
Cultural Content in English Textboo
k
Visual Grammar Analyis
Astria
Muzdalifah and Nicke Moecharam
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Jl. Setiabudhi number 229, Bandung, Indonesia
{astriamuzdalifa, nicke}@upi.edu
Keywords: Cultural content, English as international language, visual grammar.
Abstract: This study was a qualitative descriptive study, which investigated how target culture and source culture were
visually communicated through pictures taken from English textbook for second grade of secondary school.
The data of this study were collected from an English textbook for second grade that implemented the 2013
curriculum entitled “Passport to the World A Fun and Easy English Book (for Grade VIII of Junior High
Schools”, published by Tiga Serangkai). The data were collected in the form of pictures taken from each unit
of the textbook and were analyzed using The Grammar of Visual Design by Kress and van Leeuwen (2006)
and the analytical framework for the cultural content was proposed by Xiao (2010). The study found that
source culture contents dominate other cultural representation. The book was classified into Source Culture
materials based and the criteria of source culture covered Geographic, Architecture, Education, Lifestyle, Art,
Costumes, Values, Gesture and Body language and Foods. The book was prepared the learners to talk about
their own culture to foreigners rather than be prepared to encounter their cultures.
1 INTRODUCTION
Culture carries cultural perspective and values of the
language users, and rarely be learner without
addressing the cultural background and context in
which it is used (Rafieyan, Majid, and Siew Eng,
2013; Xiao, 2010). In this case, English textbooks that
highlight the uses of source culture and target culture
need to carefully deliberate the appropriateness of
their representations.
Xiao (2010) had put new grounds on the same
research that Cortazzi and Jin (1999) initiated; Xiao
(2010) believed that the English textbook based on its
origin is divided into three different categories. They
are source culture materials, target culture materials,
and international culture materials textbook. Source
and Target culture materials is the most possible fit
textbook for EFL students whose goals are to write,
read, listen and speak in English. Lastly, the
International target culture materials involve a wide
variety of cultures set in English-speaking countries
or in countries where English is not a first or a second
language but is used as an international language.
This book belongs to the learners whose needs and
goals are EIL as it is suggested by McKay (2002) and
Xiao (2010), which the primary aim is to enable
people to share their thoughts and ideas with other
people from other cultures successfully.
Pictures as visual aids in textbook are able to give
realistic portrayals of all cultures, including facts, up
to date information and nonverbal language (Xiao,
2010). Therefore, this study focuses on the analysis
of how the cultures in the Target Language (TL) and
Source Language (SL) are visually communicated
through pictures taken from an English textbook for
secondary school. The analysis was undertaken
within the framework of visual grammar as outlined
by Kress and van Leeuwen (2006), as well as the
concept of cultural content proposed by Xiao (2010)
and other supporting theories which are relevant.
2 VISUAL GRAMMAR AS
ANALYTICAL TOOL
The Grammar of Visual Design is believed to
describe the way in which depicted element, such as
people, places and things to combine in visual
statements (Kress & Van Leeuwen, 2006). There are
three metafunctions of linguistics that can be
extended to visual communication.
Muzdalifah, A. and Moecharam, N.
Cultural Content in English Textbook - Visual Grammar Analyis.
DOI: 10.5220/0007161700410045
In Proceedings of the Tenth Conference on Applied Linguistics and the Second English Language Teaching and Technology Conference in collaboration with the First International Conference
on Language, Literature, Culture, and Education (CONAPLIN and ICOLLITE 2017) - Literacy, Culture, and Technology in Language Pedagogy and Use, pages 41-45
ISBN: 978-989-758-332-2
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
41
2.1 Representational meaning
Representational meaning demonstrates between the
represented participants in the image and involved
interactive participants and represented participants
(Kress and van Leeuwen, 2006).
The Actor is the participant from which the vector
comes, while the Goal is where the participant at
which the vector points meanwhile Transaction is
something done by the Actor to a Goal (Kress and van
Leeuwen, 2006).
The Representational meaning then is divided into
two major processes, Conceptual and Narrative
processes.
Figure 1: Main type of visual representation structure.
(Adopted from Kress & van Leeuwen, 2006, p.59).
The Narrative process is a process of doing
something which is connected by the vector (Kress
and van Leeuwen, 2006). The first process is the
Action process. The Action process occurs when
there are vectors and action formed by the represented
participant (Kress and van Leeuwen, 2006).
Secondly, there is a process where the vector is
formed by the eyeline or by the direction of the glance
without creating the transaction and this process is
called Reactional process.
The Conceptual representation represents the
visual structures which the participants are illustrated
to be more generalized, more or less stable and
timeless. Similar to Narrative process, the Conceptual
process is divided into different kinds as well.
First process is the Classificational process and
the analytical process. This process relates
participants in terms of a part-whole structure, the
whole is called the Carrier and the parts are called
Possessive Attribute (Kress and van Leeuwen, 2006).
The in-depth analysis and elaboration of
representational meanings in the textbook (Djatmika
et al,. 2014) presented in the followings.
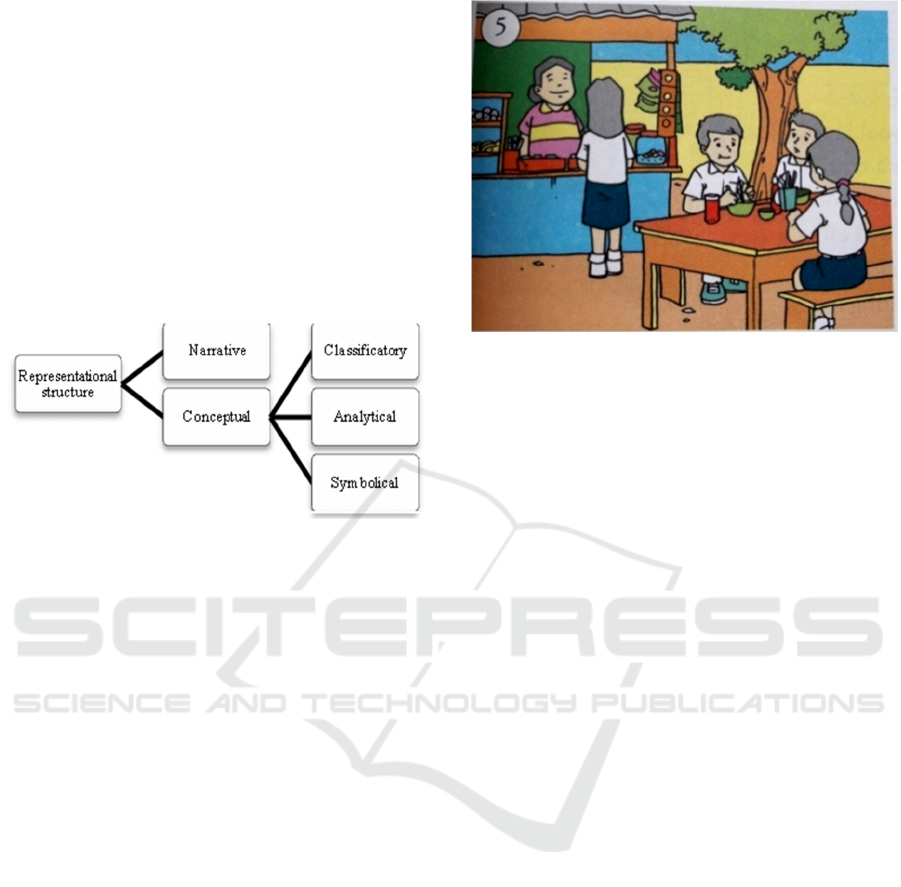
Figure 2: At canteen. (Djatmika et al., 2014).
Figure 2 illustrates the canteen, defined by the
simple dining tables and a variety of foods displayed.
Forshee (2006) mentions this place in this place as
warung, a place to buy meals, sweets, and any other
treats while having a sit to enjoy the snacks. The
realistic impression which is made by color the
differentiation eases the viewers to recognize each of
the tiny elements such as the bakso or Indonesian
meatball and mie or noodle.
This picture has five represented participants;
four are students claimed by the possessive attributes
in uniforms of white and blue they wear and the other
participant is the shopkeeper who stands inside the
warung whose job is to serve the customers. The hair
of the female participants in this picture is depicted in
short hair or long hair with ponytail which giving the
viewers a representation of how Indonesian students
in their uniform. It is typical Indonesian secondary
school uniform and its regulation.
The vector made by the represented participant
as the Actor lend to the food he eats as the Goal with
the smile depicted on his face indicated that he is
enjoying his meal a bowl of mie bakso. The other
smile is also depicted by the shopkeeper as the
Reaction of the vector formed by the eyeline to the
customer as the Phenomenon who serving her
offering the act of friendliness.
In terms of information value, the students eating
on the table are referred as the New. Therefore, the
topic being discussed in this picture is the activity at
the canteen.
This picture may not the visual aids for initiating
conversation since Transaction or Bidirectional
process is not made, instead it gives information and
ambiance about canteen from Source culture that is
useful for English descriptive text. The picture is
emphasizing its meaning in the Representational
process as it is aiming on offering information and
CONAPLIN and ICOLLITE 2017 - Tenth Conference on Applied Linguistics and the Second English Language Teaching and Technology
Conference in collaboration with the First International Conference on Language, Literature, Culture, and Education
42

representing the participants from SL culture as the
item of descriptive text.
Figure 3: Boy Scout. (Djatmika et al., 2014).
Figure 3 represents several salient elements,
which are the two Boys Scout, a tent and two different
sizes of hammers.
In visual grammar, the terms ‘represented
participants’ are meant for the objects or elements
represented in the image. Therefore, the two Boys
Scouts in the image are the represented participant;
however, their roles will be decided by the type of
vector they formed. The vector is formed by the
represented participant on the left, since he is the only
participant who has visible eyes and facial
expression. However, if this process was translated
into; He is building a tent together, then it would be
inaccurate.
Each of the participants is holding a hammer as
their Symbolic attributes, but in different sizes. In this
case, the attributes do not define their identity, but it
is explaining the activity that they are doing. Then,
the attributes are translated into; they are building a
tent.
The participant on the right form a gesture
towards the Actor creating Bidirectional Transaction,
it means that the participant who is earlier acted as the
Actor then changed to Goal. They are not explaining
or describing their activities but creating the format
of interaction. The representational meaning itself is
interpreted into; He offers/asks the (bigger) hammer
to him.
To offer such information, the eye contact with
the viewers is unnecessary. Medium long shot
enables viewers to recognize the setting and also the
relief of each object, this kind of frame also creates
distance for the viewers to see the participants as
common people in general. Eye-level camera’s high
shoot also demand viewers to see them equally.
In conclusion, this picture gives the idea to the
viewers about representational meaning in how the
interaction process in English is demonstrated.
2.2 Interactive meaning
Interactive meaning is the “visual communication
resources for constituting and maintaining
interaction” (Kress and van Leeuwen, 2006, p. 114).
The first communicative function is the image act
and gaze. This process occurs when represented
participants look directly to the viewers. When the
participant’s gaze goes toward to the viewers, it
labelled as a ‘Demand’. On the other hand, all images
which do not contain human or quasi-human
participants looking directly at the viewer are
identified as ‘Offer’.
The second function is the size of frame and social
distance. The matter of the depiction of the object and
the choice of distance suggests different relations
between the represented participants and the viewers.
Figure 4: Tari Baris Bali. (Djatmika et al., 2014).
In figure 4, the represented participant wears a
traditional costume full of colors. The image
producers put color differentiation in large scale to
the use of a varied palette in order to give a realistic
impression to the viewers. This dance is known as
Tari Baris which originally comes from Bali,
Indonesia. The placement of the participant is
symmetrically placed at the center, formed no vector,
and directly addressed his eyes to the viewers, then
the participant is no longer Actor but Carrier.
The Carrier is depicted to represent what he wears
to a certain community which is traditional costumes
of Bali. The participant’s look addressed directly to
the viewers’ eyes indicates that the vector is formed
by the eyeline. This process creates a connection
between the participants and the viewer. The smile
curved in his face defines happiness, the picture is
trying to give the impression that participants like to
dance.
Cultural Content in English Textbook - Visual Grammar Analyis
43

The muted setting implies the represented
participant in the picture is the item of descriptive
information. It is emphasized on the description about
what he likes and represents it to the viewers about
what he wears, what he does, and other description
regarding to the dance or probably its origin.
Figure 5: Salsa has a black backpack. (Djatmika et al.,
2014).
The image above is depicting a girl named Salsa
who carries a red and black backpack. The image
producers seem consistent to create the characters of
students in the textbook; the participant in this picture
also wears uniform of white and blue to tell the
viewers that she is also a secondary school student.
She is the only participant in this picture, so there is
no vector formed. Moreover, the participant is placed
symmetrically at the center and addressed directly to
the viewers. In Analytical process, the participant is
called Carrier which conveys for interaction and
emotion with the viewers.
The eye contact made by the participant with the
viewers creates Demand. Additionally, the backpack
she carried is the most salient element in this picture
since the backpack is placed on the foreground, has
more details, sharp focus, large size and dominance
by the color. Accordingly, the demand that the
represented participant wants from the viewers is to
pay more attention to the backpack she carried, since
the information will be about the backpack.
Medium close shot visualizes the participant from
the head to the waist. It means, the focus is led not
only to the object but also the relationship that the
participant conducted. In this close personal distance,
the represented participant is inferred to be close to
the represented participant as if she is the one who
gives the descriptive information about the bag. Thus,
this picture is created to fulfill the Interactive
meanings, where the represented participant creates
an imagery relation with the Interactive participant to
present or transfer descriptive text in English.
3 CULTURE IN ENGLISH
LANGUAGE TEACHING
Learning a language together with the culture helps to
develop students’ awareness and improve their
cultural learning and intercultural communicative
competence. English language learning should focus
on improving the learners’ ability to understand
cultures, including their own and to communicate
with people even from a variety of linguistic and
cultural backgrounds.
According to the distribution of cultural content
by Xiao (2010), the textbook (Djatmika et al,. 2014)
contains the cultural content which includes the
source and target culture. The elaboration of the
distribution for each category of cultures is presented
in order. First, the distribution for the category of SL
cultural content of little “c” is mostly emphasized on
geography, education, architecture and art, while little
‘c’ is lifestyle, hobbies, values, gesture and body
language and foods. Moreover, English teaching
materials usually adopt English names to present
Target culture (Xiao, 2010); instead, this textbook
upholds common local names like Budi, Utami, Rini,
and Yanti, the names which are very common and
familiar among Indonesians.
The educational cultural content of Source culture
is represented through the use of school uniform in
the most representative participants and the
regulation system of the school. This book also inserts
architectural contents which features travel
destinations and city landmarks in SL culture. In
order to preserve culture and encourage learners to
appreciate their own, the big ‘C’ culture of Art is also
distributed; this textbook provides learners with
traditional art and dance.
SL cultural content is also communicated in the
little “c” cultures through lifestyle, values, body
language and foods. First, lifestyle in the way of a
person or group of people lives and works, including
daily routine schedules, etiquette in eating, and
activities in leisure time. Textbook by Djatmika et al,.
(2014) contains both categories of Target culture in
big “C” culture and little “c” culture. However,
appearance of native speakers of TL in the textbook
(Djatmika et al,. 2014) is rarely presented.
By seeing the fact that source culture gets more
attention than the others and dominates the other
cultural content presentation, the textbook by
Djatmika et al,. (2014) is designed intentionally to
introduce EFL to the language learners in beginner
CONAPLIN and ICOLLITE 2017 - Tenth Conference on Applied Linguistics and the Second English Language Teaching and Technology
Conference in collaboration with the First International Conference on Language, Literature, Culture, and Education
44

level in familiar topics, so as to ease the SL learners
to connect with the language use in appropriate
context. In conclusion, the images in this textbook are
categorized to Source Culture materials which
prepare the learners to talk about their own cultures
to foreigners rather than prepare them to encounter
other cultures.
4 CONCLUSION
The aim of the study is sought to investigate how SL
and TL cultures are visually communicated through
selected pictures in an English textbook, ‘Passport to
the World’ (Djatmika, Priyanto and Dewi, 2014) for
secondary schools. This study employed two
frameworks; the visual grammar theory by Kress and
van Leeuwen (2006) and the concept of cultural
contents by Xiao (2010).
The pictures in ‘Passport to the World’ (Djatmika,
Priyanto and Dewi, 2014) as visual aids provide the
learners realistic portrayals of TL, SL and
international cultures. The pictures also provide
examples of communicative action for learners to
take on roles and to understand the feelings, values,
attitudes and interaction of the represented
participants from each culture. The SL culture
presented in the textbook helps the learners in
understanding their own culture. While the TL
culture, international and free culture helps the
learners to increase learners’ cultural awareness.
REFERENCES
Cortazzi, M., Jin, L. 1999. Cultural mirrors: Materials and
methods in the EFL classroom. In E.Hinkel (Eds.).
Culture in second language teaching and learning (pp.
196-219). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Djatmika, Priyanto, A. D., Dewi, I. K. 2014. Passport to the
world: A fun and easy english book. Solo: Tiga
Serangkai Pustaka Mandiri.
Forshee, J. 2006. Culture and customs of Indonesia.
Conecticut: Greenwood Press.
Kress, G & van Leeuwen, T. 2006. Reading images the
grammar of visual design. New York: Rouledge.
McKay, S.L 2002. Teaching English as an International
Language: The Role of Culture in Asian Contexts. The
Journal of Asia TEFL. 1(1), 1-22.
www.asiatefl.org/main/download_pdf.php?i=1&c=139
1753773.
Rafieyan, Majid, and Siew Eng. 2013. Relationship
between attitude toward target language culture
instruction and pragmatic comprehension development.
Canadian Center of Science and Education.
Xiao, J. 2010. Cultural Contents of an in-use EFL textbook
and English major students’ attitudes and perceptions t
owards culture learning at Jiangxi University of Scienc
e and Technology, China. (Master’s thesis, Prince Son
gkla University, Hat Yai, Thailand). Retrieved from kb
.psu.ac.th/psukb/bitstream/2010/7836/1/326069.pdf.
Cultural Content in English Textbook - Visual Grammar Analyis
45
