
Sharia Maqashid on the Fiscal Policy, the Urgency in the Modern Era
Any Setianingrum
Economics Faculty, YARSI University, Jakarta, Indonesia
anysetianingrum@yahoo.com, any.setianingrum@yarsi.ac.id
Keywords: District expenditures, district revenue, religions’ treasure, the level of benefits.
Abstract: The universality of shariah maqasid values is an instrument in designing economic policy according to current
human needs. Based on the results of Analytic Network Process (ANP), the ideal fiscal policy based on
maqashid shariah is the synergy of sources of income derived from existing APBD (regional income and
expenditure budgets) and religious property managed according to sharia. Sharia mechanisms requiring the
existence of special sources and allocations for the poor, the linkage of sources of income and allocation, the
separation of halal & haram sources, incentives on agricultural activities that contain technology and job
creation, and the implementation of priority-based spending based on the basic needs, infrastructure, MSMEs,
staff salaries and office buildings. The most recommended indicator of budget realization success is first gini
ratio, the second combined economic growth-gini ratio-volume of zakat. The next prospect of Islamic fiscal
will be able to improve equity distribution development, reduce expenditure irregularities, conflict of interest
and ultimately reduce dependence on taxes.
1 INTRODUCTION
The purpose of this research is to formulate the ideal
revenue and spending policy for modern governance
based on sharia maqashid. The purpose and target
above are due to the classic problem in almost all of
governments, including in Indonesia every year that
is the limited regional government budget and the
weaknesses in the system of spending priority in
dealing with many political conflict of interest.
Therefore tax incentives in social contributions by
individuals or households collected from various non-
profit organizations are an important source for the
basis of public finance (Bonke et al. (2011),
Carmichael (2012), Setianingrum, (2016)). The
pattern and philosophy of Islamic fiscal policy can be
empowered to minimize the limitations and
strengthen the benefits of conventional systems
(Afzalurrahman (1997), Chapra (2002, 1995, 1979),
Faridi (1995), Hafidhudhin (2002), Mannan (2000),
Metwally (1981&2008), Ra’ana (1997), Rahman
(1992), Sabzwari (1985), Yusoff (2006),
Setianingrum (2016)).
The maqashid shariah instrument can be used to
explore the pattern and philosophy. The universality
of sharia maqashid values is the instrument in
designing the economic policy to meet the needs of
modern people. Maqashid shariah will provide a
rational and substantial pattern of thought in
formulating economic policies and Islamic financial
products. Fiqh thinking alone will lead to a
formalistic and textual pattern of thought. It isshariah
only with the maqashid shariah approach that macro
and micro shariah policies can develop well and can
respond to the rapidly changing economic and
business progress (Auda (2011), Setianingrum,
2016)).
How to apply the pattern and philosophy of
Islamic fiscal policy required in the modern era?
Indeed, the financial policy of the local government
of Bekasi City cannot be compared to the Islamic
governance for apple-to-apple. However, the pattern
and philosophy of Islamic policy can be empowered
to strengthen the existing policy by synergizing both
systems and making it suited to the existing
regulation (Setianingrum, 2016). In Indonesia, the
step forward synergy has been marked by the law
number 38 of 1999 and number 17 of 2000. The law
states that zakah on income paid to official
institutions may be used as a deduction of taxable
income. The synergy of both must run in harmonious
and non-conflicting rules. The goals to be achieved
are determining the priority income instrument and
the scale of priorities of government spending in the
Setianingrum, A.
Sharia Maqashid on the Fiscal Policy, the Urgency in the Modern Era.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Islamic Economics, Business, and Philanthropy (ICIEBP 2017) - Transforming Islamic Economy and Societies, pages 5-9
ISBN: 978-989-758-315-5
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
5
maqashid sharia perspective in the modern era. The
management of criteria and sub criteria for
determining the priority of the revenue instrument
and the scale of the expenditure priorities, using the
analytical network process method.
2 RESEARCH METHOD
2.1 Analytic Network Process (ANP)
The stages in the ANP method are as follows ((Saaty
& Sodenkamp (2008), Yuksel & Dagdeviren (2007),
Gencer & Gurpinar (2006), Saaty et al. (2006),
Taslicali & Ercan (2006), Cheng & Li (2004)):
1) Interview Phase I: Conducting interviews to in-
depth informants on issues that are examined to
experts and practitioners who understand and
master the problem of government finances
comprehensively.
2) Decomposition: Decomposition to identify,
analyze, and structure the complexity of the
problem into the ANP network (details can be
seen in the ANP model constructs described
later).
3) Prepare the Questionnaire: Prepare a pair-wise
comparison based on ANP networks that have
been created.
4) Advanced Interview & Questionnaire Filling:
Conduct second interview in the form of
charging questionnaire to experts and
practitioners.
5) Informant ANP: Informants who fill the
questionnaire on the ANP method are: elements
of the Indonesian Ulema Council, as well as
academics, as many as 2 informants, the element
of National Amil Zakat as much as 1 informant,
the leadership element of Bekasi City
Government as much as 2 informants, local
legislative council, city of Bekasi as many as 3
people, academic elements as much as 1
informant.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The results show the consensus from the experts and
practitioners on how to strengthen the system of
Regional Government Budget management ideally
(which should) based on sharia maqashid as follows:
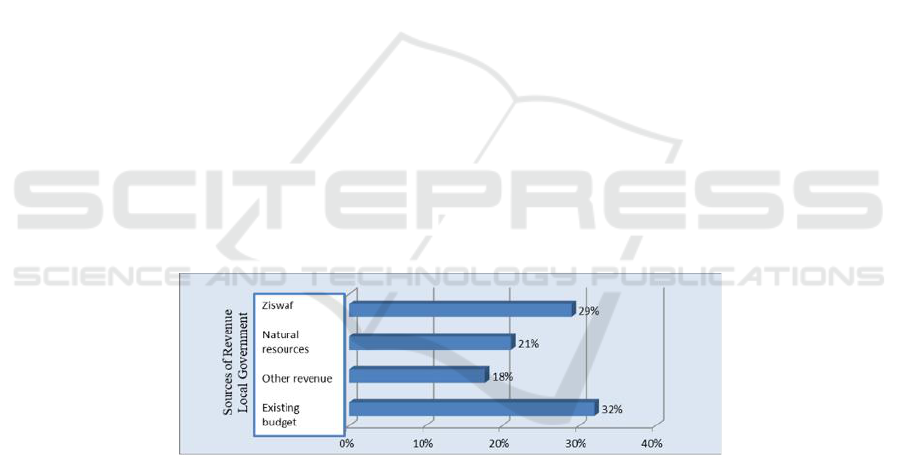
In Figure 3.1, the results of priority in the
intensification and extensification clusters of the
sources of revenue of local government show that, the
existing Regional Government Budget still becomes
the most influencing source for 32%, followed by
ZISWAF revenue (29%).
Figure 1: The Results of Synthesis in the Revenu in Strengthening the System of the Sharia Maqashid Based Regional
Government Budget Management.
The same part, the cluster of existing revenue
sources, the priorities in strengthening the system of
the sharia maqashid based regional government
budget are as follows: tax, retribution, duties (bea
perolahan) for 30%; followed by the central tax and
non-tax profit sharing (28%); Local companies,
Regional Owned Enterprises, Natural Resources
management (23%), profit sharing from Islamic bank
(11%), Conventional bank interest rate in the last
position (8%). For more results, it can be seen in
Figure 2.
ICIEBP 2017 - 1st International Conference on Islamic Economics, Business and Philanthropy
6
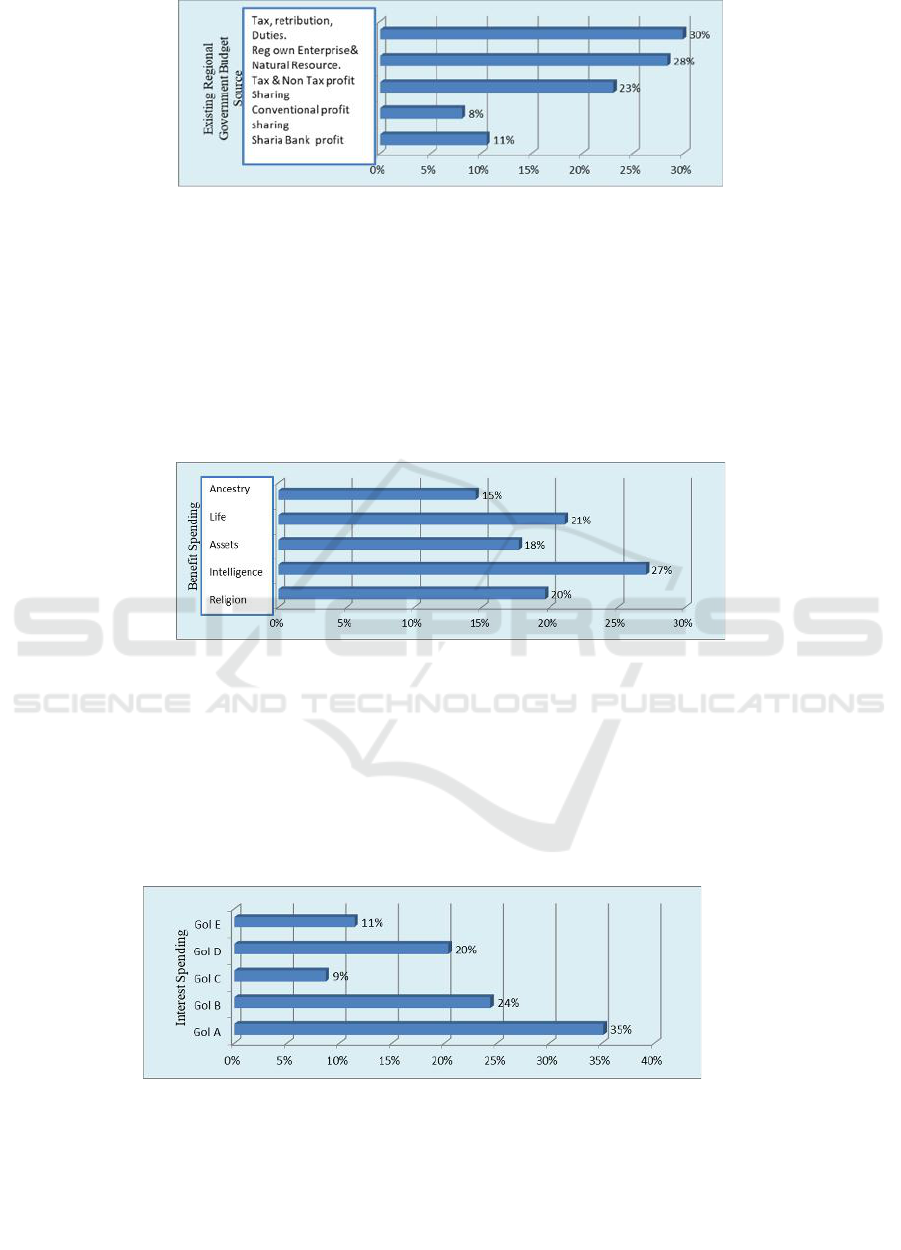
Figure 2: The Results of Synthesis of the Revenue in the Source of Revenue Aspect of Existing Regional Government Budget.
Based on the results of synthesis in this research,
the priority scales of the spending of local
government based on the ideal benefit, as seen in
Figure 3.6, are as follows: Intelligence spending
(belanja akal) (science and technology) 27%,
Followed by life spending (belanja jiwa) (Healthcare)
21%, Religion spending (belanja agama) (da’wah,
religion education) 20%, Assets spending (belanja
harta) (economic development) 18%, Ancestry
spending (belanja keturunan) (youth generation and
sustainable development). The results of consensus
from the ANP experts are different from the opinion
of Ash-Shatibi, who states that the order of benefit
priority, consecutively, is religion, life, intelligence,
ancestry, and assets.
Figure 3: The Results of Synthesis in Spending Based on the Level of Benefit
Meanwhile, in the aspect of priority scale, the
spending of local government based on the ideal
interest, as seen in Figure 3.7, are: Type A spending
(35%): General & Religion Education, Healthcare,
Poverty Reduction, Basic Needs Fulfillment. Type B
(24%): Public Infrastructures and Facilities. Type D
(20%): Economic Development, SME, Job
opportunity, Food Security, Living Environment,
Energy, Technology. Type E (11%): Employee
spending, Interest, Hibah (Grants), Social and
Financial Assistances. Type C (9%): Construction of
office building and infrastructures of the bureaucracy.
Figure 4: The Results of Synthesis in the Spending in Strengthening the System of Regional Government Budget Management
based on Sharia Maqashid.
While the indicator of success of local
government (see Figure 3.8), the type of indicator that
is considered most appropriate according to the
experts is gini ratio (43.3%), then mixed indicators
consisting of economic growth, per capita income,
gini ratio and volume of zakat (27.9%). Other
Sharia Maqashid on the Fiscal Policy, the Urgency in the Modern Era
7
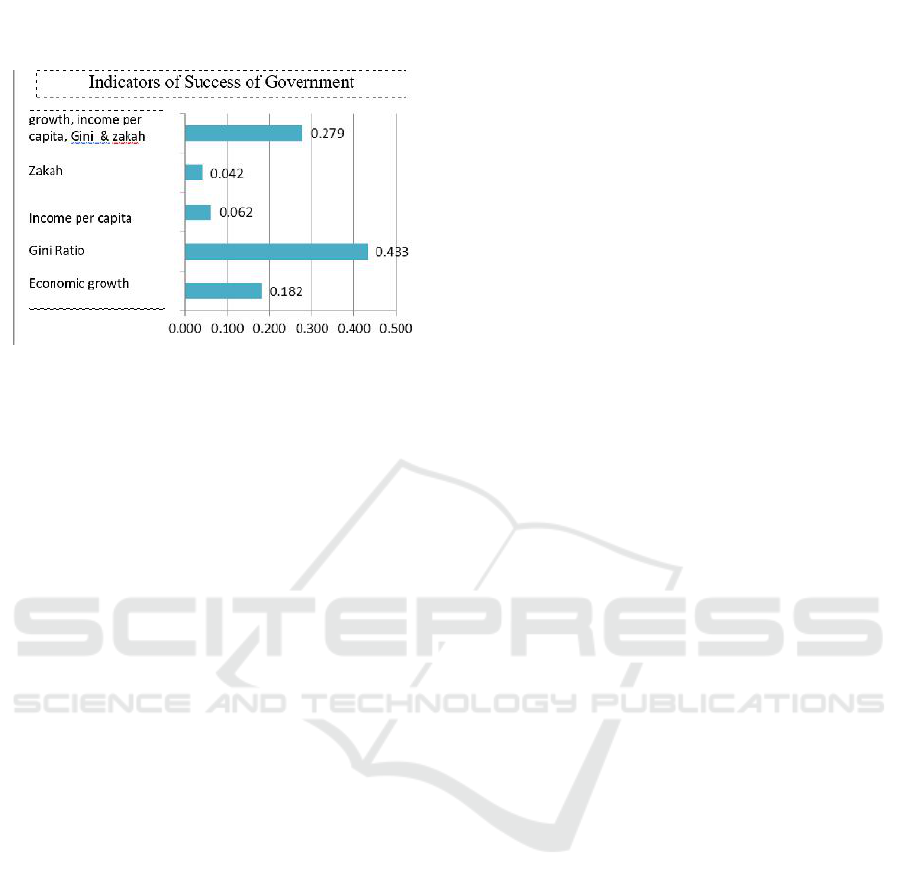
indicators are regional economic growth (18.2%), per
capita income (6.2%) and volume of zakat (4.2%).
Figure 5: Indicators of Success of Government.
4 CONCLUSION
In general, the sharia maqashid based on ideal
formulation of revenue and spending policy are as
follows: The instruments of revenue consist of
existing Regional Government Budget, Natural
Resources, and religion's treasures. Require a linkage
between the revenue and allocation in order to reduce
the deviation or misallocation and to improve the use
of Regional Government Budget. The benefit-based
spending priority is protection against religion, life,
intelligent, ancestry, and assets. The implementation
of sharia maqashid based spending priority is as
follow:1) General & Religion Education, Healthcare,
Poverty Reduction, Basic Needs Fulfillment; 2)
Public Infrastructures & Facilities; 3) Economic
Development, SME, Job opportunity, Living
Environment, Energy, Technology; 4) Employee
Spending, Interest, Grants, Social and Financial
Assistances; 5) The construction of the office
building and infrastructures of the bureaucracy
Indicators of successful development are: Gini
ratio as main incator, supporting indicators are
economic growth, income per capita, zakah volume.
A need to separate the halal and non-halal sources on
revenue and allocation.
Implementation of shari'ah maqashid values in
fiscal policy will have additional funding prospects
for development, increased community participation
through infaq, shadaqah, waqf (public fund
participation), and create more substantive spending
priority standards based on the benefit levels of
daruriyat, hajiyat and tahsiniyat. The prospect of
subsequent effects will be able to improve equity
distribution development, increased government
investment, MSME sector and employment, reduce
expenditure deviations, reduce dependence on taxes,
and controlling the tax rate so as not to disrupt the
business world.
REFERENCES
Afzalurrahman, 1997. Muhammad: Encyclopedia of
Seerah, volume II, London, The Muslim School Trust,
1982. Edisi Indonesia Muhammad sebagai Seorang
Pedagang. Yayasan Swarna Bhumi, Jakarta.
Auda, J., (2011). A Maqaside Approach To Contemporary
Application of The Share’ah. Intellectual
Discourse:Kuala Lumpur, Vol.19, Iss 2, 2011:193-217.
Bonke, T., Massarrat, N., Sielaff, M.C., 2011. Charitable
Giving in The German Welfare State:Fiscal Incentives
and Crowding Out. Journal Springer Science &
Business Media, LLC
Carmichael, C.M., 2012. Dispensing Charity:The
Deficiencies of An or Nothing Fiscal Concept.
Voluntas, Volume 23, Issue 2, Pages 392-414. Springer
Science & Business Media, Baltimore, Netherlands.
Chapra, M.U., 1979. The Islamic Welfare State and its Role
in The Economy. Leicester, UK: The Islamic
Foundation.
Chapra, M.U., 1995. Reading in Public Finance in Islam:
Goverment Borrowing Needs. IRTI, IDB, Jeddah,
Saudi Arabia
Chapra, M.U., 2002. The Future of Economics, An Islamic
Perspective, SEBI, Jakarta
Cheng, E.W.L, Li, H., (2004). Construction Selection
Using The Analytic Network Process. Construction
Management and Economics (December 2004) ISSN
0144-6193 print/ISSN 1466-433Xonline @2004,
Taylor & Francis Ltd. http://www.tandf.co.uk/journals
DOI:10.1080/0144619042000202852 . Department of
Building and Real Estate, The Hong Kong Polytechnic
University, Hunghom, Kowloon, Hong Kong
Faridi, F.R., 1995. Readings In Public Finance In Islam:
Theory of Fiscal Policy in an Islamic State. Islamic
Research And Training Institute, Islamic Development
Bank, , Jeddah, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Gencer, C., Gurpinar, D., 2006. Analytic NetworkProcess
in Suplier Selection: A Case Study in an Electronic
Firm. Applied Mathematical Modelling 31 (2007)
2475-2486. Gazi University, Faculty of Engineering
and Architecture, Department of Industrial
Engineering, 06570 Maltepe/Ankara, Turkey.
Hafidhuddin, D. (2002). Zakat dalam Perekonomian
Modern. Jakarta: Gema Insani Press
Mannan M.A. 2000. Effects of Zakah Assessment and
Collection on the Redistribution of Income in
Contemporary Muslim Countries, in Imtiazi et al (ed),
Management of Zakah in Modern Muslim Society.
Jeddah: IRTI-IDB.
Metwally, 1981. Macroeconomic Models of Islamic
Doctrines. JK Publisher
ICIEBP 2017 - 1st International Conference on Islamic Economics, Business and Philanthropy
8

Metwally, 2008. Fiscal Policy in a Islamic Economy. Fiscal
Policy and Resourches Allocation in Islam, Edited by
Ahmed, Z., Iqbal, M., Khan, M. IRTI and Institute of
Policy Studies, Islamabad
Ra'ana, Irfan Mahmud, 1997. Ekonomi Pemerintahan
Umar ibn Al – Khattab, Pustaka firdaus, Cet ke-3,
Jakarta
Rahman A, 1992. Doktrin Ekonomi Islam Jilid 1. PT Dana
Bakti Wakaf, Yogyakarta.
Saaty, T.L and Sodenkamp, M, 2008. Making Decision In
Hierarchic And Network System. Journal of Applied
Decision Sciences, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 24–79, 2008.
Saaty, Thomas L and Vargas, Louis G. 2006, Decision
Making with the Analitic Network Process. Economic,
Political, Social and Technological Applications with
Benefits, Opportunities, Costs and Risks. Springer.
RWS Publication, Pittsburgh.
Sabzwari, 1985. Economic and fiscal System During
Khilafat E-Rashida, dalam jurnal of Islamic Banking
and Finance, Karachi, Vol.2, No.4,1985.
Setianingrum, A., 2016. Dissertation: Strengthening of
Local Government Revenue and Spending Management
System based on Sharia Maqashid at Bekasi City, Post-
Graduate Program, Airlangga University, Surabaya,
Indonesia.
Taslicali, A.K., Ercan, S., 2006. The Analytic Hierarchy &
The Analytic Network Processes in Multicriteria
Decision Making: A Comparative Study. Turkish Air
Force Academy Aeronautics and Space Technologies
Institute Yesilyurt, Istanbul. Journal of Aeronautics
and Space Technologies, July 2006 Volume 2 Number
4 (55-65).
Yuksel, I and Dagdeviren, M, 2007. Using The Analytic
Network Process (ANP) In A SWOT Analysis: A Case
Study For A Textile Firm. Information Sciences, vol.
177, no. 16, pp. 3364–3382, 2007
Yusoff, M.B, 2006. Fiscal Policy in An Islamic Economy.
IIUM Journal of Economics and Management,Vol:
14/Issue: 2, 2006.
Sharia Maqashid on the Fiscal Policy, the Urgency in the Modern Era
9
