
Correlation between Power of Limb Muscle with Smash Skill Kedeng
on Sepaktakraw
Hasan Hasan
1
and Fahrizal Fahrizal
2
1
Universitas Negeri Jakarta, Jakarta, Indonesia
2
Universitas Negeri Makassar, Makassar, Indonesia
harapahposyandu@gmail.com
Keywords: Physical components, Games, Sport.
Abstract: This study aims to determine the correlation between power of limb muscle (X) with smash skill kedeng on
sepaktakraw (Y). The research was conducted in the gymnasium of sepaktakraw State University of Makassar
South Sulawesi in March 2017. The sample of the study is 38 students on student activities sepaktakraw
Faculty of Sport Science, State University of Makassar. This method used in this study is an associative
quantitative descriptive method with correlation analysis models. The collecting data uses test and
measurement techniques as a primary data through some tests, namely smash skill kedeng test and power of
limb muscle test. The results of this study finds that the correlation table generates a probability value of 0.05
is greater than the probability value sig or [0.000 < 0,975], significant meaning and have a positive correlation
to smash kedeng with the level of relations is (r) 0,975 showed a very strong positive correlation and
coefficient of determination (Kd) or Pearson correlation by: Kd = r 2 x 100%, (0.975) 2 x 100% = 0,950,0 x
100 = 95.0, which means smash skill kedeng determined by power of limb muscles and the rest influenced by
another factor of 5,0.
1 INTRODUCTION
Sepaktakraw is one sport that has been played and
recognized by the world community. Especially in
Indonesia, sepaktakraw has been used as a sports
education, recreation and achievement. As a sporting
achievement and therefore, we need to increase the
quality and quantity of coaches, athletes and
organizational management was good early on,
especially the development of students is an asset
most essential and the potential to be developed, so
the achievement sepaktakraw nationally is very well.
Sepaktakraw is a historic sport, culture of the
nation, and the state of nature as well as the results of
the Earth Indonesia (Achmad, 2015). Sepaktakraw or
sepak raga was played in the era of the kingdom of
Sriwijaya, Majapahit and Gowa. In Indonesia there
are many naming of sepaktakraw as in Minangkabau
called football Rago, in Riau with high Rago name.
Bengkulu named smacking, in Nias called fa Rago /
Famai Rago, Southern Sulawesi named marraga or
maddaga while in Makassar "addaga" (Syam). The
basic technique in a game that is servicing
sepaktakraw, soccer precepts and smash. Smash skills
kedeng including mastery skill category in
sepaktakraw with appropriate backs performed as a
player to attack the opponent's area by means back to
the net.
Sepaktakraw sport in Indonesia has existed since
1971 was marked by the establishment of sports
organizations (Engel, 2010). Performing with power
requires a combination of aerobic and anaerobic
fitness that can be accentuated with special methods.
An example is a single speed bike which
encouragesthe muscles contract more forcefully
(Lemond, 2015). High intensity training (HIT),
involves using high training loads throughout the year
and performing all working sets to at least positive
failure (Bompa, 2015)
Poor strength in the lower extremities results in
loss of stability when landing, and high-impact forces
are excessively absorbed by the passive restraints of
the body (James, 2012). Early fatigue also becomes a
problem for athletes without adequate development
of lower-extremity strength. These factors will result
in the deterioration of performance during exercise
and will cause the athlete to approach overuse levels
much more rapidly, thus subjecting the athlete to
possible injury (Donald, 2013)
Structure and composition are separate yet
interrelated aspects of the body that contribute to
what has been defined as physique (Widiastuti, 2015).
Hasan, H. and Fahrizal, F.
Correlation between Power of Limb Muscle with Smash Skill Kedeng on Sepaktakraw.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education (ICSSHPE 2017) - Volume 1, pages 259-262
ISBN: 978-989-758-317-9
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
259
Body composition, the third aspect of physique, refers
to the amounts of the various constituents in the body
(Shephard, 2000). Results of the study states that the
measurement of activity performance for persons
with upper limb amputation is needed. And the
Conclusions is: Analyzes support reliability and
construct validity of the T-MAP, level of evidence: 2c
"outcomes" research. Based on the background
mentioned, as well as the identification of the
problem definition problem in this research is
formulated as follows.
This research aimed to study and respond the
hypothesis of is there a positive correlation between
the power of limb muscle with smash skill kedeng on
sepaktakraw. The benefits of this research can be
reviewed from two aspects are theoretical and
practical.
2 METHODS
2.1 Participants
Faculty of Student Activities office Makassar is one
of the coaching centers and exercise sepaktakraw
which serve as a platform of education and training
talented students as a form of training delivery system
to achieve the desired result (outstanding athlete). It
is as research objects chosen by the researchers
because already fostering achievement for students of
sport science faculty. Sampling using total sampling
that examines the total population were 38 male
students with characteristics of age between 20 -22
years, height between 160-170 and weight between
50-70 kg.
2.2 Procedures
This research used correlation analysis (Carroll,
2005) model that aims to measure the level of direct
and indirect correlation between one variable to
another variable (variable X with variable Y).
Retrieval of data held in the sports hall sepaktakraw
Faculty of Sport Science, State University of
Makassar, South Sulawesi province.
2.3 Instruments
Collecting data in this study using the technique of
test and measurement and documentation primarily
through skills tests smash kedeng and power of limb
muscle. The analysis technique used in this study is
hypothesis filing descriptive statistics inferential.
Before testing the hypothesis test is conducted prior
requirement that descriptive analysis of the data, the
frequency distribution analysis, the data normality
test, tests of significance, the level of correlation
analysis test and hypothesis testing.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Descriptive Data
Descriptive data analysis performed on each of the
variables studied. Descriptive analysis of data can be
seen in the following table.
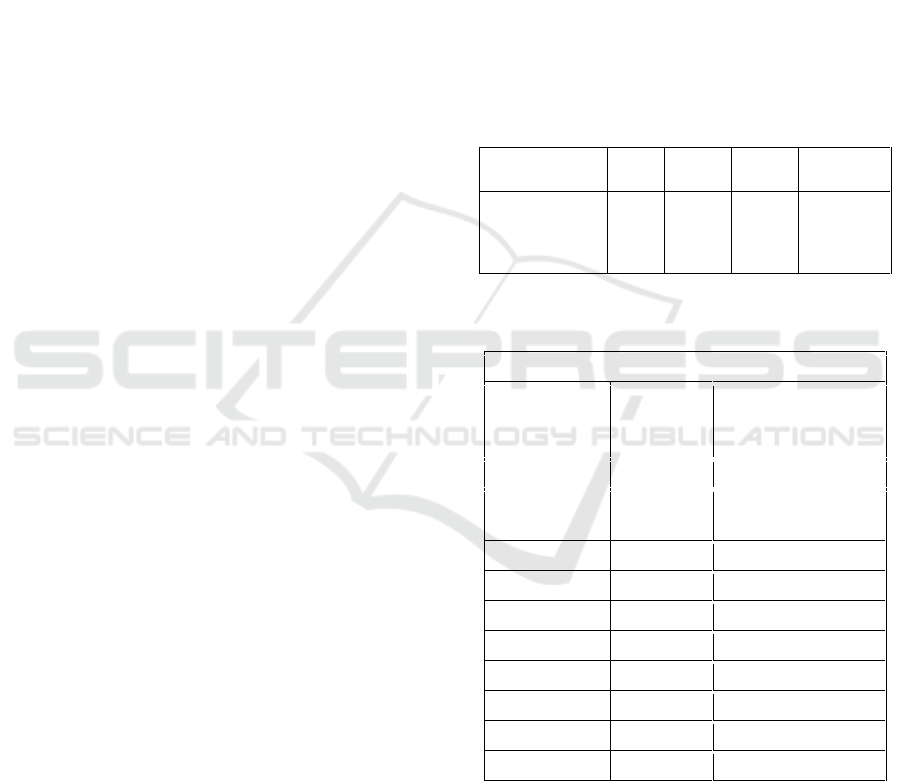
Table 1: T test results power of limb muscle with smash
skill kedeng on Sepaktakraw.
Model
r
T
count
T
table
Result
Smash Skill
Kedeng on
Sepaktakraw
0,55
5,880
2,024
H
1
accepted
Table 2: Descriptive data power of limb muscle and smash
skill kedeng on sepaktakraw.
Statistics
N
Power of
Limb
Muscle
Smash skill Kedeng
on Sepaktakraw
Mean
114.08
18.74
Std. Error of
Mean
.823
.279
Median
113.50
19.00
Mode
115
19
Std. Deviation
5.074
1.719
Variance
25.750
2.956
Range
17
6
Minimum
106
16
Maximum
123
22
Sum
4335
712
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
260
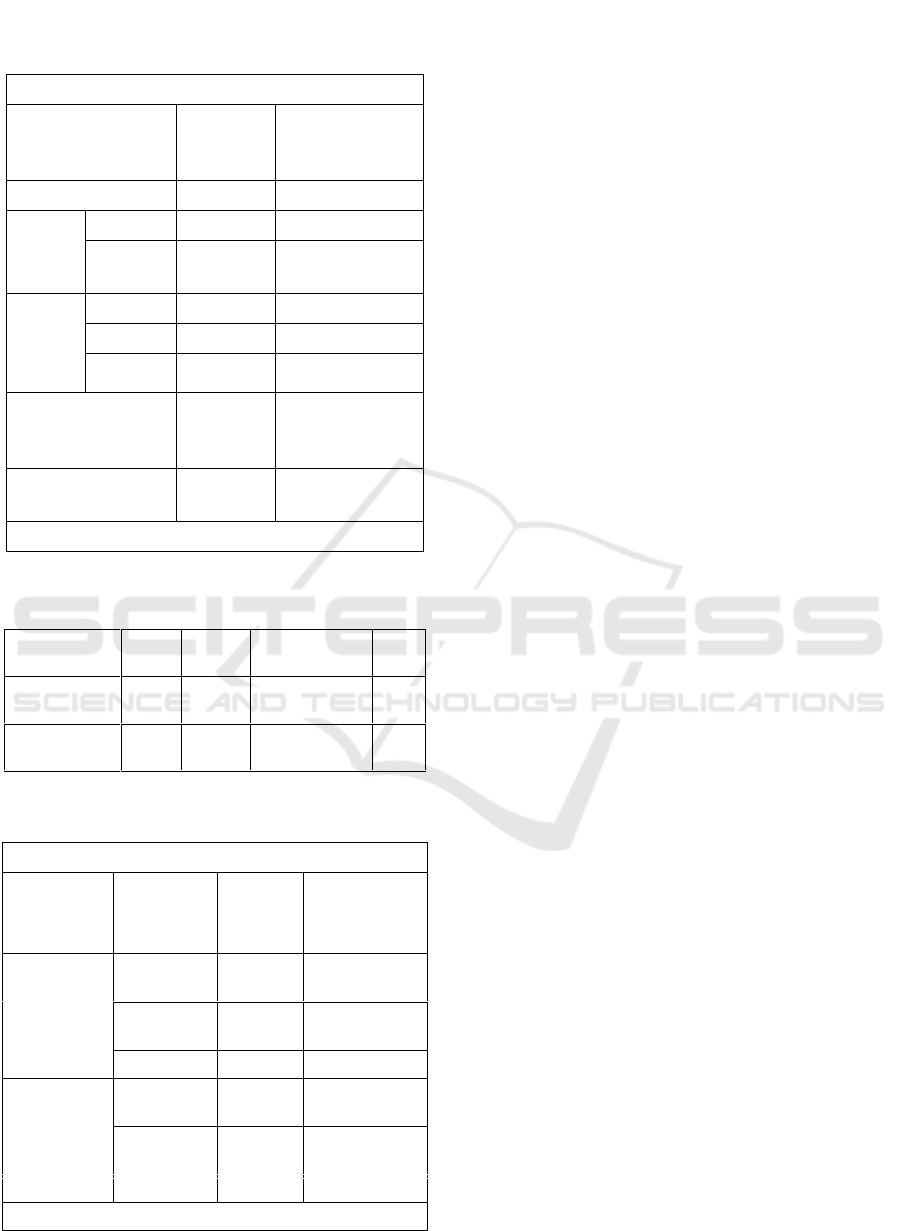
Table 3: Summary results of the normality test power of
limb muscle and smash skill kedeng on Sepaktakraw
students.
Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test
Power of
Limb
Muscle
Smash skill
Kedeng on
Sepaktakraw
N
38
38
Normal
Paramet
ers
a
Mean
114.08
18.74
Std.
Deviation
5.074
1.719
Most
Extreme
Differen
ces
Absolute
.096
150
Positive
.084
.150
Negative
-.096
-.113
Kolmogorov-
Smirnov Z( Test
Statistic)
.591
.923
Asymp. Sig. (2-
tailed)
.875
.362
a. Test distribution is Normal.
Table 4: F-test the power of limb muscle to smash skill
kedeng on sepaktakraw.
Varians
DF
F
count
F
table
(α =
0,05)
Sig
Regresi
Residual
3
34
74,55
2,88
000
Total
Reduksi
37
-
-
-
Table 5: The results of correlation power of limb muscle
and smash skill kedeng on sepaktakraw.
3.2 Discussion
Description on the overall results of hypothesis
testing showed a significant positive correlation. The
first about data analysis for variable power of limb
muscle X1 with a mean score of 114,08, the range of
17, minimum score 106 and score maximum 123, it
indicates that the students of the faculty of sport
sciences who practice in the bureau activities of
university students sepaktakraw have the ability
power of limb muscle with an average of 114 or
52.6%, with the number of frequency of 20 people.
This means that the power of the limb gives the
effect of 95.0% against kedeng on sepaktakraw smash
skills. This shows that power of leg muscle
contributes strongly to the skill of doing smash
kedeng. It is means if the better power of leg muscle,
so the better the ability to do smash kedeng, and vice
versa if the power of leg muscle of an athlete is low
then the ability to smash also low (Brow, 2005). This
can be seen when athletes are able to perform sharp
smash and plots smash (plash) directed.
Descriptive analysis of data obtained by the mean
power of limb muscle of 114,08, standard deviation
of 5.074, 25.750 variance, maximum score 123,
minimum score 106, range 17, median 113.50, Mean
smash skill kedeng of 18.74, standard deviation of
1.719,variance of 2.956, maximum score 22,
minimum score 16, range of smash skills kedeng 6,
median 19,00.
Terms of normality analysis of data using the
Kolmogorov-Smirnov test aims to determine whether
the data were normally distributed. The hypothesis
will be tested with a 0.05 significance level α are: H0:
If the probability < 0.05, then H0 is rejected to mean
the population is not normally distributed. H1: If the
probability ≥ 0.05, then H1 is accepted means that the
population is normally distributed.
Normality test data smash skill kedeng on
sepaktakraw (Y) Probability value of 0.362 so that the
p-value = 0.362 > α 0,05). The data were normally
distributed of smash skill kedeng on sepaktakraw. But
Normality test data power of limb muscle (X)
Probability value of 0.649 so that the P-value = 0.649
> α 0,05). The data were normally distributed of
power of limb muscle.
Analysis of the correlation power of limb muscle
to smash skill kedeng on sepaktakraw. In the
correlation table generates a probability value of 0.05
is greater than the probability value sig or [0.000 <
0,05] H0 rejected and H1 accepted meaning
significant and have a positive correlation to smash
skill kedeng on sepaktakraw with the level of
relations X1 with the variable Y is (r) 0.975 shows
Correlations
Power of
Limb
Muscle
Smash Skill
kedeng on
Sepaktakraw
Power of the
Limb Muscle
Pearson
Correlation
1
.975
**
Sig. (2-
tailed)
.000
N
38
38
Smash Skill
kedeng on
Sepaktakraw
Pearson
Correlation
.975
**
1
Sig. (2-
tailed)
.000
N
38
38
**. Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed).
Correlation between Power of Limb Muscle with Smash Skill Kedeng on Sepaktakraw
261

very strong positive correlation and coefficient of
determination[15] (Kd or Pearson correlation by: Kd
= r2 x 100%, (0.975)2 x 100% = 0.95 x 100 = 95.0,
which means smash skill kedeng on sepaktakraw
determined by the power of limb muscle and the rest
influenced by another factor of 5.0.
Correlation power of limb muscle with smash
skill kedeng on sepaktakraw. From the calculation
Thitung 4.555 > 2,024 Ttable then H0 rejected H1
accepted. This means there is a significant correlation
between the power of limb muscle with smash skill
kedeng on sepaktakraw. But the results from the
calculation of Fhitung 74.55 > Ftabel 2.88 then H0
rejected H1 accepted. This means there is a
significant correlation between power of limb muscle
to smash skill kedeng on sepaktakraw. Meanwhile
body size refers to the volume, mass, length and
surface area of the body, whereas body structure
refers to the distribution or arrangement of body parts
such as the skeleton and muscle-fat distribution
(Masson, 2015)
Therefore, for better results then general physical
education concerns with the process of teaching-
learning so that the students get a bunch of knowledge
or movement skills or biomechanics value which are
obtained significantly. Differences in physical
education with sport education lie in the purpose and
the setting of teaching and learning. And order of
magnitude as those associated with uncertainties in
limb lengths.
4 CONCLUSIONSS
Based on data analysis and discussion, the results of
this study can be summarized as follows. The results
of testing hypothesis states there is a positive
correlation between power of limb muscle to smash
skills kedeng sepaktakraw. This indicates that power
of limb muscle strong contribution to the smash skill
kedeng on sepaktakraw means the better power of
limb muscle, the better the ability to smash kedeng.
REFERENCES
Achmad S. 2015. Sepaktakraw for students. Jakarta: Eagle
Pers. 3.
Syam A. 2015. Beach Sepaktakraw. Jakarta: Eagle Pers. 25-
27.
Engel, R. 2010. Basics Sepaktakraw. ASEC Internasional:
PT Intan Sejati.
Lemond G., Hom M. 2015. The Science of Fitness Power,
Performance, and Endurance, Kidlington, Oxford OX,
UK. 51.
Bompa. & Carrera M. 2015. Conditioning young athletes.
USA: Human Kinetics.75.
James T., Puspitorini W. 2012. Sports Coaching, Sports
Performance Coaching Edisi II. Jakarta.
Donald A. Chu and Gregory D. Myer. 2013. Plyometric,
Human Kinetics United States of America.
Widiastuti. 2015. Sport and Measurement Sports. Jakarta:
Eagle Pers.
Shephard R.J. And Astrand. 2000. Endurance In Sport,
Blackwell Science, International, Olympic Committee,
Australia.
Carroll B. 2005. Asssessment in Physical Education: A
Teacher’s Guide to the Issues, the Taylor & Francis e-
Library.
Brow, L.E & Ferrigno, V.A. 2005. Training for spedd,
agilty and quickness. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics,
USA. 87-89, 2005.
Masson, M.-A. Bégin, M. Lopez Poncelas, S.K. Pelletier.
2015. Contribution of limb momentum to power
transfer in athletic wheelchair pushing [J] Journal of
Biomechanics. European Journal of Business and
Social Sciences, Vol. 4, No. 01, p158-173.
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
262
