualitative method altogether. This research is
conducted in order to analyze the tendentious
learning difficulties of ADHD students, its causes
and teachers’ effort in guiding ADHD students
‘learning difficulties. Using participative -
collaborative in examining the worthiness of
hypothetic counselling model (cognitive -
behavioral) to attack learning difficulties of ADHD
students (Dobson, 2001).
The result of this research showed that
counselling model (cognitive - behavioral) in effect
to optimizing cognitive ability and adaptive
behavior of ADHD students and to decrease its
causes such as; less of concentration, hyperactive
behavior, and impulsive ADHD students both of
Elementary and Secondary level on high or lower
lever showed the effective result (Muro and Kottman,
2005). Cognitive - behavioral model effectively
decrease almost all of indicator problems of
optimizing cognitive ability and adaptive behavior
of ADHD students.
2 RESEARCH HYPOTHESES
Hypotheses is a theory or temporary solution on the
problems examined, and the validity should be
tested. In this research, the researcher concludes the
main hypotheses as follows: “Cognitive - Behavioral
Counselling Model gives contribution to
optimization of cognitive development and adaptive
behavior of ADHD student”.
3 RESEARCH METHODS
Final objective of this research is to obtain
(cognitive-behavioral) counselling model to
handle learning problem of ADHD students caused
by concentration and attention deficit, and impulsive
behavior. The framework and model component are
composed based on study on concept and theory of
ADHD children, their cognitive development and
adaptive behavior, study on (cognitive - behavioral)
counselling concept, relevant previous research,
problem analysis of ADHD children and their
learning process, and empirical study on actual
condition of counselling related with handling of
ADHD students’ learning problem (Borg and Gall,
2003).
In this research, both qualitative and quantitative
approach is used. According
to Creswell (2002), there are three qualitative –
quantitative models, which are: two-phase design,
dominant- less dominant design, and mixed method
design sequence. This research uses mixed method
design. Sequence approach, since the integrated
qualitative and quantitative approach is used and
both are support each other. Quantitative approach is
used to examine cognitive ability optimization,
adaptive behavior, and (cognitive - behavioral)
counselling model effectiveness to handle ADHD
students’ learning problems caused by concentration
and attention deficit, and impulsive behavior. While
the qualitative approach is used to find out the
rational validity of (cognitive - behavioral)
counselling hypothetic model in handling
concentration and attention deficit, and impulsive
behavior (Tilley, 1999).
The relation and influence among variables as
describe in those framework, Harun Al Rasyid
(1998) can be visualize in paradigm scheme as
follows:
ICES 2017 - 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences
406

Figure 2: Research paradigm scheme.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The result of this research is obtained through
preliminary study to gain empirical data of: (1) data
profile of implementation of cognitive counselling,
behavioral counselling, and (cognitive-behavioral)
counselling to optimize cognitive ability and
adaptive behavior of ADHD students; (2) profile of
optimization problem of cognitive ability and
adaptive behavior of ADHD students; (3) profile
of cause factor of optimization difficulties of
cognitive ability and adaptive behavior of ADHD
students; and (4) profile of teacher’s efforts in
implementing (cognitive - behavioral) counselling
model to optimize cognitive ability and adaptive
behavior of ADHD students (Lightsey and Hulsey,
2002).
The description of research results are as follows:
a) Data profile of implementation of cognitive
counselling, behavioral counselling, and
(cognitive-behavioral) counselling to optimize
cognitive ability and adaptive behavior of ADHD
students
Based on data analysis of this research, from 13
students as research subject, the score of cognitive-
ability and adaptive behavior of ADHD
students who receive cognitive counselling, increase
by 54.83 % in average. While the score of
cognitive ability and adaptive behavior of ADHD
students who receive behavioral counselling,
increase by 52.47% in average. Hence, we can
conclude that cognitive ability and adaptive
behavior of ADHD students who receive (cognitive
- behavioral) counselling, increase significantly.
b) Profile of optimization problem of cognitive
ability and adaptive behavior of ADHD students
Research shows that at elementary and junior high
school levels, there are 72.63% ADHD students with
problems on cognitive ability and adaptive behavior
optimization is on high category and the rest or
27.37% is on low category.
c) Profile of cause factor of optimization
difficulties of cognitive ability and adaptive
behavior of ADHD students.
Profile of cause factor of ADHD students’ learning
problem at elementary and junior high school level
are as follows: (1) minimum concentration and
attention; (2) hyperactive behavior; and (3)
impulsive behavior. The research shows that
learning problems in ADHD students due cause
factor of minimum concentration and attention is
54.42% at high category and 45.58% at low
category. The learning problems in ADHD students
due to cause factor of hyperactive behavior is
59.18% at high category and 40.82 at low category.
d) Profile of teacher’s efforts in implementing
(cognitive-behavioral) counselling model to
optimize cognitive ability and adaptive behavior
of ADHD students
The research shows that teacher’s effort in
implementing (cognitive - behavioral) counselling
model shows percentage of success of 55.32% at
high category and 44.68% at low category. The
implementation of cognitive counselling model to
optimize cognitive ability and adaptive behavior
shows percentage of success of 55.32% at high
category and 44.68% at low category. While
teacher’s effort to implement instructional
behavioral counselling model shows percentage of
success of 59.57% at high category and 40.43% at
low level. Teacher’s effort to implement prompting
behavioral counselling shows percentage of success
of 51.06 at high category and 48.94% at low
category.
5 DISCUSSION
Based on the statistical calculation U Mann-Whitney
test on first hypothesis with real degree (significant
level) 0.005 prove that H0 is rejected and H1 is
accepted (Furqon, 2002). This means that ADHD
students who receive cognitive counselling reach a
higher cognitive ability score compare with ADHD
students who receive behavioral counselling. Base
Cognitive-Behavioral Counseling Model to Optimize Cognitive Potentiality and Adaptive Behavior of Attention Deficite Hyperactivity
Disorders (ADHD) Students
407

assumption is that the relation between visual (see
objects, words), motor (holding, writing, and
tracing), and auditory (mentioning objects,
letters/words simultaneously as the student write of
tracing a word) as the implementation of cognitive
counselling, is a suitable counselling process to help
ADHD students who usually has cognitive ability
disorder, such as: understanding concept of objects,
reading difficulties, which is difficulties in
understanding the relation between letters and
sound, and sound similarities (McNamara and
Horan, 2006).
Furthermore, the study on second hypothesis
shows that H0 is accepted and H1 is rejected at real
degree (significant level) 0.05, or it is shown that
there are no significant differences between the
cognitive ability’s score of ADHD student who
receive cognitive-behavioral counselling and ADHD
students who receive cognitive counselling. Base
assumption of this is the cognitive ability disorder of
ADHD students in understanding relation between
speaking, sound, and symbol. This can be handled
through visual learner or visual thinking and tactile
procedure, as the implementation of cognitive-
behavioral counselling. The cognitive weakness of
ADHD students shows that their way of thinking is
nonverbal. Cognitive skill of ADHD students can be
achieved without spoken language or other process.
According to Gardner (1983), linguistics intelligence
are numbers of intelligence consist of different
neurophysiology and are not related one to another
The third hypothesis also shows that H0 is
rejected and H1is accepted at the real degree 0.05 or
in other words the ADHD students who receive
cognitive-behavioral counselling reach higher
cognitive ability score compare with students who
receive behavioral counselling. If the fourth
hypothesis is analysed, it proves that H0 is rejected
and H1 is accepted at real degree 0.05. It can be said
that ADHD students who receive behavioral
counselling, reach higher adaptive behavior compare
with ADHD students who receive cognitive
counselling. With assumption that ADHD students
can remember adaptive behavior examples easily
through structured visual stimulation in stages, while
the implementation of cognitive counselling process
is focused more on increasing memory aspect and
object understanding concept (cognitive process)
through multisensory technique.
Based on the fifth hypothesis, it is shown that H0
is rejected and H1 is accepted at real degree 0.05. It
can be said that ADHD students who receive
Behavioral counselling reach higher adaptive
behaviour ability score compare with students who
receive cognitive - behavioural counselling (Watson
et al., 2003). Behavioral counselling is one of the
relevant counselling method that is used to stimulate
the adaptive behavior ability of ADHD children in
stages. The sixth hypothesis shows that H0 is
accepted and H1 is rejected at real degree 0.05, or it
can be said that there is no significant difference
between the score of adaptive behavior ability of
ADHD student who receive cognitive - behavioral
counselling compare to ADHD students who receive
cognitive counselling. Furthermore, if the ADHD
students who receive cognitive counselling is
compared with ADHD students who receive
behavioral-cognitive counselling, it shows no
significant increase on their adaptive behavior
ability.
6 CONCLUSION
The conclusion of the study of (cognitive-
behavioral) counselling model development to
optimize the cognitive ability and adaptive behavior
of ADHD students are as follows:
a) ADHD students who receive cognitive
counselling reach higher cognitive ability score
compare with ADHD students who receive
behavioral counselling. Hence the conclusion
is cognitive counselling is more effective than
behavioral counselling in optimize cognitive
ability of ADHD students
b) There are no significant differences between
cognitive ability’s score of ADHD students
who receive behavioral-cognitive counselling
and ADHD students who receive cognitive
counselling. Hence the conclusions behavioral
–cognitive counselling has the same effect with
cognitive counselling in enhancing cognitive
ability of ADHD students,
c) There is no significant difference between
cognitive ability’s score of ADHD students
who receive (cognitive-behavioral) counselling
and ADHD students who receive cognitive
counselling. Hence the conclusion is
(cognitive-behavioral) counselling has the
same effect with cognitive counselling in
enhancing cognitive ability of ADHD students.
d) ADHD students who receive (cognitive-
behavioral) counselling reach higher cognitive
ability’s score compare with ADHD students
who receive behavioral counselling. The
conclusion is (cognitive - behavioral)
counselling is more effective with behavioral
counselling in enhancing cognitive ability of
ADHD students.
e) ADHD students who receive behavioral
counselling reach adaptive behavior ability’s
score compare with ADHD students who
ICES 2017 - 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences
408

receive cognitive counselling. Hence the
conclusion is: behavioral counselling is more
effective than cognitive counselling in
enhancing adaptive behavior ability of ADHD
students.
f) ADHD students who receive behavioral
counselling reach higher adaptive behavior
ability’s score compare with ADHD students
who receive (cognitive - behavioral)
counselling. So, the conclusion is: behavioral
counselling is more effective than (behavioral-
cognitive) counselling in enhancing adaptive
behavior of ADHD students.
g) There is no significant difference between
adaptive behavior ability’s score of ADHD
students who receive (cognitive-behavioral)
counselling with ADHD students who receive
cognitive counselling. Hence the conclusion is:
(cognitive-behavioral) counselling has the
same effectiveness with cognitive counselling
in enhancing adaptive behavior ability of
ADHD students.
h) Rational validation of counselling experts to
the hypothetic model of (cognitive -
behavioral) counselling to handle the problems
of optimize cognitive ability and adaptive
behavior of ADHD students shows that the
developing method is suitable as the model of
problem counselling.
i) (Cognitive - behavioral) counselling model to
handle the problem of optimize cognitive
ability and adaptive behavior of ADHD
students show effective result to reduce cause
factor such as: concentration deficit,
hyperactive and impulsive behavior of ADHD
students at elementary and junior high school
level at middle and high category.
j) (Cognitive - behavioral) counselling model is
proven effective to reduce all indicator of
problems in optimize cognitive ability and
adaptive behavior of ADHD students and
reduce significantly after using (cognitive -
behavioral) counselling approach.
REFERENCES
Barkley. R. A., 2007. The Children with attention deficit,
Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 20, 3, 263 –
288.
Borg, W. R., Gall, M. D., 2003). Educational Research: An
Introduction, Longman, Inc. London.
Bowers, L. J., Hatch, P. A., 2002. The National Model
for School Counselling Programs, American School
Counsellor Association. California.
Creswell, W. J., 2002. Research Design: Qualitative &
Quantitative Approaches, SAGE Publications. London.
Dobson, S. K., 2001. Handbook of Cognitive-Behavioral
Therapies, The Guilford Press. London.
Furqon, F., 2002. Statistika Terapan untuk Penelitian,
Alfabeta. Bandung.
Harun Al Rasyid, 1998. Teknik Pernarikan Sampel dan
Penyusunan Skala, Program Pascasarjana Universitas
Padjadjaran. Bandung.
Harun Al Rasyid (1998). Analisis Jalur (Path Analysis).
Bandung: LP
3
E, Fakultas Ekonomi Universitas
Padjadjaran.
Lightsey, R. O., Hulsey, C. D., 2002. Impulsivity, Coping,
Stress, Burnout and Problem Gambling Among
University Students, Journal of Counselling Psychology.
Vol 49. No.2. 202-211.
McNamara, K., Horan, J. J., 2006. Experimental construct
validity in the evaluation of cognitive and behavior
treatments for depression, Journal of Counseling
Psychology, 33,23-30.
Muro, J. J., Kottman, T., 2005. Guidance and Counselling in
Elementary School and Middle School, Brown and
Benchmark Publisher. Iowa.
Quill, K. A., 2000. Teaching Students with Attention
Deficit and Hyperactivity: Strategy to Enhance
Communication and Socialization, Delmar Publishers
Inc. New York.
Tilley, A., 1999. Psychological Research and Statistics,
Pineapple Press. Queensland
Watson, J. C., Gordon, L. B., Stermac., L., 2003.
Comparing the effectiveness of process-experiential
with cognitive-behavioral psychotherapy in the
treatment of depression, Journal of Consulting and
Clinical Psychology. 71, 773-781.
Willson, R., Branch, R., 2006. Cognitive Behavioural
Therapy (CBT) for Dummies, John Willey & Sons,
Ltd. USA.
Cognitive-Behavioral Counseling Model to Optimize Cognitive Potentiality and Adaptive Behavior of Attention Deficite Hyperactivity
Disorders (ADHD) Students
409
