
Improving Basic Football Technique Skill through Small Sided
Games
Agus Rusdiana, Muhammad Yusuf Rojali Rahmatillah and Dikdik Fuad Asidik
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Jln. Dr. Setiabudhi No.229, Bandung, Indonesia
Yusufrojali@student.upi.edu
Keywords: Small Sided Game, Basic Football Technique.
Abstract: The purpose of this study is to see the impact of the implementation of the form of Small Sided Games training
on improving the skill of basic techniques of playing football. The basic techniques that become the focus of
this research are: passing, dribbling and shooting. The research method used is experimental method and
research design of one group pretest-posttest group design on football athlete’s PS UPI U-19 who were
decided by purposive sampling. This stage begins with an initial test of basic engineering skills, then is treated
by using the Small Sided Games and ends with a final test. Data obtained from the pre and post-test and
processed by using SPSS. The result shows that there is a significant improvement in the basic soccer skills
by using the form of the Small Sided Games exercise.
1 INTRODUCTION
Small Sided Game (SSG) has gained the attention of
trainers and researchers around the world to get
special effects in an exercise (Joo et al., 2016). Small
Sided Games (SSG) is a game that has been modified
by the trainer to fit into a training context that has the
purpose of preserving and simplifying the
characteristics of the game sports (Clemente et al.,
2014). Characteristics of Small Sided Game (SSG)
are the reduced number of players and the reduced
size of the field is (Joo et al., 2016). Small Sided
Game (SSG) has been widely used by trainers to train
and develop some aspects of the practice such as: ball
control, technique, tactical, and physical players
adapted to actual soccer games (Joo et al., 2016;
Clemente et al., 2014; Dellal et al., 2011; Dellal et al.,
2012).
To face the competition, soccer players need
preparation in the form of ergonomic-looking
exercises where a form of training is tailored to the
actual game (Kelly and Drust, 2009). For professional
soccer teams, coaches tend to pay more attention to
improving skills and performance skills while
playing. In the meantime, the exercises for children
focus more on technical development and
coordination (Radziminski et al., 2013).
In the last decade, Small Sided Games (SSG) has
been widely used in the training process (Michailidis,
2013). The use of Small Sided Game is a basic capital
in training that has been recommended to trainers to
encourage in terms of significantly improving the
performance and efficiency of the exercise process
through a combination of physical components,
techniques and tactics (Owen et al., 2014). For soccer
players, the form of the Small Sided Games (SSG)
training can give high value to the touch with the ball
(Dellal et al., 2011). The study used Small Sided
Games (SSG) training form with 3 vs 3 + 2 Goal
Keepers or without Goal Keeper at all.
This research is intended to be able to answer
some questions that are:
Does the form of training of Small Sided
Games provide a significant influence on the
improvement of basic passing technique skills
in football?
Does the form of training of Small Sided
Games provide a significant influence on the
improvement of basic dribbling technique
skills in football?
Does the form of the training of Small Sided
Games give a significant influence on the
improvement of basic shooting technique skills
in football?
Rusdiana, A., Rahmatillah, M. and Asidik, D.
Improving Basic Football Technique Skill through Small Sided Games.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education (ICSSHPE 2017) - Volume 2, pages 245-247
ISBN: 978-989-758-317-9
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
245

2 METHODS
2.1 Participants
24 soccer athletes at one of the University clubs
namely PS UPI u-19 which is determined by
purposive sampling.
2.2 Procedures
The research method used is experimental method
with one group pretest-posttest design (Fraenkel et
al., 2013). The sample performs a pre-test then is
treated by using a Small Sided Games (SSG), and
ends with a post-test. This study was conducted four
times a week with a total of 16 meetings.
2.3 Instruments
This research instrument uses skill test Passing,
Dribbling, and Shooting. Data processing is done by
paired Sample t Test (SPSS).
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Passing
Figure 1 illustrates the difference from the initial test
results of passing test skills and final skill test results.
when viewed from the picture, the treatment by using
the form of exercise small sided games in improving
the basic engineering skills of passing in football
gives a significant influence. In this exercise the
player is required to be able to play as if they are in a
real game. So, it makes the player to be able to do a
lot of passing.
This suggests that small sided games can improve
basic passing skills in football.
Figure 1: Differences from preliminary test results
and final tests of passing.
3.2 Dribbling
Figure 2 illustrates the difference from the initial test
results of passing test skills and final dribbling skill
test results. Dribbling skills test based on time, the
faster the dribbling the better dribbling ability of a
football player is. The picture above shows a
significant improvement on the improvement of basic
dribbling technique skills after being treated by using
the form of Small Sided Games (SSG) training.
Football players often happen when facing the
opponent directly, therefore a football player is
required to be able to pass the opponent by using
dribbling.
Figure 2: Differences from preliminary test results
and final tests of dribbling.
This suggests that using a small sided games form
of exercise can have a significant effect on improving
basic dribbling technique skills in football.
3.3 Shooting
Figure 3 illustrates the differences from the initial test
results of shooting test skills and final shooting skill
test results. The picture above shows a significant
improvement on the basic shooting technique skills
after being treated by using the form of Small Sided
Games (SSG) training. When viewed from the goal of
playing football, that each team must score against the
opponent's goal. In addition to passing and dribbling
techniques, the form of small sided games training
also requires players to create as many goals as
possible. Therefore, this form of exercise is designed
so that players are trained to score goals like the
atmosphere in the actual game.
This suggests that using a small sided games form
of exercise can have a significant effect on improving
basic shooting technique skills in football.
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
246
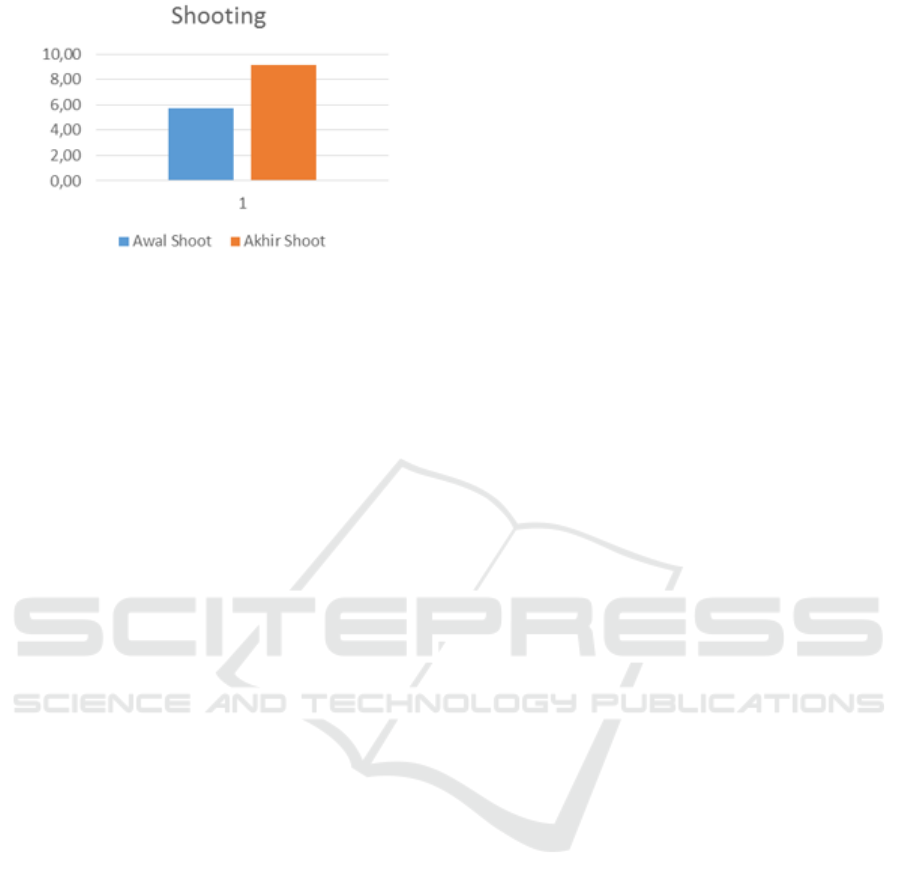
Figure 3: Differences from preliminary test results and
final dribbling tests.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The application of the training form of Small Sided
Games at the time of the exercise is very helpful in
improving the basic soccer technique skills. Good
basic soccer technique skills are essential to every
player in order to support performance during the
game. With the form of Small Sided Games (SSG)
training a lot of open for trainers to be able to use this
form of Small Sided Games (SSG) training in
creating an efficient exercise and improve exercise
performance. It has been shown that using Small
Sided Games (SSG) training can improve basic
technique skills in football games. The form of the
Small Sided Games (SSG) Training has a strong
reason so it will be very good if it is researched and
developed so we will get a variation of this form of
Small Sided Games (SSG) training.
REFERENCES
Clemente, F. M., Martins, F. M. L., Mendes, R. S., 2014.
Periodization Based on Small-Sided Soccer Games.
Strength and Conditioning Journal. 36(5), 34–43.
https://doi.org/10.1519/SSC.0000000000000067.
Dellal, A., Hill-Haas, S., Lago-Penas, C., Chamari, K.,
2011. Small-Sided Games in Soccer: Amateur vs.
Professional Playersʼ Physiological Responses,
Physical, and Technical Activities. Journal of Strength
and Conditioning Research. 25(9), 2371–2381.
https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181fb4296.
Dellal, A., Lago-penas, C., Wong, D. P., Chamari, K., 2011.
Effect of the number of ball contacts within bouts of 4
vs 4 small sided soccer games.pdf, 322–333.
Dellal, A., Owen, A., Wong, D. P., Krustrup, P., van Exsel,
M., Mallo, J., 2012. Technical and physical demands of
small vs. large sided games in relation to playing
position in elite soccer. Human Movement Science.
31(4), 957–969.
Fraenkel, J. R., Wallen, N. E., Hyun, H. H., 2013.
BİBLİYOGRAFİSİ Bulunacak. Climate Change 2013-
The Physical Science Basis. (Vol. 53).
https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004.
Joo, C. H., Hwang-Bo, K., Jee, H., 2016. Technical and
Physical Activities of Small-Sided Games in Young
Korean Soccer Players. Journal of Strength and
Conditioning Research. (Vol. 30).
https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0000000000001319.
Kelly, D. M., Drust, B., 2009. The effect of pitch
dimensions on heart rate responses and technical
demands of small-sided soccer games in elite players.
Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport. 12(4), 475–
479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2008.01.010.
Michailidis, Y., 2013. Small sided games in soccer training.
Journal of Physical Education and Sport. 13(3), 392–
399. https://doi.org/10.7752/jpes.2013.03063.
Owen, A. L., Wong, D. P., Paul, D., Dellal, A., 2014.
Physical and technical comparisons between various-
sided games within professional soccer. International
Journal of Sports Medicine. 35(4), 286–292.
https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1351333.
Radziminski, L., Rompa, P., Barnat, W., Dargiewicz, R.,
Jastrzebski, Z., 2013. A Comparison of the
Physiological and Technical Effects of High-Intensity
Running and Small-Sided Games in Young Soccer
Players. Int J Sports Sci Coach. 8(3), 455–465.
https://doi.org/10.1260/1747-9541.8.3.455.
Improving Basic Football Technique Skill through Small Sided Games
247
