
Philosophy, Methodology and Paradigm Shift in Big Data
Baihaqi Siregar
1*
and Muhammad Zarlis
2
1
Doctoral Program, Faculty of Computer Science and Information Technology, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Indonesia
2
Faculty of Computer Science and Information Technology, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Indonesia
Keywords: big data, philosophy, methodology, paradigm shift
Abstract: Through information technology, such as social media, sensors, video surveillance or the intelligent network.
This ocean data produce a single Big Data terminology. Data plays an important role in strategic decision
making. Therefore, the parts that can process and use the data available in large, fast and different volumes
can certainly benefit greatly. The Big Data philosophy is a branch of philosophy with the basics, methods and
implications of Big Data involving large data sets that have a large volume, velocity, variety, value, and
veracity. The power of large data is in the analysis in which the results of the analysis are taken. Big data or
small data do not enter and in itself has value. This is only useful if we can get information from the data.
And this intuition can be used to combine our decisions. Along with Big Data, there is also a paradigm shift
in terms of analytical focus, from descriptive analysis to predictive and prescriptive analysis.
1 INTRODUCTION
Data are facts and statistics collected together for
reference or analysis. Information is a given or
learned fact about something or someone. The
Philosophy of Information is a new development with
a capacity to revolutionize philosophy and human
interactions with science, technology, data, and
reality. Both can be used as a basis for reasoning or
calculation. There are several opinions that define
data as facts and statistics, and information as
knowledge derived from facts and statistics. Kitchin
outlines the binary visions that the data itself is
neutral in terms of elements of reality or elements of
social construction like other elements. The position
of the data is neutral to reality without any policy or
agenda. Only people are interested in corrupt data and
direct it to their own interests, not the basic science
itself. Another point of view is that data are an
epistemological unit, socially constructed with all
prejudices, agendas and political forces that can be
incorporated into constructive social interests. As a
result, how the ontological data are defined are not
neutral, technical, but normative, political and ethical
processes. This type of known and common binary
vision exists for science in general, discussing
whether science is objective or requires subjectivity
because it is socially constructed. It would be difficult
to prove that science or data of biases from the
systems of thought and the tools at the base of their
production. He supports proposed the idea of the
required dataset by taking this explicitly different
influence, such as place, subjectivity, political
economy, institutions, rules and systems of thought.
Data science is the extraction of knowledge from
data. Data science covers large data and is intended
as a broader discipline that uses mathematical
engineering, theory, statistics, and information
technology such as machine learning, to discover data
models in which predictive models can be developed.
Intensive data processing requires a large set of data
sets that may require scientific computational
techniques for modelling, and observation of
complete dimensional data for experiments and can
be performed in distributed and copied networks.
2 GENERAL DEFINITIONS
Philosophy is the study of the nature of knowledge,
of truth, of reality and of existence. Its purpose is
largely composed in three general categories:
ontology, epistemology and ethics. Ontology refers to
existence; what are Big Data, how it looks, how it
works in the world; definitions and classifications.
Epistemology deals with knowledge; how Big Data
helps us learn about the new world, how real these
discoveries are, what the knowledge is needed to
Siregar, B. and Zarlis, M.
Philosophy, Methodology and Paradigm Shift in Big Data.
DOI: 10.5220/0010038900970100
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and Technology (ICEST 2018), pages 97-100
ISBN: 978-989-758-496-1
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
97

engage in the science of Big Data. Ethics discusses
how big data are made, how some types of results can
be obtained and why; Aesthetics is also part of this
category. Any philosophy should provide a concise
definition of what is and articulate its purpose and its
dimensions.
The philosophy of science is a branch of
philosophy that focuses on the foundations, methods
and implications of science. The main questions
about what science considers, the reliability of
scientific theory and the purpose of science. Various
data / information philosophy, Big Data, scientific
data and intensive data science can be understood in
this case as the basic structure, methods and
implications. Philosophy Data / Information is a
branch of philosophy that deals with the bases,
methods and implications of data and information;
existence, definition, conceptualization, method,
knowledge of possibilities, truth standards and
working practices with data and information. The Big
Data philosophy is a branch of philosophy that deals
with the basics, methods and implications of Big
Data; definition, intent, conceptualization, possible
knowledge, standards of truth and practice in
situations involving high volumes, high speed, large
amounts of information and data. Philosophy of data
science is the branch of philosophy that focuses on
the foundations, methods and implications of data
about science, the science of extracting knowledge
from data using techniques and the theory of
mathematics, statistics, and information technology.
The philosophy of intensive data science is a branch
of philosophy that deals with the basics, methods and
implications of intensive data science; Definition,
meaning, knowledge production, conceptualization
of science and discovery, definition of knowledge,
testing standards, and the practice of intensive
computational science in modelling situations,
observation, and a large-scale experiment.
3 PHILOSOPHIES IN BIG DATA
The Big Data philosophy concerns the basics,
methods and implications of Big Data; definitions,
meanings, conceptualizations, possible knowledge,
truth standards and practices in situations involving
large volume variety data sets at high speed. The
philosophy of the Big Data emerges as distinct and
different fields. The symbiotic productive
relationship between Big Data between scientists and
philosophers is necessary for further developments in
the field. The idea of Kant as a reference that
perception without conception is blind, and
conception without perception is empty. Different
types of blindness, conceptual and perceptive must be
investigated in the science of Big Data, for example
to avoid the case of fundamentalism data that blindly
trust the results of big data. Likewise, stresses that
such statistics, there is not a single version of the truth
in the science of Big Data. So we have to be critical
of the visualization of narrative data and data based
on history.
There is no consensus on how to define Big Data.
This term is often used as a synonym for related
concepts such as business intelligence and data
mining. It is true that these three terms concern data
analysis and in many cases advanced analysis. But the
concept of Big Data differs from two other factors
when the volume of data, the number of transactions
and the number of data sources are so large and
complex that they require special methods and
technologies to draw data. For example, traditional
data warehouse solutions may fail when dealing with
Big Data. Many parts try to define Big Data. Big Data
is a capacity, high capacity and / or diversified
information that requires the use of economic and
innovative information that enables better
understanding, decision making and process
automation. Everything refers to 3V: Volume,
Variety, Velocity, and some elements of Veracity and
Value:
Volume refers to a very large or perhaps
unlimited size of data storage media;
Variety data come from different data sources.
For the former, data can come from both
internal and external data sources. More
importantly, data can come in various formats
such as data tables, data structures and data
models, such as text, images, video streams,
audio reports and more. There is a shift from
individual structured data with unstructured
data or a combination of both;
Velocity is associated with large amounts of
data about transactions with high refresh rates
that produce high-speed data streams and the
time to act on these data streams will often be
very short. There is a shift from batch
processing to real-time streaming;
Meanwhile, the characteristics of Veracity and
Value are related to the uncertainty of the data
and the benefit value of the information
generated. In Big Data, data is too large and
too fast or incompatible with the conventional
database architecture structure. To get value
from data, technology should be used to
extract and obtain more specific information.
ICEST 2018 - 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and
Technology
98
4 BIG DATA TERMINOLOGIES
Big Data terminology is often associated with data
science, data mining, and data processing. However,
Big Data involves more data mining infrastructures,
or data processing techniques than ever before. In
implementing Big Data technology in an
organization, there are 4 important elements that
become challenges, namely data, technology,
processes and human resources :
Data;
The basic description of the data points to objects,
events, activities and transactions that are
documented, classified and stored but not set to give
a particular meaning. Data that has been organized
to give meaning and value to the recipient is called
information. Data availability is the key to Big Data
technology. There are many organizations that have
a lot of data about their business processes,
structured and unstructured data.
Technology;
This is related to the infrastructure and tools in the
operation of Big Data, such as calculation and
analysis techniques, as well as media storage.
Normally, organizations will not suffer significant
limitations in technology because technology can
be acquired by buying or working with third parties.
Process;
In the process of adopting Big Data technology, a
change in organizational culture is required. For
example, before Big Data, the leader in managing
the organization, make decisions based only on
intuition based on values, beliefs or hypotheses. But
after Big Data technology, leaders can act on data-
driven decisions means making decisions based on
accurate data and relevant information.
Human resources.
When applying Big Data technology, human
resources must be able to analyse and create
creativity, that is, skills / competences to learn new
methods that can be collected to collect, interpret
and analyse data, computer programming skills and
commercial skills. to understand business goals.
Data sources in Big Data technology can be
structured and unstructured data. Structured data have
predefined data types, formats and structures. While
in unstructured data, text data with incorrect
formatting or no built-in structure, making it
structured to require more effort, tools and time. This
data is generated by internet applications such as
social media. Unstructured data sources are those
with little or no control over the format. Text data,
video data and audio data fall into this category.
Unstructured data is complicated because the
meaning of byte is not predetermined. Structured and
unstructured data include semi-structured data. Semi-
structured data are data that can be irregular or
incomplete and have structures that can change
quickly or unpredictably. It usually has a structure,
but does not fit the fixed pattern. Web logs are a good
example of semi-structured data.
5 METHODOLOGIES
Is it more important to work with Big Data than
traditional data? By reading large amounts of data, we
might start thinking that just because Big Data has a
high volume, speed and variations are somehow
better or more important than other data. This is not
the case. The power of large data is in the analysis in
which the results of the analysis are taken. Big data or
small data do not enter and in itself has value. This is
only useful if we can get information from the data.
And this intuition can be used to combine our
decisions. Since the introduction of Big Data in data
collection and analysis, this technique has been
compared with previously conducted conventional
methods, such as surveys. The comparison between
the two methods appears as follows :
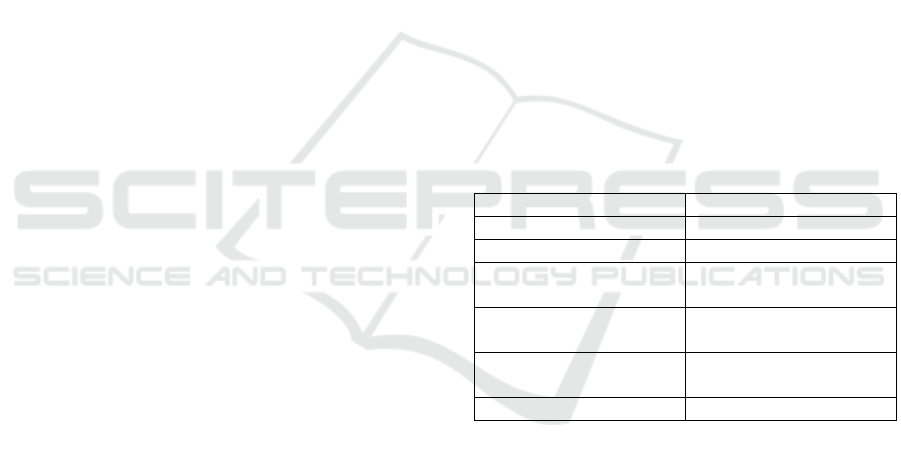
Table 1. Comparison Method Between Conventional and
Data Analytics
Legacy Data Analytics
Confirmative Explorative (Predictive)
Small Data Set Large Data Set
Small Number of
Variable
Large Number of
Variable
Deductive
(No Predictions)
Inductive
Numeric Data Numeric and
Non-Numeric Data
Clean Data Data Cleaning
The phases of activities and technical support on
Big Data are as follows:
Obtain, related resources and how to obtain
data;
Access, related to the power of data access; the
data already collected require governance,
integration, storage and calculation to be
managed for the next step;
Analytical, related to the information to be
obtained, to the results of the data
management that has been processed. The
analysis can be descriptive, diagnostic,
predictive (foresee future events) and
prescriptive (recommending options and
implications of each option);
Application, related to the visualization and
results of analysis reports.
Philosophy, Methodology and Paradigm Shift in Big Data
99

There are several important ways in which Big
Data is different from traditional data sources. Frank
[10] suggests the following ways Big Data can be
viewed differently from traditional data sources.
First, Big Data can be a completely new source of
data. The transactions we perform are not transactions
that are fundamentally different from what we would
traditionally do. An organization can acquire Web
transactions, but the transaction is actually just the
same transaction that has been acquired from years.
However, it actually captures browsing behavior
because customers make transactions by creating new
fundamental data. Secondly, it can sometimes be
argued that the speed of data feeds increases so as to
qualify as a new source of data. Third, the more semi-
structured and unstructured data that arrive. Most
traditional data sources exist in structured areas.
6 PARADIGM SHIFT IN BIG DATA
Along with Big Data, there is also a paradigm shift in
terms of analytical focus. It is a passage from a
descriptive analysis to predictive and prescriptive
analysis. Descriptive analysis answers the question
"what happened in the past?" This usually involves
reporting. Predictive analysis aims at something
about "what could happen next?" This is more
difficult and involves the extrapolation of trends and
patterns in the future. While the prescriptive analysis
tries to answer, "how do I manage this"? This is where
the analysis starts to work. It's really corporate and
depends on the case. The three types of analysis
existed before the era of Big Data, but the focus was
on traditional reports. The difference that Big Data
brings to the table is an appetite and long-sighted
vision skills and appetite and ability for a quick and
usable vision.
7 CONCLUSIONS
The philosophy of the Big Data emerges as distinct
and different fields. The symbiotic productive
relationship between Big Data between scientists and
philosophers is necessary for further developments in
the field. The idea of Kant as a reference that
perception without conception is blind, and
conception without perception is empty. Different
types of blindness, conceptual and perceptive must be
investigated in the science of Big Data.
Big Data terminology is often associated with data
science, data mining, and data processing. But the
concept of Big Data is different from the others when
the volume of data, the number of transactions and the
number of data sources so large and complex that
requires special methods and technologies to attract
data. Traditional data storage solutions may fail when
dealing with Big Data.
By reading large amounts of data, we might start
thinking that just because Big Data has a high
volume, speed and variations are somehow better or
more important than other data. This is not the case.
The power of large data is in the analysis in which the
results of the analysis are taken. Big data or small data
do not enter and in itself has value. This is only useful
if we can get information from the data. And this
intuition can be used to combine our decisions.
Along with Big Data, there is also a paradigm shift
in terms of analytical focus, i.e. descriptive,
predictive and prescriptive analysis. The three types
of analysis existed before the era of Big Data, but the
focus was on traditional reports. The difference that
Big Data brings to the table is an appetite and long-
sighted vision skills and appetite and ability for a
quick and usable vision.
REFERENCES
L. Floridi, Philosophy of Information, Oxford, 2011.
R. Kitchin, The Data Revolution: Big Data, Open Data,
Data Infrastructures and Their Consequences, Sage
Publications, 2014.
V. Dhar, "Data science and prediction," Communications
o
f
the ACM, 2013.
M. Swan, "Philosophy of Big Data: Expanding the
Human-Data Relation with Big Data Science
Services," in
B
ig Data Computing Service and
A
pplications (BigDataService), 2015 IEEE First
International Conference on, 2015.
J. Kobielus, "Transforming the agile data warehouse in
the age of the in- memory cloud," 2014.
M. A. Beyer and D. Laney, "The Importance of 'Big Data':
A
Definition," Gartner, 2012.
K. Aryasa, "Big Data: Challenges and Opportunities,"
2015.
R. R. Kelly and C. G. Cegielski, Introduction to
Information Systems, John Wiley & Sons, 2009.
J. Friedman, "Data Mining and Statistics: What are the
Connections?," 1997.
B. Franks, Tamin
g
the bi
g
data tidal wave, Wile
y
, 2012.
ICEST 2018 - 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and
Technology
100
