
Development Strategy For Islamic Microfinance Institution In
Indonesia: Ifas-Efas Matrix Approach
Tika Widiastuti
1
, Aam S. Rusydiana
2
and Irman Firmansyah
3
1
Faculty of Economic and Business, Airlangga University, Jl Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
2
SMART Consulting Indonesia, Perumahan Haji Cimahpar, Bogor, Indonesia
3
Siliwangi University, Jl Siliwangi 24, Tasikmalaya, Indonesia
tika.widiastuti@feb.unair.ac.id, aamsmart@gmail.com, irmanfirmansyah@unsil.ac.id
Keywords: Strategy, IFAS-EFAS matrix, Islamic Microfinance Institutions, SWOT analysis.
Abstract: The emergence of IMFIs (Islamic Microfinance Institution) in Indonesia is an answer to Islamic Banks
development that shows middle-top class orientation. In fact, IMFIs have evolved as alternative solution for
Indonesian economic relief, especially as partners for small businesses in capital provision. Despite rapid
growth, IMFIs still face many obstacles in their development. Those obstacles come from both internal and
external factors. This study aims to identify causes and dominant inhibitors for the development of IMFIs in
Indonesia by using SWOT (Strengths-Weaknesses-Opportunities-Threats) analysis as well as IFAS-EFAS
(Internal Factor Analysis Summary-External Factor Analysis Summary) matrix approaches. Data analysis
will be followed by proposed recommendations. According to IFE (Internal Factor Evaluation) result, the
primary strength of IMFIs is their segmentation on Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) and
followed by local society high initiative. Meanwhile, highest rank for weakness of IMFIs is human
resources’ and entrepreneurship training cost and followed by legal registration cost. On the other side, EFE
(External Factor Evaluation) analysis result indicate that highest opportunity for IMFIs is flexibility on
economic sector with society’s high willingness to conduct sharia-based transaction as the second place.
Meanwhile, the highest rank of threat is high competition among IMFIs, while weak regulations and legality
for the IMFIs become their second-ranked threat. Mutual commitment between the stakeholders such as the
regulators, academicians, and practitioners is needed to encourage development of IMFIs as part of Islamic
financial industry.
1 INTRODUCTION
The background of IMFI establishment was to be the
answer to the demands and needs of Muslims. In
Indonesia, BMT’s growth in 2010 positioned on
average range in terms of assets between 35% -
40%, with financing to deposit ratio (funds
disbursed) still around 100% (Suharto, 2010). It
proves community’s acceptance of IMFI’s existence
as an institution that can empower the marginalized
segment of community. However, the existence of
IMFIs with significant numbers, is not supported by
the much-needed supporting factors that would
enable IMFI to continue growing and working
properly. moreover, many IMFIs face declination
and even went out of business.
Then, majority of businesses in Indonesia are run
as MSMEs - sectors that do not have large capital -,
so this factor becomes a very potential segment for
IMFIs to develop. Therefore, if the IMFI is widely
known by the public, then the financing will be
easily distributed. IMFI is an institution whose
existence is very helpful for the community,
especially among micro segments.
In addition, Muslim societies fare far worse than
the rest of the world in the matter of addressing the
problem of poverty. In Indonesia alone with world’s
largest Muslim population, over half of the national
population are poor or vulnerable to poverty with
incomes less than merely US$2 a day. Those poverty
levels have also been associated with high inequality
alongside low productivity (Karim et al., 2008).
Therefore, in this case microfinance institution has
an important role in solving the problem. This is in
line with the results of research conducted by
(Rahim, 2010; Wajdi, 2008; Adnan and Ajija, 2015).
Therefore the study on development strategy for
Islamic microfinance institution in indonesia
Widiastuti, T., Rusydiana, A. and Firmansyah, I.
Development Strategy For Islamic Microfinance Institution In Indonesia: Ifas-Efas Matrix Approach.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Islamic Economics, Business, and Philanthropy (ICIEBP 2017) - Transforming Islamic Economy and Societies, pages 707-711
ISBN: 978-989-758-315-5
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
707

becomes interesting. This study used an IFAS-EFAS
matrix that never been used in such cases, and
because it generally can be used in strategic
management research.
2 LITERATUR REVIEW
IMFI is a non-governmental organization in the form
of people's economic institution that has several
advantages in microfinance sector when compared
to the conventional financial institutions, such as
implementation of Islamic scheme of transaction,
family targeting rather than focusing on women
clients, importance of religion as social capital,
availability of various sources of financing (Yumna
and Clarke, 2009)
There are several studies that try to find ways to
develop IMFI. Research of Rusydiana and Devi
(2013) try to identify the dominant factors that has
become obstacles in the development of BMT in
Indonesia using Analytic Network Process (ANP).
The results show that main problems can be divided
into four aspects, namely Human Resources,
Technical, Legal and Structural, and
Market/Communal.
On other study, Muhar (2009) analyzes the role
of MFIs for small communities as well as strategies
undertaken in developing an MFI. The results show
that MFIs are able to provide financing to micro-
enterprises to leverage capital of these micro-
enterprises. In this journal, the researchers provide
solutions to strengthen the institutional of MFIs in
legal bills and regulations.
Research of Abdul and Dean (2013) suggested
solutions for lack of fund mobilization and high
administrative costs, and the effectiveness of Islamic
MFIs in alleviating poverty include a collective
resolution in increasing bank participation in
microfinance and diversifying their portfolios,
provision of education and training, better
coordination and networking, technical assistance
through waqf and zakah funds, and the development
of an enabling regulatory and policy environment.
Based on research of Manan and Shafiai (2015),
there are issues and challenges being faced by the
institutions of Islamic microfinance that could give
impact towards their sustainability. Findings of the
study indicated that the institutions had taken the
necessary steps in managing the risks.
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The research starts from preliminary survey and
literature study, then continued to identification and
problem formulation, method determination,
questionnaire compilation, data collection, data
analysis and result processing, SWOT analysis,
drafting conclusions and suggestions. Respondents
in the research are experts that understand overall
condition of IMFIs in Indonesia, both internally and
externally.
Data analysis consists of several stages, first
stage is scoring matrix Internal Factor Evaluation
(IFE) and External Factor Evaluation (EFE) – which
overall weight of internal factors and external is 1 –
to determine current position and condition of IMFIs
and what strategies that can be applied, second stage
is preparing the SWOT matrix after IE matrix
obtained to develop alternative strategies that can be
used for the development of IMFIs in Indonesia.
4 ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Problems Identification
Based on literature review and in-depth interviews
with the expert respondents, internal factors that
become the strengths are: 1) high initiative of local
community – society is demanding the existence of
microfinance institutions that are based on sharia; 2)
IMFI does not require large capital – capital
requirement to build an IMFI is not large; 3) IMFIs
are free from usury and economic wrongdoings – the
concept of sharia-based IMFI will prevent the
community from the pressure of return that is very
burdensome to them; and 4) IMFIs focus on small
and medium micro enterprises segment – MSMEs is
majority of businesses in Indonesia. Meanwhile, the
weaknesses are: 1) cost of human resource training
and entrepreneurship training for community – in
order to build professionalism of the human
resources; 2) cost of obtaining legal permits from
government – in high level; 3) cost of monitoring
and mentoring financing customers for reducing risk
– in high level; and 4) cost of socialization and
marketing to be more active in conducting
socialization.
ICIEBP 2017 - 1st International Conference on Islamic Economics, Business and Philanthropy
708
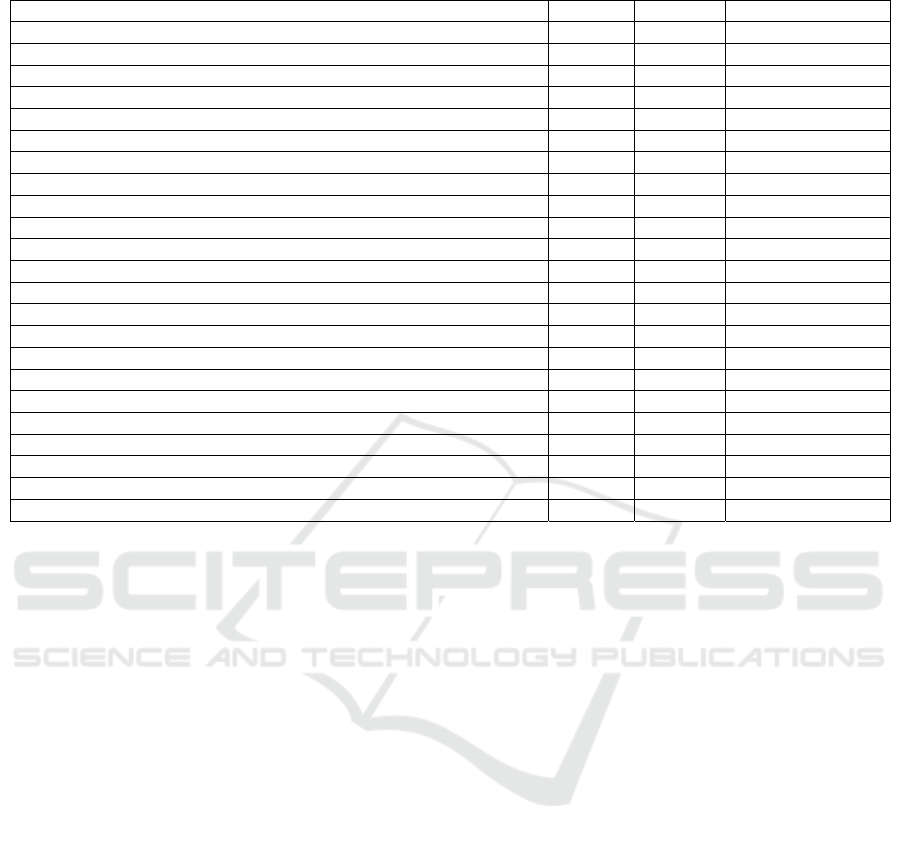
Table 1: IFE – EFE Assessment.
Internal Factors Evaluation
(
IFE
)
Wei
g
ht Ratin
g
Wei
g
ht*Ratin
g
Stren
g
ths 1.519
1
)
hi
g
h local
p
eo
p
le initiative 0.105 2.8 0.294
2) non-
b
ig capital requirement 0.098 1.8 0.176
3) Free of usury and economic wrongdoings 0.164 2.0 0.328
4) MSMEs segmentation 0.164 4.4 0.722
Weaknesses 1.492
1
)
HR and entre
p
reneurshi
p
trainin
g
costs 0.149 4.0 0.595
2
)
le
g
al license cost 0.119 3.2 0.382
3) cost for mentoring and monitoring of customers’ financing 0.089 2.0 0.179
4) socialization and marketing cost 0.112 3.0 0.336
TOTAL 1.000 3.011
External Factors Evaluation
(
EFE
)
Wei
g
ht Ratin
g
Wei
g
ht*Ratin
g
O
pp
ortunities 1.367
1) High public interest on sharia economy 0.104 2.6 0.270
2) Arising regional autonomy 0.104 2.6 0.270
3) Flexibility on financed sectors 0.156 4.2 0.654
4
)
Hi
g
her numbers of small businessmen com
p
ared to bi
g
businessmen 0.096 1.8 0.173
Threats 2.015
1
)
Ga
p
b
etween abilit
y
to save with financin
g
funds utilization 0.104 2.6 0.270
2) Weak regulation and legality of IMFI 0.141 3.8 0.535
3) Moral Haza
r
d
ris
k
0.126 3.4 0.427
4
)
Com
p
etition 0.170 4.6 0.784
TOTAL 1.000 3.382
On the other hand, external factors that regarded
as opportunities are: 1) public interest toward sharia
transaction is getting bigger; 2) development of
regional autonomy era – Some cities and regencies
issued the Sharia Regulations; 3) financed sector is
very flexible – there is no limit of minimum
financing; and 4) number of small entrepreneurs are
bigger than big businessman. While the threats are:
1) Gap between the ability to save and utilize credit
– a lot of citizens in Indonesia has consumptive
culture; 2) weak regulation and legality of IMFI –
The absence of sufficient law; 3) Moral Hazard Risk
– risk that inherent in the company's operations; and
4) Competition - conventional and Islamic basis
competitor.
4.2 Discussion
After problem identification, the next step is
strategic factor evaluation. The evaluations are done
by giving weight and rating values to each internal
factor (strengths and weaknesses) and external factor
(opportunities and threats). The “weight” description
interpret level of importance, the higher weight
means higher level of importance. Then, the “rating”
description interpret level of influence to
development of IMFI, the higher rating means
higher level of influence. Afterwards, the way to
know the evaluation factor is by multiplying the
weight and rating. Those evaluation of the mention
factors can be seen in the table 1.
Moving on the next step, this study use IFE-EFE
quadrant to determine IMFI assessment in Indonesia.
Assessment value of internal factor evaluation (IFE)
is 3.011 and external factor is 3.382. This value in
quadrant I that is "grow and develop". The existence
of internal and external factors basically becomes a
huge support for IMFI.Each SWOT component in
IFE-EFE quadrant is assigned with weight and
rating. The weight is derived from factor rotation
value multiplied by variance value (eigenvalue).
While rating obtained from assessment of variables
tested. The weighting and subsequent valuations are
summed for each SWOT component and then the
difference between internal components (S and W),
and difference between external components (O and
T) will be calculated. Difference of internal
component then becomes the x-axis value (value =
0.44), and the result of the external component
difference then becomes the y-axis value (value =
0.35), so in the IFE-EFE quadrant there is a
concentric position in the IVA quadrant. In that
quadrant, the existence of IMFI shows a very good
strength in the external environment, but the threats:
Development Strategy For Islamic Microfinance Institution In Indonesia: Ifas-Efas Matrix Approach
709

Table 2: SWOT Analysis Matrix.
Are greater than the strengths they have.
Therefore IMFIs should be more vigilant about the
existence of the surrounding environment because
if they do not utilize and manage their strengths
well, development of IMFI will be hampered.
Alternative strategy for current IMFI operation
is S-T strategy because the S-T strategy is a
strategy to optimize strengths it has to avoid or
minimize impact of enormous threats. The
alternative S-T strategy can be seen in the SWOT
strategy analysis results.
4.2.1 Strategy Alternative for Developing
IMFI from SWOT Analysis
Formulation of alternative strategies of IMFI
development in Indonesia with SWOT analysis is a
combination of internal factors (strengths and
weaknesses) with external factors (challenges and
threats) consisting of:
Combined strength and opportunity factors;
Combined factors of weakness and
opportunity;
Combined factor of forces and threats;
Combined factors of weakness and threat.
Detail of the alternative strategies for IMFIs’
development in Indonesia as follows on table 2.
As described previously IMFI is a powerful
poverty alleviation tool. According to Obaidullah
and Khan (2008), in a typical developing economy
the formal financial system serves no more than
twenty to thirty percent of the population.
Financial exclusion thus, binds them into a vicious
circle of poverty. Building inclusive financial
systems therefore, is a central goal of policy
makers and planners across the globe.
5 CLOSING REMARKS
5.1 Conclusions
Internal factor evaluation results show that IMFI's
highest strength is its nature as usury and
economic wrongdoings-free as well as small and
medium business segmentation. While the highest
weakness is cost of human resource training and
entrepreneurship training in the community. The
IFE analysis results that the highest rating of the
strength is small and medium enterprises
(MSMEs) segmentation followed by high local
initiatives. While highest rating on the weakness is
the cost of human resource training and
enterpreneurship training followed by cost of legal
licensing.
On external factor evaluation, it shows highest
opportunity is flexibility on financed sectors
followed by high public interest toward the sharia
transaction and growing of regional autonomy era.
Meanwhile, highest threat factor consists of
competition and weakness on regulation and
legality of IMFI. The results of EFE analysis also
STRENGTHS (S) WEAKNESSES (W)
1) high local people initiative
1) HR and entrepreneurship training
costs
2) non-
b
ig capital requirement 2) legal license cos
t
3) Free usury and economic wrongdoings
3) cost for mentoring and monitoring
customers’ financing
4) MSMEs segmentation 4) socialization and marketing cost
OPPORTUNITIES (O)
1) High public interest on sharia economy
1. Optimizing approach to potential investors
despite little capitalization concerning high
public interest to sharia economy (S2-O1)
1. Increasing government’s role to
facilitate ease on IMFI’s legal license
process (W2-O2)
2) Arising regional autonomy
3) Flexibility on financed sectors
2. Enactment of regional regulation
concerning sharia economy to support IMFI
(S3-O2)
4) number of small businessmen is higher
than big businessmen
THREATS (T)
1) Gap between ability to save with
financing funds utilization
1. Socialization to MSMEs on managing
funds from IMFI’s financing to enhance their
ability to save and manage funds (S4-T1)
1. Coordination with PINBUK on
training events, either to IMFIs
management and to society as a way to
reduce moral hazard ris
k
(W1-T3)
2) Weak regulation and legality of IMFI
3) Moral Hazard ris
k
2. Development of innovative products in
accordance with sharia principles to enhance
IMFI’s ability to compete other financial
institutions (S3-T4)
4) Competition
ICIEBP 2017 - 1st International Conference on Islamic Economics, Business and Philanthropy
710

shows that highest rating of the opportunity is
flexibility on financed sector followed by high
public interest to sharia transaction. On the other
side, highest rating of threat is competition
followed by weak regulation on IMFI. From
aforementioned results, there are 6 IMFI
development strategies in Indonesia from SWOT
analysis that combine internal-external factor
evaluation.
5.2 Recommendations
Based on the explanation, this paper’s
recommendations are two. First, it is expected that
there will be joint commitment from various
parties. Second, through this research, it is
expected to expand the study of academic research
related to IMFIs as micro segment of sharia
economy, especially findings on best strategies to
improve development of IMFI.
REFERENCES
Abdul, R. R., Dean, F., 2013. Challenges and solutions
in Islamic microfinance. Humanomics. 29(4), pp.
293–306.
Adnan, M. A., Ajija, S. R., 2015. The effectiveness of
Baitul Maal wat Tamwil in reducing poverty The
case of Indonesian Islamic Microfinance Institution.
Humanomics. 31(3), pp. 354–371.
Karim, N., Tarazi, M., Reille, X., 2008. Islam micro
finance: an emerging market niche.
Manan, S. K. A., Shafiai, M. H. B. M., 2015. Risk
Management of Islamic Microfinance (IMF) Product
by Financial Institutions in Malaysia. Procedia
Economics and Finance. Elsevier B.V., 31(15), pp.
83–90. doi: 10.1016/S2212-5671(15)01134-X.
Muhar, 2009. Kebijakan dan Strategi Pengembangan
Lembaga Keuangan Mikro. jurnal inovasi. 6(4).
Obaidullah, M., Khan, T., 2008. Islamic Microfinance
Development: Challenges and Initiatives. SSRN
Electronic Journal. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.1506073.
Rahim, A. R. A., 2010. Islamic microfinance: an ethical
alternative to poverty alleviation. Humanomics.
26(4), pp. 284–295. doi:
10.1108/08288661011090884.
Rusydiana, A. S., Devi, A., 2013. Challenges in
Developing Baitul Maal Wat Tamwiil (Bmt) in
Indonesia Using Analytic Network Process (ANP).
Business and Management Quarterly Review. 4(2),
pp. 51–62.
Suharto, S., 2010. Outlook BMT 2011, Permodalan BMT
Center. Jogjakarta.
Wajdi, D. A., 2008. Banking for the poor: the role of
Islamic banking in microfinance initiatives.
Humanomics. 24(1), pp. 49–66.
Yumna, A., Clarke, M., 2009. Integrating zakat and
Islamic charities with microfinance initiative in the
purpose of poverty alleviation in Indonesia. 8th
International Conference on Islamic Economics and
Finance. pp. 1–18. Available at:
http://conference.qfis.edu.qa/app/media/222.
Development Strategy For Islamic Microfinance Institution In Indonesia: Ifas-Efas Matrix Approach
711
