
Production of Lip Balm from Natural Dyes
Irmawati Akma Abdul Hapiz
1*
, Jemima Japakumar
1
, Jivinthiran Jayagobi
1
, Mohamad Azfar
Jamaluddin
1
and Sharmila Arumugam
1
1
Department of Agrotechnology and Bio-Industry, Nilai Polytechnic, Malaysia
Keywords: Cosmetics,
natural dyes, organics, lip balm, extraction, solvent
Abstract: Recently, demands for natural products increases especially in the cosmetics industries. Lip balm is one of
the widely used cosmetic products whose purpose is to give a colour to the lip as well as prevent lip dryness
and acts as lip treatment. The purpose of this study is to extract natural dyes from five selected plant sources
which are roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa), dragon fruit (Hylocereus costaricensis), beetroot (Beta vulgaris),
betel leaf (Piper betle) and red cabbage (Brassica oleracea) and also to produce a good quality, good colour
consistency and effective dyes in the production of natural lip balm. There are several methods used to extract
the dyes from selected plant which involved different kind of solvent. Results from this study shows that the
best solvent used for all the extraction processes is ethanol compared to methanol and distilled water. It is
proved by the higher yield of extracted dyes that comes from extraction using ethanol as a solvent. The plant
roselle produces 117.6 ml of dyes, soaked dragon fruit produces 300 ml of dyes, for other sources which are
beetroot, red cabbage and betel leaf produces 300 ml, 250 ml and 100 ml respectively. Roselle produce dark
red dyes as appears on lip balm, dragon fruit produces dark purple dyes and turn to pink when mixed with
natural ingredient in lip balm. Whereas, dragon fruit peel produces light pink dyes and appears yellowish on
lip balm. Beetroot produces dark purle dyes, followed by red cabbage produces light purple dyes while in lip
balm it appears purple and betel leaf produces dark green dyes while appears green in lip balm. In addition,
the colour obtained from betel leaf on lip balm is darker compared to dyes produced by roselle, dragon fruits,
beetroot and red cabbage. The lip balm was applied on a piece of paper to check the colour visibility as well
as the consistency of colour which applied on human skin for 10 minutes to check the itchiness or any changes
on the skin. In summary, natural dyes from different plant sources were successfully extracted to produce
high quality of dyes on cosmetic product. This product has higher marketing potential where the production
cost is cheaper and it is considered as organics product.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, people increasing interest in natural
products, as the public becomes aware of ecological
and environmental effects related to the use of
abundant chemicals in the daily products. Cosmetics
made from natural sources as raw material considered
as organic cosmetics which are believed as safe and
sometimes may act as health cure. Furthermore, no or
mild chemical reactions are involved in the
preparation of the product and it claims as
harmonized with nature. Organic cosmetics refer to
the cosmetics that made by 95% of the raw materials
comes from natural sources, while natural products
contain at least 5% organics raw materials as an
ingredient (Fernandes et al., 2013). One of the main
source of raw materials in cosmetic is dye or
colourant. Natural dyes refer to the colorants
produced from the natural sources such as plant,
animal, insect or minerals. The dyes also can be used
widely in the colouration of textiles, foods, medicine
and craft products as well as in cosmetics. Although,
some processing was required in the process to obtain
the dyes but essentially the dye itself was obtained
from natural sources. The greatest sources of dyes
were been the Kingdom Plantae, notably fruits and
leaves.
Lip balm refers to the formulations that can be
applied onto the lips to prevent drying and protects
lips against adverse environmental factors (Kadu et
al., 2014). There are many established companies
produce lip balm in the market such as The Body
Shop, Nivea, Mentholatum etc which may contains
chemical origin. However, it is necessary to balance
the concentration of the main ingredients to formulate
202
Abdul Hapiz, I., Japakumar, J., Jayagobi, J., Jamaluddin, M. and Arumugam, S.
Production of Lip Balm from Natural Dyes.
DOI: 10.5220/0010040502020206
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and Technology (ICEST 2018), pages 202-206
ISBN: 978-989-758-496-1
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

lip balms including the base, oils, colouring agents
and flavouring agents. Natural lip balms offer a
natural way to maintain and promote healthy lips
(Fernandes et al., 2013). Lip balms are also often
eaten away by the user and it is imperative that the
ingredients are not dangerous to humans on
consumption. There are four main components as key
formulations ingredients for natural lip balm (Kadu et
al., 2014). Basically, waxes are used as base to give
the more stable structure and make it easier to form
desirable shape of lip balm. Oils are required to blend
properly to the waxes, so that provide a suitable film
on the applied lip skin to protect and moisturizes the
lip. Colouring agents or dyes is mainly used to impart
a distinctive appearance to the products. Dye is an
important ingredient of cosmetic formulations as user
desire controlled by three senses namely sight, touch
and smell (Kadu et al., 2014). Dyes used is cosmetic
should not affected by oxidizing or reducing agents
as well as pH changes and it also should not interferes
with the tests and assays. The usage of synthetic dyes
was done commercially for attractive colours but it is
hazardous to skin and environment (Devi et al.,
2013). The natural dyes have not commercially
succeeded as synthetic dyes due to lack of the
botanical knowledge and precise technical
knowledge on the extraction methods and dyeing
procedure (Devi et al., 2013). Flavouring agents is
required to mask the four basic taste sensations
namely salt, bitter, sweet and acid from the other
ingredients. This is optional to give a value added in
the products. In this research, natural dyes from the
plant roselle, dragon fruit, betel leaf, beetroot and red
cabbage was extracted to produce a high quality of
desirable natural dyes mainly because of the quality
of colour that can be created with them.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Collection of Plant Materials
Traditionally, the sources used from 5 varieties of dye
yielding plants were collected from different farms in
Malaysia. Firstly, the plant roselle was collected from
two different farms which are located at sek 36 Shah
Alam and the other one is from Tropical Fruit Farm
located at Jalan Teluk Bahang, Penang. Next, dragon
fruit were collected from Multi Rich Pitaya farm
which is located at Sepang. In addition, red cabbage
and beetroot were collected from same place which is
from Titi Eco Farm Sdn. Bhd, Kuala Klawang, Negeri
Sembilan. Finally, the betel leaf was collected from a
small farm in Kampung LBJ, Jalan Labu. The local
and scientific names of dye yielding plants used in
this study are given in Table 1.
Distilled water, laboratory grade ethanol and
methanol are used as solvent in the extraction
methods. Petroleum gel and virgin coconut oil has
been used to solidify the product and added as the
treatment for lip.
Table 1: Local and scientific names of dye plant sources.
Local name Scientific name Plant parts
used
Roselle Hibiscus sabdariffa Calyces
Dragon fruit Hylocereus costaricensis Fruits (peel
and flesh)
Beetroot Beta vulgaris Tuber
Red cabbage Brassica oleracea Leaf
Betel leaf Piper betle Leaf
2.2 Selection and Preparation of Raw
Material
The process to obtain a dye was basically done in four
stages which are extraction of dyes from five different
plant sources, formulation of product, effectiveness
of dyes & skin irritation test. Matured plants used
which are harvested in a healthy condition. The plant
sources were collected and wash thoroughly with
running water and then with deionized water to
remove the impurities. After drying at room
temperature, the samples were ground into powder
form with grinder.
2.3 Dye Extraction
In an attempt to prepare dye solution from the plant
sources, the solvent extraction method was used. It is
a process where natural colours were extracted using
organic solvents such as acetone, ethanol and
methanol (Mirjalili and Karimi, 2013). The cleaned
samples were crushed, dissolved in deionized water
and was boiled for 2 hours in a hot water bath for
quick extraction. After 2 hours, the total color was
extracted. The solution was then double filtered and
used for further analysis. The solvent extraction
method was chosen because it able to extract both
water-soluble and water-insoluble substances from
the plant sources. The extraction yield is thus higher
as compared to the aqueous method as a larger
number of chemicals and coloring materials were
extracted (Mitra and Das, 2015). Purification of
Production of Lip Balm from Natural Dyes
203
extracted dyes were easy as the solvents can be easily
removed by using rotary evaporator (Saxena and
Raja, 2014).
Next aqueous extraction were also used to extract
dyes from plant source. In this aqueous extraction, the
dye containing material were broken into powdered
and sieved in order to improve extraction efficiency
(Uddin, 2015). It is then soaked with distilled water
for a long time usually overnight to loosen the cell
structure and then boiled to get the dye solutions
which were filtered to remove non dye plant
remnants. The process of boiling and filtering is
repeated to remove as much dye as possible
(Wanyama et al., 2014).
Table 2: Solvent used for solvent extraction methods.
Plant sources as
raw materials
Solvents used Solvent’s
volume
(ml)
Roselle Ethanol 132.4
Distilled wate
r
132.4
Dragon
fruit
Dried &
grinded
Ethanol 490
Distilled wate
r
490
Soaked
dragon
fruit
Ethanol 490
Beetroot Ethanol 490
Distilled wate
r
490
Red cabba
g
e Ethanol 375
Betel
leaf
Dried &
blended
leaf
Ethanol 143.35
Methanol 143.35
Distilled wate
r
143.35
2.4 Formulation of Lip Balm
The prepared dye solution from different plant
sources was then added to petroleum gel and virgin
coconut oil. The mixture then double boiled to melt
all the ingredients until mixed thoroughly. Petroleum
gel, virgin coconut oil and extracted dyes (solution)
were prepared with the ratio 1:1:1. The materials were
weighted using analytical balance. Each ingredient
was weighted equally.
The mixture then was put in the water bath until
all materials in the mixture were melt and transform
to liquid form. After melting completely, a mixture
was poured into the container and it was let to be air
dried at room temperature. Next, it was put into the
refrigerator for about 48 hours so that it will solidify.
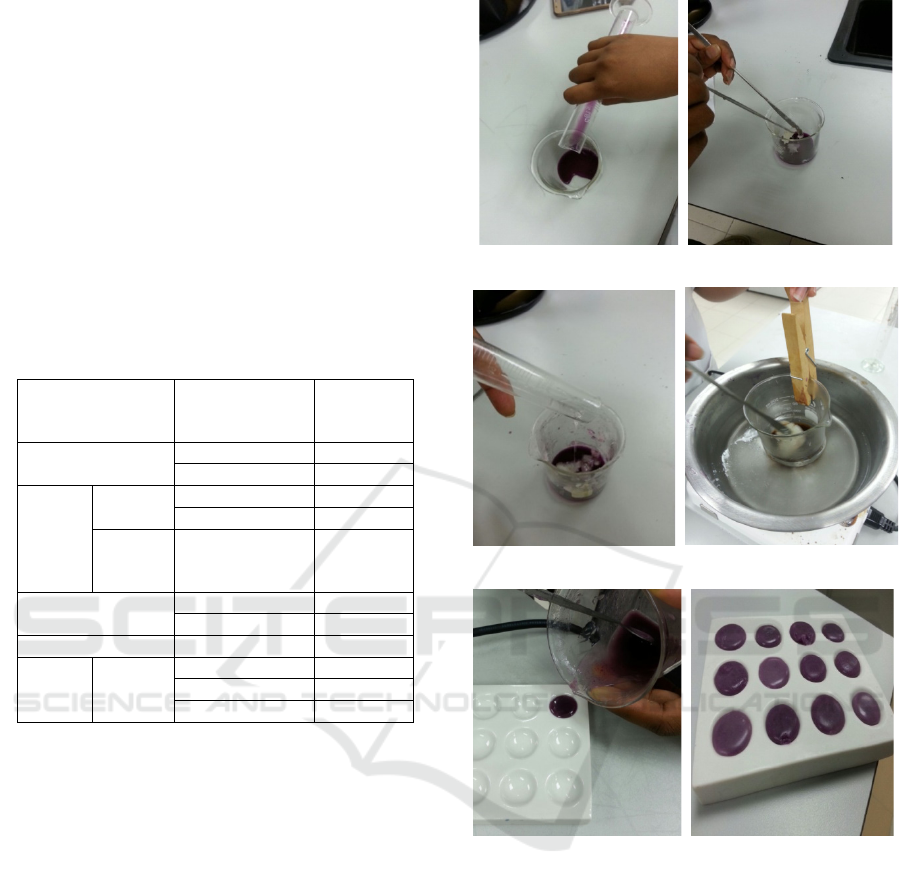
(a) prepared dye on the beaker (b) petroleum gel was added
(c) virgin coconut oil was (d) double boiled the mixture
(e) poured into suitable container (f) the mixture was allowed
to solidified
Figure 1: Preparation steps for lip balm formulation as
follows: (a) prepared dye on the beaker (b) petroleum gel
was added (c) virgin coconut oil was added (d) double
boiled the mixture (e) poured into suitable container (f) the
mixture was allowed to solidified at room temperature
before kept on chiller for 48 hours.
2.5 Evaluation of Lip Balm
2.5.1 Effectiveness Test on Papers
Finally, after taking out the lip balm from chiller, it
was tested by applying the lip balm on a piece of
paper. This process is important to determine colour
obtained from different sources. It also can determine
the effectiveness of the colour produced.
ICEST 2018 - 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and
Technology
204

2.5.2 Skin Irritation Test
It is carried out by applying lip balm on the skin for
10 minutes.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Three different solvents used for the extraction
processes. The best solvent is ethanol compared to
methanol and distilled water. It is proved by the
higher yield of extracted dyes solution that comes
from extraction using ethanol as a solvent. This result
is very useful since ethanol is non toxic compared to
methanol and it can be used safely in cosmetics. The
plant roselle produces 117.6 ml of dyes, soaked
dragon fruit produces 300 ml of dyes, for other
sources which are beetroot, red cabbage and betel leaf
produces 300 ml, 250 ml and 100 ml respectively.
The extracted dye solution can be left for evaporation
so that the dyes will become more thicker in colour.
Table 3: Dye solution obtained from solvent extraction
methods.
Plant sources Solvents Sample
weight
(g)
Solvent
volume
(ml)
Dyes
obtain
ed (ml)
Roselle Ethanol 26.48 132.4 117.6
Distilled
wate
r
26.48 132.4 114.6
Dragon
fruit
Dried
&
grinded
Ethanol 327 490 215
Distilled
wate
r
327 490 290
Soaked
dragon
fruit
Ethanol 327 490 300
Beetroot Ethanol 327 490 300
Distilled
wate
r
327 490 240
Red cabba
g
e Ethanol 250 375 250
Betel
leaf
Dried &
blended
leaf
Ethanol 28.67 143.35 100
Methanol 28.67 143.35 90
Distilled
wate
r
28.67 143.35 80
The colour value of dyes was analyzed visually
and compared with different plant sources. Change in
colour characteristics in terms of hue and lightness
was observed. Based on the Figure 2, the colour of
betel leaf on lip balm is darker compared to the others
and the colour of dragon fruit on lip balm is lesser,
followed by the colour of red cabbage, roselle and
beetroot. Even though, the 5 types of extracted dyes
shows different properties in term of colour
consistency ,yet all the 5 extracted dyes have shown
the colour on the lip balm. This shows that the
application of extracted dyes on lip balm is successful.
Figure 2: Different plant sources produces different colour.
From left: red cabbage, roselle, dragon fruit, beetroot and
betel leaf.
For the colour assessment, the visual aspect was
considered as good. No colour changes was
observed on the lip balm from the evaluation day
onwards.
Table 4: Analysis of colour and rating of the dye from
different sources.
Plant sources Colour Rating
Red cabbage Light purple Good
Roselle Dark red Good
Dragon fruit Light red Good
Beet root Dark purple Good
Betel leaf Dark green Good
Other than that, the lip balm was applied on a
piece of paper to check the visibility of natural dye as
well as the consistency of colour. The developed
formulation of natural lip balm exhibited an
appropriate appearance after several months,
regardless of storage conditions. It shows that the
composition and ration of ingredients were adequate.
Figure 3: Lip balm applied on a piece of paper. From left:
beetroot, roselle, red cabbage, dragon fruit and betel leaf.
Finally, all five different lip balms show no skin
itchiness and irritation when applied onto the skin for
more than 10 minutes.
Production of Lip Balm from Natural Dyes
205

4 CONCLUSION
The dye yield resulted from the solvent extraction
method and the colour strength produced after
formulation of lip balm indicated that dye plants
under this study have considerable potential for
application as a source of natural dye for cosmetic
purpose. Ethanol showed the best solvent in this
extraction method. This research results also showed
that all the lip balm made from natural dyes were
stable and had a good force of application. In
addition, after 1 year storage in the room temperature,
the condition of the product was still good. Finally yet
importantly, this product did not cause irritation to
lip. Meanwhile, they were safe to apply as organic
cosmetics. In order to produce the high quality of
extracted dye for the purposes in the cosmetic;
integrated knowledge of the extraction procedures
and the treatments of the plant parts that want to apply
as a dye are needed. There are broad of procedures
that will make the production of dyes are present in
many conditions. For instant, the selection of solvents
and the adjustment concentration of solvents used
will make the yield of dye extracted in a variety of
colours are need to be focused.
REFERENCES
A. A. Aher, S. M. Bairagi, P. T. Kadaskar, S. S. Desai and
P. K. Nimase, (2012) Formulation and evaluation of
herbal lipstick from colour pigments of Bixa Orellana
(Bixaceae) seeds, International Journal of Pharmacy
and Pharmaceutical Sciences. 4, 357-359.
A. Mitra and S. K. Das, (2015) Fabric dyeing with natural
dye extracted from Basella alba fruit and spectroscopic
analysis of the extract at different conditions;
Department of Chemistry, Maharaja Bir Bikram
College, Agartala, Tripura (West) PGT Shalgara H. S.
Udaipur, Udaipur, Gomati District,Tripura, India., 1-8.
A. R. Fernandes, M. F. Dario, C. A. S. Pinto, T. M. Kaneko,
A. R. Baby and M. V. R. Velasco, (2013) Stability
evaluation of organic lip balm, Brazilian Journal
Pharmaceutical sciences. 49, 293-298.
M. Kadu, S. Vishwasrao and S. Singh, (2014) Review on
natural lip balm, International Journal of Research in
Cosmetic Science. 5, 1-7.
M. G. Uddin, (2015) Assessment of antimicrobial
effectiveness of natural dyed fabrics. Bangladesh
Journal Science India 48, 179-184.
M. Mirjalili and L. Karimi, (2013) Extraction and
characterization of natural dyes from green walnut
shells and its use in dyeing polyamide: focus on
antibacterial properties; Department of Textile
Engineering, Yazd Branch, Islamic Azad University,
Yazd, Iran,Young Researchers and Elites Club, Science
and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University, Tehran,
Iran 1-4.
P.A.G. Wanyama, B.T. Kiremire, J.E.S.Murumu, (2014)
Extraction, characterization and application of natural
dyes from selected plants in Uganda for dyeing of
cotton fabrics 185-195.
S. Saxena and A. S. M. Raja, (2014) Experiments on
machine dyeing cotton fabrics with natural dye -
chrysanthemum flowers, in naturally, crafts council of
India, Chennai 160.
V. N. Meena Devi, V. N. Ariharan and P.P. Nagendra,
Annatto: (2013) Eco-friendly and potential source for
natural dye, International Research Journal of
Pharmacy. 6, 106-108.
APPENDIX
ICEST 2018 - 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and
Technology
206
