
The Role of Rubber Resistant against Swimming Breaststroke 25
Meters
Ani Pristiawati, Sriningsih Sriningsih, and Akhmad Olih Solihin
STKIP Pasundan Cimahi, Indonesia
Anipristia19@yahoo.com
Keywords: Media, Breaststroke, Swimming.
Abstract: In this study, the authors found a deep problem. The problem taken is the role of a media to help the
learning. The tool used by the writer for the research is rubber, its function is to produce the speed of
swimming in chest pool. The problem formulation in this research is, (1) does the rubber give effect to 25
meter breaststroke? (2) is this tool significant to the 25-meter breaststroke? This study authors conducted
research, with the number of samples of 50 people, purposive sampling technique. Based on the results of
processing and data analysis, it can be concluded with a large influence of the use of rubber media to the
speed of force pool 25 heartburn 16 seconds, and the influence without using media to the speed of the force
pool 25 heartburn 17 seconds. The main objective of this study was to obtain facts about: (1) The
effectiveness of exercise with the use of rubber media for swimming speeds for novice students; (2) The
effectiveness of exercises without using rubber media in speed for beginners; (3) The difference between
two exercises is between exercise with rubber medium and without medium in swim rate for novice
students.
1 INTRODUCTION
According to one study, swimming is one of the best
sports because swimming involves all members of
the body or in other words the whole body is
actively moving. But obstacles, this sport needs
special skills so not everyone can do it. In
breaststroke, the swimming technique is particularly
important since the motion is complicated and the
heaving and pitching motions of the body are large
(Nakashima, 2012). But in my opinion, as long as
there is intent, swimming can be learned. Additional
insights suggest aspects of embodied health that are
enhanced by outdoor swimming, especially in
relation to bodies perceived to be inactive due to
age, illness or disability (Balan, 2015). Swimming
for recreational purposes and competition done by
people in the pool. Humans also swim in rivers, in
lakes, and in the sea as a form of recreation.
Swimming facilities the voices and experiences of
regular swimmers should be considered (Ward,
2017). Swimming sports make the body healthy
because almost all the muscles of the body are used
while swimming. Swimming sports make the body
healthy because almost all the muscles of the body
are used while swimming.
Swimming activity four times heavier than rest
time. This is because in the movement in the water
the whole body will move and the body indirectly
overcome the greater water pressure. Like the
muscles, lungs, heart, and all the organs in our body
work more extra. Swimming is a popular
recreational activity, gaining recognition as an
effective option in maintaining and improving
cardiovascular fitness (Lazar, 2013). In addition, the
cold stimuli that we feel from the water have good
effects for our bodies and will cause fresh feelings.
As has been discussed earlier, that since long ago
people have known swimming and use water as one
of the tools of healing therapeutics. It can be said
that swimming can calm people with mental illness
and relax all the stiffness in our body relaxation.
Swimming provides fun, relaxation, challenge,
competition, and the ability to save oneself in an
emergency in the water (Thomas, 2000).
Breaststroke techniques like other pool styles
consist of several movement, namely: start, body
position, arm movement (outside and sweep catch,
sweep in and recovery), limb movements, breathing,
and coordination between arm movements, limb
movements and retrieval movements breat (Thomas,
2000). Swimming can heal people who have asthma,
Pristiawati, A., Sriningsih, S. and Solihin, A.
The Role of Rubber Resistant against Swimming Breaststroke 25 Meters.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education (ICSSHPE 2017) - Volume 1, pages 227-230
ISBN: 978-989-758-317-9
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reser ved
227

because with swimming, respiratory muscles can
become strong. The horizontal attitude of
swimming, and with the pressure in the water that
can reduce the weight of our body so that our body
will feel relaxed and this can be used to reduce
abnormalities or errors in the body. Nowadays
modern therapies for many paralyzed diseases are
trained walking in the water. Swimming is the only
sport to be recommended in more than 80% of the
medical cases and to have a large target audience,
accessible to both children and the elderly from a
psychological perspective, swimming reduces the
mental tensions and anxiety, caused by everyday
stress and the competition one, while avoiding
hostility and frustration in life, in a beneficial way
(Petrescu , 2005; Foley, 2017). Swimming is a sport
done in the water, and has four swimming styles.
These styles are: free style, breaststroke, backstroke
and butterfly style.This author's tool is created to
provide the weight of the workout produced by the
person's own weight. With the help of rubber
resistant movement will be restrained and will feel
heavy. This Rubber Resistant is a tool made of
rubber which has 4 unified rubber ends, where the
upper end is used on both shoulders and the lower
end is used for the feet, which serves to train limb
power. Twenty-four recreational and twenty-four
competitive swimmers swam 25 m at 80% of their
maximal speed (Seifert, 2011). With reference to the
background mentioned above then the formulation
of the problem in this study are as follows:
1. Does the rubber resistant give effect to 25
meter breaststroke?
2. Is the rubber resistant significant against 25
meter breaststroke?
2 METHODS
In this study the authors used the experimental
method, that is by applying two forms of exercise to
train the pace of the first new student following the
breaststroke exercises. Two forms of exercise are
exercises using rubber resistant, and exercises
without rubber resistant. With sample number 50.
The technique used in sampling is purposive
sampling technique. Techniques to determine the
sample of research with some specific
considerations that aims for data obtained later can
be more representative.
Table 1: Static group comparison.
Group
Treatment
Post test
Experiments
X
O
2
Control
-
O
2
3 RESULTS
Table 2: Calculating the standard deviation.
Variabel
X
1
X
2
Pening
katan
S
1
S
2
Exercise
with
Rubber
Resistant
27.54
24.54
4.41
4.54
3.80
Exercise
without
Rubber
Resistant
27.08
24.92
5.09
5.15
4.70
From the table 2 can be put forward, the group of
exercises using the average rubber resistant averaged
the initial test of 27.54, with a final test of 24.54,
there was an increase in exercise outcome with an
average of 4.41. While the exercise group without
using the average rubber-resistant averaged the
initial test of 27.08, with a final test of 24.92, an
increase in training hash with an average of 5.09.
Table 3: Calculating the normality test with liliefors
test of groups A and B.
Group
Lo count
L list (25 :
0.05)
Result
Group A
0.0129
0.173
Normal
Group B
0.0189
0.173
Normal
From the table 3, it can be said that in group A
obtained Lo calculate of 0.0129 compared to List L
(25: 0.05) of 0.173 means Lo calculate is smaller
than L list thus it can be argued that the distribution
of group A data is normal.
Then the distribution of group B data obtained
Lo calculate of 0.0189 compared with L list (25:
0.05) of 0.173, means it can be argued that the
distribution of group B data is normal.
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
228
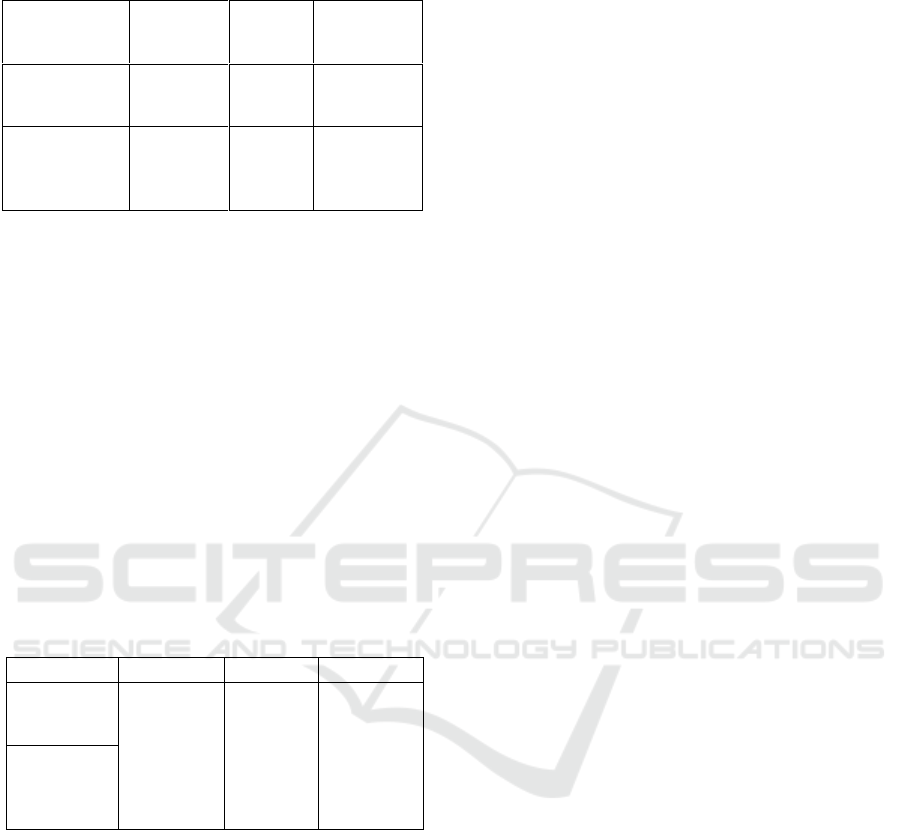
Table 4: Significantly improved test results of exercise
group A and group B.
Group
T count
T table
(0.05
:48)
conclusion
Exercise with
rubber
resistant
44.58
2.02
significance
Exercise
without
rubber
resistant
52.42
2.02
significance
In the above 4, the calculation of the increase of
group A exercise results obtained t value of 44.58
compared with t table 0.975 = 2.02. it turns out t
count> dati t table, it means the exercise with rubber
resistant give a significant effect on the movement
and speed in the swimsuit sports especially for
swimming style of chest at the student of PJKR
force 2009 in STKIP Pasundan Cimahi.
Furthermore, in group B, obtained t value counted
5242 compared with t table 0.975 = 2.02. it turns out
t count> from t table, it means that exercise without
using rubber resistant aids give significant influence
to movement and speed in swimming sport
especially for swimming breaststroke at student of
PJKR force 2009 at STKIP Pasundan Cimahi.
Table 5: Result of significance test calculation difference
of exercise result of group A and group B.
Group
T count
T table
Result
Exercise
with Rubber
Resistant
18.54
2.02
Signifikan
Exercise
without
Rubber
Resistant
In the table 5, the calculation of differences in
the results of the exercises of groups A and group B
obtained t value of 18.54 compared with t table of
0.975 = 2.02. it turns t count> from t table, it means
that exercise without using rubber resistant tool is
more significant improvement compared with
exercise by using rubber resistant to movement and
speed in sport pool especially for swimming
breaststroke.
4 DISCUSSION
Swimming is a sport discipline in which the
movement is realised in the water with the help of
the arms and legs (Balan, 2015). From result of data
processing effect of rubber resistant with technique
of swimming at breaststroke is known significant
result. In this case the presence of media or rubber
resistant gives positive support to swimming
technique on breaststroke. So can be interpreted that
the learners who have less good ability, the easier it
is to pool style that technically has a complex level
of coordination. Media or rubber resistant is very
supportive. Learning media in general is a tool of
teaching and learning process. Everything that can
be used to stimulate mind, taste, attention and skill.
These limits are broad enough and deep
understanding of understanding, environment,
human and methods are utilized for learning /
training purposes. With rubber resistant or media
term used also in the field of teaching or education.
to channel the message, can stimulate the mind,
feelings, and willingness of learners so as to
encourage the creation of learning process in the
learners themselves the same thing with the theory.
The characteristics and capabilities of each media
need to be addressed by the teacher so that they can
choose which media suit the conditions and needs
(Daryanto, 2013).
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the discussion that has been put forward on
the comparison of the effect of exercise by using
rubber resistant and exercises without using rubber
resistant to speed swimming breaststroke, the
authors formulated the following conclusions,
Exercise with high-resistance rubber and positive to
increase the swimming ability for beginners.
Exercise without rubber resistant significant to the
increase of swimming styles for beginners. With
reference to the conclusions in this study, the authors
suggest to swimming advisors to apply the use of
rubber resistant in the training process and learning
process. And can innovate and be creative to find
useful learning media for the future
REFERENCES
Nakashima, M., Terauchi, H., Wakayoshi, K. 2012.
Simulation analysis of the influence of breathing on the
The Role of Rubber Resistant against Swimming Breaststroke 25 Meters
229

performance in breaststroke. Procedia Engineering, 34,
736-741.
Ward, M. 2017. Swimming in a contained space:
Understanding the experience of indoor lap swimmers.
Health & place, 46, 315-321.
Thomas, D. G. 2000. Renang Tingkat Mahir. Jakarta. PT.
Raja Grafindo Persada. pp 1.
Thomas, D. G. 2000. Renang Tingkat Mahir. Jakarta. PT.
Raja Grafindo Persada. pp 11.
Petrescu, S., Piţigoi, G., Păunescu, M. 2014. The Effects
of Practicing Swimming on the Psychological Tone in
Adulthood. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences,
159, 74-77.
Seifert, L., Leblanc, H., Hérault, R., Komar, J., Button, C.,
Chollet, D. 2011. Inter-individual variability in the
upper–lower limb breaststroke coordination. Human
movement science, 30(3), 550-565.
Balan, V. 2015. Aspects of the swimming lesson design at
disabled children. Procedia-Social and Behavioral
Sciences, 197, 1679-1683.
Foley, R. 2017. Swimming as an accretive practice in
healthy blue space. Emotion, Space and Society, 22,
43-51.
Lazar, J. M., Khanna, N., Chesler, R., Salciccioli, L. 2013.
Swimming and the heart. International journal of
cardiology, 168(1), 19-26.
Daryanto, 2013. Media Pembelajaran. Yogyakarta.
Gavamedia.. p 25. 2013.
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
230
