
Governance and Trust in Zakat Institution
Erika Takidah and Ajeng Pratiwi
Accounting Education Department, Faculty of Economics, Universitas Negeri Jakarta Indonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia
erikatakidah@unj.ac.id, ajengpratiwi14.ap@gmail.com
Keywords: Governance, Accountability, Transparency, Sharia Compliance, Trust, Zakat Institution.
Abstract: As one of the five basic pillars in Islam, zakat is an obligatory upon every adult, mentally stable,and
financially-able moslem. As a result, millions of moslems donate their zakat through zakat institusions. In the
management of zakat funds, it is very to obtain the trust from the zakat payers (muzakki). This paper seeks to
explore the zakat payers perception of governance and and its effect to the trust in a zakat institution.
Perception of accountability, transparency and sharia compliance represents the governance of Badan Amil
Zakat Nasional (Baznas), as a zakat management institution. The survey method was applied in this research
and with quantitative approach. The paper examines relation among accountability, transparency, sharia
compliance and 100 zakat payers’ trust in Baznas. The result of this research showed that the accountability,
transparency and sharia compliance influenced a muzakki’s trust in Baznas. Sharia compliance performs the
strongest influence on trust among the studied variables. The paper relies heavily depend on a muzakki
perception of Governance and Trust. Selection of limited indicators for this research may affect the results of
the study. This paper highlights the need of an increasing trust through relevant disclosure of accountability,
transparency and shariah compliance information to build a muzakki perception based on the annual report of
zakat institution.
1 INTRODUCTION
As the largest moslem country Indonesia has huge
potential of zakat therefore the responsibility of
paying zakat is part of worship and duties on each
moslem. The research results of Badan Amil Zakat
Nasional (BAZNAS) in 2015 stated that the potential
of zakat in Indonesia reached Rp 442 trillion or
equivalent to 3.4 percent of Indonesia's Gross
Domestic Product (GDP). But in fact, the zakat that is
absorbed and managed by zakat management
institution until 2016 reaches only Rp 4.4 trillion or
one percent of its potential. This shows that Muslims
currently have less interest to pay zakat in zakat
management institutions.
The development of zakat management
institutions has not been accompanied by the
increasing interest of the community to pay zakat in
zakat management institution. The cause is
optimalisation of zakat institution and public trust to
zakat management institution is still low. Muzakki
trust is very influential to zakat collection targets. The
creation of muzakki trust, is expected to increase
muzakki both in terms of quantitative and qualitative,
so that zakat collection targets are achieved.
Furthermore, muzakki trust will also lead to the
purpose of zakat management, namely community
empowerment and poverty alleviation.
Regard to zakat institution confidence issues,
there are several factors that are considered on
muzakki trust. The first factor is accountability. The
management of zakat, infaq, and shadaqah are
considered to have weaknesses in aspects of public
accountability, accountability, transparency, and
institutional arrangement (Shabri, 2014) . That is why
the government issued Undang-Undang No. 23
Tahun 2011 on the Management of Zakat. The current
phenomenon, the issue of accountability and
transparency is still the main problem that
overwhelms most of the zakat management
institutions in Indonesia, whether managed by the
government or private.
The second factor that affects trust is transparency
or openness. The phenomenon that often happens
people have doubts to pay their zakat through zakat
management institution because it is considered less
transparent. Therefore, transparency of financial
statements, management and attitudes is important to
increase the trust of muzakki to zakat management
institution (Mukhlis and Beik, 2013).
870
Takidah, E. and Pratiwi, A.
Governance and Trust in Zakat Institution.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Islamic Economics, Business, and Philanthropy (ICIEBP 2017) - Transforming Islamic Economy and Societies, pages 870-875
ISBN: 978-989-758-315-5
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

The third factor affecting trust is sharia
compliance. Sharia compliance has become one of
the important pillars in the development of sharia
institutions (Sulaiman and Jamil, 2015). Violation of
sharia compliance can occur due to weak supervision
will adversely affect the image and credibility of
sharia institutions, thus reducing public confidence.
The fourth factor affecting muzakki's trust is
honesty and integrity. Integrity is an element of
character that underlies the emergence of professional
recognition. Integrity requires an Amil Zakat to be
honest and objective without having to sacrifice the
secrets of muzakki or mustahik.
The last factor is professionalism. The
professionalism of zakat management institution
requires a management organization that is filled by
people who have the capacity, both managerial and
scientific understanding of religious scholarship
(Abdullah, 2010). In addition, management
professionalism also needs to base itself on a good
governance system as it has become a demand for the
implementation of today's public governance
management.
In accordance with the mandate of the Undang-
undang to become a professional institution, zakat
management institutions must have competence,
totality in work, get payment (wages), always want to
learn, awareness that all behavior and actions have
social and religious responsibility. Through such a
competent institution, zakat will be channeled
appropriately and will influence the public trust.
1.1 Trust in Zakat Institution
Luarn and Lin (Ferrinadewi, 2008) define trust is a
specific belief in integrity (honesty of trustworthy
parties and ability to keep promises), benevolence
(thoughtfulness and motivation believed to act in the
interests of trust them), competency (ability of the
trusted party to carry out the trusting needs) and
predictability (consistency of the behavior of the
trusted party).
According to Mayer and Davis (1999), the three
dimensions of the trustee arise from the ten existing
literature: ability, virtue, and integrity. This is
reinforced by Gefen and Silver's theory that the belief
dimension consists of: (1) Competence, the company
has the ability to deliver its promises to clients; (2)
Integrity, a company acts in a consistent, reliable, and
honest manner when delivering on its commitment;
(3) Kindness, a core company in the right place and
putting the client's attention above his or her interests.
Muhammad and Saad (2016) examined the
reliability and validity of trust’s dimensions namely;
public governance’s quality, quality of zakat
distribution, zakat service quality and perceived
board capital. The result shows that all the constructs
are reliable measured of trust toward intention to pay
zakat in Kano Nigeria
Ghazali et al. (2016) The commitment-trust
theory is utilized as the underpinning theory. An
extensive literature review found that shared values,
communication, non-opportunistic behavior and
perception on distribution are the potential factors
that influence trust towards zakat institution.
1.2 Accountability and Trust in Zakat
Institution
Barlow explains that accountability means an
obligation to present and report all acts and activities
performed in accordance with the mandate / mandate
that it carries on to a higher party or superior.
Strengthening the definition of accountability is also
put forward by Patricia Douglas, the accountability of
an organization implies (a) the availability of
information about decisions / policies and actions
taken during the operation, (b) asking external parties
to review the information, and (c) taking corrective
action if needed.
In the shariah accounting point of view, Tapanjeh
(2009) defines that: Accountability is an attempt to
generate correct, fair and transparent disclosures. The
accountability of the disclosure is done first is for
God. The fundamental concept of Islamic
accountability is believing that all resources are
available to individuals in the form of trust.
Therefore, correct disclosure of financial facts, and
accurate information must be freely available to the
user.
Islamic accountability framework in the zakat
funds management (Saad et al., 2014) accountability
in the zakat fund management is driven by the Islamic
foundation, which cannot be separated from the
Islamic teachings and pathways. For this reason, the
zakat contribution is essential, which all the Muslims
have to abide by, through the shadowing of the
intangible relations within the human beings i.e.
Muslims and submission to Allah
The four main dimensions of accountability are
strategic accountability, fiduciary accountability,
financial accountability and procedural
accountability. (1) Strategic accountability is
associated with the core objectives, the disclosures
include: organizational intentions, that is, their vision
and mission; actions, that is, activities and programs
to fulfill their intentions; and results that measure the
impact of their actions and the extent to which their
Governance and Trust in Zakat Institution
871

intentions have been achieved. (2) Fiduciary
accountability emphasizes honesty and compliance,
and at operational levels, governance and control. (3)
Financial accountability is concerned with their
financial outlook and the main trends and factors
underlying their financial development (Dhanani and
Connolly, 2012). Hence the researchers assume that
the accountability as apart of governance, ia a factor
to build the muzakki trust towards zakat institution.
Therefore, the following hypothesis is formed as
below.
H1: Accountability should have a significant
positive relationship with muzakki trust in zakat
institution
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Transparency and Trust in Zakat
Institution
According to Andrianto (2007), public transparency
is a genuine, thorough disclosure, and provides a
place for the active participation of all levels of
society in the process of managing public resources.
Any policy issued by the organizer must be openly
accessible by allowing sufficient space for the public
to participate widely in it. Muhammad (2006), all
Zakat Institution has implemented public
accountability in the framework of transparency of
zakat fund management in various forms such as
preparing routine reports to muzakki, bulletins, and
publications in the mass media.
Komite Nasional Kebijakan Governance
(KNKG) 2005 define transparency is a condition
where the institution provides material and relevant
information in a way that is easily accessible and
understood by stakeholders. Meanwhile, according to
the National Committee on Governance, the
managers are obliged to carry out the principle of
openness in the decision process and in conveying
information. Openness in conveying information
means that the information submitted must be
complete, correct and timely to all stakeholders.
Indicators of transparency are formulated using
several expert theories, the principle of transparency
are: (1) Availability of adequate information on every
process of formulation and implementation of public
policy; (2) Access to ready, accessible, free and
timely information.
Meanwhile Krina (2008) revealed, transparency
indicators are: (1) Provision of clear information on
responsibilities; (2) Establish a grievance mechanism
in the event of any breach or demand for payment of
bribes; (3) Ease of access to information; (4)
Increasing the flow of information through
cooperation with mass media and non-government
institutions.
According to Kamil and Ahmad (2002), Distrust
toward zakat institution, especially in term of
transparency and ineffeciency in zakat distribution
management. In congruence with above discussion, it
is assumed that trnparency in zakat institution will
determine muzakki trust. Thus proposed hypothesis
is:
H2: Transparency should have a significant
positive relationship with muzaki trust in zakat
institution.
2.2 Shariah Compliance and Zakat
Institution
Shariah Compliance Shariah compliance is the ability
to follow Islamic sharia law. The meaning of Islamic
law here is Al Qur'an and Al-Hadist which is a
guideline for Muslims. One of the fundamental
aspects that differentiates the sharia and conventional
financial industry is the compliance with sharia
principles (sharia compliance). One of the legal
aspects of the sharia financial industry is the
regulation of sharia compliance Yudha and Roby
(2016). Shariah compliance is an important part for
sharia financial industry in terms of management and
operational. This is supported by the existence of
Sharia Supervisory Board for every shariah-based
financial institution.
Performance of Shariah compliance, legality and
institutional measured six measures covering aspects
related to the Sharia Supervisory Council (SSC),
Vision and Mission, Organizational Structure,
Employee Education Level, Regular Training
Program, and the percentage of fulltime employees
Shabri (2014)
The supervision of sharia by the Sharia
Supervisory Board (SSC) is an inseparable part of
Shariah compliance. In this context, the regulation of
sharia supervision, of course, includes the existence
of a sharia board, which is an important part of the
framework of regulatory rules as sharia compliance.
Based on the above-mentioned thinking, the study
related to shariah supervisory institutions in sharia
financial institutions, it is important to do. Wahab and
Rahman (2011) argued that in the case of zakat
institutions in a Muslim country like Malaysia, good
governance is important since it may contribute
towards efficiency and effectiveness in zakat funds.
Closer examination of the various governance
ICIEBP 2017 - 1st International Conference on Islamic Economics, Business and Philanthropy
872
mechanisms is important because zakat institutions
control significant financial resources.
Consistent with the above argument, it is expected
that a high level of shariah compliance would
contribute to a greater trust in zakat institution.
Therefore, the following hypotheses is offered :
H3: Shariah compliance should have a significant
positive relationship with muzaki trust in zakat
institution.
3 METHODOLOGY
Based on the review literature and previous research
results the conceptual model in this study is shown in
Figure 1.
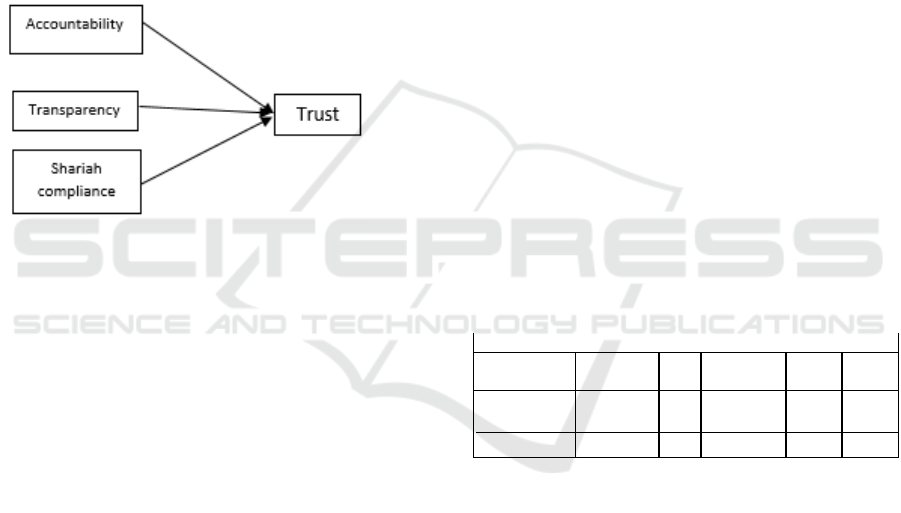
Figure 1: Conceptual model.
The model postulates that picture above shows
that trust in zakat institution is influenced by
governance: Accountability, Transparency and
Shariah compliance. The framework also postulates
that the independent variable are expected to have a
direct positive influence on the dependent variable of
this paper. This means that the greater accountability,
transparency and shariah compliance, the higher the
trust of muzakki in zakat institutions and vice versa.
The object of this research is the Badan Amil
Zakat Nasional (BAZNAS) Jakarta. The method used
in this research is survey method. The population in
this study is all muzakki paying zakat in BAZNAS
which amounted to 11,779 people. The sample in this
research is 100 samples with sampling technique is
purposive sampling. Sample criteria in this research
are; (1) Muzakki BAZNAS domiciled in Jakarta; (2)
Has been registered as Muzakki within a minimum
period of 5 years; (3) Has paid zakat to BAZNAS
more than 5 times; (4) Not including muzakki
affected by autodebet salary or working in an agency
that has partnered with BAZNAS through zakat
payroll system.
Data collection was done by distributing
questionnaires to the respondents. The questionnaire
consisted of 4 variables, namely 1) a confidence
variable with 14 statement items, 2) shariah
compliance variables with 8 statement items, 3)
accountability variables with 16 statement items, 4)
transparency variables with 11 statement items. The
scale used is Likert scale with answer range 1 to 5.
Data analysis method used in this research consisted
of classical assumption test and hypothesis test.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Based on table 1, the results showed a high and
positive significant correlation between all constructs
of governance (accountability, transparency and
shariah compliance) and muzakki trust. coefficient
value F equal to 95,576> F table 3.09 and significance
number 0,000 <0,05. From these results can be said
that accountability, transparency and shariah
compliance were perceived as important to the trust
in zakat institution. This is consistent with prior zakat
literature (Ghazali, 2016; Wahab and Rahman,2011)
and also with the governance studies (Wahab and
Rahman, 2011; Mukhlis and Beik 2013).
The framework also proposes a positive
relationship between the independent and dependent
variables such relationship is also supported by other
scholars (Hasanah, 2013; Muhammad and Jaffri,
2016).
Tabel 1: F test.
ANOVA
a
Model
Sum of
Squares
Df
Mean
Square
F
Sig.
Regression
3375,596
3
1125,199
95,576
,000
b
Residual
1130,194
96
11,773
Total
4505,790
99
a. Dependent Variable: Trust
b. Predictors: (Constant), Accountability, Transparency and
Shariah Compliance
As summarized at table 2, relationship between
trust and governance as follow :
Influence of accountability on trust;
The value of the obtained path coefficient is
positive at 0.302 and the significance value of
0.001 (0.001 <0.005);
The effect of transparency on trust;
The value of the obtained path coefficient is
positive at 0.297 and the significance value of
0,000 (0.000 <0.005);
Effect of Shariah compliance on trust;
The value of path coefficient obtained is
positive equal to 0.369 and significance value
of 0,000 (0.000 <0.005).
Governance and Trust in Zakat Institution
873

From these results it can be answer all of research
Hypothesis: H1 accepted cause of accountability has
a direct and significant influence on trust. H2
accepted because transparency has a direct and
significant influence on trust. H3 can be accepted
because that the shariah compliance has a positive
and significant impact on trust. This result also
consistent with Zainal et al. (2016), Kamil and
Ahmad (2002) that Accountability, Transparency and
Shariah Compliance has a positive and significant
correlation with muzakki trust.
Tabel 2: T test.
Coefficients
a
Model
Unstandardized
Coefficients
Standardized
Coefficients
T
Sig.
B
Std.
Error
Beta
(Constant)
4,431
3,108
1,426
,157
Accountability
,271
,082
,302
3,305
,001
Transparency
,284
,073
,297
3,874
,000
Shariah
Compliance
,857
,180
,369
4,763
,000
a. Dependent Variable: Trust
Tabel 3: Determination Coefficient.
Model Summary
Model
R
R Square
Adjusted R
Square
Std. Error of the
Estimate
1
,866
a
,749
,741
3,431
a. Predictors: (Constant), Accountability, Transparency and
Shariah Compliance
Table 3 showed that the overall explanatory factor
of muzakki trust in zakat institution were statistically
significant at 5% significant level with adjusted R-
squared off 74,1% Hence with this condition it
revealed that the independent explains 74.1% of the
variance muzakki trust. This finding concurred with
Zainal (2016) study where stakeholder trust influence
by governance.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The results of data analysis and discussion can be
concluded that governance which represented by
accountability, transparency and shariah compliance
has a significant effect on muzakki trust in zakat
management institution. The highest influence
coefficient (dominant) on trust among variables is
sharia compliance. The issue of zakat management is
argued in this paper as closely related to the
governance relationships in the zakat institution.
Differ from western understanding over
accountability transparencies and shariah
compliances, Islamic governance framework
proposed and analyzed here provides a broad and
integrated understanding over the governance in
zakat fund management that can help the relevant
parties to manage the zakat fund more effectively and
efficiently.
REFERENCES
Abdullah, R. B., 2010. Zakat Management In Brunei
Darussalam : A Case Study Zakat Management In
Brunei Darussalam : A Case Study Rose binti Abdullah.
Seventh International Conference.
Dhanani, A., Connolly, C., 2012. Discharging not‐for‐profit
accountability: UK charities and public discourse.
Accounting, Auditing and Accountability Journal. Vol.
25 Issue: 7, pp.1140-1169.
Andrianto, N., 2007. Good e-Government: Transparansi
dan Akuntabilitas Publik Melalui e-Government, Bayu
Media. Malang.
Ferrinadewi, E., 2008. Merek dan Psikologi Konsumen,
Graha Ilmu. Yogyakarta.
Ghazali, M. Z., Saad, R. A. J., Wahab, M. S. A., 2016. A
Conceptual Framework for Examining Trust towards
Zakat Institution International Journal of Economics
and Financial Issues. Special Issue for International
Soft Science Conference (ISSC 2016). 6(S7) 98-102.
11-13 April 2016, Universiti Utara Malaysia, Malaysia.
Hasanah, N., 2013 Analisis Pengaruh Layanan Lembaga
Amil Zakat Terhadap Kepercayaan Muzakki (Studi
Pada Lembaga Amil Zakat Dompet Dhuafa
Yogyakarta), Repository UGM. Yogyakarta.
Kamil, M. I., Ahmad, M. A., 2002, Peranan sikap dalam
gelagat kepatuhan zakat pendapatan gaji. Analisis. 9 (1-
2), 171-191.
Krina, 2008. Indikator dan Alat Ukur Prinsip Akuntabilitas,
Transparansi, dan Partisipasi, Sekretariat Good Public
Governance, Badan Perencanaan Pembangunan
Nasional. Jakarta.
Mayer, R. C., Davis, J. H., 1999. The effect of the
performance appraisal system on trust for management:
A field quasi-experiment. Journal of Applied
Psychology. Vol 84 No. 1, pp. 123-136.
Mukhlis, A., Beik, I. S., 2013. Analisis Faktor-faktor yang
Memengaruhi Tingkat Kepatuhan Membayar Zakat:
Studi Kasus Kabupaten Bogor. Jurnal Al-Muzara’ah. I
(1), 83–106.
Muhammad, R., 2006. Akuntabilitas Keuangan pada
Organisasi Pengelola Zakat (OPZ) di Daerah Istimewa
Yogyakarta. Jurnal Akuntansi dan Investasi. Vol. 7 No.
1, hal: 34-55.
Noman, A., 2003. Imperatives of Financial Innovations For
Islamic Banks. International Journal of Islamic
Financial Services. Vol. 3.
Muhammad, S. A., Jaffri, S. R. A., 2016. Determinants of
Trust on Zakat Institutions and its Dimensions on
Intention to Pay Zakat: A Pilot Study. Journal of
Advanced Research in Business and Management
ICIEBP 2017 - 1st International Conference on Islamic Economics, Business and Philanthropy
874

Studies. ISSN (online): 2462-1935 | Vol. 3, No. 1. Pages
40-46.
Saad, R. A. J., Aziz, N. M. A., Sawandi, N., 2014. Islamic
Accountability Framework in the Zakat Funds
Management. Procedia - Social and Behavioral
Sciences. 164 (August), 508–515.
Shabri, H., (2014). Performance Comparison Amil Zakat
Institutions Managed By The Government And Private
Organization In West Sumatra Province, 103–117.
Sulaiman, H., Jamil, N., 2015. Information security
governance model to enhance zakat information
management in Malaysian zakat institutions.
Conference Proceedings - 6th International Conference
on Information Technology and Multimedia at
UNITEN: Cultivating Creativity and Enabling
Technology Through the Internet of Things, ICIMU
2014.
Tapanjeh, 2009. Corporate Governance from The Islamic
Perspective: A Comparative analyse with OECD
Principles Critical Perspectives on Accounting.
Elsevier- Critical Perspectives on Accounting.
Undang-Undang No. 23, 2011. Tentang Pengelolaan Zakat.
Wahab, A. N., Rahman, A. A. R., 2011. A framework to
analyse the efficiency and governance of zakat
institutions. Journal of Islamic Accounting and
Business Research. 2 (1), 43-62.
Yudha, A. N., Roby, C., 2016. Manajemen Pelayanan
Pemberdayaan Anak Yatim pada Lembaga Amil Zakat
Yatim Mandiri di Surabaya. Al Tijarah. Vol. 2, No. 1.
Zainal, H., Azizi, A. B., Ram, A. J. S., 2016. Reputation,
Satisfaction of Zaka Distributuin and Service Quality as
Determinant of Stake Holder Trus in Zakat Institution.
International Journal of Economics and FInancia
Issues. 2016 6(S7).
Governance and Trust in Zakat Institution
875
