
The Effect of Learning Models on the Teenagers‘ Volleyball Low
Passing Improvement
Muhammad Rizki Mauludin, Arief Abdul Malik and Katam Katam
School of garaduate studies, Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Jl. Dr. Setiabudhi No. 229, Bandung 40154, Indonesia
rizki99.mr@student.upi.edu
Keywords: Problem Based Learning, Direct Instruction, Volleyball.
Abstract: This research is raining to know the effect of two models of learning on set-up underarm passing technique
in volleyball game. Learning model in this research is Problem Based Learning (PBL) and Direct Instruction.
This research uses experimental method with design "randomized pre-test and post-test design". Technique
of data retrieval in this research use randomized samples so that the sample used amounted to 30 students
which divided into two experiment group that is group with treatment of PBL and DI. The instrument used is
the accuracy of the bottom passing. Data analysis performed using t test with significance 0,05. The result of
analysis shows that PBL learning model gives more significant effect to the set-up of passing technique with
t_count 4,450 > t_table 2.05.
1 INTRODUCTION
Learning method is a series of ways or strategies that
are arranged to create learning conditions to take
place as expected, students can improve their activity
in the learning process and produce good learning
outcomes (Joyce, Weil and Calhoun 2009; Parkay,
2010). Learning is effective if implementing PBM
that can improve student learning activities and get
optimal learning outcomes. The effectiveness of
learning can be measured by the students' ability to
apply the knowledge they acquire (Guthrie and
Schuermann, 2011; Wong and Wong, 2005).
Problem Based Learning is a method of learning
by exposing students to real problems, so that from
the problem students can improve their knowledge
and understanding (Liu, Liau and Tan, 2009; Marsh,
2010; Baden and Major, 2004; Wood, 2003). The
PBL has six stages of the learning process; (A).
Discovery of the problem, (b). Problem investigation,
(c). Identification of learning problems, (d). Peer
teaching, (e). Integration of knowledge and (f).
Solution problem (Claire, Jamie and Author, 2013).
Another approach based on the principle of
behavior is Direct Instruction (DI). DI is an effective
group teaching method, especially for low-
performing students at risk of academic failure
(Lickona and Davidson, 2005). DI refers to
instructional tactics that focus on systematic and
explicit instruction. The basic elements of DI include
(a) The scripting lessons very regular, (b) ability to
group students, (c) repetition of content, (d) use of
time, (e) instruction usage, (f) response to instruction,
(g) Fast learning phase (fast pacing), and (h) mastery
of previous content that previously switched to more
difficult content (Cadette, Wilson, Brady, Dukes and
Bennett, 2016).
Based on previous studies, applied PBL into the
sports curriculum is an effective means to motivate
students to be directly involved with more learning
experiences (Engelmann and Becker, 1976). On the
other side, the use of DI methods can improve the
ability of basic football techniques in children age 12-
14 years old (Maria, 2014). But from existing
research there is no one to compare PBL and DI in
basic techniques of volleyball.
This research is intended to answer some
questions, namely: 1). Does the Problem Based
Learning model have a significant effect on
improving the bottom passing technique in a game of
volleyball?; 2). Does the Direct Instruction
instructional model have a significant effect on
improving the bottom passing technique ?; 3). Which
is the more significant influence between the Problem
Based Learning model and the direct instruction
Mauludin, M., Malik, A. and Katam, K.
The Effect of Learning Models on the Teenagers‘ Volleyball Low Passing Improvement.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education (ICSSHPE 2017) - Volume 2, pages 61-63
ISBN: 978-989-758-317-9
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
61
learning model on improving the bottom passing
technique in a volleyball game?.
2 METHOD
2.1 Participants
The sample consisted of 30 randomly determined
people. The grouping of samples was done using
ordinal pairing technique.
2.2 Procedures
The method used in this research is a method with
pre-test design and post-test experimental design
(14). This study starts from 18 May 2016 to 20 June
2016. There are 18 meetings that are held every 3
times per week with a 60 minute meeting / meeting.
2.3 Instruments
The instrument used is a passing ability test under a
volleyball game (15). Data processing is done by
using t-test statistic.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Differences in Mean Score of
Underarm Pass or Bump Value
between Pre and Post-test on
Problem Base Learning
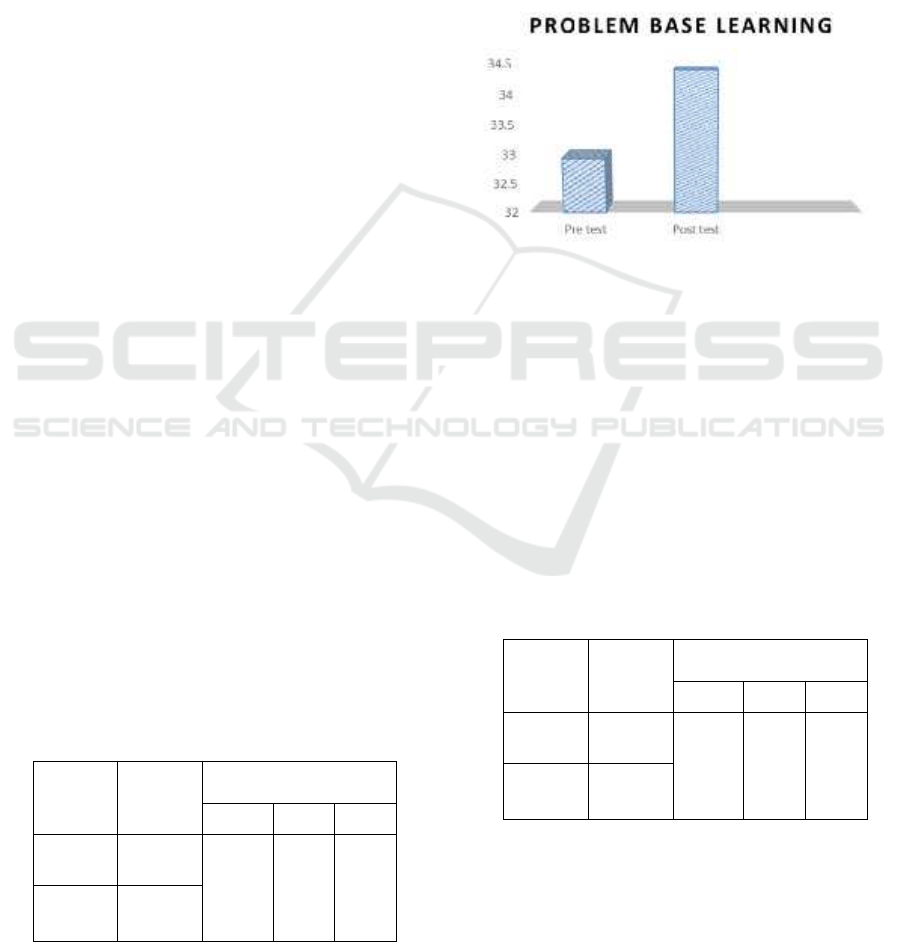
Table 1 shows an increase in lower passing skills in
students treated by PBL. This can be seen from the
increase in the average passing score under the
students. In the initial test the average student score
was 32.93, while in the final test the student score
increased to 34.40.
Table 1: Increase in lower passing skills in students treated
by PBL.
Average
t-test for Equality of
means
t-count
t-table
α
Initial
Test
32,93
81,29
2.05
0.05
Final
Test
34,40
This implies that the treatment of PBL is linear
with the improvement of lower passing skills by the
students. From result of t-test can be seen that t_count
81,29 dan t_table 2.05 with significant value equal to
0.05. Because t_count 81,29 > t_table 2.05. Then this
result shows there is significant influence. Thus the
alternative hypothesis Ho which reads "problem
based learning model gives significant influence to
the improvement of passing technique under
volleyball game, accepted and got the truth in this
research.
Figure 1: Problem based learning.
3.2 Differences in Mean Score of
Underarm Pass or Bump Value
between Pre and Post-test on Direct
Instruction
Table 2 shows an improvement in lower passing skills
on students given Direct Instruction modelling
treatment. This can be seen from the increase in the
average passing score under the students. In the initial
test the average student score was 30.60. While in the
final test, the student score increased to 31.93.
Table 2: improvement in lower passing skills on students
given Direct Instruction modelling treatment.
Average
t-test for Equality of
means
t-count
t-table
α
Initial
Test
34,40
89,16
2.05
0.05
Final
Test
31,93
From t-test results can be seen that t_count 81.26
and t_table 2.05 with α 0.05. Then this result shows
there is significant influence. Thus Ho alternative
hypothesis which reads "Direct Instruction learning
model gives a significant influence to the
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
62

improvement of passing technique under volleyball
accepted truth in this research.
Figure 2: Direct instruction.
3.3 Differences in Gain Score (Pre and
Post-test) of Underarm Pass or
Bump between Problem Base
Learning and Direct Instruction
Based on the result of the analysis from the
independent table, the test sample for the column of
assumption variance assumption (t-test) is known as
tct = 4.450 and the value of ttable 2.05, Ha result is
accepted at significance level α = 0.05 (5%). PBL
learning model gives more significant influence to the
improvement of passing technique under volleyball
because from table independent sample test for
column equal variance assumption (t-test) known
value tcount = 4.450> ttable value 2.05, then Ho is
rejected and Ha accepted at significance level α =
0.05 (5%).
Table 3: Differences in gain score.
Average
t-test for Equality of
means
t-count
t-table
α
Problem
Base
Learning
34,40
4,450
2.05
0.05
Direct
Instruction
31,93
4 CONCLUSIONS
Mastery of passing techniques under the game of
volleyball shows a positive improvement both with
PBL and DI models. The PBL model is more
significant than the DI model for the lower passing
learning outcomes in the game of volleyball.
REFERENCES
Baden M S, Major C H. 2004. Foundation of problem-
based learning. New York: McGraw-Hill Inc.
Cadette J N, Wilson C L, Brady M P, Dukes C, Bennett K
D. 2016. The Effectiveness of Direct Instruction in
Teaching Students with Autism Spectrum Disorder to
Answer “Wh-” Questions. J Autism Dev Disord. 2016;
46(9):2968–78.
Claire J L, Jamie M, Author C. 2013. The implementation
of problem based learning styles to teach the Coach-
Athlete relationship to undergraduate Sport and
Exercise Science students. 2013; 3(8):859–64.
Engelmann S, Becker W C. 1976. Analysis of achievement
data on six cohorts of low-income children from 20
school districts in the University of Oregon Direct
Instruction follow through model [Internet]. 1976 [cited
2017 Jun 6]. Available from:
https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED145922
Fraenkel J, Wellen N, Hyun H. 2012. How To Design And
Evaluate Research In Education. New York: McGraw-
Hill Inc.
Guthrie J., Schuermann P. 2011. Leading schools to
success: constructing and sustaining high performing
learning culture. Los Angles: SAGE Publication, Inc.
Joyce B, Weil M, Calhoun E. 2009. Model of teaching.
Boston: Prentice Hall.
Lickona T., Davidson M. 2005. Smart and good high
schools: Integrating excellence and ethics for success
in school, work, and beyond. Washington DC:
Character Education Partnership.
Liu W C, Liau A K, Tan O S. 2009. E-portfolios for
problem-based learning: scaffolding thinking and
learning in preservice teacher education. In: Problem-
based learning and creativity. Singapore: Cengage
Learning Asia Pte Ltd. p. 205–23.
Maria F. 2014. The influence of direct and indirect teaching
method in the development of selected technical skills
in the sport of football to children aged 12-14 years old.
J Phys Educ Sport. 2014; 14(3):413–20.
Marsh C J. 2010. Becoming a teacher: knowledge, skills
and issues. 5th ed. French Forest: Pearson Australia.
Nurhasan. 2001. Tes dan Pengukuran Dalam Pendidikan
Jasmani : Prinsip-Prinsip dan penerapannya. Jakarta
Pusat: Depdiknas. Ditjen Dikdasmen. Ditjen Olahraga.
Parkay F A, Stanford B H. 2010. Becoming a teacher. 8th
ed. Upper Saddle River: Pearson Education, Inc.
Wong H K, Wong R T. 2005. How to be an effective
teacher: the first days of school. Montain View: Harry
K. Wong Publication, Inc.
Wood D F. 2003. Problem based learning what is problem
based learning ? Bmj. 2003; 326(February):328–30.
29.5
30
30.5
31
31.5
32
Pre test Post test
D I R E C T
I N S T R U C T I O N
The Effect of Learning Models on the Teenagers‘ Volleyball Low Passing Improvement
63
