
Instrument Development for Measuring Responsibility of Student in
Elementary School
A Case in Physical Education
Sri Santoso Sabarini
1
, Adang Suherman² and Yudy Hendrayana²
1
Universitas Sebelas Maret
2
Faculty of Sport and Health Education, Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Jl. Dr. Setiabudhi No. 229, Bandung 40154
sririni76@yahoo.com
Keywords: Responsibility, Physical Education.
Abstract: Any studies stated that model of "Teaching Personal Social Responsibility" (TPSR) by Hellison (1995)
could improve the character of responsibility of the student in physical education. This study wanted to
construct instrument for measuring level of students’ responsibility in primary school. The instrument were
developed by adapting from some existing responsibilities as Tool for Assessing Responsibility Based
Education / TARE (Wright and Craig, 2011) and rubric TPSR by Paul M. Wright (2009). Research
instrument was structured to facilitate teachers and students for measuring student's responsibility when
teaching physical education in the classroom through observation and reflection. Observations carried out
by the observer, while the reflection carried out by the students themselves. The scope of responsibilities of
the measured indicator was about respect, participation and effort, self-direction, and caring and helping
others while them do "game" in physical education. The instrument consisted of 18 items was construct
questions that poured into the enclosed questionnaire. The construction of instrument indicators and each
question was tried-out at 29 students of fourth grade in Nusukan Primary School in Surakarta, Central Java.
The results of the analysis with SPSS showed that reliability of both the instruments had a Cronbach's Alpha
value for the instrument observations of 0.921 and 0.863 amounted reflection instrument. The validity of the
instrument to 18 grains of all above 0.36. As with F table at a significance level of 5%, these figures suggest
that all items are valid instrument. The implication of this research is to produce a measuring instrument
used to measure the level of responsibility of students, especially students in fourth grade .which are more
simple and practical, according to the characteristics of children in Surakarta, Central Java.
1 INTRODUCTION
Physical education is an integral part of the overall
education which involved utilizing physical activity,
healthy living habituation, and integrating character
that applied in everyday life. To produce holistic
changes in individual quality, both in terms of
physical, mental and emotional through physical
activity and sport. The main purpose of education is
to develop individuals into individuals who are
creative, inventive and capable of adapting to their
environment. Thus the expected goal of physical
education is not just a physical accomplishment
alone, but the physical education has ideal goal is to
develop the overall personality, cover physical,
mental, emotional, intellectual, social, moral and
aesthetic. In addition to the positive effect of
physical education should be able to support the
development of cognitive, affective and
psychomotor ideal for students.
To learn the responsibility attitude to the students
at the school in physical education lessons Hellison
have found Teaching Personal Social Responsibility
(TPSR). This model is an approach that be
developed through his personal experience working
with students who have difficulty in physical
education, then it helps the student to take
responsibility for their welfare and help them to
become more sensitive and responsive to the others
welfare. It turned out have the best contribution that
can be done, especially personal and social problems
that students faced (Hellison, 1995: 4). The TPSR
approach was not intended to replace the physical
education contents, but rather to provide a
framework program for its contents (Hellison, 1995:
Sabarini, S., Suherman, A. and Hendrayana, Y.
Instrument Development for Measuring Responsibility of Student in Elementary School - A Case in Physical Education.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education (ICSSHPE 2017) - Volume 2, pages 5-8
ISBN: 978-989-758-317-9
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
5

52). The TPSR program was used responsibility as a
theme to teach a variety of physical activities.
Learning strategies includes of responsibility
awareness, experiences were used as a reflection of
the responsibility attitude, in individuals and groups
in decision-making (empowerment) (Martinek and
Hellison, 1997: 45). For more details, see table 1.
Table 1: TPSR rubric for assessing responsible behavior.
Adapted: Paul M. Wright (2009) University of Memphis.
Responsible
Behavior
Description Always Most
of the
time
Some
of the
time
Never
Self-control Student does no
harm to others
verbally or
physically;
includes/works
well with
others; resolves
conflicts
peacefully if
they emerge
3 2 1 0
Participation Student will try
every activity
and take on
various roles if
asked
3 2 1 0
Effort Student tries
hard to master
every task and
focuses on
improvement
3 2 1 0
Self-
direction
Student will
stay on task
without direct
instruction or
supervision
whether
working alone
or with others;
does not seem
to follow bad
examples or
p
eer pressure
3 2 1 0
Caring Student will
help, encourage
others, and
offer positive
feedback
3 2 1 0
This opinion was reinforced by Deb Wuest in his
article, he stated that TPSR model was developed to
help students learn the responsibility by giving them
an increasing number of responsibilities and
carefully shift a significant portion of the
responsibility for their decision-making. So from
some opinions can be concluded that through the
TPSR model, the teacher can improve self-
responsibility and social responsibility through
empower students to take more responsibility for
their actions and lives and teach them to care about
the rights, feelings and other’s needs. This model
seeks to help students so that they feel empowered,
to give experience to make a commitment to
themselves and others, to live by a set of principles,
and be concerned with the others welfare.
Level of TPSR model can be described as
moving from not responsible to responsibility,
moving from self-respect to respect and concern for
others. This behavior was first developed in physical
education classes and then used outside the gym, in
the home and community settings. The research
question is: “How the applicative instrument for
measuring the responsibility of fourth grade students
of elementary school? “
This study will construct a measurement tool to
determine the responsibility level of students in
elementary schools, especially those used in
Indonesia. The instrument development is adopting
some of existing responsibilities instrument such as
Tool for Assessing Responsibility Based Education /
TARE (Wright and Craig, 2011) and rubric TPSR of
Paul M. Wright (2009). Research instrument was
structured to facilitate teachers and students to
measure student’s responsibility when teaching
physical education in the classroom through
observation and reflection. Observations carried out
by the observer, while the reflection carried out by
the students themselves. The scope of
responsibilities indicators are including of respect,
participation, sincerity and effort, independence, and
empathy of students while carrying out the “game”
in physical education.
2 METHODS
The steps to construct this instrument including of
determining the instrument specification, writing the
instrument, determine the instruments scale, define
scoring guidelines, review the instrument, assemble
instrument, perform limited test, analyze test
results., repair the instrument, implement the
measurement, and interpret measurement results.
Instrument that are constructed from lattice,
indicator, and the questions then tested
(experimented) to the 29 students of fourth grade SD
Negeri Nusukan Surakarta, Central Java. The results
were analyzed with SPSS to look for instruments
reliability and validity.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The study instruments are including of attitude
observation sheets with the attitude scale were taken
from Helison’s responsibility theory. With as
follows procedural:
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
6
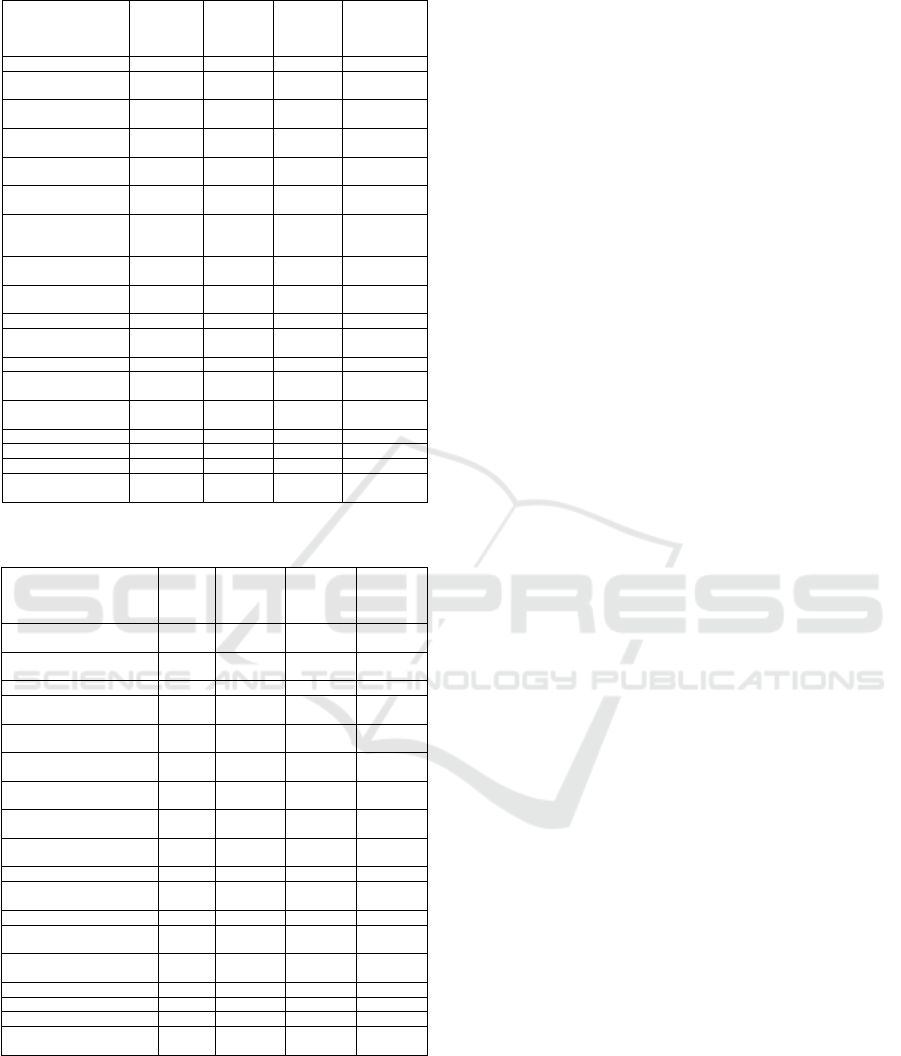
Table 2: Item-total statistics observations.
Test questions
Scale Mean
if Item
Deleted
Scale
Variance if
Item
Deleted
Corrected
Item-Total
Correlation
Cronbach's
Alpha if Item
Deleted
acts that could hurt others 63.38 150.958 .420 .920
perform acts that may
harm others.
62.66 143.734 .701 .914
can work with good
p
eers,
63.48 139.259 .611 .917
can solve social conflicts
b
y well when there.
63.21 141.241 .712 .913
try each exercise provided
b
y the teacher
62.55 143.613 .676 .915
tried all the role of the
teacher when requested
62.66 143.734 .701 .914
worked hard to master th
material provided by th
e
teacher
62.72 147.421 .480 .919
focus on improving
learning outcomes
62.76 146.761 .482 .919
practice without anyone
watching.
63.38 150.958 .420 .920
have a target in learning 63.07 139.495 .723 .913
resistant to interference
and pressure of friends
63.21 141.241 .712 .913
away from misconduct 62.66 143.734 .701 .914
trying to realize the good
b
ehavior
63.62 151.601 .328 .923
love, help, and support
their peers in learning
62.90 151.810 .406 .921
do each other well, 63.07 139.495 .723 .913
show sportsmanship 63.21 141.241 .712 .913
p
rovide support fellow 63.24 145.047 .626 .916
provide positive feedback
among friends.
62.55 143.613 .676 .915
Table 3: Item-total statistics selfchek.
The data analysis results used SPSS 2.0. The
instrument validity is as follows. The SPSS analysis
results shown that reliability of both instruments has
Cronbach’s Alpha value for the instrument
observation of 0921, and the reflection instrument of
0863, these calculations results are high. The 18
instrument items validity is all above 0.36. In
accordance to the Rtable at a significance level of
5%, these numbers suggest that all of instrument
items are valid.
Discussion on the study results was indicated
that this instrument was developed to assist teachers
in measuring students’ responsibility where they feel
empowered, given the experience to make a
commitment to themselves and to others, to live by a
set of principles, and be concerned with the others
welfare. This instrument has fulfilled responsibilities
indicator that emphasizes effort and directing the
student to achieve personal welfare. Social welfare
are including of respect to the rights, considering the
others feelings, and caring to the other. In addition
this instrument aimed help teachers and students to
be aware of their behavior and to focus their efforts
in establishing responsibility. Simplifying of
questionnaires questions items that should be filled
teachers and students were expected to facilitate
teachers and students in measuring the student’s
responsibility. In addition, teachers can used this
level for framework of planning, teaching, and
evaluating of student learning.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Through responsibility instrument adopted from
TPST model, teachers can measure personal and
social responsibility of students to empower students
to take responsibility for actions and their lives and
to teach them about caring for the rights, feelings,
and needs of others. TPSR was not intended to
replace the contents of the physical education
material, but rather to provide a framework for
physical education teaching, so the physical
education teachers should integrated with other
physical education learning models. Responsibility
instruments were adopted from TPSR learning
model which has been constructed over more simply
felt could be used to measure the students’
responsibility, especially fourth grade students of
elementary school with easier language to be
understand, and it’s using is in accordance to the
characteristics of children in Surakarta Indonesia.
REFERENCES
Amparo Escartí,*, Paul. Wright, Carmina Pascual Melchor
Gutiérrez, 2015. Tool for Assessing Responsibility-
based Education (TARE) 2.0: Instrument Revisions,
Inter-rater Reliability, and Correlations between
Scale
Mean if
Item
Deleted
Scale
Variance if
Item
Deleted
Corrected
Item-Total
Correlation
Cronbach's
Alpha if
Item
Deleted
I do anything that could hurt
others
61.90 102.810 .418 .858
I do anything that can harm
others
61.52 107.044 .258 .863
I can work with good peers 62.00 94.643 .549 .852
I can solve social conflicts by
well when there
62.21 107.813 .117 .870
I tried every workout provided
b
y the teacher
61.07 96.638 .682 .847
I tried all the role of the teacher
when requested
61.17 98.362 .620 .850
I worked hard to master the
material provided by the teacher
61.24 99.475 .497 .855
I focus on improving learning
outcomes me
61.28 100.207 .439 .857
I practiced without someone
watching
61.90 102.810 .418 .858
I have a target in learning 61.59 94.823 .655 .847
I'm resistant to interference and
p
ressure of friends
62.41 101.037 .407 .859
I avoid the bandwagon do ba
d
61.17 98.362 .620 .850
I am trying to realize the good
b
ehavior
62.17 101.791 .261 .869
My love, help, help, and
support their peers in learning
61.41 103.180 .423 .858
I treat others well, 61.52 107.044 .258 .863
I showed sportsmanship 61.72 97.278 .591 .850
I provide support fellow 61.76 96.618 .695 .847
I give positive feedback among
friends.
61.07 96.638 .682 .847
Instrument Development for Measuring Responsibility of Student in Elementary School - A Case in Physical Education
7

Observed Teaching Strategies and Student Behaviors.
Universal Journal of Psychology 3(2): 55-63.
Bucher, C. A. 1979. Foundation of Physical Education.
The CV Mosby Company London Teaching Physical
Education. Third Edition, Mayfield Publishing.
Child Trend. 2014. Measuring Elementary School
Students’ Social and Emotional Skills. Child Trens
Publication.
David Kirk, Ann MacPhail. 2002. Teaching Games for
Understanding and Situated Learning: Rethinking the
Bunker-Thorpe Model. Loughborough University:
Journal of Teaching in Physical Education, 2002, 21,
177-192. Human Khinetic Publisher INC.
Deb Wuest. 1999. Disciplining Students by Promoting
Responsibility: Physical Education Central.
www.pecentral.org/climate/january99article.html.
Escartí A, et all. 2011. Application of Hellison's Teaching
Personal and Social Responsibility Model in physical
education to improve self-efficacy for adolescents at
risk of dropping-out of school. Span J Psychol. 2010
Nov; 13(2):667-76.
Goudas Marios, Magotsiou E. 2007. The Effect of a
Cooperative Physical Education Program on Student’s
Social Skill, University of Thessaly journal of applied
Sport Psychology.
Hellison, D, 1995. Implementation Of the Personal and
Social Responsibility Model to Improve Self-Efficacy
During Physical Education Classes for Primary School
Children. International Journal of Psychology and
Psychological Therapy.
Holt, N. L., Strean, William B., Bengoecha, E. G. 2002.
Expanding the Teaching Games for Understanding
Model: New Avenues for Future Research and
Practise. Journal of Teaching in Physical Education.
Canada: University Of Alberta.
Hooper, T. 1998. Teaching Games Centered Games using
Progressive Principles of Play. Victoria: CAHPERD.
Kulwinder Dhillon, Carrie Moody, Nicole Strain. 2008.
Improving Student Wellness and Social ellness and
Social Interactions the actions through Physical
Activity. Green Timbers Elementary School Action
Research Team: Consisted Of all the enrolling
teachers and the administrators. Journal Leadership
for Learning, Volume 7(2).
Lickona, Thomas, Matthew Davidson, 2004. Smart and
Good High School: Integrating Excellence and Ethics
for Success in Schools, Work, and Beyond. Cortland:
Center for 4th and 5th Rs.
Lickona, Thomas, 1991. Educating for Character: How
Our Schools can Teach Respect and Responsibility,
New York: Bantam Books.
Li Weidong et all. 2008. Measuring Students’ perception
of personal and Social Responsibility and the
Relationship to Intrinsic Motivation in Urban Physical
Education. Journal of Teaching in Physical Education.
Hal 167-178. Human Kinetics, Inc.
Michael W. M. 2000. Instructional Models for Physical
Education. Allyn and Bacon Apearson Educational
Company, Needham Heights, Massachusetts: Georgia
State University.
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
8
