
The Model of Ecovillage Value Investment as Independence Village
and Cultural Environment at Cimaung, Bandung-Indonesia
Mupid Hidayat, Maulia D. Kembara, Dina S. Logayah, and Firman Ghozali
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Bandung, Indonesia
hidayatmupid@gmail.com
Keywords: Cimaung community, ecovillage values, education model.
Abstract: The research models of ecovillage value investment in communities of Cimaung district there is in Bandung-
Indonesia, aims to identify the ecovillage values of Cimaung community in forming independent villages and
cultured environment, analyzing the implementation, and mechanisms to defend the values as a manifestation
of the harmony of life with environment, and explore the ecovillage values of Cimaung community basis for
developing an education model for shaping the character of the students in interacting with the environment.
The research approach used in this study is qualitative descriptive, because it assessed the ecovillage context
of the values of wisdom contained in traditional societies. This research was conducted in Cimaung Bandung-
Indonesia contained two indigenous groups and 10 farmer groups. Subjects in this study were the community
leaders and farmers at Cimaung as a data source. Subjects of this study involves the community Cimaung.
The data taken is through interview, observation and documentation. Validation of data is done through
triangulation which serves as a cross-check the data that refers to the dimensionality through plural viewpoints
and stability.
1 INTRODUCTION
Humans in everyday life has a dependency that very
closely with their environment. As with any other
living beings, human beings in daily life is influenced
and affected the surrounding environment, good for
the environment or not alive. On the other hand,
especially the man must meet the needs of biological
primary and, among other things need air to breathe,
water to drink, as well as the types of plants and
animals for food sources. As for the primary needs of
human beings need our satisfaction will be material
objects or wealth exploited from nature and recreation
and entertainment to enjoy the beauty of nature.
Another problem, people sometimes do not
realize where they are living and staying, as if human
life freely and despite the support of the environment
around us. Thus, humans are often less wise in the
process of nature and the environment. Human
behavior indiscretion that can be observed by cutting
down forests that resulted in fires that forest
ecosystem becomes disrupted, household waste in
rivers causing siltation of rivers and river pollution
becomes impaired, as well as the urbanization of rural
areas to cities so much land in the countryside is
untreated. From those example, it seems that people
without the support of the environment such as air,
water, other types of plants, as well as animals, not
human beings can’t make his life. Therefore, it is
appropriate that we in everyday life need to maintain
and manage our environment. Especially in a variety
of development programs that have the primary
purpose of increasing levels of well-being of human
life that needs to be backed up by economic capital,
social capital and capital of natural resources and the
environment or ecosystem.
Thus, the development program has been agreed
upon by the leaders of countries in the world, that the
development paradigm is no longer emphasizing only
on economic growth, but also by integrating the social
factors, cultural, and environmental. The
development paradigm known as sustainable
development. Development in general can be seen as
a conscious effort to change human culture, in the
form of conscious efforts to improve the kind, quality,
quantity that must be met for the satisfaction of the
main or primary needs in efforts to improve the
welfare of human life. If the elements of human
culture, especially a very important benefit for human
life include the elements of economics and
technology that must be changed and adapted to the
efforts to improve the welfare of people's lives, the
development activities that cause changes to the
system social and ecosystem. For example, a building
Hidayat, M., Kembara, M., Logayah, D. and Ghozali, F.
The Model of Ecovillage Value Investment as Independence Village and Cultural Environment at Cimaung, Bandung-Indonesia.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education (ICSE 2017) - Volume 2, pages 513-521
ISBN: 978-989-758-316-2
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
513

may be to change the social system, and cause a
change in the ecosystem. Likewise, the development
is changing the ecosystem, but the effects can cause
changes in the social system (Suparlan, 2005: 117).
For example, the construction of Planted Forest
Industry by altering the ecosystem of primary forests
to planted forests, such as land clearing for palm oil
plantations or otherwise. Due to changes in primary
forest ecosystem that can cause changes in the social
system of the local community. Ultimately, changes
in the social system of the local community can also
cause changes in the ecosystem. Thus, in a
development program should aspects of economic,
social, cultural and environment can be integrated
into one inseparable whole, according to the
paradigm of sustainable development.
In accordance with the policy of sustainable
development in Indonesia as outlined in Agenda 21,
sustainable development should have to pay attention
to poverty reduction. It is recognized that poverty is
one of the causes of environmental degradation and
negative impacts of development. Conversely,
deterioration of environmental carrying capacity can
be a cause of the emergence and development of
poverty (KLH, 1997: 7). In other words, preservation
of natural resources is essential for the development
of capital and to provide guarantees for the poor
whose lives are still dependent on natural resources
or the biophysical environment.
One of the concepts of sustainable development
are ecovillage (village self-sufficiency and cultural
environment) which was introduced in September
1991 in a seminar GAIA Trust in Thy, Denmark
compiled by Diane and Robert Gilman. Ecovillage
interpreted an ideal concept of the balance between
social, ecological and spiritual in human interaction
and the environment to the sustainability of life on
earth as a solution to the major environmental
problems, and ensure equality, human health and
safety. In this case ecovillage proponents, have
assumed that traditional life policies are good enough
to make it happen. Indonesian society that has
diversity in cultures and customs must have local
different knowledge from each other that is reflected
by the ordinance of natural and social environment.
Associated with the local knowledge and
sustainable development with the ecovillage concept
that aims to change the public mindset in behavior
change to better care for the environment. To achieve
independence regarding the sustainability of rural
communities the availability of resources in the
village is the main objective of developing ecovillage.
Therefore, the ecovillage development must be
supported by all members of the village community.
Thus, the development of ecovillage would be very
good if initiated by the nongovernmental. Ecovillage
community members united by a common ecological,
social, economic, and cultural. A village or town
which is classified ecovillage usually filled by people
or people who care about the environment by seeking
to optimize the resources of their environment.
Citarum watershed is a pilot project that is being
undertaken by the government of West Java province
became a pilot ecovillage. Citarum watershed
locations that are vital to the needs of human life.
West Java Provincial Government has launched the
Citarum Clean Movement, Healthy and Beautiful
2014-2018. Therefore, Citarum watershed is the
largest and longest river in West Java Province. But
now, the Citarum River in danger. Economic
development and high population growth have
threatened the sustainability of the Citarum River.
Deforestation in the upper basin have destroyed the
ecosystem resulting in soil erosion and siltation of
rivers and floods occur. Peoples, towns and villages
as well as industry with all its activities have changed
and treat the Citarum river as trash and waste
disposal. Currently the Citarum river is known as one
of the dirtiest rivers in the world.
Cimaung in Bandung- Indonesia is one location
that participates in the development of cultured
village or ecovillage environment. Cimaung has
potential in agriculture and plantations so that the
existence of the Citarum river when needed for
irrigation water for farming and gardening. In
addition, Cimaung also has the potential of typical
agricultural production of commodity that is arnet
and rancang sweet potato.
Accordingly, the identification model of
ecovillage value investment (village self-sufficiency
and cultural environment) contained in the
community, especially at Cimaung, in relation to
forming responsible environmental behavior
becomes strategic to do. Aside from being a vehicle
for wealth of local knowledge possessed, is also more
important, can be used as one approach to learning
Socio-Cultural Education as one of the forming of
responsible environmental behavior.
2 THEORETICAL APPROACH
2.1 Ecovillage Value
Humans are the perpetrators and environmental
management system that has a value in interacting
with its environment. Environmental degradation,
among others because there is a value system that puts
human beings are not part of nature (Yusuf, 1991). In
this case the man acting as conqueror, regulators, and
superior. The emergence of environmental problems
is the implication of the gap between the spiritual side
in this mentality with the physical construction itself.
ICSE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education
514

Ecovillage is a spatial concept and region
residents pay attention to quality and ecological
quality holistically because it involves all the
dimensions of our life. Ecovillage is the development
of rural areas who consider quality achievements of
individuals, families, communities and the quality of
sustainable natural environment. It is expected to
increase the welfare of rural communities without
damaging the environment. Furthermore, is also
expected to happen backflow from the city to the
village that can reduce the problems of population,
urbanization, energy issues, as well as urban social
problems are increasingly complex.
Realizing the independence of the village
community with attention to the sustainability of
resource availability in the village is the main
objective of the development of the ecovillage.
Therefore, the development of the eco village must be
supported by all members of the village community.
Thus, the development of an ecovillage will be very
good if an initiated by NGOs of the village.
Ecovillage community members United by a
commonality of ecologically, socio-economic, and
cultural and spiritual values. An ecovillage is usually
categorized village populated by people who care
about environmental sustainability by working to
optimize transactions are material and energy with
their surroundings. Nevertheless, the Government
still has the responsibility and the most important role
for the development of an ecovillage. Build
awareness with the extension, providing adequate
means for the development of an ecovillage and real
support in the form of mentoring in realizing the
ecovillage is indispensable. Good cooperation
between the community, Government, private sector
and research institutions (colleges) to ecovillage
development keys to success.
According Euis Sunarti (2012: 5) ecovillage
development is considered important because it has a
variety of purposes and benefits. First, as a way out
of inequality and imbalance of urban-rural
development of the region by restoring rural life
comfortable and provide opportunities and business
opportunities for the fulfillment of basic needs and
the evolving needs of its population. Second, to
reduce urban density, lower urbanization and its
consequences through equitable development and
improving the quality of life in rural areas. Third, to
optimize resources and efficiency of fuel use, thereby
encouraging energy independence of rural
communities. Thus, it is expected to be an effort to
improve the quality of life of individuals, families,
and communities especially those living in rural
areas.
The scope of the ecovillage according to Euis
Sunarti:
1. Develop a model of spatial and landscaping of
rural areas in the provision of space to support
the fulfillment of the principal inhabitants
2. Develop an optimization model transformation
and transactional materials and energy in
fulfilling the basic needs of individuals,
families, and society;
3. Formulating the right strategy and effective in
solving the problem of poverty in rural areas by:
(1) developing regional economic models that
support employment and business opportunities
(especially for poor families) either through
increased productivity and potential exploration
of local natural resources, as well as through an
increase in value-added economic activities; (2)
the application of appropriate technology to
increase the added value of primary products
and derivatives; (3) developing the institutional
system, facilities and infrastructure, as well as
rural infrastructure and agricultural support
sustainable development; (4) develop a model of
increased resilience and family empowerment
and community empowerment, among others
through coaching and mentoring system
development of rural areas independent of
economic, technological, social and cultural, as
well as covering the fields of agriculture, animal
husbandry, fisheries, and industry.
4. Designing materials design and eco-house
thermal system that meets the requirements that
promote comfort (temperature-resistant, water-
resistant, soundproof, and ergonomic aspects) of
life of individuals and families, as well as
energy saving household.
5. Design optimization of natural resources for the
provision of rural carrying capacity of matter
and energy to the community through
technology, infrastructure, as well as adequate
infrastructure.
2.2 Challenges and Criteria in Applying
Ecovillage
According to Gilman (1991) unit ecovillage is a scale
where each individual can identify and recognize the
community, and the extent to which each individual
can have an affect other opportunities. Ecovillage
community members united by a common ecological,
social, economic, and spiritual and cultural values. A
village categorized ecovillage, usually filled by
people who care about the environment, seeking to
The Model of Ecovillage Value Investment as Independence Village and Cultural Environment at Cimaung, Bandung-Indonesia
515

optimize transactions matter and energy with the
environment. Kampong that categorized ecovillage
filled by people who are trying hard to save energy,
such as by selecting alternative system of waste
management, water, and electricity independently.
Conversely, a consumptive lifestyle community,
doing things that affect the destruction of natural
habitats, and rely too much on fossil fuels (oil, gas,
coal).
Ecovillage is not easy to achieve, because the
diverse challenges that accompany it. For some
people, ecovillage realize such a dream. Therefore,
according to Gilman, R. (1991) there are challenges
for citizens who want to realize the ecovillage
namely:
a. residents together to build the realization of a
dream ecovillage,
b. ecovillage vision to develop and maintain it,
c. build relationships and bonds between citizens,
d. seeks outside assistance for independent,
e. maintains balance and sustainability, and
f. character building society open and honest.
Ecovillage demands skills to live together in one
place. Ecovillage is a settlement that is a Full featured
a mostly normal life functions, inadequate food
supply, the industry, the function of recreation and
social life, and the commercial aspects provided
proportionally. This does not mean that the ecovillage
to be self-sufficient in meeting all the needs of its
inhabitants. Ecovillage demanding provision of jobs
to offset the working-age population, and the
availability of specialization of work life balance as
well as human beings with other living creatures.
Feature or another important principle in the
ecovillage is the cycle of resource use material that
led to the use of renewable energy resources
(sunlight, wind, water) than fossil sourced fuel use;
enactment of garbage composting organic, and
sustainable community systems. (Eusi Sunarti, 2012).
According Fickeisen, D.H (1991) there is a life
skill that demanded the resident’s ecovillage is
respect for difference and diversity, the value of
heroism, understand the various personality styles
and learning styles of individuals, generation and
maintenance of motivation, understanding and skills
related to the process of group formation, related to
the participation and influence in a group, recognition
of and adherence to the task. Likewise, with other
basic life skills such as decision making,
communication skills, conflict resolution, leadership
and management. These life skills are united in the
life of an ecological village.
Challenges in the development of other ecovillage
is the integration of all components and dimensions
of life as well as its association with the assuredness
of a sustainable environment in regular development
planning and implementation. It takes coordination,
consolidating the synergy and harmony between all
components of the construction company. The criteria
ecovillage is the reference of the Citarum are:
a. Changing the mindset and behavior towards the
environment (saving water, saving energy, and
others),
b. management of waste through the 3R (Reduce-
Reuse-Recycle),
c. management of solid and liquid wastes, waste
management household (sanitary),
d. Management of agricultural activities that pay
attention to environmentally friendly
conservation through tree planting, protection of
water resources,
e. Technology of water and soil conservation
(biopori, infiltration wells, swales, etc.).
3 RESEARCH METHODS
3.1 Approaches and Methods
The approach used in this study is qualitative. This is
done because it studied the context of value
investment ecovillage contained in village
communities. Thus, through this approach is expected
information can be obtained in the focus and depth.
Methods in qualitative approach was conducted in a
descriptive way that is phenomenal can bring things
that stand out involve planting ecovillage values as an
independent village and cultured environment.
3.2 Subjects Research
Subjects in this study were the community leaders at
Cimaung, Bandung- Indonesia and the community
members of implementing ecovillage activities in
Cimaung as a data source. This research subject must
involve the community of Cimaung.
3.3 Instrument Data Collection
Data will be captured through interviews, observation
and documentation. Intensive interviews about
research to dig up information about the values held.
In addition, do also to other residents as a cross check.
Interviews were conducted using the guidelines, so as
not to deviate from the goal. The observations were
made to see firsthand the implementation of the
values ecovillage in interaction with everyday
environment at Cimaung. Studies conducted to
explore the documentation through secondary
sources to supplement the results of the field.
ICSE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education
516
Validation of data is done by means of
triangulation which serves as a cross-check the data
that refers to the dimensionality through plural
viewpoints and stability (Alwasilah, 2000).
Interviews were conducted with residents to match
the correctness of data from sources that have been
obtained. Thus, the data obtained can be analyzed as
a valid research results.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In developing and assessing the potential of rural
values need to involve public participation
proportionally. This is necessary for any development
program received the full support of the community,
ranging from data collection, assessment, community
service processing, utilization and the formation of
the model values Cimaung. By developing
community participation, the development model of
the values ecovillage would be more effective and
efficient because people will be more responsible
towards self-sustainability and cultured village or
ecovillage environment. Implementation of the
development of models of value investment
participatory ecovillage which can be reached by
steps as follows:
a. Invite the sub-district heads, represented by the
secretary of the district and community leaders
to provide an explanation ecovillage activities at
Cimaung.
b. Sharing opinions together with community
leaders about the program ecovillage activities
to be carried out with Mr. Eyang (a community
figure).
c. Assessment of values Cimaung ecovillage to
develop potential through village meetings
attended by the village, Village Consultative
Body, Institute of Rural Community
Empowerment, village institutions and
community leaders.
d. The collection potential of the village and the
needs of society by each family, then gathered
in the deliberations of citizens to be sent to the
village government as a reference for
developing value investment ecovillage.
e. The Government of the village gather and assess
the potential of rural ecovillage character and
needs of society as well as inputs from agencies.
f. Each team of developers doing field survey and
assessment to formulate development priorities
to really be implemented effectively and
efficiently.
g. Produce a model of value investment Cimaung
ecovillage.
4.1 Research Model Ecovillage Values
Investment
4.1.1 The Geographical Characteristics of
Cimaung
Cimaung located at an altitude of 741 masl to 2224
masl, flanked by Soreang Banjaran, Arjasari and
Pangalengan. In the study ecovillage, it is important
to know how the geographical conditions affect the
survival of the population, which was then called the
ecological carrying capacity. It shows the relationship
between ecological parameters (Table 2) are in sub
closeness to nature and a healthy food.
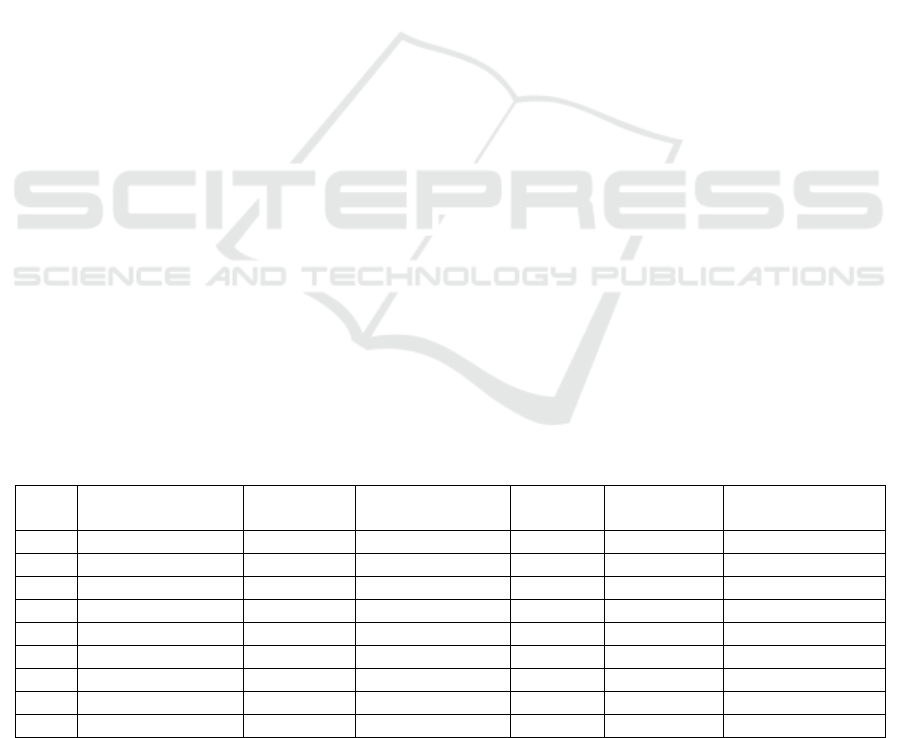
Tabel 1: The ecological conditions and carrying capacity of Cimaung.
No
Village
Rice fields
Area (Ha)
Rate of less Rice
fields (Ha/years)
Amount
of crops
Population
Ecological
Carrying capacity
1
Campaka Mulya
189.99
12.024
11.3994
8718
0.020661
2
Cikalong
292.59
4.572
17.5554
11275
0.099643
3
Cimaung
345.69
21.862
20.7414
10470
0.031325
4
Cipinang
126.36
8.874
7.5816
9009
0.011983
5
Jagabaya
371.7
16.386
22.302
12914
0.039174
6
Malasari
46.8
2.592
2.808
5629
0.009007
7
Mekarsari
306.63
12.906
18.3978
7153
0.061108
8
Pasirhuni
119.16
7.146
7.1496
7152
0.016669
9
Sukamaju
138.69
3.042
8.3214
5117
0.074142
Table 1 shows the variation of the ecological
carrying capacity of the region to ten villages at
Cimaung. Although quantitative, but it is the basis of
how important do ecovillage in addition to other
environmental related reasons including the issue of
The Model of Ecovillage Value Investment as Independence Village and Cultural Environment at Cimaung, Bandung-Indonesia
517

damage to Citarum watersheds. Parameter
Ecovillage.
4.1.2 Ecovillage is built based on the
integration of the four factors
including the factor of social,
economic, ecological and religious.
Based on the application of the curriculum according
to the ecovillage (Gaia Education, 2015) the fourth
factor must be translated into several parameters
(Figure 1) more operational so it is expected to obtain
the characteristics of a region ecovillage in this case
at Cimaung.
Similarly, Kasper (2008), that the ecovillage
should reflect the activities of the population,
valuable communities of spiritual, social and
ecological. Also, added by (Kasper, 2008) that in
addition to these three things are more important
things to be identified associated with zoning for
agricultural management, sale (market) and
settlements. In addition, it should be ensured the
availability of various facilities that can be shared by
the whole community. As well as meeting halls and
places for recreation. This is important to increase
employment opportunities and social interaction in
the community. For research purposes, ecovillage is
part of human interaction with the environment,
especially on matters related to the socio-economic
factors. More detail again (Hall, 2015) explains that
in an ecovillage, must have a main element 21, as
shown in Figure 1 below:
Figure 1: Important Element of Ecovillage (Hall,2015).
Of the 21 elements, will be rare in the area of
industry, urban areas or even in a residential complex.
Thus, if the element applied to see how ecovillage in
Cimaung conditions are met or not depends on the
twenty-one elements of the fine or not. So, Cimaung
can be regarded as the Ecovillage.
1. Ecology Parameters
Cimaung is a rural area (rural). In the ecovillage,
village not only as a residence but rather an
integral part of the system's life. Meaning how
they (residents) can live from his village and
how the village could have followed the
principle inhabitants live. From these
conditions, it can be concluded that the village
or somewhere that has ecovillage should have
only one or a set of potential that can be used to
feed its population naturally.
Based on the elements proposed by (Hall,
2015) and see the current situation that Cimaung
have more than 80% of agricultural area (Figure
3) and 603 residents directly related to
agriculture, the ecological parameters of
Cimaung are as follows:
Tabel 2: Ecovillage Eelements for ecology Parameters.
No
Ecovillage
Element
Yes
not
Explanati
on
14
Healty food
x
16
Close with
environment
x
17
Environment
activity
x
18
Eco-Friendly
(ERB)
x
2. Social Parameters
Based on Table 1, note less educated population
is widely followed by well-educated people at
the secondary level by 3236 the population
employed in non-Agriculture sector, is believed
to give effect to the social conditions of the
Cimaung population. Here's an overview of the
social factor in Cimaung:
Tabel 3: Ecovillage Eelements for social Parameters.
No
Elemen
Ecovillage
Yes
No
Explanation
2
Shared Work
(Gotong
royong)
x
Volunteer
x
4
Deliberation
x
5
Conflict
Minimalizatio
n
X
6
Selebration
x
7
Upholding the
values and
norms
x
8
Good personal
relationship
with openness
x
ICSE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education
518

9
Physical
contact
between
individuals
and groups
x
10
The dominant
relationship
between
parents and
children
x
11
Self-
development
x
12
Inclusive
x
13
The local
art and culture
x
15
Sports
x
3. Economy Parameters
The extent of agricultural land, not on
domination by people who work in agriculture,
making Cimaung areas into areas that tend to
lose an agricultural pattern. But the element
ecovillage based on economic factors obtained
the following data:
Table 4: Ecovillage Eelements for economy Parameters.
No
Elemen
Ecovillage
Yes
No
Explanation
1
Pooled Economy
X
2
Shared Work
X
3
Minimum
working time
X
4
Volunteer
X
5
Paid work
X
5 SUPPORTING AND
OBSTACLES FACTORS
During research, ecovillage parameters are not fully
can’t be obtained. So, there is a shortage obstacle in
analyzing the ecovillage character of each village
around Cimaung.
Culture and religion Parameter are relatively
difficult to obtain. Unlike the components of
ecological, social and economic. Therefore, in this
study only involves three parameters, namely the
ecological, social and economic.
5.1 Cimaung Ecovillage Charactersitic
1) Ecovillage characteristics on ecological
parameters (Figure 2 and Table 5) shows the
condition of the respondents. In fulfillment of
the food, the dominant population in Cimaung
prioritizing optimal foods (with adequate
protein and rice as the main carbohydrate
source).
Figure 2: Ecovillage characteristics on ecological parameters.
10
10
10
30
5
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
0
10
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
Healthy food
Rice
Buy on restoraunt
How you use rice fileds
Mini rice
Vend
Ecovillage Elements (Ecological Factors) Frequent How the measure of healthy food you eat
Ecovillage Elements (Ecological Factors) Rather often How the measure of healthy food you eat
Ecovillage Elements (Ecological Factors) Infrequently How the measure of healthy food you eat
Ecovillage Elements (Ecological Factors) No How the measure of healthy food you eat
The Model of Ecovillage Value Investment as Independence Village and Cultural Environment at Cimaung, Bandung-Indonesia
519

Table 5. Results of the questionnaire about the
ecological parameters
Ecovillage Elements (Ecological Factors)
Frequent
Rather
often
Infrequently
No
How the measure of healthy food you eat
Healthy
food
10
Protein
10
Rice
10
Noodles
10
Buy on
restoraunt
10
Amount
30
10
10
0
How you use rice fileds
Plant
5
Mini rice
10
Crops and
vegetables
10
Vend
10
Houses or
fishpond
10
There is a relationship of the results of the
questionnaire. The tendency of the population
who use the fields for rice (5 respondents) and
alternating with arable crops and vegetables (10
respondents) without having to sell it (10
respondents). They know exactly how to keep
the dependence on nature (fields) as an
important part to support life. Although not all
villages have the same availability of rice fields
(table 1), so that the ecological carrying capacity
of his farm can vary.
2) Social Economy Parameters
Explanation characteristics ecovillage on
ecological parameters (Figure 7 and Table 6)
shows the condition of inhabitants of the
villages in Cimaung, in terms of social and
economic activities. There is a national trend for
cooperation / mutual assistance in cases that
often occur in the community. This shows that
the village as a center for the development and
cultivation of the values of local wisdom or
known by local genius in good condition, this is
evidenced by "they still have the notion that by
working together, many things can be done
efficiently, effectively and feels light ".
Figure 3. Ecovillage Elements
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
Death disaster
Environmental Hygene
Healthy pramacies
Values and norms
Polite clothing
Pregnancy or free sex
Ex-convict
Ecovillage Elements (Social-economic Factors) Frequent What to do work together
Ecovillage Elements (Social-economic Factors) Rather often What to do work together
Ecovillage Elements (Social-economic Factors) Infrequently What to do work together
Ecovillage Elements (Social-economic Factors) No What to do work together
ICSE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education
520
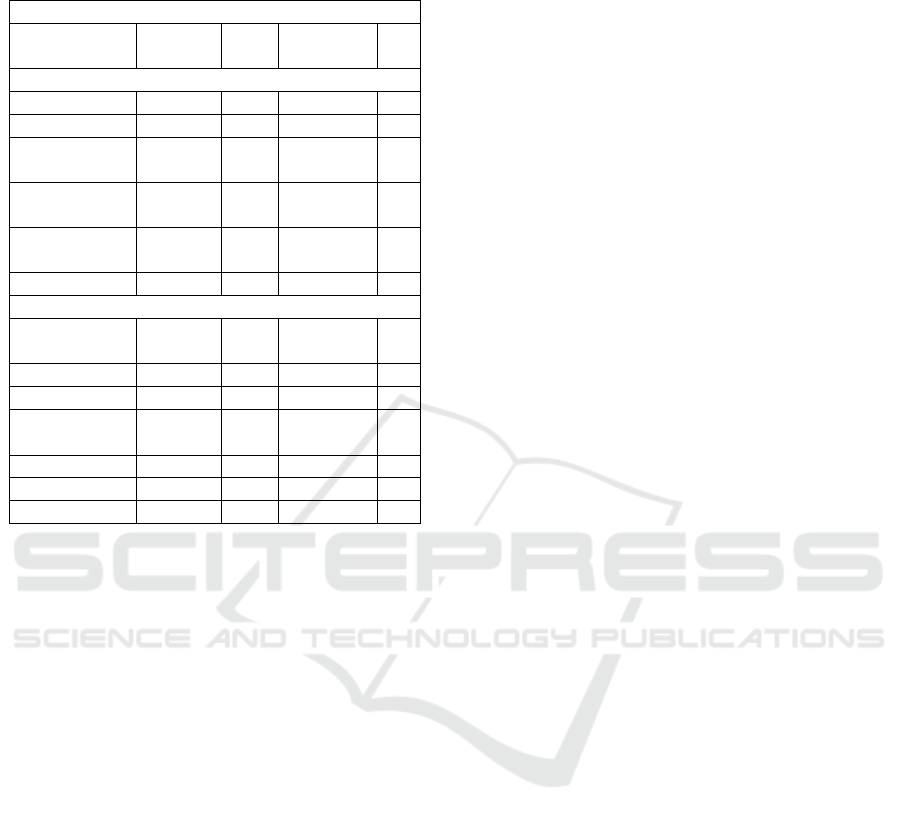
Tabel 7. Results of the questionnaire about the social
economy parameters.
Ecovillage Elements (Social-economic Factors)
Frequent
Rather
often
Infrequently
No
What to do work together
Death disaster
10
Confinement
5
5
Environmental
Hygene
10
Development
society
7
Healthy
pramacies
5
5
Amount
15
22
5
5
Values and norms
Religious
education
10
Polite clothing
1
8
1
Subpoena
1
9
Pregnancy or
free sex
2
8
Drugs
2
6
Ex-convict
2
6
Amount
26
9
14
21
6 CONCLUSION
1) In implementing the ecovillage in rural areas
can be found diversity of socio-cultural
elements are quite high, so that hope to create an
ecovillage models that can be used for other
villages could not be implemented.
2) The shape of physiographic region of the village
and the ecological carrying capacity of the
village can give you the high and low linkages
with the activities of people with the ability to
apply the principles of ecovillage.
3) The implementation of the principles of
ecovillage in Cimaung have not been able to
integrate entire existing parameters of the
principles of ecovillage, so that implementation
is centered on one factor alone, for example
cleaning the river.
REFERENCES
Balai dan kajian Budaya Melayu. 2007. Nilai Budaya Lokal
Jadi Bagian Pembelajaran. Dapat diakses
http://melayuonline.com/ind/news/read/900/temuan-
dokumen-sejarah-sulawesi-tenggara-surat-tertua-
kerajaan-buton-dari-abad-ke--17 [online]. Diakses
September 2016.
BAPESITELDA. 2009. Sosial Budaya Jawa Barat. Dapat
diakses
http://www.indonesia.go.id/id/index.php?option=com_
content&task=view&id=6078&Itemid=1804 [online].
Diakses September 2015.
Bappeda. 2010. Grand Design Pengembangan Ekonomi
Masyarakat Kabupaten Bandung. Dapat
diakses:http://bapeda.bandungkab.go.id/index2.php?o
ption=com_docman&task=doc_view&gid=163&Itemi
d=37. Diakses Maret 2016.
Basrowi. 2008. Memahami Penelitian Kualitatif. Jakarta :
Rineka Cipta.
Bungin, Burhan. 2003. Analisis Data Penelitian Kualitatif.
Jakarta : PT. Raja Grafindo Persada.
Chen , S. (2014). Integrating Remote Sensing and GIS for
Ecological Capacity Assessment : The Case of
Regional Planning in Melbourne, Australia.
Proceedings of Digital Landscape Architecture 2014
(pp. 145-151). Zurich: Herbert Whichmann Verlag,
VDE VERLAG GMBH.
Gaia Education. (2015). Ecovillage Design Education. The
GEESE.
Hall, R. (2015). The Ecovillage Experience as an Evidence
Base for National Wellbeing Strategies. Intellectual
Economics, 30–42.
Hamidi. 2008. Metode Penelitian Kualitatif, Pendekatan
Praktis, Penulisan Proposal,dan Laporan Penelitian.
Malang: UMM Press.
Hasan, Hamid. 1996. Pendidikan Ilmu Sosial. Jakarta :
Departemen Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan Direktorak
Jendral Pendidikan Tinggi Proyek Pendidikan Tenaga
Akademik.
Kasper, D. V. (2008). Redefining Community in the
Ecovillage. Research in Human Ecology, 12-24.
Koentjaraningrat. 1974. Kebudayaan Mentalitet dan
Pembangunan. Jakarta : Gramedia.
Sunarti, Euis. 2012. Pengembangan ecovillage: jalan
mewujudkan kehidupan penduduk serta lingkungan
yang berkualitas. Dapat diakses
http://euissunarti.staff.ipb.ac.id/pengembangan-
ecovillage-community-development/. Diakses Maret
2016.
The Model of Ecovillage Value Investment as Independence Village and Cultural Environment at Cimaung, Bandung-Indonesia
521
