
Contribution of Intelligence and Physical Condition on the Punch and
Kick Pencak Silat
Aridhotul Haqiyah and Dani Nur Riyadi
Program Studi PJKR, Fakultas Keguruan dan Ilmu Pendidikan, Universitas Islam 45 Bekasi, Jl. Cut Meutia No. 83,
Margahayu, Kota Bekasi , Indonesia
aridhotulhaqiyah@yahoo.com
Keywords: Intelligence, Eye-Hand-Leg Coordination, Pencak Silat Kick and Punch Coordination.
Abstract: This study aims to determine the effect of intelligence, eye-hand-leg coordination, as well as the balance
towards the coordination of pencak silat kicks and punches on the students as members of the Pencak Silat
Student Club of University of Islam 45 Bekasi. The research method is a survey, and the analysis technique
is path analysis. The sampling technique used is total sampling of 30 people. The instruments used are a test
of pencak silat kick and punch coordination, intelligence test with IST (Intelligenz Structure Test), test of
eye-hand-leg coordination, and test of balance by using modified bass test of dynamic balance. The
conclusions are: (1) Intelligence directly affects the coordination of pencak silat kick and punch, (2) Eye-
hand-leg coordination directly affects the coordination of pencak silat kick and punch, (3) Balance does not
directly affect the coordination of pencak silat kick and punch, (4) Intelligence directly affects the balance,
(5) Eye-hand-leg coordination directly effects the balance, (6) Intelligence directly affects the eye-hand-leg
coordination.
1 INTRODUCTION
Pencak Silat is the original culture of Indonesia and
currently continues to grow up, both in the
regulation and organization. Pencak silat
organization in Indonesia is called as the Ikatan
Pencak Silat Seluruh Indonesia (Indonesian Pencak
Silat Association), which is abbreviated into IPSI. It
was initiated by Mr. Wongsonegoro and inaugurated
on May 18, 1948 in Surakarta with the aim to unite
and foster all pencak silat institutions that exist in
Indonesia.
Efforts to foster and develop pencak silat are
organized through various ways, such as through
formal education from primary school to college. In
the Faculty of Education, University of Islam 45
Bekasi, pencak silat coaching is conducted inside
and outside the lecturing hours. In the curriculum,
pencak silat is determined as one of the compulsory
subjects in the community life (MBB), while the
activities of sport coaching which is done outside the
lecturing hours are well known as student club or
Unit Kegiatan Mahasiswa (UKM). UKM pencak
silat is a place for students to develop their interests,
talents and expertise in pencak silat.
UKM pencak silat is designed with the
orientation of skill mastery and performance
improvement. The exercise program developed in
the UKM pencak silat consists of the improvement
of physical condition and technique at the match
category, the category of single, double and team.
One of the skills that are trained to the students as
members of UKM pencak silat of University of
Islam 45 Bekasi is attacking skill using hand (punch)
and leg (kick).
In the effort to obtain the excellent score at the
pencak silat match, it needs to be trained attack
motor coordination alternately. It is intended that the
attacks carried out will effectively on time and
obtain high score (Mulyana, 2013). In a pencak silat
match, an assessment of the attack with legs that go
on target, without being obstructed by blocks,
avoidance or evasion, then the opponent scored two,
while the attack with a hand that goes on the target,
without being obstructed by blocks, avoidance or
evasion, then the opponent scored one.
The problem that emerge in training pencak silat
kick and punch coordination is the lack of factors
that are known to be able to support and should be
improved to support these skills, such as: hand-eye-
leg coordination as well as balance (These two
fitness components are presumed to be very
influential in improving the coordination of attack
(Schmidt, 2000 & Nuraini, 2014). In addition to a
fitness component, intelligence factor is presumed to
Haqiyah, A. and Riyadi, D.
Contribution of Intelligence and Physical Condition on the Punch and Kick Pencak Silat.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education (ICSSHPE 2017) - Volume 1, pages 243-246
ISBN: 978-989-758-317-9
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
243
also affect motor coordination and ability to recall
(memory) (Edwards, 2011).
Based research Van Fels, et al about the
relationship between motor skill and cognitive skills
in 4 – 16 years old typically developing children: a
systematic review, the result is there was either no
correlation in the literature, or insufficient evidence
for or against many correlation between motor skills
and cognitive skills. However, weak to strong
evidence was found for same correlation between
underlying categories of motor and cognitive skills,
including complex motor skills and higer order
cognitive skills. Furthermore, a stronger relationship
between underlying categories of motor and
cognitive skills was found in pre-pubertal children
compart to pubertal children (older than 13 years).
The difference result of previously-related
research and this study is sample of research in
intelligence and coordination variable on the pencak
silat kick and punch coordination with sample as
members of the Pencak Silat Student Club of
University of Islam 45 Bekasi (19 – 23 years old).
Based on the above explanation and previously-
related research result, this study aims to determine
the effect of intelligence, eye-hand-leg coordination
and balance towards pencak silat kick and punch
coordination.
2 METHODS
The method used in this study was survey method
with measurement techniques and tests. The analysis
technique used was path analysis. The study was
conducted at the University of Islam 45 Bekasi, Jl.
Cut Meutia No. 83 Bekasi. The population in this
study was the pencak silat club athletes of
University of Islam 45 Bekasi with the total of 30
students. The sampling technique used was total
sampling, in which the entire population becomes
the sample of the study. Therefore, there were 30
people as samples in this study.
The instruments used were a test of pencak silat
kick and punch coordination (Lubis, 2014),
intelligence test with IST (Intelligenz Structure
Test), test of eye-hand-leg coordination (Abidin,
2015) and a balance test by using modified bass test
of dynamic balance (Widiastuti, 2015).
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Descriptive statistics calculation results can be seen
in the table below:
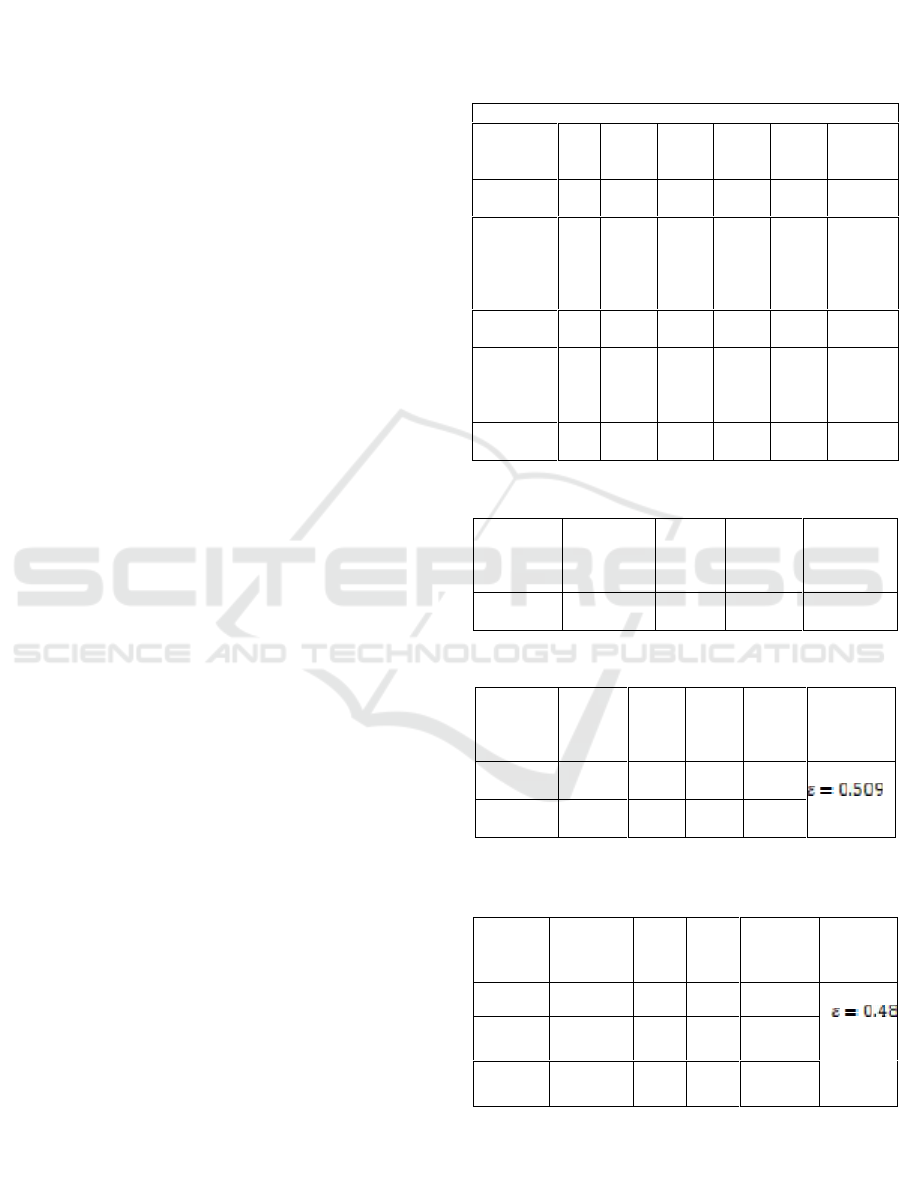
Table 1: Descriptive Statistics Calculation Result.
Descriptive Statistics
Variables
N
Min
Max
Mea
n
Std.
Devi
ation
Varian
ce
Intelligen
ce
30
80
113
92.5
7
8.07
6
65.220
Eye-
Hand-
Leg
Coordina
tion
30
14
36
25.0
0
5.38
2
28.966
Balance
30
25
50
40.3
3
7.87
1
61.954
Pencak
Silat
Kick and
Punch
30
23
55
40.5
0
9.10
8
82.948
Valid N
(listwise)
30
Table 2: Result Summary of Structural Test 1.
Direct
Effect
inter
Variables
Path
Coefficient
t-cal
p-value
Conclusion
X
1
on X
2
(ρ
21
)
0.780
6.593
0.000
Significant
Table 3: Result Summary of Structural Test 2.
Direct
Effect
inter
Variables
Path
Coeffic
ient
t-cal
p-
value
Concl
usion
Remarks
X
1
on X
3
(ρ
31
)
0.464
2.960
0.006
Signif
icant
X
2
on X
3
(ρ
32
)
0.448
2.861
0.008
Signif
icant
Table 4: Result Summary of Structural Test 3 before
Trimming.
Direct
Effect
inter
Variables
Path
Coefficient
t-cal
p-
value
Conclusio
n
Remarks
X
1
on Y
(ρ
y1
)
0.331
1.892
0.070
Significan
t
X
2
on Y
(ρ
y2
)
0.494
2.845
0.009
Significan
t
X
3
on Y
(ρ
y3
)
0.107
0.574
0.571
Insignific
ant
Based on the analysis presented in the table 1,
table 2, table 3, table 4, there is a path coefficient is
not significant, that is the path coefficient X3 on Y
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
244

(ρy3) = 0.107 so that the model needs to be fixed by
removing X3 from the model which is commonly
called as trimming.
Trimming model is a model that is used to fix a
path analysis structure by removing the exogenous
variables of the model which the path coefficient is
insignificant. The result of trimming makes the
result of the third structural change.
For the final result of the structural 3 calculation
after trimming can be seen in Table 5 below:
Table 5: Result Summary of Structural Test 3 after
Trimming.
Direct
Effect
Inter
Variabl
es
Path
Coefficient
t-cal
p-
valu
e
Conclusi
on
Rema
rks
X
1
on Y
(ρ
y1
)
0.381
2.53
6
0.01
7
Significa
nt
X
2
on Y
(ρ
y2
)
0.542
3.60
8
0.00
1
Significa
nt
The next step is testing the model compatibility
with the sample size (n) = 30, and the number of
path coefficient which is not significant (d) = 1, then
the chi-square statistic test with W = - (n-d) ln Q = -
(30-1) in (1.000313) = 0.009, from chi square table
with df = d = 1, at a significance level of α = 0.05
obtained tab = (0,05;1) = 3,84.
Because W = 0.009 < 3.84, then H0 is accepted.
Thus, the model obtained is appropriate or suitable
(model fit) with the data.
Based on the results of data processing research,
can be described model of constellation path
analysis (the causal model between variables X1,
X2, and X3 to Y). As for the image of the
constellation path analysis model can be seen in the
picture below:
Figures 1: Causal Models of Variable X1, X2, X3 to Y.
Based on the above explanation and previously-
related research result, Irene M.J. Van Fels, Sanne
C.M te Wierike, et al about the relationship between
motor skill and cognitive skills in 4 – 16 years old
typically developing children. The result of this
review are interesting in the contex of training
programs focusing of optimizing motor and/or
cognitive skills in children, as it would support the
concept that intervention in one domain (motor or
cognitive skill). Complex motor skills, coordination
of movement in rhytm, and sequenced movements
should be included in motor intervention programs
to improve higer order cognitive skills or vice versa
(Magill, 2011).
The results of data processing and analysis in my
research, the conclusions of this study are as
follows: (1) Intelligence directly affects the
coordination of pencak silat kick and punch, (2)
Eye-hand-leg coordination directly affects the
coordination of pencak silat kick and punch, (3)
Balance does not directly affect the coordination of
pencak silat kick and punch, (4) Intelligence directly
affects the balance (Haqiyah, 2016), (5) Eye-hand-
leg coordination directly effects the balance, (6)
Intelligence directly affects the eye-hand-leg
coordination.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of data processing and analysis,
the conclusions of this study about pencak silat kick
and punch coordination, intelligence and eye-hand-
leg coordination directly affects the coordination of
pencak silat kick and punch, while balance does not
directly effect the coordination of pencak silat kick
and punch. Intelligence and eye-hand-leg
coordination directly effects on intervening variables
(balance) and intelligence directly affects the eye-
hand-leg coordination.
Some suggestions to be given with respect to the
results of this study are for lecturers, coaches,
trainers, and physical education teachers, the results
of this study can be used as a reference and
information in the search for talented pencak silat
athletes on the match category based on the level of
intelligence and good physical condition.
REFERENCES
Bompa, T. O., Buzzichelli, C. 1999. Periodization-: theory
and methodology of training. Human kinetics.
Abidin, D. 2015. Keterampilan Smes Bola Voli (Studi
Eksperimen Efektivitas Metode Latihan Beban Dengan
Pemulihan Aktif Dan Pasif Dan Koordinasi Mata-
Tangan dan Kaki Terhadap Keterampilan Smes Bola
Voli Pada Mahasiswa Penjaskesrek UNISMA
BEKASI), Disertasi PPS UNJ.
Edwards, H. W. 2011. Motor Learning and Control: Form
Theory to Practice. USA: Wadsworth.
Contribution of Intelligence and Physical Condition on the Punch and Kick Pencak Silat
245

Haqiyah, A. 2016. Pengaruh Inteligensi, Kekuatan Otot
Tungkai dan Keseimbangan Terhadap Hasil Belajar
Jurus Tunggal Tangan Kosong Pencak Silat. (Tesis).
Universitas Negeri Jakarta, Jakarta.
Lubis, J., Wardoyo, H. 2014. Pencak Silat Edisi Kedua.
Jakarta: Rajawali Sport.
Magill, R. 2011. Motor Learning And Control: Conceps
and Application. New York: Mc-Graw Hill.
Van Fels M.J., Irene, Sanne C.M te Wierike, et al. The
Relationship Between Motor Skill And Cognitive
Skills In 4 – 16 Years Old Typically Developing
Children: A Systematic Review. Elsevier, Journal of
science and medicine in sport 2015; 18: 697 – 703.
Mulyana. 2013. Pendidikan Pencak Silat. Bandung: PT.
Remaja Rosdakarya
Nuraini, S. 2014. Hasil Belajar Jurus Tunggal Pencak
Silat Tangan Kosong, Studi Eksperimen Tentang Gaya
Mengajar, Umpan Balik dan Motor Educability pada
Mahasiswa Fakultas Ilmu Keolahragaan Universitas
Negeri Jakarta. (Disertasi). Universitas Negeri
Jakarta, Jakarta.
Peraturan Pertandingan Pencak Silat (Hasil MUNAS XII
IPSI Tahun 2007).
Schmidt, R. A. 2000. Motor Control And Learning. United
State America: Human Kinetics.
Widiastuti. 2015. Tes dan Pengukuran Olahraga. Jakarta:
Rajawali Pers.
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
246
