
Application of Hellison Learning Model to Increase Student’s
Responsibility Value in the Use of Physical Education Learning Tools
Gilang Ginanjar and Mimin Karmini
Faculty of Sport and Health Education, Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Jln. Dr. Setiabudhi No. 229, Bandung, Indonesia
gilginanjar10@gmail.com
Keywords: Hellison Learning Model, Responsibility Value, and Physical Education Learning Tools.
Abstract: This research is motivated by the problem of student responsibility attitude in the use of learning tool of
physical education in elementary school. This study aims to determine whether Hellison learning model can
improve the value of student responsibility in the use of learning tools of physical education. This research
uses classroom action research method, with adaptation research model from Elliott. The study was
conducted in two cycles; each cycle was carried out twice. The subjects of the study were Class V SD
Negeri Tilil 2 Bandung City as many as 33 people consisting of 17 students and 16 students. Data collection
techniques, are observation, field notes, and in documentation of further learning activities data analysis is
done. Data analysis technique used is the percentage technique. The percentage result of the cycle I action I
was 43% cycle II action II 63%, cycle II action I was 83% and cycle II action II was 90%. Based on the
results of research on the value of student responsibility in the use of learning tools of physical education
has shown that the Hellison model can improve student responsibility.
1 INTRODUCTION
PJOK Subjects are very closely related to the value
of discipline and responsibility. Students are
required to always uphold the discipline in learning
activities. Students should come just in time and
follow the whole set of theory and practice lessons
well. In addition, each student must also be
responsible with the task of theory and practice
provided by the teacher. Students are expected to
cooperate well with a group of friends if they are
doing a group game sport.
To achieve all of these objectives, Physical
Education (Penjas) needs to be taught or properly
implemented by each Penjas teacher; which
involves learning models, an atmosphere that keeps
children motivated, including tools that bring out
activities that make children feel happy to participate
fully in learning.
In the learning process that acts as a source of
message delivery can be teachers, books, or other
sources. One of the most common sources of
messaging that can be used is by using media. Media
is one of the tools or educational equipment. As
described by Happy and Mudjianto (2009) are:
Equipment (Appartus) is something that can be
used by students to perform activities/activities
above it, below, in/among which is relatively easy to
move around. Physical education means everything
that can be used to be carried out in doing physical
activity.
The learning tool at SD Negeri Tilil 2 Bandung
is sufficient or complete, but because of the lack of a
sense of personal responsibility to the students in
taking care of the equipment they use during the
learning took place. They further damage or
eliminate the tools available so that when the next
learning of Spam tools cannot be reused.
With these problems many ways can be done by
parents, teachers, trainers, community or adults to
develop a sense of responsibility to each individual
self. Associated with some of the problems above,
the authors are interested to apply a model of
learning that the author feels very suitable to
overcome the above problems, namely by applying
Hellison learning model.
One model of physical education learning
included in the category of social reconstruction
model is the Hellison model (Hellison, 1995),
entitled Teaching Responsibility through Physical
Activity (Hellison, 1995). Learning physical
education in this model more emphasis on the
234
Ginanjar, G. and Karmini, M.
Application of Hellison Learning Model to Increase Student’s Responsibility Value in the Use of Physical Education Learning Tools.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education (ICSSHPE 2017) - Volume 2, pages 234-237
ISBN: 978-989-758-317-9
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reser ved

welfare of individuals in total, the approach is more
student-oriented, namely self-actualization and
social reconstruction. Hellison's model of physical
education is named the level of affective
development. The purpose of this Hellison model is
to improve personal development and student
responsibility of irresponsibility, self-control,
involvement, self-direction (Brockett) and caring
through various activities of the movement learning
experience according to the applicable curriculum
(Brockett and Hiemstra, 1991).
According to Hellison (1995) cited by Suherman
(2006). This Helison model is often used to foster
student discipline (self-responsibility) for that model
is often used in schools that have problems with the
discipline of their students. Hellison holds the view
that: the change of feelings, attitudes, emotions, and
responsibilities is most likely to occur through
gambling, but does not happen by itself. This change
is most likely to occur when the plot is planned and
exemplified well by reflecting the desired qualities.
This potential is reinforced by Hellison's belief that
students naturally desire to do something good and
extrinsic rewards are counterproductive. Through
this model the teacher hopes that students participate
and enjoy activities for their own benefit rather than
to gain extrinsic rewards. Fair play in the Penjas will
be reflected in everyday life. Therefore, this Hellison
model is basically designed to help students
understand and practice a sense of personal
responsibility (self-responsibility) through Penjas.
2 METHODS
The method used in this research is classroom action
research method (Stringer, 2008). This classroom
action research is a research conducted in the
classroom, the class here is meant at a place where
the interaction between teachers and students so that
the process of teaching and learning happen. The
research design used in this research is the design of
action research model by John Elliott (in Arikunto,
2012). The stages are as follows: (1) planning, (2)
implementation, (3) observation, and (4) reflection.
The four stages are called a cycle.
This classroom action research was conducted at
SD Negeri Tilil 2, Kec. Coblong, Bandung City. In
this study, the intended sample is a class V student,
amounting to 33 people, consisting of 17 female
students and 16 male students. As explained by
Subroto et al. (2016) there are three variables studied
in classroom action research, namely (1) input
variables (students of grade V SDN Tilil 2
Bandung); (2) process variables (Hellison learning
model); and (3) the output variable (attitude of
responsibility).
After determining the method used in the
research, further data is needed to solve the problem,
in this study to measure the data of the sample under
study used the instrument. According to Sugiyono
(2010) research instrument is a tool used to measure
the observed nature or social phenomena. The
instrument used is Hellison's behavioural
observation sheet.
Table 1: Hellison Responsible Behavior Observation
Format.
No
Name
Hellison Responsible
Score Scale
Total
0
1
2
3
4
1.
2.
3.
4.
Etc.
After that, it draws a conclusion made by the
researcher to achieve a meaning and explain what is
done to the data that has been collected in order to
obtain an appropriate conclusion so that the
conclusion can be verified during the study.
The data processing of the observation format of
the implementation of learning Penjas, the
calculation as follows:
(1)
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Results
Stages of action research implementation is an
application of a series of plans that have been
prepared to find solutions and reduce the students’
difficulties in carrying out the teacher's learning.
Research entitled: The Application of Hellison
Learning Model to Increase Student Responsibility
in Using Learning Tool of Penjas, everything that
has been arranged and prepared by researchers from
the stage of preparation of the plan, the
implementation of the action, observation to the
stage of reflection, can provide a positive answer to
the problem which arise in students as well as
improve student success in learning. In this chapter
the researcher will report the results of the research
done by discussing and describing it gradually.
Application of Hellison Learning Model to Increase Student’s Responsibility Value in the Use of Physical Education Learning Tools
235
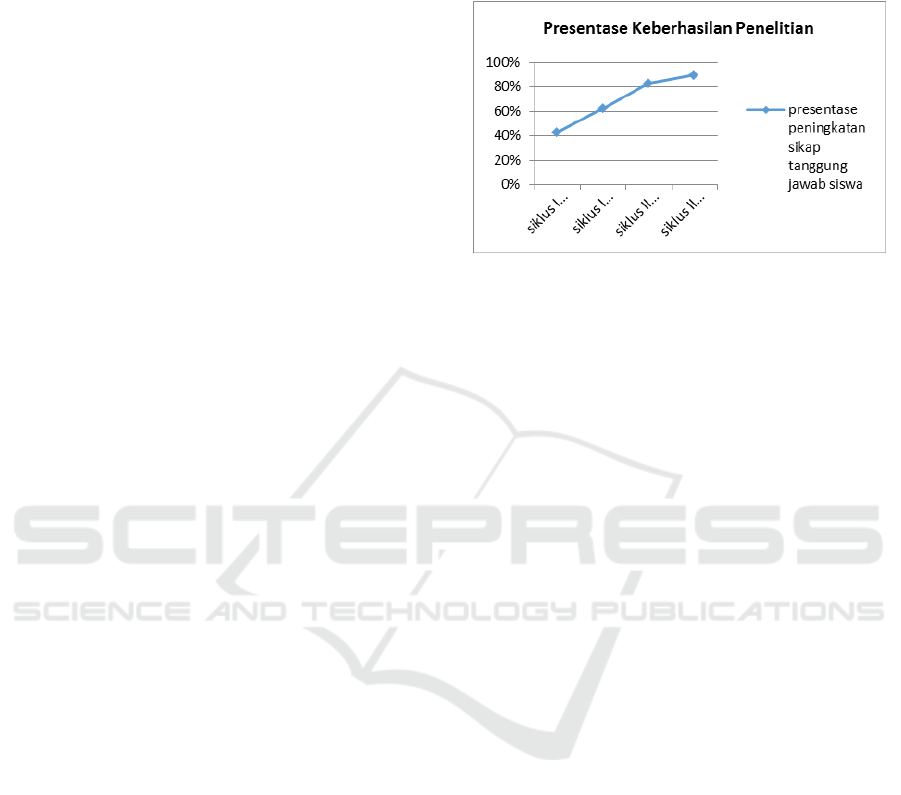
The following results of the overall data of the
affective values of affective attitudes of personal
responsibility Hellison model of each student from
cycle I action I and action II until the cycle II action
I and action II obtained data percentage increase
affective value of student responsibility attitude
model Hellison from cycle I action I for 43% cycle
II action II is 63%, cycle II action I is 83% and cycle
II action II is 90%.
3.2 Discussion
The application of Hellison learning model to
increase the value of student responsibility in the use
of learning tool of Penjas is achieved with positive
attitude such as enthusiasm in learning, has a
concern by helping to prepare the tool at the same
time clearing the learning tool, arises the desire to
try and want to do the task of motion well without
being energetically eager to repeat, helping his
friends who cannot. Encourage his friend or his
group. This shows a positive result; the process of
improvement is the result of research efforts by
always alerting or providing supervision when
learning so that students are encouraged to continue
better.
The process of the researcher in improving the
quality of responsibility attitude above is in line with
Hellison's theory that is cited by Widiyatmoko
(2014):
There are seven learning strategies that Hellison
has used in teaching responsibility through Penjas:
“1) Teacher Talks dan Awarness Talks, 2) Conseling
Time, 3) Group Talk, 4) Modelling, 5)
Reinformance, 6) Throught Reflection Time, 7)
Specifik Level-Related Strategies”.
The strategy of teacher talks and awareness talks
provides the circulation of each stage that will be
done both cognitively and by experience, placing
students, directing important moments in learning.
The counselling time strategy is the time given to
students to consult if anyone is having trouble. The
group talk strategy is intended to discuss all matters
relating to group issues and provide an opportunity
for them to be able to determine the actions or
solutions to be undertaken in the group. The
modelling strategy is intended to provide an example
of behaviour on every development. Reinformance
strategy is the process of teacher to give
reinforcement to every attitudes or behavior that
students do relate to the stages of development. The
strategy of through reflection time is the time given
to the students to think or evaluate attitudes and
behaviours that have been done related to the stage
of development of responsibility. Specific level-
related strategies are conducted to improve
interaction with the stages being undertaken.
Figure 1: Improvement of Student Responsibility.
Increased levels of student behaviour of each
action in the absence of students at behavioural level
0 and 1, reduced students at level 2 by level 3 to be
stable and achievement of the most improved level
of responsibility at level 4 (Caring). With the
emergence attitude of responsibility to friends,
teachers, and the environment of each student it
gives a sense of its own that students have been able
to carry out the attitude of responsibility in the
learning environment of Level 4 (Caring). This
shows the learning process that is expected to be
achieved by the application of Hellison learning
model in the use of effective learning tool of Penjas
can increase the sense of responsibility with the
improvement and development of a sense of
responsibility of students is quite good and can be
said to be succeed.
The Hellison learning method emphasizes the
total individual learner, the more self-oriented
approach and self-actualization and social
reconstruction (Parker and Hellison, 2001). The
purpose of this Hellison model is to enhance
personal development and student responsibility of
irresponsibility, self-control, involvement, self-
direction and caring through sharing activity of
motion learning experience according to applicable
curriculum. Hellison model is often used to foster
self-discipline for this model is often used for
schools with discipline student’s problems (DeBusk
and Hellison, 1989).
The change can occur when physical education is
planned and exemplified by reflecting the desired
quality. A learning process involving a learning
model, an atmosphere that keeps children motivated,
includes tools that deliver activities that make the
child feel happy to participate fully in learning. The
programmatic process of programmed physical
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
236

activity which contains the development of more
specific characters with other fields of study or
social processes can foster the development of
learners into social beings that are beneficial to the
environment wherever they are.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of research on the Application
of Hellison Learning Model to increase student
responsibility in the use of Physical Education
learning tools in SD Negeri Tilil 2 Bandung, found
that Hellison model can increase the value of student
responsibility with the increase and development of
student responsibility value obtained data percentage
increase the affective values of students'
responsibility attitude of Hellison model from cycle
I action I by 43% cycle I action II by 63%, cycle II
action I by 83% and cycle II action II by 90%. This
is indicated by the absence of students at the level of
behaviour 0 and 1, the decrease of students at level
2, the stability of student responsibility at level 3
(Self-Responsibility) and up to the best attitude at
level 4 (Caring).
REFERENCES
Arikunto, S., 2012. Penelitian Tindakan Kelas, Bumi
Aksara. Jakarta.
Brockett, R. G., Hiemstra, R., 1991. Self-Direction in
Adult Learning: Perspectives on Theory, Research,
and Practice, Routledge Series on Theory and Practice
of Adult Education in North America. Routledge,
Chapman and Hall, Inc., 29 West 35th Street, New
York, NY 10001.
DeBusk, M., Hellison, D., 1989. Implementing a physical
education self-responsibility model for delinquency-
prone youth. Journal of teaching in physical
education. 8(2), pp.104-112.
Hellison, D., 1995. Teaching Responsibility Through
Physical Activity, Human Kinetics. Champaign, IL.
Hellison, D. R., 1995. Teaching responsibility through
physical activity.
Stringer, E. T., 2008. Action research in education,
Pearson Prentice Hall. Upper Saddle River, NJ.
Suherman, 2006. Model Pembelajaran Pendidikan
Jasmani, UPI Bandung. Bandung.
Sugiyono, 2010. Metode Penelitian Pendidikan
Pendekatan Kuantitatif.
Parker, M., Hellison, D., 2001. Teaching responsibility in
physical education: Standards, outcomes, and beyond.
Journal of Physical Education, Recreation & Dance.
72(9), pp.25-27.
Widiyatmoko, F., 2014. Pengembangan Sikap
Bertanggung Jawab Siswa Melalui Model Hellison
dan Canter Assertive. Program Pasca Sarjana UPI
Bandung. Bandung, Tesis.
Application of Hellison Learning Model to Increase Student’s Responsibility Value in the Use of Physical Education Learning Tools
237
