
Internalization of Values Academic Integrity and Its Effect on
Performance of Financial Management at Universitas Tanjungpura
Pontianak Indonesia
Witarsa Witarsa
Universitas Tanjungpura, Pontianak, Indonesia
witnessed@yahoo.com
Keywords: Internalization, Academic Integrity Value, Performance.
Abstract: The Research Problems came from Universitas Tanjungpura, Pontianak Indonesia because in 2016 managing
funds amounting to 100 billion Rupiah and managed by 9 faculties, agencies and unit. Management of these
funds need to be escorted to the values of academic integrity. The purpose of the study (1) to determine the
process of internalizing the values of academic integrated, (2) to determine the effect of partial and
simultaneous honesty, fairness, trust, respect, and commitment on the performance of financial management
staff. The method used is survey method with explanation approach. The research sample as many as 30
people. The results showed (1) the process of internalizing the values of academic integrity conducted by
three processes, namely the transformation, transaction, internalization, (2) there is a partial effect and
simultaneous values of academic integrity which includes honesty, fairness, trust, respect, and commitment
on the performance of financial management staff.
1 INTRODUCTION
The value of academic integrity in the context of life
developing in someone's personality. Personal values
evolve from a State to the outside world and can
change from time to time. Integrity in the application
of the values it refers to continuity; people have
integrity if they apply their values appropriately
regardless of arguments or negative reinforcement
from others. Values are applied appropriately when
they are applied in the right area. For example, it
would be appropriate to apply religious values in
times of happiness as well as at the moment of
despair. Similarly, the value of academic integrity is
practiced in most educational institutions, known in
the mission statement and represented in the code of
honor.
Factors integrity of the academic community is
determined by the performance of employees in
charge of implementing academic service. Bruce et
al. (2012) which conducts research on Academic
Integrity: a review of the literature, Studies in Higher
Education, shows that of the Review 115 articles and
reality that occurs in universities in Hong Kong that
values academic integrity is very important in
improving academic services.
Ishak et al. (2016) conducted a study on The
Effect of Job Satisfaction, Integrity and Motivation
on Performance. Research results indicate that among
job satisfaction, integrity and motivation, integrity is
a variable turns the dominant influence on the
performance of 78.10%. While the influence of job
satisfaction and motivation by 18.90% amounting to
14.90% of the performance.
Baharom (2014) conducted a study on The Role
of Integrity as Mediator between Satisfaction Work
and Work Performance in the Perspective of Islam:
An Empirical Approach using SEM / Amos Model.
The results showed that the Mediator Integrity
Influence on work satisfaction in the perspective of
Islam Spiritual, Intellectual, Social, Materials, and
Work Performance.
Pay attention to the results of the study, the value
of the value of academic integrity is very important to
note because the effect on the performance of
employees. The value of academic integrity value
attached to the personality of employees who daily
carry out services at Universitas Tanjungpura that
drive performance improvements.
The Center for Academic Integrity (CAI) (2006)
defines academic integrity as a commitment, even in
the face of adversity, to five fundamental values:
Witarsa, W.
Internalization of Values Academic Integrity and Its Effect on Performance of Financial Management at Universitas Tanjungpura Pontianak Indonesia.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education (ICSE 2017) - Volume 2, pages 207-211
ISBN: 978-989-758-316-2
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
207

honesty, trust, fairness, respect, and responsibility.
From these values flow principles of behavior that
enable academic communities to translate ideals into
action.
Academic integrity is the commitment to five
fundamental values: honesty, trust, fairness, respect
and responsibility. This view of integrity as a
"clustering of values beyond honesty" (Davis and
Bertram, 2009), involves much more than a
commitment from students not to cheat. The Center
for Academic Integrity (CAI) (2006) makes explicit
that academic integrity is multi-dimensional and is
enabled by all those in the educational enterprise,
from students to parents, instructors and
administrators.
Institutional Framework for Promoting Academic
Integrity among Students (2015) state that: Academic
integrity is important because, without its core values,
true academic discourse becomes impossible,
learning is distorted and the evaluation of student
progress and academic quality is seriously
compromised. Consequently, the University is
committed to: (1) defending the academic credibility
and reputation of the University; (2) protecting
student achievement standards and the standards of its
awards; (3) ensuring that students receive due credit
for the work they submit for assessment; (4) making
reasonable adjustments to assessment that maintain
the integrity of the University’s courses and awards;
(5) protecting the interests of those students who do
not cheat; (6) advising its students of the need for
academic integrity, and providing them with guidance
on best practice in studying and learning; and (7)
educating students about what is intellectual property,
why it matters, how to protect their own, and how to
legitimately access other people's work. (Institutional
Framework for Promoting Academic Integrity among
Students, 2015).
The International Center for Academic Integrity
states that there are core values of integrity includes:
(1) honesty, (2) trust, (3) fairness, (4) respect, (5)
responsibility. Academic Integrity Guidelines (2006)
Academic Integrity is a mode of conduct based on an
individual and institutional commitment to the
principles of honesty, trust, fairness, respect, and
responsibility, to be Terrenes through (1) Honest and
ethical conduct in all activities Relating to the life of
the College, (2) Truthful, complete, and accurate
representation of all personal and academic
information, (3) Integrity of products of the academic
process, such as tests, essays, research papers,
laboratory reports, and any other class of course-
related preparations produced by individuals or
explicitly specified as group assignments, (4)
Universal application of the principles of the
Academic Integrity throughout the institution [4].
Gary (1997), Director of Judicial Programs and
Student Ethical Development, University of
Maryland stated that "Promoting student moral
development requires affirming shared values. More
colleges are starting to focus on one value that goes
to the heart of the academic enterprise: a commitment
to honesty in the pursuit of truth."
Academic Integrity relates to new management
techniques included in financial management. Ian
(2005) states The liberal, collegial values of the
Dearing Committee, listed above, contrast with the
expectations of New Managerialism. Pollitt (1990)
argues that the new managerialism can be seen as a
generic package of management techniques the which
include: (1) Strict devolved financial management
and budgetary controls. (2) Efficient use of resources
with an emphasis on productivity. (3) Extensive use
of quantitative performance indicators. (4) The
development of consumerism and the discipline of the
market. (5) The manifestation of consumer charters as
mechanisms of accountability. (6) The creation of a
disciplined, flexible workforce, using flexible /
Individualized contracts, staff appraisal systems and
performance related pay. (7) The assertion of
managerial control and managers' right to manage
(Ian, 2005). Referring to the expert opinion of the
above, the core values of integrity includes: (1)
honesty, (2) trust, (3) fairness, (4) respect, (5)
Commitment. The core values of integrity are very
important in maintaining the performance of the
individual so that the resulting performance as the
embodiment of earnest sincerity to implement quality
of service.
Bernardin and Russel provide an understanding of
the performance as follows: "performance is defined
as the record of the outcomes produced on a specified
job function or activity during time period. Bernadin
(1997) suggests performance is the systematic
description of the job relevant strength and
weaknesses of an individual and organization. The
performance is "A way of measuring the contribution
of individuals to Reviews their organization".
According to J. Campbell (1990) written by Jex
(2002): Performance should be distinguished from
effectiveness, productivity, and utility. Effectiveness
is defined as the evaluation of the results of an
employee's job performance. This is an important
distinction Because employee effectiveness is
determined by more than just job performance. For
example, an employee who is engaging in many
forms of productive behavior may still receive a poor
performance rating (a measure of effectiveness)
ICSE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education
208
because of performance rating errors, or simply
Because he or she is not well liked by the person
assigned to do the rating. Productivity is closely
related to both performance and effectiveness, but it
is different Because productivity takes into account
the cost of Achieving a given level of performance or
effectiveness.
From the opinion of experts, it can be concluded
that the performance is a performance of the functions
of the job or the activities of a particular person in
carrying out the duties charged to him based upon
know-how, experience and commitment within a
certain period.
2 RESEARCH METHODS
The method used is survey method with approach
explanatory research that explain the causal
relationship associative between Honesty (X1), Trust
(X2), Fairness (X3), Respect (X4), and commitment
(X5) with Employee Performance Financial (Y),
good quality of causality partially or simultaneously
through hypothesis testing. The study population was
an employee of the financial management and Acting
Commitment (KDP) in the university environment
Tanjungpura totaling 30 people. Because of the
relatively small population, then the population is
decided taken all as a sample. Tests using the research
instrument validity and reliability. test results of
research instrument of the subject supposed to know
about the variables studied showed that the variables
of honesty (X1), variable trusts (X2), variable fairness
(X3), variable respect (X4), variable commitment
(X5) and variable performance financial officer (Y)
indicates that the value of the validity of each
variable> 0.30, and the value of reliability Cronbach's
Alpha or Ri> 0.60. Data analysis technique used is the
technique of multiple linear regression analysis.
3 RESEARCH RESULTS
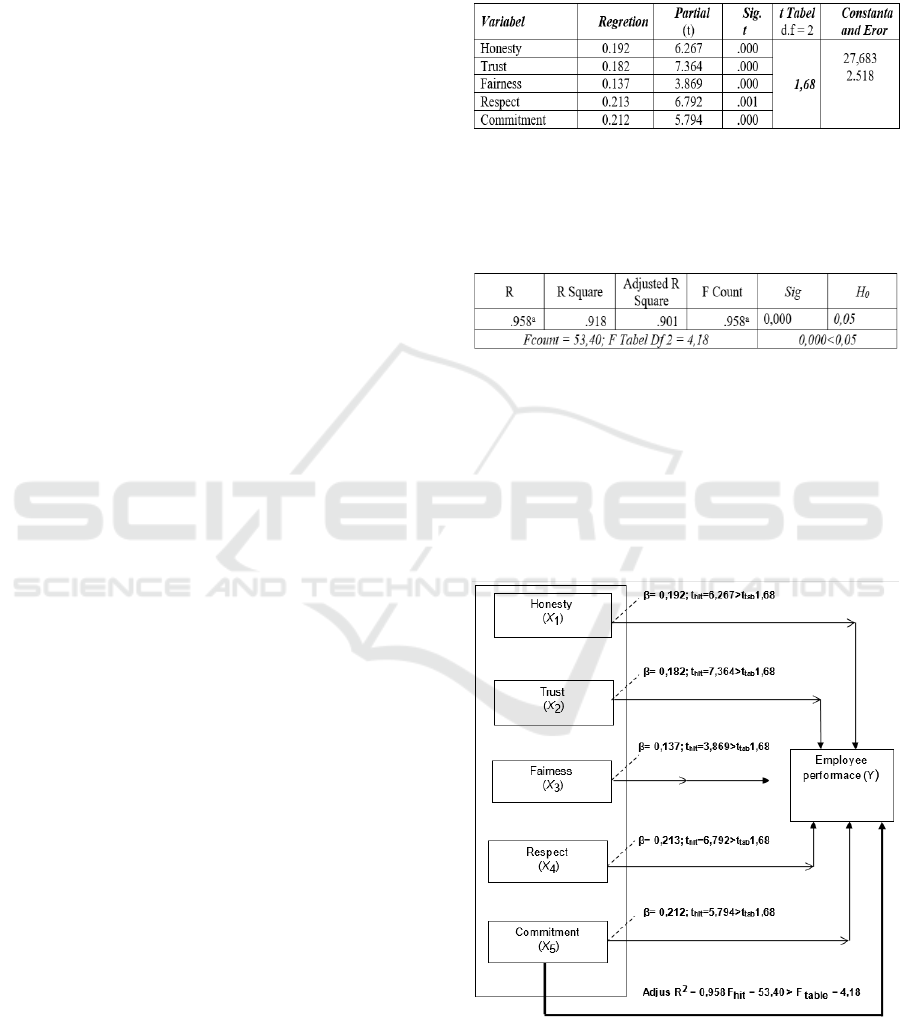
Analysis of the influence of partial as in table 1, it can
be seen that there is a partial influence of variable
Independent variable i.e. honesty (X 1), variable trust
(X 2), fairness (x 2) variables, variable respect (X 2),
variable commitment (X 2), against Financial
Manager officer performance variable (Y), can be
seen in the following table 1:
Table 1: Influence of Partial variables of honesty (X 1),
variable trust (X 2), fairness (x 2) variables, variable respect
(X 2), variable commitment (X 2), partially against the
employee who manages the financial performance of the
variable (Y).
Table 2. The simultaneous influence of Independent
variable that is honesty (X 1), variable trust (X 2), fairness
(x 2) variables, variable respect (X 2), variable commitment
(X 2), partially against the employee who manages the
financial performance of the variable (Y).
The results of adjusted R-Square acquired for
0.901. This shows that simultaneously there is a
strong influence of the variable honesty (X 1),
variable trust (X 2), fairness (X 3) variables, variable
respect (X 4), variable commitment (X 5), against
financial manager officer performance variables (Y)
of 90.10 percent While the rest of 9.90 percent
affected by other variables which are not examined in
this study.
Figure 1: The influence of Simultaneous and partial of
Honesty Variables (X 1), variable Trust (X 2), Fairness (X
3) Variables, variable Respect (X 4), variable Commitment
(X 5), against Financial Manager Officer Performance
Variables (Y).
Internalization of Values Academic Integrity and Its Effect on Performance of Financial Management at Universitas Tanjungpura Pontianak
Indonesia
209

4 DISCUSSION
The Effect of honesty variable (X1), significantly
affect the financial manager of employee
performance variable (Y). Empirical results find that
honesty in a positive effect on employee performance
variable financial manager. The results of this study
are supported by Frederick, et al., (2008). There are
two reasons why we undertake a further investigation
into the effects of honesty on budgeting. First,
previous studies such as Evans et al. (2001) and
Hannan et al. (2006) have difficulty isolating the
effects of honesty Because The reporting behavior of
the subordinate directly Affects the distribution of
wealth between the superior and subordinate.
Therefore, deviations from self-interested behavior
can be Attributed either to honesty or to other no
pecuniary motivations such as preferences for the
distribution of wealth. Evans et al. (2001) recognizes
the importance of the subordinate's concerns for the
distribution of wealth between the superior and
subordinate and note the need for further research to
refine our understanding of the factors that influence
the extent of honesty. We address this issue by
manipulating the subordinates' mode of budget
communication, including one treatment where a
factual assertion is required and another treatment
where no factual assertion is required. While other-
regarding preferences may operate and in both cases,
only in the former case should be relevant honesty
Because only in that case is it possible to make-an
UNTRUE representation. By exploring both forms of
communication, we are Able to estimate the
incremental effect of honesty (Frederick et al., 2008).
The Effect of trust variables (X2), significantly
affect the financial manager of employee
performance variable (Y). Empirical results find that
trust has positive influence on employee performance
variable financial manager. This was confirmed by
Amena and Shahid (2013) which states "Trust must
be treated as precious, highly Admired, and a
cherished organizational trait. Trust is an extremely
substantial commodity to any affiliation. A point that
needs to be promoted, is that trust is a dainty property
of human relationships, in that is powered by conduct
far more than by words, it may take time to constitute,
but is can be Abolished very quickly intervening.
Integrity is imperative to personal success and for
expanding leadership skills. Individuals that have
integrity build trust in their relations with others;
Become precious and they are respected as friends,
colleagues, mentors, and supervisors. They are
respected and counted on to do what is right. They are
Able to balance dignity and accountability, and they
are Able to Reviews their share values with others
(Amena and Shahid, 2013). Charles (2014) states The
research highlights five fundamental skills and
qualities that leaders need in order to be trusted.
The Effect of fairness variable (X3), significantly
affect the financial manager of employee
performance variable (Y). The results of the empirical
finding that fairness has positive influence on
employee performance variable financial manager.
The results of this study are supported by Sara et al.
(2012) which states; We have taken two variables in
our research Initially. The independent variable is
"fairness" the which leads towards "organizational
performance". By "fairness" we will be measuring
fairness in the working environment, sustainable
amount of work load for the employees, fairness in
providing them with required facilities to work
comfortably and fairness in appraisal system. After
carrying out a thorough literature review we have
found that "fairness" encompasses such virtues as
moral rightness, equity, honesty, and impartiality.
Fairness, or justice, is one of the most fundamental
concerns in society (Sara et al., 2012).
Influence respect variable (X4), significantly
affect the financial manager of employee
performance variable (Y). The results of the empirical
finding that respect positive influence on employee
performance variable financial manager. Respect is a
form of self-efficacy. Jacob and Jolly (2013), Success
in a realm is closely linked to self-efficacy in the
realm (Bandura, 1997). Higher self-efficacy in a
realm is associated with good outcomes, ranging from
greater job satisfaction and performance (Judge and
Bono, 2001), to better physical and mental health
(Bandura, 1997), to better academic performance
(Bandura, 1997; Robbins et al., 2004). For example,
students with higher academic self-efficacy show
better academic performance (Robbins et al., 2004).
Priming a high self-efficacy component of a self-
schema for a realm Might result in outcomes similar
to Reviews those found for individuals who have
characteristically high self-efficacy in a realm.
Related to this notion, previous research in other areas
indicates that manipulating individuals' perceptions
with respect to motivation will have an impact on
their performance (DeDonno and Demaree in Jacob
and Jolly, 2013).
The Effect of commitment variable (X5),
significantly affect the financial manager of
employee performance variable (Y) The results
empirically found that the commitment has positive
influence on employee performance variable
financial manager. This result is supported by the
opinions Luthans et al. (2007) which states, others
ICSE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education
210

where there are moderating effects between
organizational commitment and performance. A
study by the Association of Professors of Pakistan
Institute of Business Administration, University of
the Punjab by Mubbsher and Mubbsher (2012) who
studied The Impact of Employees Commitment On
Employee Satisfaction Role of Employee
Performance as a Moderating Variable. Research
results show that there is a difference between job
satisfaction among employees who have high
performance with employees who are not high
performance. Commitment direct influence on
employee performance.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The process of internalizing the values of academic
integrity are: honesty, fairness, trust, respect, and
commitment on employee financial manager at the
Universitas Tanjungpura Pontianak conducted by
three stages: (1) the process of transformation as a
process undertaken to inform good value and the bad.
(2) Transaction Process in this process the value of
academic integration is done through two-way
communication so that automatically there is a
process of interaction between researchers and
employees. (3) internalization process. At this stage
of internalization is not only carried out with verbal
communication but also the mental attitude and
personality. So at this stage personality who played
an active role communication.
There are partial and simultaneous influence of
variable independent variable variables i.e. honesty,
trust, fairness, respect variables variables, variable
commitment to financial manager officer
performance variables.
REFERENCES
Amena, S., Shahid, M. A., 2013. Integrity & Trust: The
Defining Principles of Great Workplaces. Journal of
Management Research. ISSN 1941-899X 2013, Vol. 5,
No. 4, pp 64-75.
Academic Integrity Guidelines, (2006) Chattanooga State
intra web. 25 Apr.
Baharom, 2014. The Role Integrity as Mediator between
Work Sutisfaction and Work Performance in the
Perspective of Islam: An Empirical Approach Usin
SEM/Amos Model International Journal of Research in
Applied. Natural and Social Sciences. 2321-8851;
ISSN(P): 2347-4580 Vol. 2, Issue 1, Jan 2014, 71-84.
Bernadin, H. J., Russel, E. A., 1997. (Human Resources
Management, An Experiential Approach, Mc Graw Hill
International Editions, Mac Graw Hill Book Co.
Singapore 1997) h, 379.
Bruce, M., Jingjing, Z., Annie, P., 2012. Academic
integrity: a review of the literature, Studies in Higher
Education, University of Hong Kong Libraries On: 02
August.
Charles, E., 2014. The truth about trust: Honesty and
integrity at work. The Institute of Leadership and
Management. London. pp 1-16.
Frederick, W. R., Steven, T. S., Richard, A. Y., 2008. The
Effect of Honesty and Superior Authority on Budget
Proposals. American Accounting Association. The
Accounting Review. Vol. 83, No. 4. 2008 pp. 1083–
1099.
Ian, M., 2005. Values, Principles and Integrity: Academic
and Professional Standards in Higher Education.
Higher Education and Management, University of
Greenwich. London, United Kingdom.
Institutional Framework for Promoting Academic Integrity
among Students, 2015. Document URL, Griffit
Universty.
Ishak, A., La, O. B. A., Sri, W. M., 2016. The Effect of Job
Satisfaction, Integrity and Motivation on Performance.
The International Journal of Engineering and Science.
Volume 5 Issue 1 PP -47-52.
Jacob, C., Jolly, J., 2013. Impact of Self Efficacy on
Motivation and Performance of Employees.
International Journal of Business and Management.
Vol. 8, No. 14; 2013, pp 80-88.
Jex, S. M., 2002. Organizational psychology: a scientist-
practitioner approach, John Wiley & Son. Canada.
Luthans, F., Youssef, C. M., Avolio, B. J., 2007.
Psychological capital: Developing the human capital
edge, Oxford University Press. New York.
Mubbsher, M. K., Zia-ur-Rehman, Muhamma, W. A.,
2012. The Impact of Employess Commitment On
Employee Satisfaction Role of Employee Performance
as a Moderating Variable. Singaporean Journal of
Business Ecnomics, and Management Studies. Vol 1,
No 2, 2012. hh. 1-13.
Sara, A., Rabiya, A., Mushtaq, A. B., 2012. The impact of
fairness in Working Condition on Organizational
Performance in Pakistas Telecommunication
Company, Limited, Islamabad. International Journal of
Economics and Management Sciences Vol. 2, No. 4,
2012, pp. 10-19.
Steven, L. M., Mary, A. V. G., 2009. Organizational
Behavior, Irwin McGraw-Hill. New York.
Internalization of Values Academic Integrity and Its Effect on Performance of Financial Management at Universitas Tanjungpura Pontianak
Indonesia
211
