
Application of Water-Playing Methods to Increase Confidence in
Mentally Retarded Children at Special Education Laboratory
Nofi Marlina Siregar and Dinti Oktaviani Haerudin
Faculty of Sport and Recreation, State University of Jakarta. Pemuda, DKI Jakarta, Indonesia
nofisiregar_fik96@yahoo.com
Keywords: Material Requirement Planning (MRP), Lot for Lot (LFL), Economic Order Quantity (EOQ), Periodic
Order Quantity (POQ).
Abstract: Action research aims to increase confidence for mentally retarded children in Special Education Laboratory
Daksinapati Building State University of Jakarta. The method used in this research is action research. in this
subjects activity is a mentally retarded children, amounting to 5 people. The study lasted for two weeks,
consisting of one cycle consisting of six meetings. This research is done until the first cycle, because there
has been an increase of confidence in the children, from 5 children all entered the criteria good including 3
children including good criteria and 2 children including criteria very good From this research can be
concluded that through the method of playing water can improve confidence of children tunagrahita in
Special Education Laboratory Building Daksinapati State University of Jakarta.
1 INTRODUCTION
Playing is an important and major media to develop
various physiological and psychological aspects in
the process of child development. According to
Fathuk Chapter Abdul Halim Sayyid in Nofi Marlina
Siregar (2013), playing is means to learn to develop
intellect and physical simultaneously.
Playing to benefit children, as Anggani Sudono
said in Nofi Marlina Siregar (2013), play is an
activity performed with or without using tools that
produce understanding or provide information, give
pleasure and develop imagination.
When playing a specific behavior change occurs
from the perpetrators, through play also happens the
process of transformation of social values and
education (Jeffrey, 2012). Psychiatry Stuart Brown
writes play as "the foundation of all art, books,
sports, movies, fashion, fun and wonders /" play is
the basics of all art, games, books, sports, movies,
fashion, fun, and wonder short, the basis of what we
think of as civilization.
When children get a chance to do activities that
involve a lot of body movement, will make the
child's body to be healthy. The muscles of the body
will grow and become strong. In addition the limbs
get a chance to be moved. The child can also
channel the excess energy so that he does not feel
uneasy (Djumidar, 2012).
According to Martin and Bateson in the
developmental psychology book "spatial
relationships can also categorize behaviors as play
behaviors, therefore playground behaviors are
generally considered play behaviors, because the
location of such behavior is specific."
1.1 Confidence
Confidence is the ability of the mind to understand
both positive and negative feelings. Self-confidence
is one aspect of personality that is the basic capital
and is formed through the process of exercise and
interaction with the social environment.
According to (Eichstaedt, 1992) self-confidence
is a mental condition or psychological self that gives
a person a strong belief in himself to do or do
something action. An insecure person has a negative
self-concept, lacks confidence in his ability, because
it often shuts down.
Confidence will create a sense of security, and
this will look at the attitude and behavior of
someone who looks calm, not easy to doubt or
hesitate, not easily nervous, assertive, and so forth
(Komarudin, 2015).
Siregar, N. and Haerudin, D.
Application of Water-Playing Methods to Increase Confidence in Mentally Retarded Children at Special Education Laboratory.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education (ICSSHPE 2017) - Volume 1, pages 219-222
ISBN: 978-989-758-317-9
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
219

Negative impact due to lack or absence of self-
confidence that is in itself that will be obtained if not
as soon as possible to overcome and find a solution.
In addition to self-confidence can be raised by
means of exercise and others, there is an alternative
form of therapy that can help overcome the problem
of lack of self-confidence in yourself (Upton, 2012).
From the above opinion it can be concluded that
self-confidence is the ability of the intellect to
understand the positive and negative feelings that
will generate a sense of security, and this will look at
the attitude and behavior of someone who looks
calm, not easy to doubt or hesitate, not easily
nervous, assertive.
1.2 Mentally Retarded Children
There are some general terms used to refer to a child
with intellectual impairment, such as:
underdeveloped child, mental handicap, mental
retardation, intellectual disability and tunagrahita.
Often people describe that a child with intellectual
impairment is difficult to adapt in the academic and
environmental sciences (Mukhtar, 2009). In 1992,
the American Association on Mental Retardation
defines disorder as follows: "Mental retardation is a
characteristic of disability that causes significant
obstacles in intellectual function and adaptive skill" /
"mental retardation is a disability characterized by
significant limitations of both in intellectual
functioning and in adaptive skills"
The above definition emphasizes that disorder is
a challenge in a person's development period to
adapt and integrate with his environment in
developing skills. Meanwhile, according to Bandi
Delphie (2006), tunagrahita child is a child with
difficulty in developing ability, having problem of
learning caused by obstacles of intellectual, mental,
emotional, social, and physical development.
A person is categorized as subnormal mental
disorder or tunagrahita, if he has a low level of
intelligence (below normal), so to pursue the task of
development requires specific assistance or services,
including in education programs (Irham, 2005).
The retardation of the child's tunagrahita is
usually associated with a person's intelligence level.
The level of intelligence in general is usually
measured through intelligence tests whose results
are called IQ (intelligence quotient):
1. Mild mental retardation has IQ score: 52-67
2. Moderate mental retardation has IQ score:
36-51
3. Severe mental retardation has IQ score: 25-36
4. Profound mental mortality has IQ score: <25
One of the barriers to a child with tunagrahita is
performing adaptive skills. Adaptive skills are
actually needed to build social relationships with the
environment around the child's tunagrahita, such as
communication skills, self-development skills, the
skills to perform home tasks, leisure skills, skills to
maintain personal health and self-directed skills in a
particular activity.
According to Mohammad Efendi (2009) child
tunagrahita can be classified as follows:
1. metally retarded children are able to learn
(debil) is a child of metally retarded who is
unable to follow in ordinary school program,
but still have ability that can be developed
through education although result not maximal.
2. metally retarded children able to train (imbecil)
is a child with a low intelligence metally
retarded so it is not possible to follow a
program that is intended for children metally
retarded able to learn.
3. metally retarded child is able to care (idiot) is a
child of metally retarded who have very low
intelligence so that he can not take care of
themselves or socialization.
2 METHODS
This study aims to improve the confidence of
children tunagrahita in Special Education
Laboratory Building Daksinapati State University of
Jakarta through the method of playing water.
This research uses Action Research research
method or action research method. This research
method developed together between researchers and
colabolators to determine the policy in every
improvement of learning aspects. This research uses
Action Research research method or action research
method. This research method developed together
between researchers and colabolators to determine
the policy in every improvement of learning aspects.
Treatment in action research is by using action
program, where the work plan program implemented
in the form of action implementation framework to
fit the research conditions (Zainal, 2009& Muchlis,
2009).
The design of this research uses an action
research model with a chart depicting four steps and
repetition starting from planning, acting, observing,
reflecting, and continuing with re-planning as the
basis for problem-solving strategies or research
action steps.
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
220

3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Initial Description
The initial test aims to find out early how the level
of confidence in the child's tunagrahita. This is an
absolute requirement that researchers and
collaborators must fathom in determining agreement
on the basic determination of the confidence level of
children treated with swimming methods.
Figure 1: First Test.
Table 1. Preliminary Test for Confidence of Mentally Retarded Childern.
Info:
oValues greater than 70 are include on either criterion
oValues greater than 60 are include in sufficient criterion
oValues greater than 50 are include on less criterion
Based on the result of the initial asismen of the
instrument Self-confidence of the children with the
tunagrahita Special Education Laboratory of
Daksinapati Building, Jakarta State University, 3
children are included in the criteria of less, 1 child is
included in enough criteria, and 1 child goes into
good criteria. More clearly can be seen in the pie
chart.
Figure 2: Cycle Research Results 1.
After going through the stages of planning,
action scenario that has been made by the researcher
is then implemented into the learning process where
the scenario that has been modified into the form of
the game is to apply the method of playing water.
The final attitude creates confidence. Learning every
meeting on Wednesday and Friday at 14.00-14.45.
in cycle I the number of meetings as much as 6 times
the meeting, the description in cycle I is as follows:
No
Naea
Dimention
Average Value
Looks Calm
Not Easy to Worry or Hesitate
Not Easily Nervous
Assertive
1
Enzi
66,7
33,3
66,7
33,3
50
2
Evi
83,3
66,7
100
66,7
79,2
3
Dimas
66,7
33,3
66,7
33,3
50
4
Revan
66,7
44,4
66,7
66,7
61,1
5
Abi
66,7
44,4
66,7
33,3
52,8
Application of Water-Playing Methods to Increase Confidence in Mentally Retarded Children at Special Education Laboratory
221
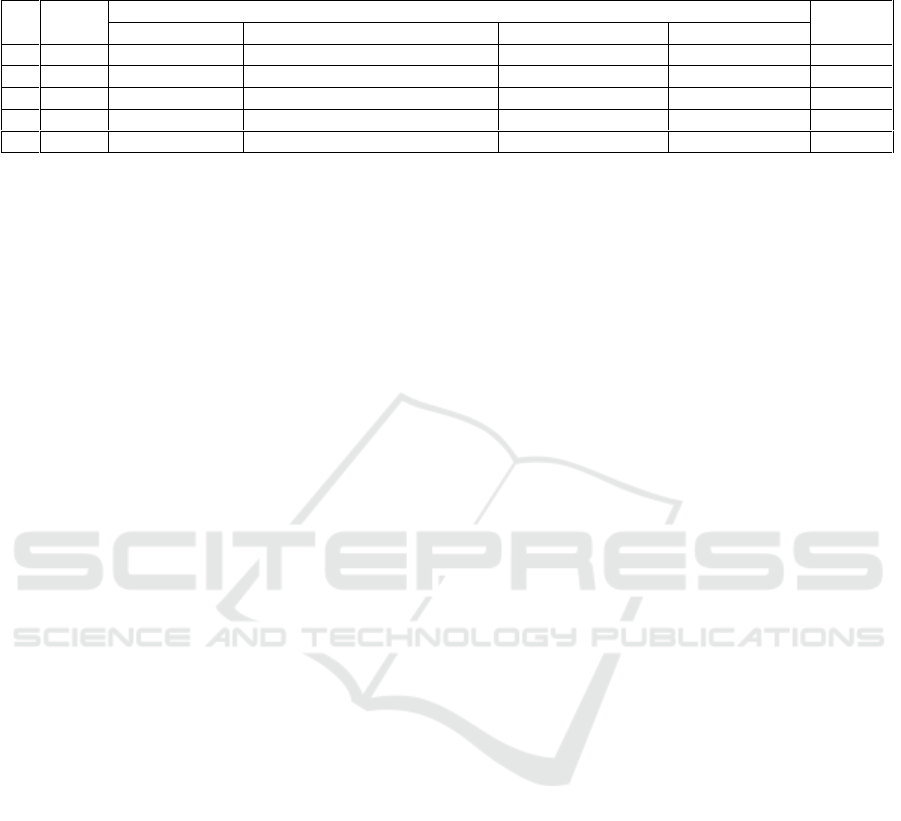
Table 2. Data Result Cycle 1 Level of Self Confidence of Mentally Retarded Children.
Name
Dimention
Average
Looks Calm
Not Easy to WorryOr Hesitate
Not Easily nervous
Asser vative
1
Enzi
83,3
66,7
100,0
50,0
75
2
Evi
100,0
88,9
100
66,7
88,9
3
Dimas
83,3
66,7
100,0
66,7
79
4
Revan
83,3
88,9
100,0
66,7
84,7
5
Abi
83,3
66,7
100,0
66,7
79,2
Info :
oValues greater than 80 are include on great criterion
oValues greater than 70 are include on either criterion
oValues greater than 60 are include in sufficient criterion
oValues greater than 50 are include on less criterion
Based on the result of the initial asismen of the
instrument Self-confidence of the children of
Tunagrahita Special Education Laboratory of
Daksinapati Building, Jakarta State University is
included in the less criteria. More clearly can be
seen in the pie chart.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of the research it can be
concluded that there is increased confidence in
children tunagrahita through the method of playing
water. With the application using the method of
playing water there are 60% of the results of
children into the criteria Good and 40% of children
into the criteria very well. With this method of
playing water can increase confidence in children
tunagrahita in Special Education Laboratory
Building Daksinapati State University of Jakarta.
Based on the findings and conclusions from the
research results can be put forward several
implications as follows:
The application of water play methods using the
game is an alternative in solving some problems
faced by teachers in an effort to activate the child in
learning as well as in the effort to transform the
values contained in physical education of sports and
health, one of which is self-confidence, because the
teacher acts as one delivery agents to improve the
quality of human resources with high intellectual
and leadership.
In every application of the method the teacher
must be able to create a conductive class in order to
interactively engage students with the teacher,
students with students can be realized so that the
classroom atmosphere becomes active and
interesting. In this case the teacher must be able to
be an example and role model of his students, not
only in words but also in daily deeds.
REFERENCES
Delphie B. 2006. Pembelajaran Anak Tunagrahita.
Bandung: PT. Refika Aditama.
Djumidar M., 2012. Psikologi Olahraga. Jakarta: CV.
Gramada Offset.
Eichstaedt B. C., Barry W. L. 1992. Physical Activity for
Individual With Mental Retardation. Canada: Human
Kinetics Books.
Jeffrey G. 2012. Play in Children’s Development, Healt
and Well being. TIE.
Irham H. 2005. Pembelajaran Adaptif Anak Luar Biasa.
Jakarta: Departemen Pendidikan Nasional.
Komarudin. 2015. Psikologi Olahraga. Bandung: PT.
Remaja Rosdakarya.
Muchlis M. 2009. Melaksanakan PTK itu Mudah. Jakarta:
PT. Bumi Aksara.
Efendi M. 2009. Pengantar Psikopedagogik Anak
Berkelainan. Jakarta: PT. Bumi Aksara.
Mukhtar, 2009. Penelitian Tindakan Kelas. Jakarta: Gaung
Persada (GP) Press.
Upton P. 2012. Psikologi Perkembangan. Jakarta:
Erlangga.
Marlina S. N. 2013. Teori Bermain. Jakarta.
Zainal A. 2009. Penelitian Tindakan Kelas. Bandung: CV.
Yrama Widya.
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
222
