
The Profile of Senior High School Students’ Critical Thinking Skills
after the Implementation of Problem Solving-Based Students’
Worksheet Using Reading Infusion
Herni Yuniarti Suhendi
1
, Diah Mulhayatiah
1
, Endah Kurnia Yuningsih
1
, Rahmalia R. Aisyah
1
, Tri
Lunggari
2
and Sulasman Sulasman
1
1
UIN Sunan Gunung Djati Bandung, Jl. A. H. Nasution No 105, Bandung, Indonesia
2
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Jl. Dr.Setiabudhi NO 229, Bandung, Indonesia
{herni.suhendi, diahmulhayatiah}@uinsgd.ac.id
Keywords: Students’ worksheet, problem solving, reading infusion, learning achievement, critical thinking skills.
Abstract: The results of a preliminary study at one of high schools in Bandung City showed that learning in school did
not enhance students' critical thinking skills. Problem solving strategy using reading infusion is one of the
solutions to overcome this issue. This study is aimed at finding out the improvement of students’ learning
achievement and critical thinking skills as a result of the implementation of problem solving strategy using
reading infusion. To this end, this study employed the one group pretest-posttest pre-experimental design.
This study took place at one of senior high schools in Bandung, involving tenth grade students. The learning
achievement was measured using a multiple-choice test, and critical thinking skills were measured using the
Cornell Critical Thinking Test. The result revealed that problem solving strategy could maintain students’
learning achievements and critical thinking skills.
1 INTRODUCTION
Physics teaching in high schools is intended as a
means to train students to acquire physical
knowledge, concepts, and principles, scientific
competence, science process skills, and critical and
creative thinking skills to solve everyday problems
(Depdiknas, 2006).
The result of an observation at one of senior high
schools in Bandung revealed that during the
instructional process, students tended to only receive
information, take notes of the teacher’s explanation,
and do exercises. This made students passive and less
involved in the instructional process so that their
thinking capacity was not in maximum use.
The results of a quiz showed an average score of
60.97, and only 39.02% of students who achieved the
minimum mastery criteria of 70. This indicated their
low learning achievement.
The results of questionnaire revealed that 35% of
students liked reading, 30% liked reading course
books, and 20% liked reading course books before
lessons. This indicated their low reading interests
especially in course books despite the fact that
reading is a very important learning activity.
Based on the aforesaid description, students were
not well facilitated to develop their potentials.
Therefore, it requires an instructional process that can
facilitate their potentials like problem-solving
instructional strategy.
Bolton J and Ross (Selcuk et al., 2008:151) stated,
“Problem solving instruction uses complex ways to
solve problems. Therefore, students should be trained
to solve problems using these ways.” In addition,
another definition is put forward by Dhillon (Selcuk
et al. 2008:151). Based on this description, problem
solving strategy can be defined as a way to present
instructional materials by exposing students to
problems they need to solve to achieve the learning
objectives. Students are expected to conduct an
authentic investigation to find solutions to a given
problem. They analyze and identify problems,
develop a hypothesis, collect and analyze
information, compile references, and draw a
conclusion (Hudojo, 2003). Similarly, Heller and
Heller (1999:20) also explain that the problem
solving strategy consists of the following phases:
visualizing problems, describing physical concepts
based on students’ problems, planning the solutions,
executing the solutions, and evaluating the solutions.
330
Suhendi, H., Mulhayatiah, D., Yuningsih, E., Aisyah, R., Lunggari, T. and Sulasman, S.
The Profile of Senior High School Students’ Critical Thinking Skills after the Implementation of Problem Solving-Based Students’ Worksheet Using Reading Infusion.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education (ICSE 2017) - Volume 1, pages 330-334
ISBN: 978-989-758-316-2
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

The problem solving strategy used in this study was
adopted and adapted from both scholars using a
problem solving-based students’ worksheet adapted
from the problem solving laboratory of the University
of Minnesota.
In the instructional process, students should be
trained to face problems, so they can think critically
to make decision (Ennis, 2011). Problem solving
instruction can train students to think critically.
Reading is a process of acquiring the writer’s
message through written textual media (Tarigan,
2008). It is a complex process involving the reader’s
comprehension, interpretation, reaction, and
application in real life conditions. He is also involved
in the textual information testing, language, ideas,
insights, application of his prior knowledge and
experience, and knowledge storage and recall.
Francais P. Robinson (1946) develops the SQ3R
method to study texts. SQ3R stands for survey,
question, read, recite, and review. Some studies
revealed that this method could improve memory and
reading comprehension.
This study needed to be conducted to give an idea
about an improvement in learning achievement and to
find out the profile of students’ critical thinking skills
after the implementation of problem solving strategy
using reading infusion. This strategy is expected to be
an alternative in the instructional activities.
2 METHODS
This study used the one group pretest-posttest pre-
experimental design. The population in this research
is all tenth graders at one of senior high schools in
Bandung, from which 36 of them enrolled in one class
was taken as the samples.
The treatment was given during three class meeting
times. The pretest was conducted before the
treatment. The purpose was to find out students’
initial knowledge about rectilinear motion concept
and their initial critical thinking skills. After the
pretest, on the same day, students were asked to read
a module on kinematic motion using SQ3R technique
under the teacher’s guidance. The posttest was
conducted after the treatment. The instructional
activity completion was checked using an observation
sheet. The instructional process was observed by
three observers.
The research procedure is illustrated in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Research Procedure.
The Profile of Senior High School Students’ Critical Thinking Skills after the Implementation of Problem Solving-Based Students’
Worksheet Using Reading Infusion
331

The research instruments included an
achievement test, the Cornell Critical Thinking Test
Level X, and observation sheets. The achievement
test was previously tried out and analyzed before use.
This included analysis of validity, reliability,
difficulty level, and discriminating power. This test
consisted of 20 multiple choice questions. The critical
thinking test consisted of 20 inductive critical
thinking items.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
During reading activities, the samples were provided
with a relevant module. The teacher guided them to
read using the SQ3R technique. The observation
result revealed that the reading completion reached
81.82%. This indicated that most of the SQ3R phases
were completed. Only at the Recite phase did the
students find difficulties to use their own words to
answer questions. Due to the time constraints, the
Review activity could not be done.
During the instructional process, students were
divided into six groups of six to seven persons. What
was done at the first instructional phase included
visualizing problems, describing problem-based
physical concepts, executing the solutions, and
interpreting and evaluation the solutions. The overall
instructional completion of each class meeting is
outlined in Table 1.
Table 1. Result of Observation of Instructional Strategy Completion
Instructional Phase
12 3
TA SA TA SA TA SA
Visualizin
g
Problems 71.43 50.00 85.71 78.57 92.86 85.71
Describin
g
p
roble
m
-
b
ased
p
h
y
sical conce
p
ts 75.00 50.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Finding Solutions 66.67 66.67 83.33 66.67 83.33 83.33
Executing the Solutions 100 100 100 100 100 100
Interpreting and Evaluating the Solutions 37.50 12.50 75.00 37.50 87.50 50.00
Avera
g
e 70.12 55.83 88.81 76.55 92.74 83.81
Note: TA : Teacher’s activity
SA : Students’ activity
The average percentage of the instructional strategy
completion is illustrated in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Instructional Strategy Completion.
3.1 Result of Learning Achievement
Test
The improvement of students’ learning achievement
was measured using the normalized gain of pretest
and posttest scores. The achievement tests consisted
of 20 multiple choice questions: 4 questions measured
C
1
(remembering), 7 question items measured C
2
(understanding), 6 questions measured C
3
(applying),
and 6 questions measured C
4
(analyzing).
The improvement of students’ learning
achievement is illustrated in Figure 3.
ICSE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education
332
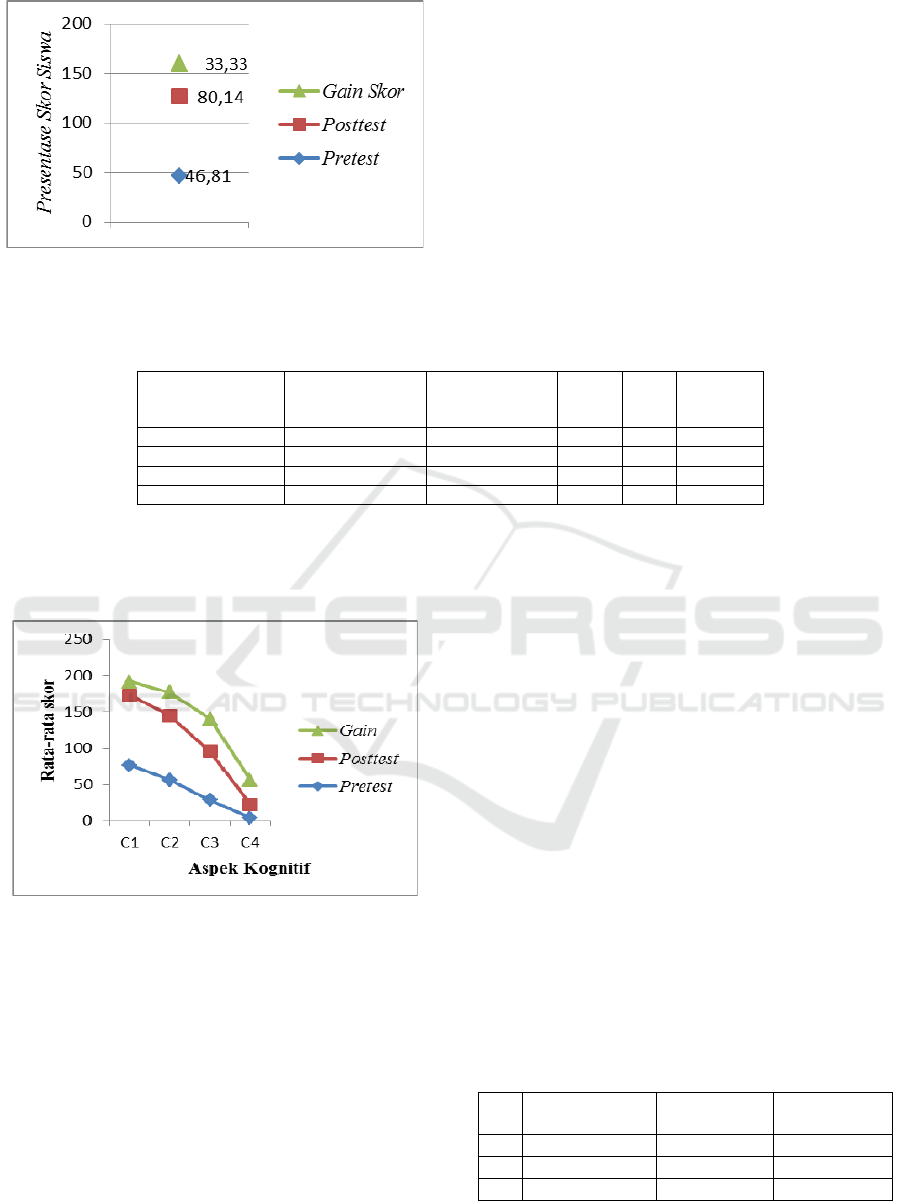
Figure 3: Improvement of Learning Achievement
The average score of the posttest was higher than that
of the pretest. The improvement is shown by the
percentage of the average gain score by 33.33. The
normalized gain score was 0.63 or moderate.
The improvement of learning achievement was
also measured in terms of cognitive aspects. The
measurement result is illustrated in Table 2.
Table 1: Learning Achievement in Every Cognitive Aspect.
Aspect Cognitive Average Pretest
Average Posttest
Gain <g>
Category
C
1
77.08 95.83 18.75 0.82 High
C
2
56.35 88.49 32.14 0.74 High
C
3
28.97 67.06 44.44 0.63 Moderate
C
4
4.37 18.65 33.33 0.35 Moderate
The data in Table 2 can also be presented in the
form of diagram as shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4: Average Score of Students’ Learning
Achievement in Every Cognitive Aspect.
Based on the result of data analysis presented in
Table 2, it can be seen that the average score of pretest
was 46.81, of the posttest was 80.14, and the gain
score was 33.3. It means that students’ learning
achievement improved after the implementation of
problem solving instruction using reading infusion.
Looking at the normalized gain score of 0.63, this
improvement was moderate. This was due to the less
optimum teacher and students’ activity completion.
The teacher and students’ activities during the lesson
really influenced the learning achievement. This is in
line with Joyce’s opinion that an instructional model
is a representation of learning environment that
includes teacher and students’ activities when the
model in question is implemented (Joyce et al.,
2009:30).
3.2 Profile of Critical Thinking Skills
The maximum score of the critical thinking test was
25, and the minimum was -12.5. The test score could
be minus (-) because the scoring used the R-W/2
formula.
Ennis (1996) said, “No test honestly can give you
score range categories like Superior, Good, Poor etc.
You must decide for yourself.” Since the Cornell
Critical Thinking Test does not have standard
category to determine one’s critical thinking level
(low, moderate, and high), groupings with reference
to Arikunto (2010) was done to profile the inductive
critical thinking skill level.
Based on the result of the study, students’ critical
thinking level could be categorized as follows:
Table 2. Students’ Critical Thinking Level.
No Category
Number of
Students
Percentage
(%)
1. Low 7 19.4
2. Moderate 23 63.9
3. Goo
d
6 16.7
The Profile of Senior High School Students’ Critical Thinking Skills after the Implementation of Problem Solving-Based Students’
Worksheet Using Reading Infusion
333

Table 3 shows that, with the percentage of 63.9%,
the majority of students have moderate inductive
critical thinking level.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of the study, it could be
concluded that the implementation of problem
solving strategy using reading infusion could improve
students’ learning achievement.
It requires further studies to pay more attention to
reading activities and other aspects of critical thinking
skills.
REFERENCES
Arikunto, S. 2010, Prosedur Penelitian Suatu Pendekatan
Praktik. Jakarta: PT. Rineka Cipta.
Depdiknas. 2006, Peraturan Menteri Pendidikan
Nasional Republi Indonesia Nomor 22 Tahun 2006
Tentang Standar Isi Untuk Satuan Pendidikan Dasar
Dan Menengah. Jakarta: Departemen Pendidikan
Nasional.
Ennis, R. H. 1996, Critical Thinking. United States of
America: The New York Times Company.
Ennis, Robert. 2011, The Nature of Critical Thinking : An
Outline of Critical Thinking Dispositions and Abilities,
[Online]. Available: http://faculty.ed.uiuc.edu/rhennis/.
[16 July 2012].
Heller., Heller. 1999, Problem Solving Labs, in
Cooperative Group Problem Solving in Physics,
Research Report. University Minnesota.
Hudojo, H. 2003, Pengembangan Kurikulum dan
Pembelajaran Matematika. Malang: JICA.
Joyce, B., Weil, M and Calhoun, E. 2009, Model of
Teaching: Model-Model Pengajaran (Edisi
Kedelapan). Yogyakarta: Pustaka Pelajar.
Robinson, F. P. 1946. Effective Study. New York: Harper &
Brothers Publishers.
Selcuk et al. (2008). The Effects of Problem Solving
Instruction on Physics Achievement, Problem Solving
Performance and Strategy Use. Latin American Journal
Physics Education volume 2 No. 3 September 2008.
Tarigan, H. G. 2008, Membaca. Bandung: Angkasa
Bandung.
ICSE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education
334
