
Japanese Language Teaching for Tourism using Content and
Language Integrated Learning Approach
Juju Juangsih
Department of Japanese Education, FPBS, Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia
jujujuangsih@upi.edu
Keywords: Teaching Material Model, Japanese Language, Content and Language Integrated Learning, Research and
Development.
Abstract: The aim of this research is (1) to figure out the current condition of Japanese language teaching material for
specific purpose; (2) to figure out design of Japanese language teaching material for tourism purpose with
Content and Language Integrated Learning (CLIL) approach; and (3) to find out the qualification of
Japanese language teaching material for tourism purpose with CLIL approach. The method used in this
research is Research and Development (R&D) from Borg and Gall (2003). Respondents are sophomores of
Tourism and Marketing Management Department (MPP) programs from Faculty of Social Science
Education (FPIPS) for limited-scale experiment. As for larger scale, the respondents are sophomores of
Indonesian Tourism Academy (Akperindo) Bandung. The expected outcome from this research is to obtain
a Japanese teaching material with specific purpose of tourism with CLIL approach that can be used in
tourism institutions. So, Japanese might be an optional language for students to learn. The implication of
this research is the creation of Japanese teaching material for tourism purpose with CLIL brings benefits for
teacher in delivering courses to their students.
1 INTRODUCTION
The aim of Japanese teaching program in Tourism
and Marketing Management Department is to enable
sophomores to apply basic Japanese for hotel
business purpose. Therefore, the researcher, a
lecturer for Japanese as second language, attempts to
create new teaching material model that in line with
the objective mentioned above. The idea of creating
new teaching material model comes up since the
conventional one does not significantly enhance
students’ communication skill. The conventional
teaching material model more focuses on writing
skill and how students are able to read Hiragana and
Katakana. For that situation, the learning focus is not
on students’ communication skill. In accordance
with the issue mentioned above, the researcher is
encouraged to create new teaching material model
that more focus on developing Japanese
communication skill even in basic level.
The new created teaching material model is
Content and Language Integrated Learning (CLIL)
based. In other words, teaching material is more
focus on integrated content and language. To be
more specific, the focus of this teaching material
model is more on students’ communication skill in
delivering speech related to hotel activities and
business. For instance, students learn how to be a
receptionist using ‘Check-in’ and ‘Check-out’ theme
or how to be a porter and serve hotel guests,
Teaching material with Content and Language
Integrated Learning approach is expected to improve
students’ motivation to learn Japanese in better way.
Students do practices in speaking Japanese with
hotel-related contents. So, in the future, the students
are expected to be able to naturally communicate in
Japanese for hotel activities and business naturally.
As pointed out by Coyle, Hood and Marsh (2010,
p.12) that this natural situation seems to be one of
the fundamentals for the importance and success of
CILL related to language and other subjects learning
process. Thinking skill in different language, even in
basic level, can give positive impact to content
learning.
Based on the need analysis result conducted to
students of Tourism and Marketing Management
Department on 2015-2016, 70% of all
correspondents expect to work on hotel after
completing study. Exactly because of that, the
content for teaching material in this research is for
520
Juangsih, J.
Japanese Language Teaching for Tourism using Content and Language Integrated Learning Approach.
DOI: 10.5220/0007170205200526
In Proceedings of the Tenth Conference on Applied Linguistics and the Second English Language Teaching and Technology Conference in collaboration with the First International Conference
on Language, Literature, Culture, and Education (CONAPLIN and ICOLLITE 2017) - Literacy, Culture, and Technology in Language Pedagogy and Use, pages 520-526
ISBN: 978-989-758-332-2
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

hotel activities and business so it became the main
target of this research.
Another crucial reason to create this new
teaching material is that other colleges or higher
school do not provide Japanese material specifically
for tourism or hospitality industry. According to
observational research done by the researcher,
compilation of some Japanese course books is the
material used to teach tourism and hospitality
students in most educational institutes. Those course
books are also commonly used in other colleges. So,
the vocabularies or phrases learnt by the students are
more general and not specific discussing about
tourism industry.
For those issues, the researcher attempts to find
best solution so Japanese teaching process for
tourism purposes might gain some benefits and
improve students’ capability in speaking Japanese.
2 THEORETICAL STUDY
2.1 Model Concept
Suparman (2014, p.107) describes model as a reality
representation which draws structure, an order, and a
concept. More than that, model also shows one of
these four forms: verbal or conceptual description,
activity steps or procedure, physical or visual
replica, and equation or formula. While Greenberger
(1976, pp. 47-49) define model as a common term
that can be applied to every single thing in which
model is created. For instances, car miniatures,
office mock ups, prototype of supersonic plane,
various board games such as monopoly;
mathematical equation to show economic
movement, engineering curve, future energy
resources projection, and so on can be presumed as
model. Thus, everything can be created as a model
and anyone can create the explained model. Also, it
is said that the most important thing in model
concept is that model itself should represent or
reflect a referred system. By doing that, everyone
can learn the referred system by noticing the existing
model. So, model is a simplified reality
representation in diagram form.
The definition of model, applied in this research,
refers to model concept of Japanese teaching
material for tourism purpose with Content and
Language Integrated Learning approach. This model
concept is created by considering the needs of
specific materials that may increase students’
Japanese proficiency. It covers four language skills,
especially on speaking capability.
2.2 Borg and Gall Model
Research is a mechanism or scientific activity
conducted by complying standardized rules or norms
of research itself that universally acknowledged.
While development is an activity referring to an
enhancement, improvement from both quality and
quantity. Also, as suggested by Borg and Gall,
Research and development is an industry-based
development model in which the finding of research
is used to design new products and procedures,
which then are systematically field- tested, evaluated,
and refined until they meet specified criteria of
effectiveness, quality, or similar standard (2003,
p.589)
Research and development is an industry model
development-based research. That research aims to
design new product and procedure that will be tested
and then evaluated systematically. After all, both
new product and procedure will be revised in order
to meet the required affectivity, quantity and
standard.
Borg and Gall (2003) describes four main criteria
for research and development as below:
(1) Studying research findings pertinent to the
product to be develop,
(2) Developing the product based on this finding,
(3) Field testing it in the setting where it will be
used eventually, and
(4) Revising it to correct the deficiencies found in
the field-testing stage.
From all four criteria defined by Borg and Gall,
the researcher should start by doing prior study to
gather related findings with the product being
developed. Then, the researcher should develop the
product based on those prior findings. Going further,
there should be a test in real situation where the
product is actually implemented. The test result
could be research reference for revisions on
discovered weaknesses.
In accordance with the definition and four main
criteria mentioned above, Borg and Gall (2003)
describe steps to be conducted on R&D as seen on
Figure 1.
Japanese Language Teaching for Tourism using Content and Language Integrated Learning Approach
521
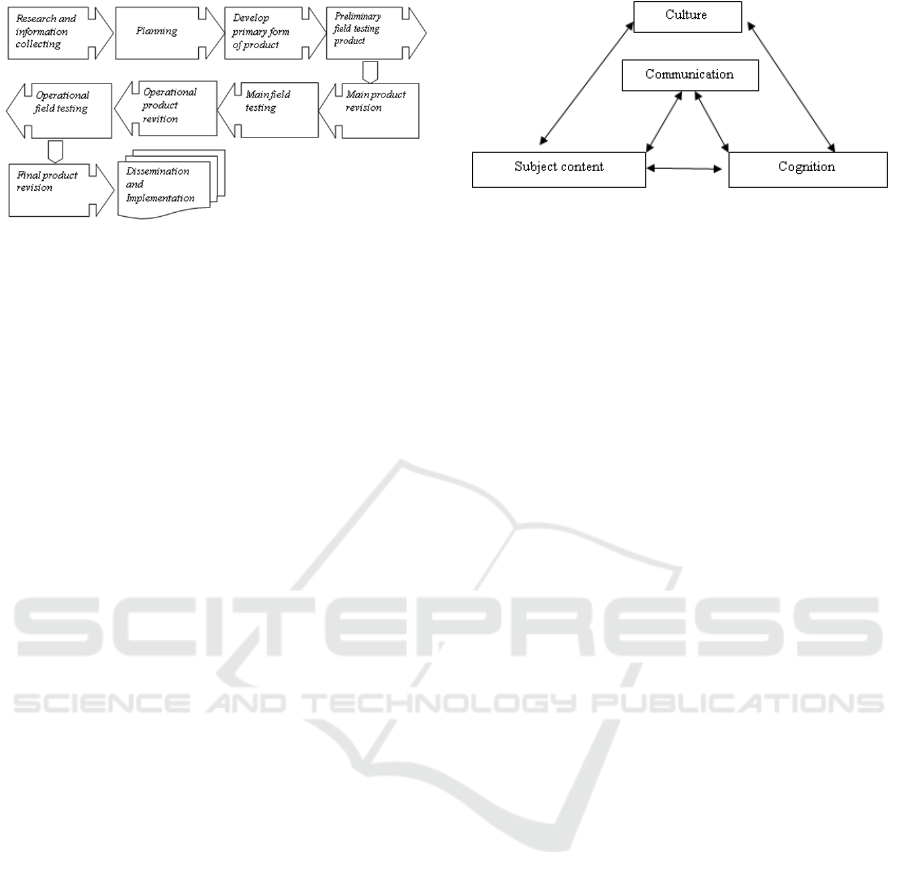
Figure 1: Borg and Gall Model (2003).
2.3 Teaching Material Concept
In term of teaching material development,
Tomlinson (2003, pp.128-129) views that (1)
making the material concept would be more
effective if it is related to students’ needs, (2)
teacher is the one who mostly understand the
students, (3) all teachers need fundamental in
writing materials, (4) all teachers is teacher for
themselves, realizing that would impact to exact
material development, (5) trial and error, and
evaluation is very important to define success for
each material.
He also emphasize that students should be the
focus in developing teaching material. In this
research, the researcher applies ‘JF Standard Can-
do, A1 level’ that has equal standard with CEFR
framework which has been used in many countries.
It also will be combined with analysis result of this
research.
2.4 Content and Language Integrated
Learning
CLIL (Content & Language Integrated Learning)
term is firstly adopted in Europe on 1994. There are
two big goals in implementing CLIL. First goal is to
learn geography, math, chemical, and other subjects
in school by using foreign language. Second one is
to learn foreign language through certain subjects’
material. Coyle, Hood and Marsh (2010) suggests
4Cs framework for CCIL (see Figure 2). These are
Cognition, Culture, Content, and Communication.
Dalton-Puffer (https://hannan-u.repo.nii.ac.jp)
describes the relationship among those frameworks
by showing communication as its center as shown in
figure 2.
Figure 2: Cs framework for CCIL.
Coyle, Hood and Marsh (2010, pp.16-26),
describes CLIL as the latest communicative method.
He points out one of main differences between
communicative language learning in 1980s and the
emerging of CLIL in 1990s.
Classes implementing CLIL involve students as
active participants in developing their potential to
gain more knowledge and skill. It is gained through
inquiry process (research) and by using complex
cognitive process for problem solving goal
(innovation).
Furthermore, Coyle, Hood and Marsh (2010,
pp.16-26) states that thinking ability in different
language, even on basic level, may give positive
impact to content learning. Because of that, CLIL
appears as a phenomenon that completes content and
language learning. CLIL is not merely an education
in foreign language. It also can be used to teach
foreign language based on linking pedagogy and
contextual method.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
3.1 Respondents
This research is conducted to sophomores in
Tourism and Marketing Management Department,
Faculty of Social Science Education (Prodi MPP
FPIPS), Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia. The
target of this research is to supply a Japanese
teaching material for specific purpose, both for the
teachers and students.
3.2 Research Approach and Method
Researcher applies qualitative and quantitative
approach by using Research and Development
(R&D) method. In implementing R&D, the
researcher employs multiple methods which are (1)
descriptive method, (2) evaluative method, and (3)
experimental method.
CONAPLIN and ICOLLITE 2017 - Tenth Conference on Applied Linguistics and the Second English Language Teaching and Technology
Conference in collaboration with the First International Conference on Language, Literature, Culture, and Education
522

3.3 Stages of Model Development
There are four stages of model development, (1)
preliminary research, (2) designing model
development, (3) validation, evaluation, and revision
of the developed model, and (4) model
implementation.
Preliminary Research: Before creating a model
for Japanese teaching material in specific purpose,
Preliminary research is firstly conducted. It is done
to both students and teachers in Prodi MPP FPIPS
by spreading questionnaire and interview.
Model Development Designing: In this phase,
needs analysis result has been obtained and
theoretical studies had been done in preliminary
phase. According to these data, steps are conducted
as follows:
Researcher compiles syllabus that will be used as
reference in creating teaching material model. It
is compiled based on students’ needs and JF
Standard Can Do that has been analyzed in
preliminary stage. Through this step, researcher
obtains draft 1 of syllabus and teaching material
model for Japanese Introduction. Also, in this
phase, researcher starts to create teaching
material since the basic and standard competency
has been defined in syllabus. The result of this
phase is Japanese teaching material in form of a
textbook. All materials written in textbook
contain these components, (1) indicator in each
theme, (2) tasks and exercises, and (3) self-
evaluation in the end of each theme. Teaching
materials consist of themes created based on
needs identification. Each theme covers four
language skills (listening, reading, speaking, and
writing), grammar, and Japanese culture.
Introduction to Japanese Language teaching
material draft, which composed as first draft, was
going through peer (Japanese teachers) and
review. In this phase, data concerned with first
teaching material draft revision is retrieved.
Teaching material draft of Introduction to
Japanese Language will be then reviewed by
peer lectures. Researcher will gain some
suggestion and revision for the draft. In this
phase, the second teaching materials are created
and ready to be implemented in limited scale.
Experiment is conducted to small group in
Introductory to Japanese Language class. The
researcher cooperates with Japanese teaching
team in Prodi MPP. Researcher also gives
questionnaire concerning the feasibility of
teaching materials being developed to both
teachers and students. Discussion with other
Japanese teachers is also done. To gain more
data, the researcher conducts an observation
during the learning process. The researcher
observes teachers’ and students’ activities related
to materials and tasks provided in teaching
material model. After each theme done, the
researcher discusses about strengths and
weaknesses of the syllabus and its teaching
material. Students’ and teachers’ opinions toward
the Introduction to Japanese teaching material
are also taken into consideration. By doing so,
the researcher obtains information of what to fix
from the current teaching material.
Based on the experiment above, the researcher
revises the second draft of the teaching material. The
revision is used as reference to create the next draft
of new Japanese teaching material model for specific
purpose. The researcher still applies CLIL approach
in line with JF Standard Can Do to meet the real
needs of teaching Japanese for specific purpose.
Before conducting experiment in larger scale, the
researcher is required to do validation, evaluation
and revision of the model. Linguistic expertise will
determine the validation. These following steps will
be done in this stage:
Assessment of teaching material by two
Japanese language expertise and two experts on
teaching material. The researcher gains data
about both strengths and weaknesses about the
teaching material. Not only to revise teaching
material, can the identified weaknesses be used
as reference for next syllabus.
Based on the assessment, the researcher revises
draft of teaching material. It creates the forth
draft of Japanese teaching material for specific
purpose in hospitality field.
Based on the result of the test, the researcher
revises the teaching material draft. This model
turns to be hypothetic model following the
experiment in larger scale.
Model Implementation: In this stage, the
researcher implements an experiment of teaching
material to students of Prodi MPP UPI. It is divided
into experimental and control class. Both classes
consist of students with identical characteristic and
competence. Control class involves A1-grade
students and uses teaching material from Tourism
Academy of Indonesia.
Japanese Language Teaching for Tourism using Content and Language Integrated Learning Approach
523

3.4 Data Source, Data Acquisition
Technique, Instrument Validity
and Reliability, and Data Analysis
Technique
Things that related with data source to data analysis
technique would be elaborated as follows.
3.4.1 Data Source
In this research, all data gathered from preliminary
until implementation stage of teaching material
model. In preliminary stage, data of needs analysis
are gained from students and Japanese teachers. The
researcher employs questionnaire, interview and
observation as instrument to gather all data needed.
3.4.2 Data Acquisition Technique
Data accumulation technique will be elaborated
here. Document analysis is conducted to current
learning instruments for teaching Japanese in Prodi
MPP. The observation covers: (1) conducted
learning process, (2) learning model performed by
the teacher, (3) students’ activities, (4) students’
portfolio and learning outcomes. To deeper
understand needs of the students and Japanese
teacher in Prodi MPP UPI, the researcher also uses
interview technique. It is applied to the teacher of
Japanese for tourism purpose. Students are also
interviewed to assess their language competence,
goals of learning Japanese, and material needed. In
term of identifying Japanese teachers’ and students’
needs, the researcher spreads questionnaire to both
of them. This following is the recapitulation table of
data acquisition technique done in this paper.
4 TEACHING MATERIAL
MODELS
As previously stated, instruments employed in this
research include questionnaire, observation sheet,
interview and post-test which have validity and
reliability. Instrument preparation is started by
ordering questionnaire formula to meet required
construct validity. Validity test is also done by
dropping invalid question (if r value ≤ r-table).
Question may be used if r value > r-table.
While on model planning and development
stage, this study also conducted reliability test on
students and peer teacher’s data. On validation stage,
expertise suggestion is further confirmed through
interview and discussion. Meanwhile, the validity of
material affectivity is tested by inter-rater reliability.
5 DATA ANALYSIS
In this research, data analysis employs qualitative
and quantitative approach. Quantitative data is
obtained from questionnaire by converting answers
to scores.
However, qualitative technique is also conducted
for theoretical study on preliminary study. This
technique is used when analysing syllabus document
and provided teaching material. It is also used in
describing discussion result with other teachers and
expertise related to the developed teaching material.
Data gained in this stage includes (a) Data of
Japanese teaching instruments in Prodi MPP UPI
such as syllabus and teaching materials, (b) profile
of Prodi MPP UPI, (c) students’ and teachers’ needs
Data (a) and (b) is qualitative ones. Meanwhile, data
(c) belongs to quantitative category since it uses
score on spread questionnaire. To identify the needs
of learning, this study use three aspects which are:
(1) requirements (2) lack, and (3) desire. In this case,
instruments used to gather data are questionnaire,
observation, and interview. To identifying lack
aspect, the researcher spread questionnaire
concerning obstacles of students and teachers during
the learning process. Besides, class observation and
interview to both students and teachers are also
employed.
On data analysis on model planning and
development stage, assessment of model
development from peer teachers are the data to
analyse. Result of limited-scale experiment is also
data to analyse. Those data are qualitative gained
from teachers’ notes about learning process by
applying developed teaching material. While
quantitative data is result of the learning process
written by students. Other that, some of teachers’
assessments and students are quantitative. It is
because both teachers and students fill questionnaire
that further turns into scores.
Assessment for developing teaching material
model provides 4 answers: Totally disagree (1
score), disagree (2 score), agree (3 score), very agree
(score 4). Agree or disagree refers to assess the
appropriateness of teaching material model being
developed.
For students, questionnaire is answered under
teacher guidance. Teacher provides explanation for
CONAPLIN and ICOLLITE 2017 - Tenth Conference on Applied Linguistics and the Second English Language Teaching and Technology
Conference in collaboration with the First International Conference on Language, Literature, Culture, and Education
524

any questions related to the teaching material being
developed.
For teaching material affectivity test, the
researcher conducts an experiment. T-Test is
employed to analyse experimental and control class.
If t value is higher than t-table with the probability
level of 0.05 and degrees of freedom N-1, then
teaching material being developed works affectively.
6 TECHNIQUE OF DATA
ANALYSIS
This research has still some ongoing process to be
completed. Thus, only data from questionnaire,
written and oral test result that will be presented as
follows.
6.1 Questionnaire Result
This below table shows the result of questionnaire
given to respondents purposively.
1. Do you feel some kind of difficulty in learning
Japanese with material presented below?
Figure 3: Difficulty level in learning Japanese on different
materials.
From figure 3, it can be seen that more than half
of respondents do not feel any difficulty in learning
material about “Hotel Check-in” and “Service to
guests”. On the other hand, only 5.2% students who
feel difficulties in learning. However, none of the
students feel it very difficult to learn the provided
teaching materials.
2. Do you have any difficulties in learning
material presented below?
Figure 4: Difficulty level in learning depends on learning
methods.
Figure 5: Results of exercises and evaluation.
From figure 4, it can be seen that more than half
of respondents consider that understanding
conversational material both in Indonesia and
Japanese is not difficult. Respondents also does not
feel difficult in following reading exercise material
and speaking exercise material. From figure 5, as for
sentence pattern material, sentence pattern exercise,
and learning evaluation, more than half of
respondents still feel quite difficult to follow.
3. Do you have any difficulties in doing activities
below?
Figure 6: Difficulty level felt by students based on
exercises and evaluation.
According to the questionnaire data (see figure
6), none of the students feel it hard to do reading and
speaking exercise. As for sentence pattern exercise,
hiragana and katakana writing exercise, more than
half of respondent still feel quite difficult to learn.
4. Do you have any difficulties in comprehending
evaluation based on materials presented below?
Figure 7: Difficulty level of comprehending evaluation
based on materials.
Figure 7 shows that more than half of
respondents think it easy to understand evaluation of
reading and do speaking exercises. While for
sentence pattern exercise, more than half of
respondents still feel some difficulties.
Japanese Language Teaching for Tourism using Content and Language Integrated Learning Approach
525

6.2 Written Test Result and Oral Test
Result
This following diagram describes the recapitulated
written and oral test results of students from
Tourism and Marketing Department. These tests are
conducted four times during research.
Figure 8: Overall results of written and oral test score.
Figure 8 shows that written test result has lower
scores than the oral test. However, none of the
respondents gain ‘A’ mark in written test. While
seven respondents receive ‘A’ mark for the oral test.
Furthermore, lowest mark of written test is ‘D’, and
‘C’ for oral and only single respondent receiving
that.
7 CONCLUSIONS
Regarding to the temporary data gathered and
accumulated, the researcher obtains a temporary
conclusion for Japanese teaching material model for
tourism purpose with CLIL approach, as followings:
1. According to questionnaire result in first phase,
it can be figured out that respondents feel no
difficulties in understanding materials and
evaluation concerned with reading and
speaking exercises. As for sentence pattern,
hiragana and katakana writing exercise, more
than half of respondents still feel quite difficult
to understand.
2. According to the test result, it can be figured
out that students do better on oral test than the
written test.
According to these conclusions, it can be said
that respondents have better comprehension and
interest to Japanese teaching material model which
emphasizes on speaking practice.
REFERENCES
Suparman, A., 2014. Desain Instruksional Modern,
Erlangga. Jakarta.
Coyle, D., Hood, P., and Marsh, D., 2010. CLIL Content
and Language Integrated Learning. Cambridge
University Press. Cambridge.
Greenberger, G., 1976. Models in the Policy Process.
Russel Sage Foundation. New York.
Tomlinson, B., 2003. Developing principled frameworks
for materials development. Developing materials for
language teaching, pp.107-129.
Borg, R.W., and Gall, M.D., 2003. Educational Research:
An Introduction (7
th
Ed.). Allyn and Bacon. Boston.
CONAPLIN and ICOLLITE 2017 - Tenth Conference on Applied Linguistics and the Second English Language Teaching and Technology
Conference in collaboration with the First International Conference on Language, Literature, Culture, and Education
526
