
Can Islamic Bank Satisfy Their Customer?
Arief Helmi and Taufan Untoro
Faculty of Economic and Business, University of Padjadjaran, Indonesia
arief.helmi@unpad.ac.id
Keywords: Islamic Bank, Customer Satisfaction, Factor Analysis.
Abstract: Not less than 85% of Indonesian population is Moslem, and in Indonesia the number of Islamic bank has been
growing significantly since the first Islamic bank was founded in 1991. However, the market share of Islamic
bank is relatively low. It was hypothesized that Islamic bank has not been able to provide their customer the
optimum level of financial service or reach their customer satisfaction. In order to measure the customer
satisfaction with Islamic bank, this study attempted to find factors which affect customer satisfaction, by using
factor analysis method. Data was collected by distributing questionnaire to 180 respondents, who become the
customer of saving program of Islamic bank and conventional bank. This study found 12 factors that affect
customer satisfaction: responsiveness, assurance, reliability, supporting facilities, empathy, bank stability,
product, social facilities, cost, convenience, accessibility, and brand. This study also rejected the hypothesis
that Islamic bank is not able to satisfy their customer.
1 INTRODUCTION
Indonesian banking now is embracing dual bank
system or dual banking system. By having dual bank
system, banks in Indonesia can choose to run their
operating system with conventional banking system
or with Islamic banking system.
The development of Islamic banking system in
Indonesia is within the framework of Indonesian
Banking Architecture, in order to serve an alternative
banking services to Indonesian people. The Islamic
banking system and conventional banking system are
expected to move synergistically to support the
mobilization of public funds, and to improve
financing capabilities for the national economic
sectors.
By observing banking industry in Indonesia, we
will find tight competition between banks year after
year. One key to deal with the competition is by
achieving customer satisfaction. Every bank in
Indonesia has been very aware of the importance of
consumer satisfaction. This is what causes the
investment of large amounts of investment programs
to increase consumer satisfaction is common in the
banking industry.
Loyalty of a firm’s customer has been
recognised as the dominant factor in a business
organization’s success (Kandampully and Dwi,
2000).
Customer satisfaction is an important issue for
marketing managers, particularly those in services
industries. However, it appears that achieving
customer satisfaction is often the end goal (Bennett
& Rundle, 2004). While, Levesque & McDougall
(1996) points out that customer satisfaction and
retention are critical for retail banks, and
investigates the major determinants of customer
satisfaction and future intentions in the retail bank
sector.
Not less than 85% of Indonesian population is
Moslem, and in Indonesia the number of Islamic bank
has been growing significantly since the first Islamic
bank was founded in 1991. However, the market
share of Islamic bank is relatively low. It was
hypothesized that Islamic bank has not been able to
provide their customer the optimum level of financial
service or reach their customer satisfaction.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Consumers not only expect service providers to be
able to provide their service properly, but consumers
expect more than that, they expect the service
providers are able to meet their desire in terms of
Helmi, A. and Untoro, T.
Can Islamic Bank Satisfy Their Customer?.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Islamic Economics, Business, and Philanthropy (ICIEBP 2017) - Transforming Islamic Economy and Societies, pages 251-255
ISBN: 978-989-758-315-5
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
251

consumer satisfaction. Satisfaction is the feeling of
pleasure or disappointment of someone who emerged
after comparing the provided performance of service
to the expected (Schiffman & Kanuk, 2012, Kotler &
Keller 2014).
Meanwhile, A Parasuraman, Zeitham and Berry
(1985) proposed a conceptual model of consumer
expectations for services. The model identified ten
major determinants of consumer expectations. The
ten determinants are : enduring service intensifiers,
personal needs, transitory service intensifiers,
perceived service alternatives, self-perceived services
roles, situational factors, explicit service promises,
implicit service, word of mouth, and past experiences,
To measure service performance A Parasuraman,
Zeithaml and Berry (1985) introduced service quality
dimensions. These dimensions need to be considered
carefully by service provider, so that consumers get
the performance of services in accordance with
expectations. The service quality dimensions which
often used in research are the five dimensions of
service quality, which consists of: reliability,
responsiveness, assurance, empathy and tangibles.
Reliability is the ability to perform the promised
service dependably and accurately. Responsiveness is
the willingness to help customers and provide prompt
service. Assurance is knowledge and courtesy of
employees and their ability to convey trust and
confidence. Empathy is caring, individualized
attention the firm provides its customers. While
tangible is appearance of physical facilities,
equipment, personnel, and communication materials.
While, Mittal & Lassar (1998) found that
satisfaction is driven more by “technical quality”
(the quality of the work performed) than by
“functional quality” (how the service work was
delivered); however, once satisfaction is achieved,
loyalty is driven more by functional than by
technical quality. This is the pattern of influence
for a “low contact” (where customers’ direct
contact with service providers is absent or
marginal) service. For a “high contact” service, the
pattern of influence is exactly the reverse. Of
significant importance to service managers, the
paper explains the dynamics of loyalty versus
satisfaction and derives their managerial
implications.
Ganguli & Roy (2011) proposed four generic
service quality dimensions in the technology‐
based banking services – customer service,
technology security and information quality,
technology convenience, and technology usage
easiness and reliability. It was found that customer
service and technology usage easiness and
reliability have positive and significant impact on
customer satisfaction and customer loyalty. It was
also found that technology convenience and
customer satisfaction have significant and positive
impact on customer loyalty.
Service quality influences relative attitude and
satisfaction, satisfaction influences relative
attitude, repurchase, and recommendation but has
no direct effect on store loyalty. Fostering
favorable relative attitude and getting customers to
recommend the product or service holds key to
fostering store loyalty. Results also indicate
support for Oliver’s four‐ stage cognitive‐
affective‐ conative‐ action model of loyalty
(Sivadas & Baker‐ Prewitt, 2000).
Measuring customer satisfaction is very
important, customer satisfaction indexes as a base for
new strategic marketing management (Karolina
Ilieska, 2013). Y.Hu (2011) found that relationships
between perceived value, customer satisfaction, and
purchase intention. While H Singh (2006) indicated
that there is also a positive connection between
customer satisfaction, loyalty and retention. Selnes,
(1993) suggested that companies should monitor and
improve both customers satisfaction and brand
reputation.
In order to measure customer satisfaction Kotler
& Keller (2014) identified four methods, including:
complaints and feedback system, mystery shopping,
lost costumer analysis, and consumer satisfaction
survey.
3 METHODS
This is an exploratory research method. Customer
survey is the main method to collect primary data.
Non-probability sampling was used to select
respondent and respondent are customer of Islamic
bank. To determine factors influencing customer
satisfaction, confirmatory factor analysis is used,
followed by measuring the customer satisfaction by
calculating customer satisfactory index.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
To determine what factors influencing customer
satisfaction of Islamic Banking, factor analysis is
used to data that has been collected through survey.
Factor analysis with the help of SPSS 17 followed the
process of testing the adequacy of data onto Kaiser-
Meyer-Olkin (KMO) value measurement and by the
measure of sampling adequacy (MSA) for subsequent
calculated Eigen value (loading factor). Based on
Eigen values of the 51 indicators, 12 groups were
obtained which has Eigen value of more than 1.00.
ICIEBP 2017 - 1st International Conference on Islamic Economics, Business and Philanthropy
252
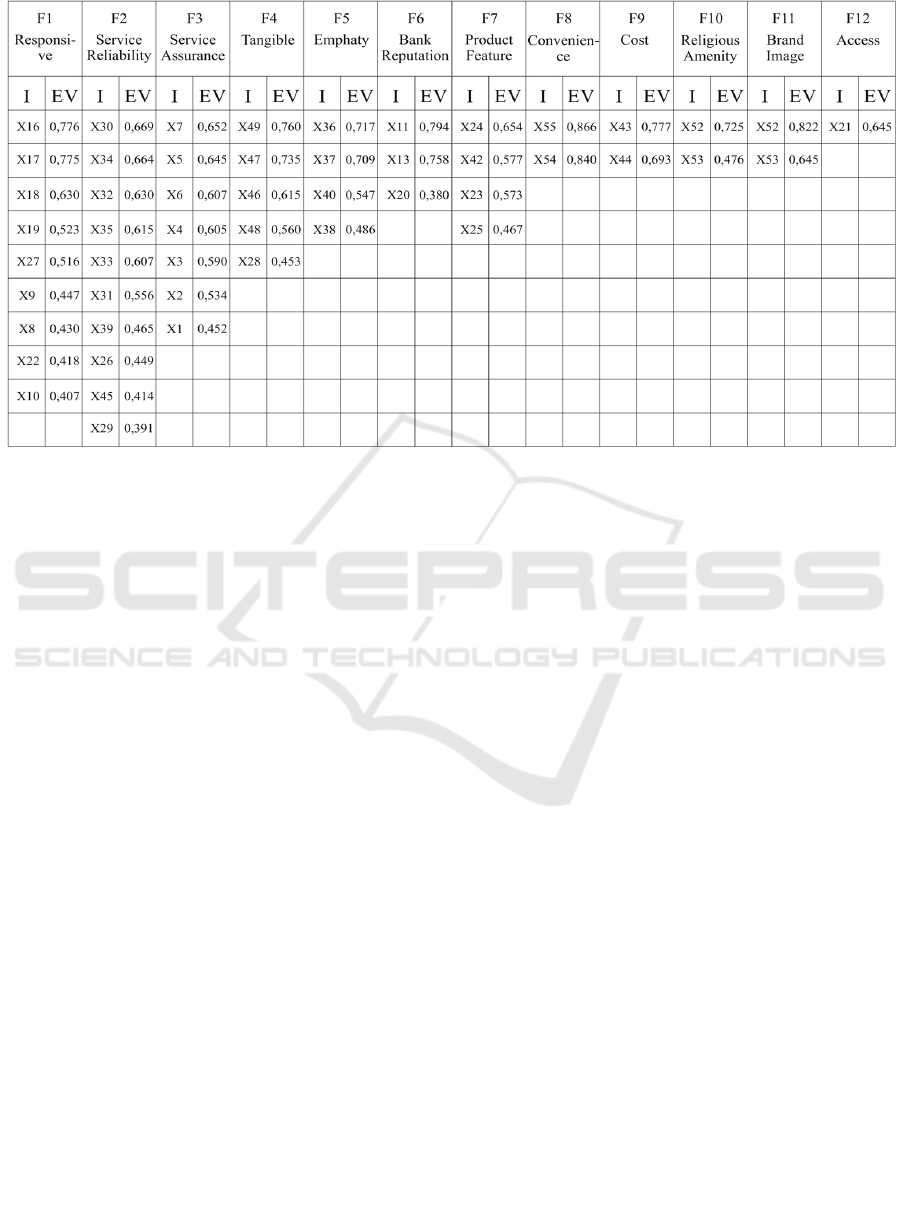
Table 1: Factor Influencing Customer Satisfaction.
The 12 groups hereinafter referred to as 12 factors
which influencing customer satisfaction of Islamic
bank. Considering the content of each factor, the 12
factors are identified as: responsiveness, service
reliability, service assurance, tangible, empathy, bank
reputation, product feature, convenience, cost,
religious amenity, brand image, access.
In an effort to find the factors that determine the
consumer satisfaction of Islamic banks, the first
factor is formed from the grouping of nine indicators.
This factor can be labeled as Responsiveness. This
factor assigns Islamic bank to manage the system and
bank employees in order to provide convenience and
speed in serving customers, such as skill, hospitality
and speed of officers when delivering bank service.
Furthermore, there are ten indicators that form on
the second factor, these 10 indicators of factor formed
from elements of assurance and empathy of service
quality. This second factor contains the customer's
expectation of the security and accuracy of the
transaction bank, the performance of the system of
recording and the accuracy of the system and the bank
officer in delivering service. Based on the indicators
which formed of this factor, then this second factor is
labeled as Service Reliability.
In order to effectively able to satisfy their
customers, Islamic banks should pay attention to the
third factor, namely Service Assurance. This factor
requires the Islamic bank to have the ability to
providing optimal operational services and according
to the promise. For example, the clarity and easiness
of bank transaction procedures, the convenience of
office hours, and the skills of bank’s officers when
serving customer.
Furthermore, the factors that determine customer
satisfaction is Tangible factor. Tangible factor is
physical evidence that strongly supports customer
satisfaction. Islamic bank must pay attention to the
availability and appearance of the office and ATM
machines, tidiness of bank officers, even the
availability of parking lots.
Pantouvakis & Lymperopoulus (2008) confirm that
the physical elements of the service are of greater
importance in determining customer evaluations on
overall satisfaction than interactive features of
service.
As a service provider, Islamic bank is also highly
expected to provide empathy to its customers. The
willingness of bank employees to understand and hear
needs, wants or problems is important. Islamic bank
must guarantee the totality of bank employees to
provide the best service during banking hour to all
customers without discrimination.
The customer's perception of the bank's health
also determines its satisfaction, Islamic bank is
expected to be health and strength as a financial
institution. The resilience of Islamic bank to
economic crisis and bankruptcy is a requirement.
The seventh factor, considering the content of
indicator clustered is appropriate to be labeled as
Product Factor. This factor requires the Islamic bank
to provide variation of saving and loan product in
accordance with the needs and wants of customers.
Can Islamic Bank Satisfy Their Customer?
253

As to this factor, the wide-ranging of bank service as
a financial institution, such as inter-bank transfer and
as payment point also become customer expectations
Customer satisfaction of Islamic bank, is also
determined by the religious amenity, which concerns
with the availability of good mosque and toilets. The
existence of this factor becomes interesting, because
as certain religion bank Islamic bank has a close
perception with the activities of worship, therefore
the availability of means of worship becomes
important.
In particular, Islamic bank customers also
emphasize their convenience when visiting the bank
office. Customer requires a fine waiting room and
clarity of banking information either that they can
read through signage or explanation officer. This
factor is called Convenience Factor.
Another intangible that also determines customer
satisfaction of Islamic bank is relying on Image Bank.
Customer expects that Islamic bank to be well-
known, highly-reputable, and financially strong.
Customer satisfaction has a significant relationship
with image (Amin and Rodrigue, 2013). Selnes
(1993) confirmed that brand reputation is the
strongest driver of customer loyalty
For Islamic bank, another important factor which
also determines customer satisfaction is
Accessibility. Customer expects Islamic bank to
guarantee access adequacy by the availability of
branch-office, ATM, branchless bank service and
reliable internet banking.
All bank to impose a certain cost of each service
they provide. As cost is also determines customer
satisfaction Islamic bank should set an acceptable
explicit costs such as fee and interest and implicit
costs such as compensation for bank errors in serving.
Except customer service, Santouridis and Trivellas
(2010) stated that pricing structure and billing
system are the service quality dimensions that have
the more significant positive influence on customer
satisfaction.
After determining 12 factors that affect customer
satisfaction, the customer satisfaction index of
Islamic bank in Indonesia will be revealed.
Table 2: Customer Satisfaction Index.
Factor
Index
Satisfaction
Responsiveness
3,79
High
Service Reliability
3,74
High
Service assurance
3,73
High
Tangible
3,67
High
Empathy
3,66
High
Bank Reputation
3,63
High
Product Factor
3,47
Moderate
Convenience
3,79
High
Cost
3,51
Moderate
Religion Ammenity
3,37
Low
Brand Image
3,93
High
Acces
3,50
Moderate
Islamic bank in Indonesia has managed to attain
customer satisfaction with high level, customer not
only get satisfied by the service reliability and
assurance which is the core product, but also satisfied
by the attribute product of Islamic bank, such as their
empathy and their service-cape, except religion
amenity. Islamic bank in Indonesia was believed to
have reliable service by implementing ‘syaria’
banking operation
Customer is also impressed by Islamic bank
reputation and image. As a financial institution,
Islamic bank in Indonesia demonstrated satisfactory
financial achievement. However, Islamic bank in
Indonesia has not really successful in fulfilling
customer need or wants to the variety of bank’s
product, bank expenses and digital access to bank
services.
5 CONCLUSION
The determinants of customer satisfaction Islamic
bank consist of twelve factors. The twelve factors are
as follows: responsiveness, service reliability, service
assurance, tangible, empathy, bank reputation,
product feature, convenience, cost, religious amenity,
brand image, and access. The level of customer
satisfaction of Islamic bank in Indonesia is high.
Customer highly satisfied by reliability, assurance,
responsiveness and reputation of Islamic bank,
however they moderately satisfied by product,
expenses and digital access.
REFERENCES
A. Parasuraman, Zeithaml Berry, 1985, A Conceptual
Model of Service Quality and its Impication for Future
Research, Journal of Marketing, Vol. 49, No. 4.
Harkiranpal Singh, 2006, The Importance of Customer
Satisfaction in Relation to Customer Loyalty and
Retention, UCTI Working Paper WP-06-06 May 2006.
Ganguli, Shirshendu and Roy, Sanjit Kumar, 2011,
Generic technology
‐
based service quality
dimensions in banking: Impact on customer
satisfaction and loyalty, International Journal of Bank
Marketing, Vol. 29 Issue: 2.
ICIEBP 2017 - 1st International Conference on Islamic Economics, Business and Philanthropy
254

Kandampully, Jay and Dwi Suhartanto, 2000, Customer
loyalty in the hotel industry: the role of customer
satisfaction and image, International Journal of
Contemporary Hospitality Management, Vol. 12
Issue: 6.
Karolina Ilieska, 2013. Customer Satisfaction Index – as a
Base for Strategic Marketing Management, TEM
Journal, 2(4).
Kotler Philip and Keller. Warren 2014, Marketing
Management, Prentice Hall.
Levesque, Terrence and McDougall, Gordon H.G, 1996,
Determinants of customer satisfaction in retail
banking, International Journal of Bank Marketing,
Vol. 14 Issue: 7
Mittal, Banwari and Lassar, Walfried M, 1998, Why do
customers switch? The dynamics of satisfaction
versus loyalty, Journal of Services Marketing, Vol. 12
Issue: 3
Santouridis, Ilias and Trivellas, Panagiotis, 2010,
Investigating the impact of service quality and
customer satisfaction on customer loyalty in mobile
telephony in Greece, The TQM Journal, Vol. 22
Issue: 3
Schiffman and Kanuk.2014.Consumer Behavior, 11th
Edition.New Jersey:Pearson
Selnes, Fred, 1993, An Examination of the Effect of
Product Performance on Brand Reputation,
Satisfaction and Loyalty, European Journal of
Marketing, Vol. 27 Issue: 9
Sivadas, Eugene and Baker, Jamie L, Prewitt, 2000, An
examination of the relationship between service
quality, customer satisfaction, and store
loyalty, International Journal of Retail & Distribution
Management, Vol. 28 Issue: 2
Y.Hu, 2006, Relationship between Perceived Value,
Customer Satisfaction, and Purchase Intention,
Advances In ComputerScience Intellegent System and
Environment
Can Islamic Bank Satisfy Their Customer?
255
