
Pragmatic Analysis of Imperative and Prohibition Speech Acts in
Quran
Yayan Nurbayan and Hilman Fitri
1
Departemen Pendidikan Bahasa Arab,Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Jl. Dr. Setiabudhi No. 229, Bandung, Indonesia
2
Prodi Pendidikan Agama Islam, Institut Agama Islam Darussalam, Ciamis
yayannurbayan@upi.edu, hilmanfitrisholihati@yahoo.co.id
Keywords: Pragmatic, Imperative, Prohibitive.
Abstract: This article examines meanings of imperative and prohibition speech acts in quran 3
rd
juz using pragmatic
approach, considering that pragmatic is one of science field that examines the meaning and context.
Therefore, it will be helpful in revealing meanings of imperative and prohibition in 3
rd
juz. In accordance
with the purpose of this research which is to collect descriptive data such as the meaning of the command
and prohibition, the research method used in this study is descriptive qualitative. The results of this study
are as follows: 1) imperative sentence used in the verses of the Qur'an juz 3 include the form were fi'il amr,
and fi'il mudhari that follows by lam 'amr, Isim fi' il amr, and mashdar as fi'il 'amr substitution; 2) the
sentence form of the disclosure aspect is direct and lateral, as there are 34 single direct and one non-literal
sentence found, while no indirect lateral and indirect lateral forms found; 3) the prohibition sentences used
the form of fi’il mudhari followed by lam nahyu, and prohibition sentences used khabari form; 4) the
prohibition sentences of the disclosure aspect are direct and literal in 8 sentences, and there is no sentence
with direct-non lateral, indirect lateral and indirect non-lateral forms.
1 INTRODUCTION
Quran is the words of God that given to last prophet
Muhammad s.a.w. In Quran written many word,
whether it is noun, verb (fi’il) with the derivation or
harf. Inside written verb is imperative (‘amr), and
prohibition (nahyi) that mention in several time.
Imperative (‘amr) is “Demanding implementation of
one job by higher class to lower class” (Jarim and
Musthafa,1797). While prohibitione (nahyi) is
“Demands the abandonment of one act that delivered
by higher class to lower class” (Jarim and Musthafa,
1797)
Imperative and prohibition sometimes didn’t
show real meaning but using other meaning that can
be identify by communication (siyaqulkalam/
context) and physic environment where one word is
using (siyaqulkalam/context). So that most of time
Moslem fall into mistake because misunderstand the
imperative and prohibition in quran. Because of their
ignorance of context and context of one speech in
quran. The other meaning of imperative itself is
disclosed by Adus (2006) that is ad du’a. aliltimas,
an nushwalirsyad, at tahdid, at tamanni, at ta’jiiz, al
ihanah, al ibahah, at takyiir, at taswiyyah, and at
ta’ajjub. However, Hasyimi (1999) add that other
meaning of imperative with al ikram,alimtinan, ad
dawam, al I’tibar, al idzn, at takwin, and at ta’dib.
While for other meanings from prohibition are ad
du’a, al itimas, annush, at tamanni, at tahdid, at
tahqir, at tai’is, and at taubikh (Adus, 2006). That to
understand imperative and prohibition meaning in
Quran need one particular field of study to review
that two case.
Researcher find some study that can use to
anayze meaning of speech act from one individual or
one particular group. There are syntax, semantics,
and pragmatic. Syntax anlyze sentence or
relationship between element of language, semantic
analyze relationship between element of language
with its object and pragmatic analyze relationship
between element of language with user or linguistic
act and situation context (Sudaryat, 2006).
In this research, researcher uses prgamatic to
analyze meaning of imperative and prohibition
speech act, because they are one of pragmatic study.
In pragmatic, speech act devided by John L. Austin
as cited by Nadar (2009), into two, that is
performative and constative. Speech that deliver to
perform something is called performative, while
786
Nurbayan, Y. and Fitri, H.
Pragmatic Analysis of Imperative and Prohibition Speech Acts in Quran.
DOI: 10.5220/0007175107860790
In Proceedings of the Tenth Conference on Applied Linguistics and the Second English Language Teaching and Technology Conference in collaboration with the First International Conference
on Language, Literature, Culture, and Education (CONAPLIN and ICOLLITE 2017) - Literacy, Culture, and Technology in Language Pedagogy and Use, pages 786-790
ISBN: 978-989-758-332-2
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
speech that deliver to tell something is called
constative.
Relates with this research, then this pragmatic
study uses to analyze imperative and prohobition
speech act meaning in quran 3
rd
juz. Researcher uses
three kind of act that offered by Searle that are
locustion, illocusi and perlocustion to analyze
imperativ and prohobition speech act meaning in
quran 3rd juz.
2 METHODS
By analysing problem characteristic in this research
using qualitative descriptive approach, because of
that approach match with the goal of this research
that to collect descriptive data such as imperative
and prohibition meanings of one speech sentences in
Quran 3
rd
Juz. Because of this research using
qualitative approach, then the instrument in this
research is researcher itself, as cited by Sukmadinata
(2011) that qualitative research using researcher as
instrument. Therefore as human instrument,
researcher serves to set research focus, choose
informant as data source, collect the data, assess data
quality, analyse the data, interpret data and make
conclusion (Sugiyono, 2013).
Based on title of the problem, this research begin
with description of verses that contain imperative
and prohibition. After that, finding some mufassir
explanation from their tafsir book that relate with
second interpretation of that speech act. Then
classifying and analysing them based on speech act
division in pragmatic.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Results
Theme of this research is “Pragmatic analysis of
imperative and prohibition speech in Quran 3
rd
juz.
Focus of this research is verses that contain
imperative and prohibitive in 3
rd
juz.
After conduct research in problem above, there
are some findings in this research as shown on Table
1 to Table 4.
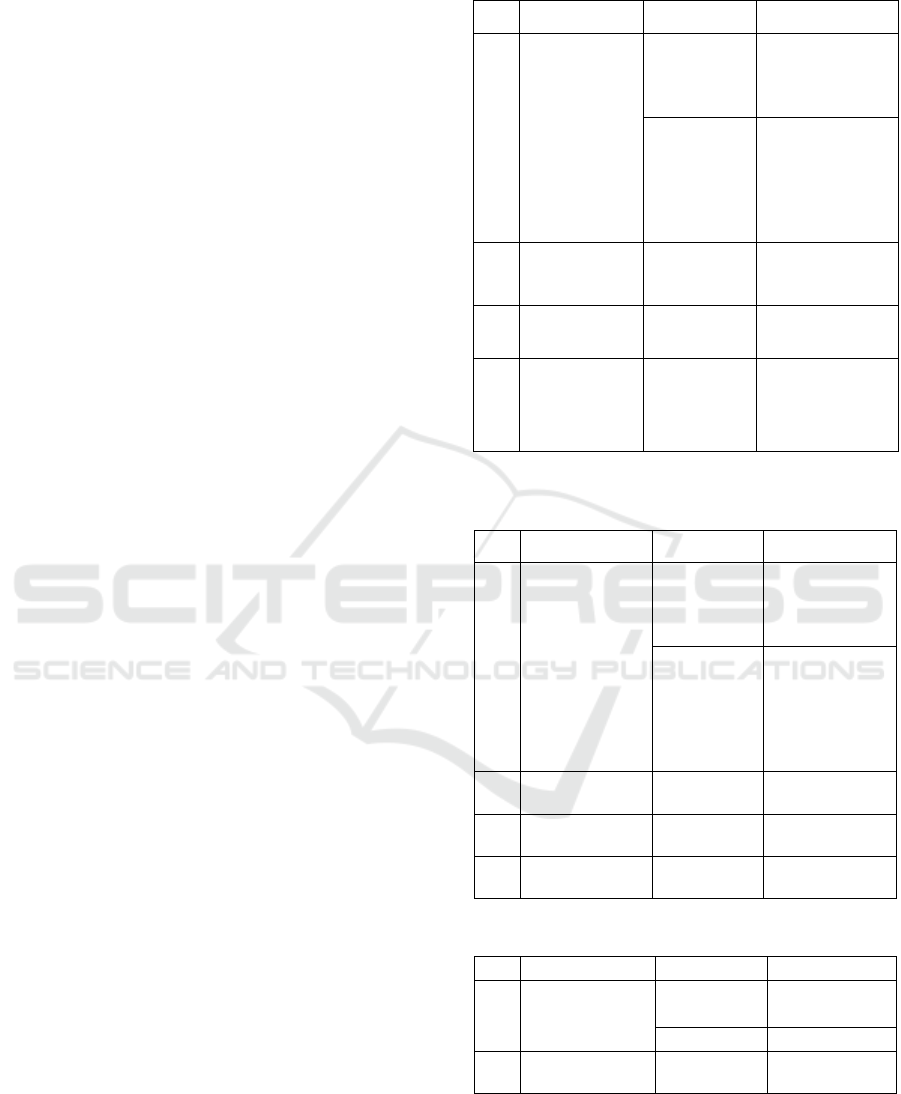
Table 1: Imperative Speech Act Based on Form Aspect.
No
Form
Surah
Verse
1
fi’il ‘amr
Albaqarah
254, 258, 259,
260, 267, 278,
279, 281, 282,
286
ali Imran
8, 12, 15, 16,
20, 26, 29, 31,
32, 35, 38, 41,
43, 50, 51, 52,
53, 61, 72, 79,
81, 84
2
fi’il mudhari
that follows
by lam ‘amr
Albaqarah
283
3
Isim fi’il amr
ali Imran
61, 64
4
mashdar as
substitute fi’il
‘amr
Albaqarah
285
Table 2: Imperative Speech Act Based on Direct Aspect
and Literal.
No
Form
Surah
Verse
1
Direct and
Literal
Albaqarah
254, 258, 259,
260, 267, 279,
281, 282, 283,
285, 286
ali Imran
8, 12, 15, 16,
20, 26, 29, 31,
32, 35, 38, 41,
43, 50, 51, 52,
53, 61, 64, 72,
79, 81, 84.
2
Direct and
Not-Literal
Albaqarah
278
3
Indirect and
Literal
-
-
4
Indirect and
Not-Literal
-
-
Table 3: Prohibitive Speech Act Based on Form Aspect.
No
Form
Surah
Verse
1
fi’il mudhari
that follows
by lam nahyi
Albaqarah
264, 267,
282, 286
ali Imran
8, 28, 60, 73
2
Albaqarah
272
Pragmatic Analysis of Imperative and Prohibition Speech Acts in Quran
787
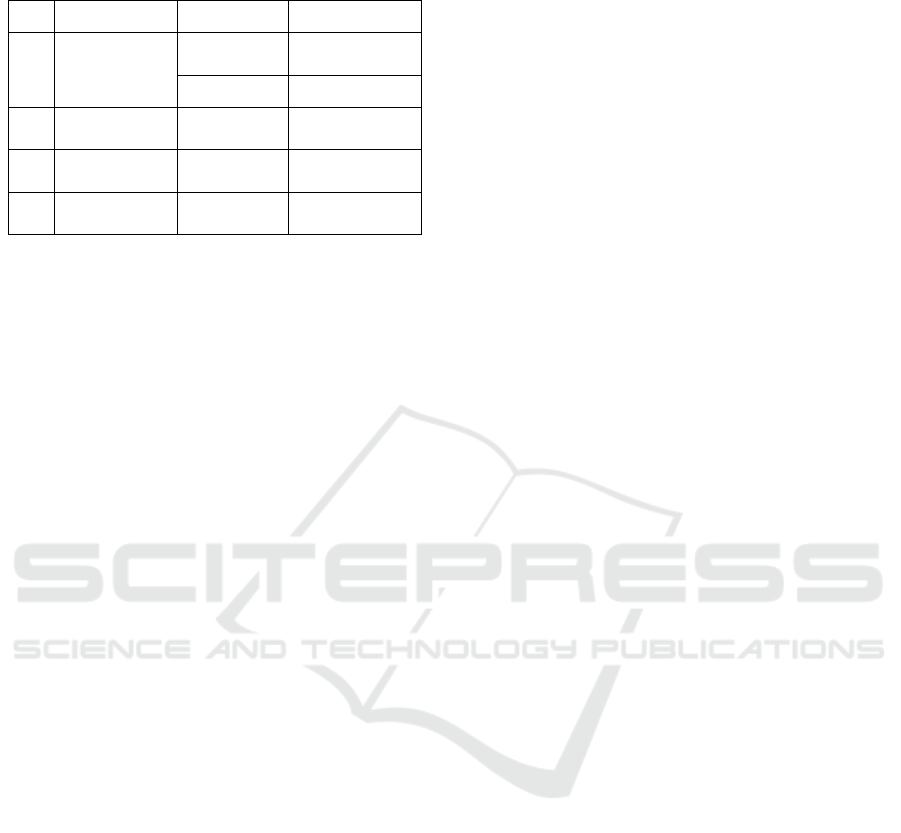
Table 4: Prohibitive Speech Act Based on Direct Aspect
and Literal.
No
Form
Surah
Verse
1
Direct and
Literal
Albaqarah
264, 267, 282,
286
ali Imran
8, 28, 60, 73
2
Direct and
Non-Literal
-
-
3
Indirect and
Literal
-
-
4
Indirect and
Non-Literal
Albaqarah
272
3.2 Discussion
Imperative is one of verb expression that include in
nahwu study and ma’ani study. In nahwu study,
study about imperative mostly found in fi’il chapter.
While in ma’ani study, it can be found in kalam
insyȃithalabi chapter because the expression is a
demand that not a must to finish while instruction
given by speaker, as state by Adus (2006) “in kalam
insyȃi one demand is not always finished when it
spoken by the speaker.” But in ushul fiqih rule there
is a rule that relates with imperative “Imperative
exactly needs refreshment in implementation of
instruction.” (Kharabasyah, 2007). Nevertheless
there are some expert state that imperative doesn’t
require refreshment, as Qazwaini (2001) states that
imperative doesn’t require refreshment and
repetition.
Definition of imperative in Dendy (2008) is as
follows:
An imperial or give a command; have the right to
give the command; give requirement; the new law
will have to be authoritative as a power – which
must be respected;2n Ling form of imperative to
verb that states prohibiton or requirement to
implemet the act: Go! Help!
Whereas according to Jarim and Musthafa (1797)
imperative is “Demanding implementation of a work
from higher class to lower class.” For example a
director in one company tell his secretary to make a
cup of coffee for his client.
Regardless of whether exist or not refreshment
demands in implementation of imperative, there are
some form (sighat) of imperative, as explained by
Abbas (1997) that imperative has four disclosure
form, as follows.
With using fi’il ‘amr;
Mashdarun naib ‘anil fi’il (mashdar as
subtitue of verb);
Mudhȃri’ al maqrȗn bi lȃmil ‘amr (fi’il
mudhari with lam ‘amr);
Isim imperatif. Thus form devided into two,
simȃ’i and qiyȃsi that using form
(fa’ȃli)
from fi’il tsulȃsi.
Beside forms above, there is another form that is
direct and indirect imperative, then literal and non-
literal (Nadar, 2013).
As seen in Table I, researcher finds some verse
in 3
rd
juz contain some imperative form, as using fi’il
amr, fi’l mudhari continued by lam amr, amr form
that use isim fi’il amr, and mashdar as substitute of
fi’il amr. Whereas in table II, researcher finds some
verse in 3
rd
juz contain imperative from direct
speech aspect and literal, such as imperative with
direct speech and literal and imperative with direct
speech and non-literal.
Next is prohibition. Prohibition almost the same
as imperative, then prohibition is one of verb form
expression that include in nahwu or ma’ani study. In
nahwu study, prohibition usually found in fi’il
chapter. Whereas in ma’ani study, it includes in
kalam insyȃi thalabi chapter. But prohibiton request
refreshment in avoiding anything that prohibited, it
differentiate with imperative. This was confirmed by
the opinion of Abbas (1997) who state that “They
have agreed that prohibiton need refreshment”
The definition of prohibition in Dendy (2008)
with three meanings as follow.
Rule that prohibit an act: Government issued ~
send gold to foreign country;
Something prohibited because it is sacred or
holy sanctified;
Something prohibited because exception: this
good ~ should not be possessed by other
people.
And it says that prohibition (nahyu) is “Must to
leave one act that delivered by higher class to lower
class.” (Jarim and Musthafa, 1797). For example a
director in one company prohibit his secretary to
wear sexy dress in office.
Whereas to prohibition form (sighat), it only has
form namely fi’il mudhȃri’ that follows with lȃ
nȃhiyah (Adus, 2006; Abbas, 1997). But Cummings
(2007) that prohibition with direct and indirect form,
along literal and non-literal because speaker talk
with recepient “The fierce dog is in the garden”
when the speaker wanto enter the garden, speaker in
this sentence is on locutions act in an information
statement form, locutions act could be in warning
someone not to enter the garden. According to
Cummings (2007) with saying “The fierce dog is in
CONAPLIN and ICOLLITE 2017 - Tenth Conference on Applied Linguistics and the Second English Language Teaching and Technology
Conference in collaboration with the First International Conference on Language, Literature, Culture, and Education
788

the garden” the speaker is succes to prevent
recepient to enter the garden, with this speech,
speaker has done perlocutions.
As seen in Table III, researcher finds some verse
in 3
rd
juz contain some form of prohibition, like
prohibition in fi’il mudhari continued by lam nahyi
and . Whereas in Table
IV, researcher find some verse in 3
rd
juz contain
some prohibition whether from direct speech and
literal aspect or indirect speech and non-literal
aspect.
To shorten the discussion, in this article
researcher will only explain about one example from
imperative and prohibition speech act. First,
imperative that using fi’il amr is verse 258 Al-
Baqarah. From direct speech and imperative literal
aspect, it included into direct speech and literal. It is
because direct speech using command sentence and
the purpose is the same with word that construct the
sentence. In imperative, the speaker is Ibrahim a.s.
and the recipient is King Nambrudz (Namrudz bin
Kus bin Kan’ȃn bin Sȃm bin Nȗha,s). Then
locutions from “
” is command. King Namrudz
asked to change the system of sunrise from east to
west to west to east. Then illocutions from “
” is li
ta’jîz (to weaken). This matter is expressed by
Baidhȃwi (1418) that “Command is to clarify
something that not clear with good example, that
decide to weaken the opponent from bring in the
sun, then it is not only to win debate with his
opponent.” Unclear example that mention before is
the example of Ibrahim who is his God can give him
life and death. But the opponent misunderstand the
meaning, then Namrudz says that can give life and
death too by cancel someone death penalty then kill
him after Namrudz cancel the death penalty.
Because the example still unclear for Namrudz, then
Ibrahim give another example like “Allah rise the
sun from east and set it up in west.” Then
perlocution act from “
” is King Namrudz will be
silent. This silent and astonishment according
Sya’rawi (1997) through three phase include
astonished, confused and fail to face it then doesn’t
want admit it. Second, one of prohibition that use
fi’il mudhari’ continue with lam nahyi is verse 286
Al-Baqarah. From direct speech and literal aspect, it
included to direct speech literal. That matter because
direct speech use command sentence, and the
meaning is same with the word that construct
sentence. Three prohibition can be find in this verse,
there are:
In this three prohibition, people may as recipient,
and Allah as speaker. Locution act from those
sentences mean prohibition. Mukmin prohibit Allah
not to punish them if they are forget or make a
mistake, charge them with same thing that Allah
gave to people before the, and charge them with
something that they can’t carry. Illocutions act of
those prohibitions is wish, a wish from mukmin to
Allah. Whereas perlocution from three prohibitions
are their wish not to punish them, not to charge them
with heavy responsibility that Allah gave to people
before them, and not to give them something that
they cannot bear.
After analysing imperative and prohibition data,
researcher finds that sometimes imperative and
prohibition didn’t use their real meaning but use
another meaning that can be interpret by reviewing
context and verse context. Another meaning from
imperative includes demanding, to weaken, show
His miracle, prohibition, warning, advice, teaching,
threatening, refusing, having attention, thankful,
hope, challenge. Whereas prohibition has another
meaning includes guide, command, advice, pray,
threat, and mubah.
4 CONCLUSSIONS
Since researcher conduct science research about
pragmatic analysis of imperative and prohibition in
Quran 3
rd
juz then try his best to find the answer of
questions that appear in this research, then
researcher conclude that:
a. There are some imperative in 3rd juz, such as:
1) Form aspect:
fi’il ‘amr, such as Q.S Albaqarah verse
254, 258, 259, 260, 278, 279, 281, 282,
286. And Q.S ali Imran verse 8, 12, 15,
16, 20, 26, 29, 31, 32, 35, 38, 41, 43, 50,
51, 52, 53, 61, 72, 79, 81, 84;
fi’il mudhari that continue with lam
‘amr, such as Q.S Albaqarah verse 283;
Isim fi’il amr, such as Q.S ali Imran
verse61 and 64;
Pragmatic Analysis of Imperative and Prohibition Speech Acts in Quran
789

Mashdar as substitute fi’il ‘amr, such as
Q.S Albaqarah verse 285.
2) Direct and literal aspect:
Direct and literal, such as Q.S Albaqarah
verse 254, 258, 259, 260, 279, 281, 282,
283, 285, 286 and Q.S ali Imran verse 8,
12, 15, 16, 20, 26, 29, 31, 32, 35, 38, 41,
43, 50, 51, 52, 53, 61, 64, 72, 79, 81, 84;
Direct and non-literal, such as Q.S
Albaqarah verse 278.
b. There are some prohibition in 3
rd
juz, such as:
1) Form aspect:
fi’il mudhari that continue with la nahyi,
such as Q.S Albaqarah verse 264, 286 and
Q.S ali Imran verse 8, 28, 60, 73.
2) Direct and literal aspect:
Direct and literal, such as Q.S Albaqarah
verse 264, 282, 286 and Q.S Ali Imran
verse 8, 28, 60, 73.
No direct and no literal, such as Q.S
Albaqarah ayat 272.
c. Sometime imperative doesn’t use real meaning
but use another meaning that can be found by
analyzing context and verse context, such as
demanding, to weakening, showing His-
miracle, pray, prohibition, warning, advice,
teaching, threat, refusing, having attention,
thankful, wish, and challenge.
d. Sometime prohibition doesn’t use real meaning
but use another meaning that can be found by
analyzing context and verse context, such as
guide, command, advice, pray, threat and
mubah.
Then researcher give some suggestion to some
party who relates with this research, such as:
To Arabic education student to gain tour need
in reading and analyzing meaning of Quran
whether from imperative and prohibition
aspect or another aspect that should
investigated continuously;
To another researcher, researcher wish that
they conduct research about imperative and
prohibition speech act and not only one or two
juz but can be more, or conduct research about
imperative and prohibition speech act in
Rasulullah’s hadits. Furthermore, analyze not
only from locution, perlocution and illocution
point of view but also from politeness and
cooperation theory is needed.
REFERENCES
Abbas, F. H., 1997. Al Balaghah Fununuhȃ Wa
Afnȃniha. Oman: Darul Furqon.
Adus, 2006. Madkhal Ilal Balaghah Arabiyah.
Oman: Darul Masirah.
Baidhȃwi, 1418 H. Anwȃrut Tanzîl wa Asrȃrut
Ta’wîl Juz 1. Beirut: Dar Ihyȃut Turȃts al
‘Araby.
Cummings, L., 2007. Pragmatik Sebuah Perspektif
Multidisipliner. Yogyakarta: Pustaka Pelajar.
Dendy, S., 2008. Kamus Besar Bahasa Indonesia.
Jakarta: Badan Bahasa Kemdikbud.
Hasyimi, A., 1999. Jawahirul Balaghah. Beirut: Al
Maktabatul ‘Ashriyyah.
Jarim, A., Musthafa, A., 1797. Al Balaghatul
Wȃdhihah. Kairo: Darul Ma’ȃrif.
Kharabasyah, 2007. Dilalatul Amri alal Wujub
bainat tahqiq wat tathbiq. Majallah Jamiah
Dimasqo lil Iqtishodiyyah wal Qonuniyyah,
23(2), p.336.
Nadar, F. X., 2013. Pragmatik & Penelitian
Pragmatik. Yogyakarta: Graha Ilmu.
Qazwaini, 2001. Taliqat ala Maalimil Ushul. Qom:
Muassasah Nasyrul Islami.
Sudaryat, Y., 2006. Makna dalam Wacana
(Unpublished). Bandung.
Sugiyono, 2013. Memahami Penelitian Kualitatif.
Bandung: Alfabeta.
Sukmadinata, N. S., 2011. Metode Penelitian
Pendidikan. Bandung: Remaja Rosdakarya.
Sya’rawi, 1997. Tafsir asy Sya’rawi Juz 2. Kairo
Mathâbi’ Akhbâril Yaum.
CONAPLIN and ICOLLITE 2017 - Tenth Conference on Applied Linguistics and the Second English Language Teaching and Technology
Conference in collaboration with the First International Conference on Language, Literature, Culture, and Education
790
