
Digital Citizenship
The Reality o
f
Students Attitude using
I
nformation and Communication
Technolo
gy
Rini Triastuti
Pendidikan Pancasila dan Kewarganegaraan,Universitas Sebelas Maret , Surakarta, Jawa Tengah, Indonesia
rinitriastuti@staff.uns.ac.id
Keywords: digital, citizenship, attitude.
Abstract: The rapid development in information and communication technology gets responded by young people today.
The latest products both hardware and software are always followed by them so that their ability to use it no
doubt. But on the other hand the news shows that now more and more often heard various abuses of such
technology ranging from the case of law about defamation, distribute information that contains elements of
SARA until the spread of news hoax. This certainly raises a concern for all. This paper intends to describe the
digital citizenship attitudes of vocational high school students in Surakarta. The approach used in this research
is qualitative. This study used questionnaire and interview instruments. The results show that the majority of
students have the poor digital citizenship. Based on it hence can be drawn tendency of student in using
information and communication technology.
1 INTRODUCTION
Since the Indonesian government developed internet
infrastructure in the 1980s the number of internet
users has been increasing from year to year.
According APJII (2014) Internet users in Indonesia in
2010 amounted to 42 million with a population of
238.5 million. It shows that the penetration is 17.6%.
Then in 2011 internet users increased to 55 million
with a population of 242 million, which means a
penetration of 22.7%. The next year internet users up
to 63 million with a population of 245.5 million,
which means penetration of 24.23%. In 2013 internet
users increased to 71.2 million with a population of
248.9 million, which means a penetration of 28%.
Then in the year 2014 internet users to 88.1 million
with a population of 252.4 million, which means
penetration of 34.9%.
The majority of internet users in Indonesia aged
between 18-25 years is almost half of the total number
of internet users in Indonesia that is equal to 49%
(APJII, 2014). This illustrates that the segment of
internet users in Indonesia is those who belong to the
digital native category.
In line with APJII research is the research
conducted on the students in SMK Surakarta shows
the result that the students are digital citizens
(triastuti, budimansyah, sapriya, 2016) and have
characteristic as digital native (triastuti, 2017). This is
because some of the following: that the majority of
students that is 43% or almost half access the internet
every day. Another fact that supports 52% of students'
access social media every day or more than half and
25% of students' access social media every hour, 90%
of students, or almost all have never attended a
training or special course in order to operate computer
programs, has a very active character using the
network of digital technology and has the ability to
operate internet-based technology.
2 CIVIC EDUCATION AND
DIGITAL CITIZENSHIP
Kalidjernih (2010) argues that, "Citizenship is the
relation of the individual (citizen) and the country in
which each party is bound to a contract of rights and
obligations reciprocally". Citizenship is defined as a
citizen of a country where between citizens and
citizens' relations with the state create mutual rights
and obligations.
Meanwhile, according to Smith (2002) citizenship
has several meanings as follows: first, a person with
political rights to participate in the process of political
right's self-governance. Second, citizenship as a more
purely legal status. Third, citizenship as referring to
who belong to almost any human association,
Triastuti, R.
Digital Citizenship - The Reality of Students Attitude using Information and Communication Technology.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education (ICSE 2017) - Volume 1, pages 495-499
ISBN: 978-989-758-316-2
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
495

whether a political community or some other group.
Fourth, citizenship to signify not just membership in
some group, but also certain standards of proper
conduct.
This citizenship is not only addressed as a political
right, but also as a citizen's legal status, membership
of a community as well as the terms and behavior of
citizens. The development of information and
communication technology has an impact that in
addition to living in the real world today we also live
in cyberspace. So in addition to being a citizen is also
a digital citizen. This makes digital citizenship
meaningful.
Hollandswoth, Dowdy dam Donovan (2011)
argue that digital citizenship can be compared to
American citizenship in that all digital citizens have
the same basic rights: to privacy, free speech how to
protect their privacy is critical. Everyone has the
rights to free speech but students need to be taught to
think about what is said and posted online, which has
far reaching effects. Students should also understand
that when something is created it belongs to the
creator. It should not be copied or altered in anyway.
Students do not fully understand copyright laws or
how to legally obtain information, songs, pictures, etc
Citizenship and civic education are inseparable.
Citizenship is related to the relationship between the
citizen and their state which raising the various rights
and duties meanwhile every state has what citizens
desire as expected. Then hope is implemented with an
education that is civic education.
The purpose of civic education is to form good
citizens. Wahab (2011) identifies good citizens as
citizens who understand and are able to properly
implement their rights and obligations as individual
citizens with social sensitivity and responsibility, able
to solve their own problems as well as problems
(Socially sensitive, socially responsible, and socially
intelligent), have the attitude of personal discipline,
creative, critical thinking, and innovative in order to
attain the personal qualities and behavior of citizens
and citizens of good society (socio civic behavior and
desirable Personal qualities).
Meanwhile, according to Winataputra and
Budimansyah (2007) smart and good citizens are
well-informed citizens supported by the competence
of citizens the civic knowledge, civic dispositions,
civic skills Adequate, committed to the
implementation of the ideals, values, concepts and
principles of democracy for welfare and justice, and
responsible as citizens manifested in their inclusion in
the making and implementation of public policy.
In the view of Branson (1995) the main components
of civic education are: civic knowledge, civic skills,
and civic dispositions. Civic knowledge relates to
content or what citizens should know about. The next
component of citizenship skills is that when citizens
practice their rights and fulfill their responsibilities as
members of a sovereign society, they not only need to
possess basic knowledge but they also need to have
relevant intellectual and participatory abilities. While
the third component of civic character intends to
imply on the public character as well as the private
character that is essential for the maintenance of
constitutional democracy.
In the view of Winataputra (2007),
psychopedagogical/andragogical and sociocultural
citizenship education should be designed,
implemented and evaluated in the context of
developing psychosocial intelligence that is reflected
in the mastery of knowledge, the embodiment of
citizenship, the appearance of civic skills, the
possession of civic commitment, the possession of
citizenship constancy, and the appearance of civic
competence that all radiates from and crystallizes
back to the virtue / civilization of citizenship.
On the other hand Mossberger, Tolbert, McNeal
(Year, 2008) states that “Digital citizenship is ability
to participate in society online”. Meanwhile,
according to Ribble and Bailey (2007) “Digital
citizenship can be described as the norms of
appropriate, responsible behavior with regard to
technology use”. Ribble and Bailey (2007) suggest
elements in digital citizenship are digital access: full
electronic participation in society; digital commerce:
the buying and selling of goods online; digital
communication: the electronic exchange of
information; digital literacy: the capability to use
digital technology and knowing when and how to use
it; digital etiquette: the standards of conduct expected
by other digital technology users; digital law: the
legal rights and restrictions governing technology
use; digital rights and responsibilities: the privileges
and freedoms extended to all digital technology users,
and the behavioral expectations that come with them;
digital health and wellness: the elements of physical
and psychological well-being related to digital
technology use; digital security: the precautions that
all technology users must take to guarantee their
personal safety and the security of their network.
Furthermore Ribble and Bailey (2004) state that
topics with digital citizenship are wide and varied, so
you will need to use these topics as a “buffet” and take
what you need, realizing that the other themes are
there. The topic of digital citizenship is important to
students and their future because this is the world that
these students are growing up in, and school need to
be a part of this process. Now the internet and social
networking application can be used on a cell phone,
ICSE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education
496

these events can occurs at any time, both in school
and out. While the technologies may change, the
concepts of using these tools appropriately will
remain the same. This is why teaching these skills to
students (even as young as prekindergarten) may
become a priority for schools.
Oxley (2010) argues that developing a digital
citizenship is critical program because three of the
biggest problems facing young people today are: their
perceived anonymity, their accumulated digital
portfolio or digital footprint and the legal implications
of thoughtless or malicious actions. Meanwhile,
Microsoft made publication that state digital
citizenship is matters thing because following reason:
the first, Today’s young people are navigating a new
digital culture in which the rules and social norms are
sometimes unclear. They must learn about digital
citizenship and develop a sense of ownership and
personal responsibility to make good, ethical
decisions in the online world. The second, the online
world presents great opportunities for young people,
but it is not without risks. We can mitigate some of
those risks by helping young people develop a strong
sense of digital citizenship. The Third, rather than
relying solely on protective measures, an approach to
online safety that includes digital citizenship will help
young people safely interact in the online world.
Teaching them about digital literacy and digital ethics
and etiquette in no longer merely an option; it is an
imperative.
Bawa, Jyoti, Choudhary (2013) explains that
there are advantages and disadvantages of digital
citizenship the advantage of digital citizenship are:
the first, digital citizenship keeps imprint of your
online identity from your whole life. The things are
revived and observed within the digital world. The
second, when you see on the side of your webpage
there are ads and websites that are not random. There
are topics relevant to your preceding searches. This
can be very crucial for you in such a way that things
you are fascinated is there in front of you. The third,
digital citizenship can be used in many various form.
You can put your views about new technology or
education on the web so that other people can make
best out of it. Anyone can elaborate your ideas even
they don’t know you from all over the world. The
fourth, it restores memories and creates the chance for
recalling in your life for future jobs and scope. The
disadvantage of digital citizenship are: the first, if you
put irrelevant content out on the net and post inimical
things about people. It could inhibit you from
grasping a job. The second, It would definitely affect
you in negative aspects in your life when you neglect
the use of digital citizenship to form your online
identity. The third, if you fill the feedback form of
your teacher that how much you hate a teacher or
how much you hate or like your boss while forming
your online identity it would refer to your online
feedback for your teacher or boss. The fourth, if you
delete everything related to your post it will stay there
because of screenshots, pictures and witness of your
post.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Results
Before being used to all samples the instrument was
tested on 30 students at SMK Negeri 4 Surakarta.
This trial was conducted using an instrument
consisting of 37 items with 4 choices of answers that
are often, sometimes, rarely and never. Positive
statements have the following scores: often have a
score of 4, sometimes have a score of 3, rarely have a
score of 2 and never has a score of 1. While negative
statements: often have a score of 1, sometimes have a
score of 2, rarely have a score of 3 and often has a
score of 4. After the instrument was tested on 30
students, it was found that 30 items fulfilled the
validity. The questionnaire was then used to measure
student’s digital citizenship in five schools. The final
score is obtained by summing the scores obtained by
the total number of scores multiplied by 100. Then
create the category by considering the minimum
mastery criteria (KKM) that is 70%. Based on the
KKM then the minimum score is 85 (table 1). The
results obtained students are then.
Table 1: KKM.
Based on the results of the research obtained the
highest score is 117 while the lowest score is 74 and
has an average of 88.89. In detail the results are as
follows: 14 students included in the excellent
category, 50 students included in the good category,
88 students included in the fair category and 128
students included in the poor category. The research
shows the percentage as follows: 5 % in the excellent
category, 18% in the good category, 31% in the fair
category and 46% in the poor category (figure).
Score Category
109 – 120 Excellent
97-108 Good
85-96 Fair
<85 Poor
Digital Citizenship - The Reality of Students Attitude using Information and Communication Technology
497
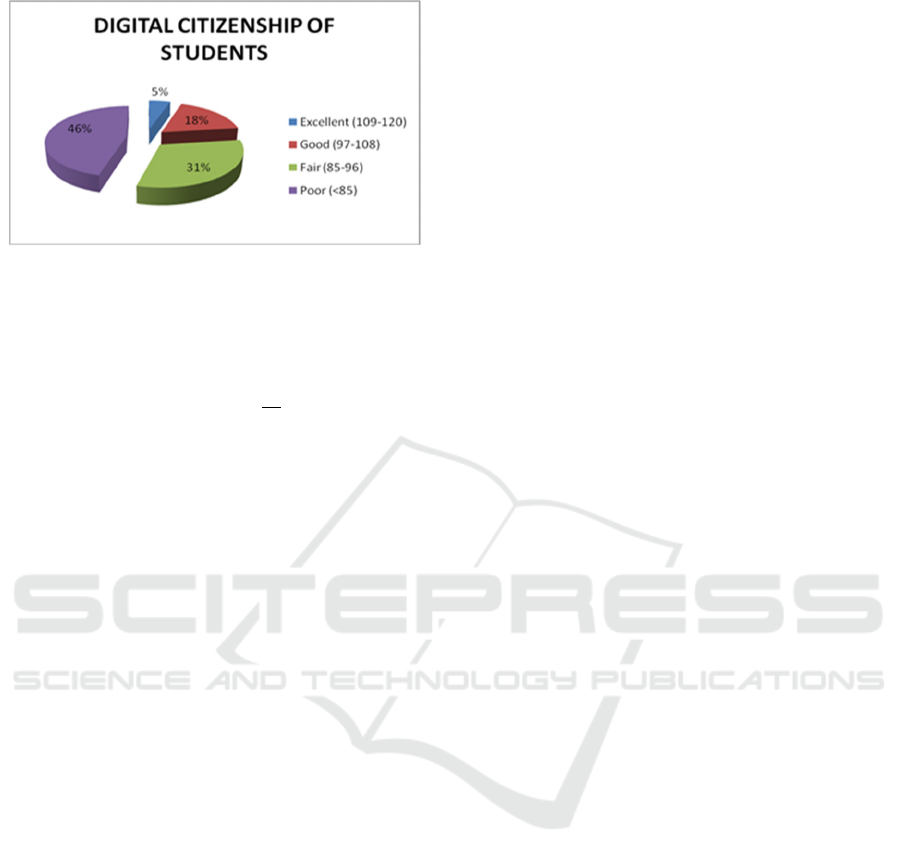
Figure 1: Results of the research.
3.2 Discussion
Citizenship education has three components that a
citizen needs to possess in order to be smart citizen,
characterized and participative IE civic knowledge,
civic skills, and civic disposition.
Civic disposition is often translated as character,
attitude, disposition or character of citizenship, but
some call it a civic value. Measuring these
components can be done through a questionnaire
technique with Likert scale model.
Meanwhile digital citizenship elements are: a. Digital
access; b.Digital commerce; c. Digital
communication; d. Digital literacy; e .Digital
etiquette; f. Digital law; g. Digital rights and
responsibility; h. Digital health and wellness; i.
Digital security. Furthermore Ribble dan Bailey state
that digital citizenship are wide and varied, so you
will need to use these topics as a “buffet” and take
what you need, realizing that the other themes are
there. Based on that opinion and considering that
civic education is a subject that focuses on the
formation of citizens who understand and are able to
exercise their rights and obligations to become
Indonesian citizens who are intelligent, skilled and
characterized, including in the perspective of
Indonesian citizenship education, there are 3 related
elements: Digital law, digital ethics, digital rights and
responsibilities.
After doing the bookkeeping on the
students the results show that the category is excellent
category 5%, good category 18%, fair category 31%
and poor category 46%. Referring to Branson's view
that the components of civic education include civic
knowledge, civic skills, and civic disposition, the
results can be attributed to the civic disposition
component. It appears how the digital citizenship,
attitude of students in using information and
communication technology. The results show that the
majority of students have poor digital citizenship
attitudes.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The majority of digital student citizenship is low with
the following details: 5% excellent category, 18%
good category, 31% fair category and 46% poor
category. Digital citizenship is measured in terms of
digital law, digital ethics, digital rights and
obligations. The results indicate that the majority of
digital student citizenship is poor because of the need
to increase the digital citizenship of students through
the cultivation of digital citizenship. Digital
citizenship is the norm of propriety, responsible
behavior in the use of technology. Digital citizenship
can be cultivated through both formal and non-formal
education. One of them is through civic education.
Civic education can be addressed as legal education.
One of the scope of Indonesian civic education is
about norms, laws and regulations then digital
citizenship can be included on it.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by LPPM UNS. We
thank to committee of UPIICSE for comments that
greatly improved the manuscript.
REFERENCES
APJII. 2014. Profil Pengguna Internet. Puskakom UI.
Maret 2015.
Bawa, K., Jyoti, C. K., 2013. Digital and Virtual Era:
Digital Citizenship. International Journal of
Engineering and Advanced Technology (IJEAT). 3 (2).
Branson, M. S., 1999. Belajar Civic Education dari
Amerika. Yogyakarta: LKIS dan The Asia Foundation.
Hollandsworth Randy, Dowdy Lena, Donovan Judy. 2011.
Digital Citizenship in K-12: It Takes a Village.
TechTrends. 55 (4).
Kalidjernih, F. K., 2010. Puspa Ragam Konsep dan Isu
Kewarganegaraan. Bandung: Widya Aksara Press.
Microsoft; Fostering digital citizenship.
Mossberger, K., Tolbert, C. J., McNeal, R. S., 2008. Digital
Citizenship, The Internet, Society, and Participation.
Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Oxley Cathy. 2010. Digital Citizenship: Developing an
Ethical and Responsible On-line Culture. Proceedings
of the 12
th
Biennial School Library Association of
Queensland, the 39
th
International Association of
School Librarianship Annual Conference incorporating
the 14
th
International Forum on Research in School
Librarianship. Brisbane QLD Australia. 27 September-
1 October.
Ribble Mike S, Bailey Gerald D., Ross Tweed W. 2004.
Digital Citizenship Addressing Appropriate
ICSE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education
498

Technology Behavior. Learning and Leading
Technology. 32 (1).
Ribble Mike. 2012. Digital Citizenship for Educational
Change. Kappa Delta Record. Oct-Dec.
Ribble, Mike, Gerald Balley. 2007. Digital Citizenship in
Schools, Washington: ISTE.
Smith, R. M., 2002. Handbook of Citizenship Studies.
London: Sage Publications.
Triastuti. 2017. Model Pengembangan Pendidikan
Kewarganegaraan Bagi Upaya Pembinaan
Kewarganegaraan Digital (Digital Citizenship)
Melalui Pemanfaatan Teknologi Informasi dan
Komunikasi di Sekolah. Bandung. Sekolah
Pascasarjana UPI.
Triastuti, budimansyah, sapriya. 2016. Digital Citizenship
Students Viewed from Digital Commerce Aspect.
Advances in Economics, Business and Management
Research, volume 15, 1st Global Conference on
Business, Management and Entrepreneurship
(GCBME-16), Atlantis Press.
Winataputra, Udin S, Budimansyah, Dasim. 2007. Civic
Education konteks, Landasan, Bahan Ajar dan Kultur
Kelas. Bandung: Sekolah Pascasarjana UPI.
Digital Citizenship - The Reality of Students Attitude using Information and Communication Technology
499
