
Initial Detection of Students’ Anxiety in The Activity of College
Orientation Through Brainwave Detector and Salivary Cortisol
Hormome Examination
Jajat Darajat Kusuma Nagara, Lucky Angkawidjaja and Agus Gumilar
Faculty of Sport and Health Education, Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Jln. Dr. Setiabudhi No. 229, Bandung, Indonesia
jajatdarajatkn@upi.edu
Keywords: Brainwave Detector (Attention), Salivary Cortisol Hormone and Level of Anxet.
Abstract: This study is aimed to obtain empirical evidence and fact in field about how the association or relatedness of
brainwave detector with salivary cortisol hormone function as initial indicator of anxiety in students who
follow the activity which is compulsory to be implemented namely College Orientation and Public Lecture.
All colleges in Indonesia conduct that activity. But this activity is regarded to be studied from its function,
benefit and level of anxiety obtained after following that activity. It is expected that this study can give the
picture about the effect of this activity on anxiety level. In this study, the researcher will take population of
two universities in west java who will follow college orientation activity. Sample are taken randomly with
total of 40 students. Based on data taken, it yields negative functional relation and contribution between
attention and cortisol response of -0.328 (p 0.039) and 10.8%, whereas between attention and anxiety yield
negative functional relation and contribution of 0.381 (p 0.015) and 14.5%. To examine the difference based
on university from three variables concerning attention and anxiety, there is no significant difference between
students in twice university, whereas in cortisol response there is significant different of 130.37% in p-value
of 0.000. In difference test based on gender in all variables, there is no significant difference between male
students and female students.
1 INTRODUCTION
Orientation time for campus acquaintance is
prevalent with various names for that activity. There
are called Orientasi Pengenalan Kampus (Ospek),
Masa Orientasi Siswa (MOS), Masa Pengenalan
Lingkungan Sekolah (MPLS), Masa Orientasi
Peserta Didik (MOPD), as study orientation which is
done in Indonesia University of Education called
masa orientasi kampus and kuliah umum
(MOKAKU), etc. Principally, all the activities above
have same purpose and they are expected to have
benefit and positive influence. Those activities not
only done in college but also done in elementary
school, junior high school and senior high school.
With that orientation activity, many students
experience mental pressure so it is worried that it
become anxiety or stress (Gómez, 2006). Stress can
be happening anytime, anywhere and whoever. This
anxiety is individual’s natural reaction toward the
problem faced.
The physical activity causes significant change in
endocrine system. Finally, this is related to protein
metabolism. Endocrine gland secrete hormone into
circulation, related to specific receptor in target cell,
and effected on specific gen expression (Blair and
Church, 2004). In cellular level. hormone can modify
membrane property and activate second messenger
which cause the change of transcription and
translation process to be occurred. In muscle cell,
cortisol is the only hormone which stimulate protein
degradation (Mooren and Volker, 2005). Cortisol is
categorized in catabolic hormone which is secreted in
physical and psychic stress condition. When
emotional, individual is in negative condition such as
stress, anxious, fear, and frustration, and his/her body
will secrete cortisol hormone. Cortisol hormone
release can activate sympathetic nerve system which
one of them is marked by heart rate increase (Linton
and Götestam, 1985). The high level of cortisol
hormone in blood also can reduce one’s thinking
ability and reaction. Cortisol hormone also play a
Nagara, J., Angkawidjaja, L. and Gumilar, A.
Initial Detection of Students’ Anxiety in The Activity of College Orientation Through Brainwave Detector and Salivary Cortisol Hormome Examination.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education (ICSSHPE 2017) - Volume 2, pages 349-353
ISBN: 978-989-758-317-9
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
349

role in reduction of mood and muscle fatigue (Daly et
al., 2004)
The anxiety will influence performance and
behavior in daily life (Hackney and Viru, 1999). In
industrial life, the higher level of stress is correlated
to disease and life excitement decline (Brown et al.,
1996).
In Korea, there are 1967 cases of stress which are
related to job. Almost half of them namely 49.5% of
974 people dead which caused by cardiac disease and
carotid artery disease (Aksorn and Hadikusumo,
2008).
This is exactly the same with what revealed by
(Belkic et al., 2004) that anxiety or stress implicate
75% cause cardiac disease and carotid artery disease.
The severe physical activity and pressures which
cause anxiety and stress will influence brain
performance which is marked by electricity activity
increase in the brain. This activity is caused by
biochemistry reaction in the brain and energy
transformation in the brain. As revealed in stress
management community in England that after stress
stimulation occurred, the brain will respond to
biological reaction in sympathetic nerve system and
will described through brain wave which is more
active. The high and low of brainwave depend on
stress factor experienced by someone. We all know
that brainwave is natural reaction occurred in the
brain which is result of stimulation then it changes to
become biochemistry reaction which produce
electricity and can be detected by using an instrument
called brainwave detector. There is various
brainwave namely delta, theta, alpha, beta and
gamma.
2 METHODS
2.1 Research Problem
In accord with explanation and background above,
then the problem of study is formulated in the form of
research question as follow:
How the amount of concentration (attention)
contribution toward cortisol hormone?
How the amount of concentration (attention)
contribution toward anxiety?
How is the association of concentration
(attention) and cortisol hormone?
How is the association of concentration
(attention) and anxiety?
2.2 Hypothesis of Study
There is contribution of significant
concentration (attention) toward cortisol
hormone;
There is concentration significant contribution
(attention) toward anxiety;
There is association of negative and significant
functional between concentration (attention)
and cortisol hormone;
There is association of negative and significant
functional between concentration (attention)
and anxiety.
2.3 The Aim of Study
The team of researchers will analyze how far the role
or contribution of brainwave toward activity of
cortisol hormone and anxiety (Brownlee et al., 2005).
In addition, the specific aim of this study is to obtain
empirical evidence about the big role of MOKAKU
activity which is related to its function, benefit and
anxiety toward freshmen of UPI and UNSIL in 2016.
It is expected that this study can open new
information which implement the importance of
MOKAKU activity toward its role and function as
freshmen orientation activity which is compulsory to
be done.
2.4 Research Methods
The study conducted is one shot case study which
obtain the data from population of two universities in
west java.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Hypothesis Testing
3.1.1 First Hypothesis
There is contribution of significant concentration
(attention) toward cortisol hormone.
Table 1: First Hypothesis.
Group of
Data
Mean
SD
r
R
2
P-Value
Conclusion
Attention
50.93
17.49
-.328
.108
.039
Significant
Cortisol
2.79
1.91
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
350
Sentence hypothesis for first hypothesis:
Ho: There is contribution of significant
concentration (attention) toward cortisol
hormone.
Ha: There is contribution of significant
concentration (attention) toward cortisol
hormone.
Criteria:
Ho is accepted if p-value > 0.05
Ho is rejected if p-values ≤ 0.05
Based on summary of calculation result of
Pearson correlation test in table 1, contribution result
is obtained of 10.8%, which means that contribution
of attention toward cortisol is 10.8and and the rest is
89.2% determined by another variable.
3.1.2 Second Hypothesis
There is contribution of significant concentration
(attention) toward anxiety.
Table 2: Summary of Calculation Result of Pearson
Correlation (Contribution) Test.
Group of
Data
Mean
SD
r
R
2
P-Value
Conclusion
Attention
50.93
17.49
-.381
.145
.015
Significant
Cortisol
2.79
1.91
Sentence Hypothesis for Second Hypothesis:
Ho: There is contribution of significant
concentration (attention) toward anxiety.
Ha: There is contribution of significant
concentration (attention) toward anxiety.
Criteria:
Ho is accepted if p-value > 0.05
Ho is rejected if p-value ≤ 0.05
Based on summary of calculation result of
Pearson correlation test in table 2, the result of
contribution obtain 14.5% which means that
contribution of attention toward anxiety is 14.5% and
the rest of 85.5% is determined by another variable.
3.1.3 Third Hypothesis
There is association of negative and significant
functional between concentration (attention) with
cortisol hormone response.
Table 3: Summary of Calculation Result of Pearson
Correlation (Contribution) Test.
Group of Data
Mean
SD
r
P-Value
Conclusion
Attention
50.93
17.49
-.328
.039
Significant
Cortisol
2.79
1.91
Sentence Hypothesis for Third Hypothesis:
Ho: There is no association of negative and
significant functional between concentration
(attention) and cortisol hormone response.
Ha: There is association of negative and significant
functional between concentration (attention)
and cortisol hormone response.
Criteria:
Ho is accepted if p-value > 0.05
Ho is rejected if p-value ≤ 0.05
Based on summary of calculation result of
Pearson correlation test in table 3, it is obtained
correlation result of -3.28 which means that if
concentration ability is decrease then cortisol
hormone response will increase.
3.1.4 Forth Hypothesis
There is association of negative and significant
functional between concentration (attention) and
anxiety.
Table 4: Summary of Calculation Result of Pearson
Correlation (Contribution) Test.
Group of Data
Mean
SD
r
P-Value
Conclusion
Attention
50.93
17.49
-.381
.015
Significant
Anextety
2.79
1.91
Sentence Hypothesis for Forth Hypothesis:
Ho: There is no association of negative and
significant functional between concentration
(attention) and anxiety.
Ha: There is association of negative and significant
functional between concentration (attention)
and anxiety.
Criteria:
Ho is accepted if p-value > 0.05
Ho is rejected if p-value ≤ 0.05
Based on summary of calculation result of
Pearson correlation test in table 4, it is obtained
correlation value of -381 which means that if
concentration ability is decrease then cortisol
hormone response is increase.
Initial Detection of Students’ Anxiety in The Activity of College Orientation Through Brainwave Detector and Salivary Cortisol Hormome
Examination
351
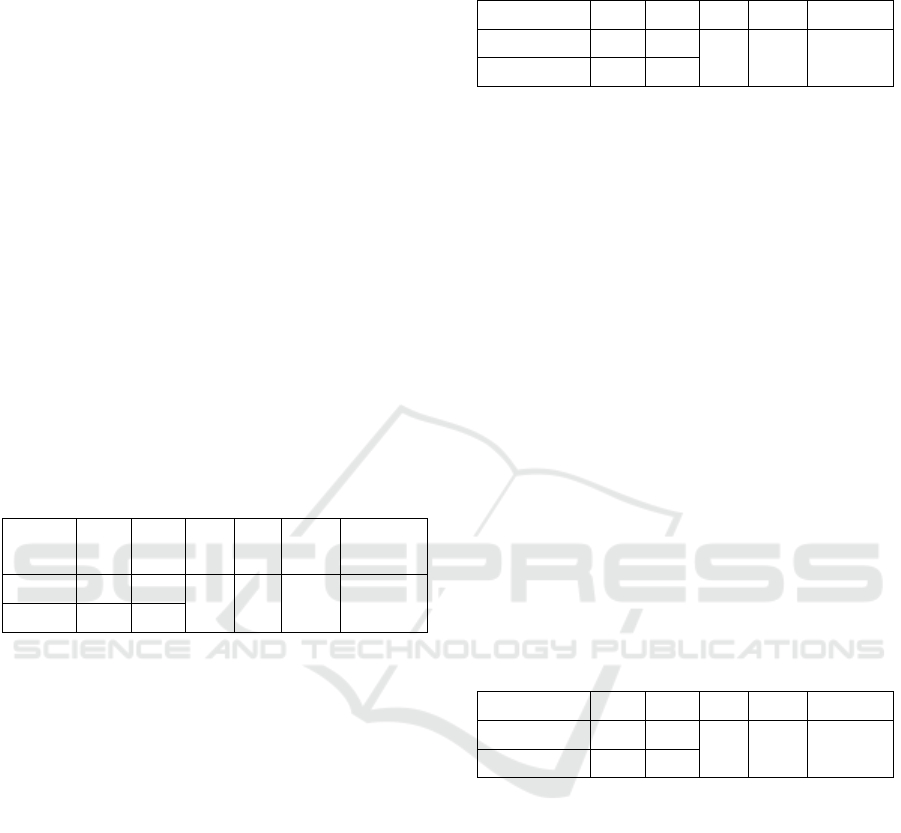
3.1.5 Difference Test
Table 5: Summary of Calculation Result of t-test
independent Based on University.
Based on table 5, sentence hypothesis for attention
difference test between UNSIL students and UPI
students:
Ho: There is no attention difference between UNSIL
students and UPI students.
Ha: There is attention difference between UNSIL
students and UPI students.
Sentence hypothesis for anxiety difference
between UNSIL students and UPI students:
Ho: There is no anxiety difference between UNSIL
students and UPI students
Ha: There is anxiety difference between UNSIL
students and UPI students.
Sentence hypothesis for cortisol difference
between UNSIL students and UPI students:
Ho: There is no cortisol difference between UNSIL
students and UPI students.
Ha: There is cortisol difference between UNSIL
students and UPI students.
Criteria:
Ho is accepted if p-value > 0.05
Ho is rejected if p-value ≤ 0.05
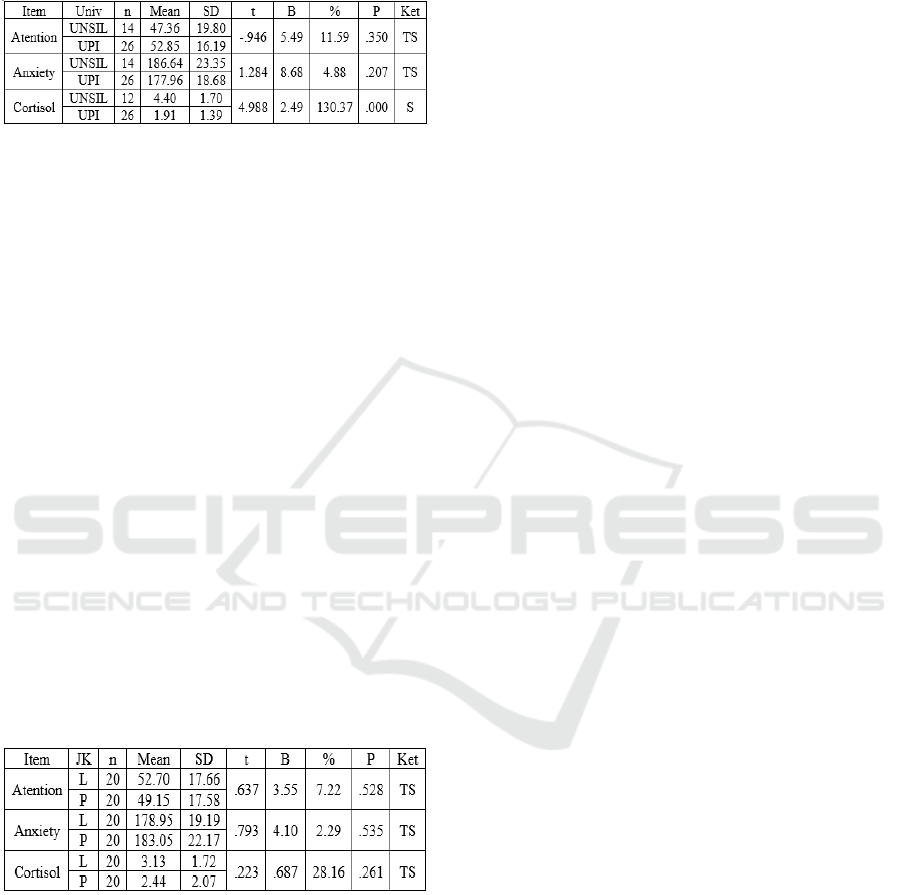
Table 6: Summary of Calculation Result of Independent t-
test Based on Gender.
Based on table 6 sentence Hypothesis for attention
difference between male students and female
students:
Ho: There is no attention difference between male
students and female students.
Ha: There is attention difference between male
students and female students.
Sentence hypothesis for anxiety difference
between male students and female students:
Ho: There is no anxiety difference between male
students and female students.
Ha: There is anxiety difference between male
students and female students.
Sentence hypothesis for cortisol difference
between male students and female students:
Ho: There is no cortisol difference between male
students and female students.
Ha: There is cortisol difference between male
students and female students.
Criteria:
Ho is accepted if p-value > 0.05
Ha is rejected if p-value ≤ 0.05
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on result of data collection, analysis result, data
processing and interpretation, study result, it can be
concluded that:
There is real contribution of concentration
(attention) toward cortisol hormone of 10.8%;
There is real contribution of concentration
(attention) toward anxiety of 14.5%;
There is negative functional association
between concentration (attention) and cortisol
hormone of -0.328;
There is negative functional association
between concentration (attention) and anxiety
of -0.381.
REFERENCES
Aksorn, T., Hadikusumo, B. H. W., 2008. Critical success
factors influencing safety program performance in
Thai construction projects. Safety Science. 46(4), 709-
727.
Belkic, K. L., Landsbergis, P. A., Schnall, P. L., Baker, D.,
2004. Is job strain a major source of cardiovascular
disease risk?. Scandinavian journal of work,
environment & health. 85-128.
Blair, S. N., Church, T. S., 2004. The fitness, obesity, and
health equation: is physical activity The common
denominator? JAMA. 292(10): 1232-1234.
Brown, J., Cooper, C., Kirkcaldy, B., 1996. Occupational
stress among senior police officers. British Journal of
Psychology. 87(1), 31-41.
Brownlee, K. K., Moore, A. W., Hackney, A. C., 2005.
Relationship Between Circulating Cortisol and
Testosterone : Influence of Physical Exercise. Journal
of Sports Science and Medicine. Vol 2005 (4) : 76-83.
Daly, W., Seegers, C., Timmerman, S., Hackney, A. C.,
2004. Peak cortisol response to exhausting exercise:
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
352

effect of blood sampling schedule. Medicina Sportiva.
8: 1-4.
Gómez, B. R., 2006. The Raletionship between the Levels
of Salivary Cortisol and the Presense of Xerostomia in
Menopasue Women. A Preliminary Study. Oral
Medicine and Pathology Journal. 11:B407-12.
Hackney, A. C. Viru, A., 1999. Twenty-four-hour cortisol
response to multiple daily exercise sessions of moderate
and high intensity.Clinical Physiology. 19 : 178-182.
Linton, S. J., Götestam, G., 1985. Relations between pain,
anxiety, mood and muscle tension in chronic pain
patients. Psychotherapy and psychosomatics. 43(2), 90-
95.
Mooren, F. C., Volker, K., 2005. Molecular and Cellular
Exercise Physiology, Human Kinetics. Champaign. IL.
Initial Detection of Students’ Anxiety in The Activity of College Orientation Through Brainwave Detector and Salivary Cortisol Hormome
Examination
353
