
Radicalism on Teens as the Effect of Digital Media Usage: Based on
Survey towards High School Students in Depok City, West Java,
Indonesia
Suraya Mansur
1,*
and Ahmad Mulyana
2
1
Lecturer at University Mercu Buana Jakarta Indonesia
2
Lecturer at University of Mercu Buana Jakarta Indonesia
Keywords Radicalism, Theory of Reasoned Action, Senior High School Student, Digital Media.
Abstract This research takes a deeper examination on the pattern of digital media consumption by teenagers.
Consumption pattern is believed to give effects on the particular teenagers. The functions of social media,
which were initially intended for connecting relations and source of information, have in fact shifted into
different meaning. In some cases, like on the Islamic digital media that publish the news about Islamic
movements, such media is believed has the power to give influence to shape its audience’s attitude into
radicalism behavior. This research is done through a survey methodology towards 100 senior high school
students in Depok city, West Java, Indonesia. The collected data is being analyzed through Pearson
Correlation Product Moment and Simple Regression Analysis. The result shows a high rate of radicalism
behavior by senior high school students in Depok city. The Influence of the frequency of digital media usage
on high school students appears to give little contribution towards radicalism behavior. Meanwhile, the
correlation between the frequency of digital media usage and the attitude of radicalism appears to be
significantly weak.
1 INTRODUCTION
Youth lives in their time. Kids and teenagers always
tend to have their own world and spaces. They like to
interact with each other and technology influences
their daily lives. The nowadays kids and teenagers are
often referred as the millennial generation, whom are
also born and raised closely with digital technology,
which consequently make them impossible to detach
with the digital media.
Quoting the words of Philip Chan, UNICEF
Australia Young Ambassador (Young and Well
Cooperative Research Centre; Youth Brains Trust;
UNICEF, 2014): “Digital media is a powerful way
for children to realize their rights, from accessing
information, playing games, to expressing themselves
freely and even anonymously. Technology has a
crucial role in empowering children by facilitating
communication, education and activism. It means
children don’t have to rely on adults and can have a
voice of their own. Yet not all children have equal
access to digital media. Even with access, digital
media poses risks for children such as Internet safety
and cyber bullying. In any new policy or decision-
making, it is absolutely important to listen to
children’s voices rst-hand, rather than assuming
what is best for them.” (Children’s Rights in the
Digital Age: A download from children around the
world, October 2014).
In July and August 2014, UNICEF (UNICEF,
2014) was conducted a research towards 148 youth
from 16 countries on young generation’s opinion and
perspective about their rights in digital era. Every kid
and teenager have the rights to use digital media; such
rights has been explained by UNICEF through the
following points; 1. Youth has the right to access, 2.
Youth is the majority of digital media users; 3.
Literacy is the most primary needs for young
generation; 4. They got dominated by narrative risks;
5. They are naturally smart in distinguishing online
and offline; 6. They are able to measure the balance
between the risk and opportunities; 7. They are able
to construct self-actualization through the use of
media; 8. Considering the perspective of young
generation; 9. They use it as the source to look for
knowledge; 10. The Government and practitioners
462
Mansur, S. and Mulyana, A.
Radicalism on Teens as the Effect of Digital Media Usage: Based on Survey towards High School Students in Depok City, West Java, Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0010044904620470
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and Technology (ICEST 2018), pages 462-470
ISBN: 978-989-758-496-1
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

maintain the communication with the youth. (2014:
8-12).
Nevertheless, according to the survey conducted
in Indonesia by the Association of Indonesian Internet
Service Providers (APJII) in partnerships with the
Center for Studies and Communication University of
Indonesia (Puskakom UI), it shows that the majority
of internet users in Indonesia, based on age grouping,
are people in the age between 18 – 25 years old
(49.0%). This means, the biggest Internet users
segment in Indonesia is included in the category of
digital natives. (Beritasatu,
2007:http://www.beritasatu.com/iptek/261297-
mayoritas-netizen-di-indonesia-berusia-1825-
tahun.html).
On the other hand, there is a result from a survey
occurred in 2011 by the Institute for Islamic Studies
and Peace (LaKIP)(Pranowo, 2011), towards 59
private schools and 41 public schools in Jakarta
reflected that the majority of students in Jakarta were
inclined to take violence action to resolve religious
issues and moral conflicts. As much as 48.9% stated
their willingness to be involved within a violence
action in regards to religious and moral issues, and on
the highlight of research’s result was to figure out that
there were actually dozens of the students were
supporting such extreme actions like suicide
bombing. (Cited from a writing by Prof., Dr.,
Bambang Pranowo, a professor of Islamic sociology
in the State Islamic University (UIN) Jakarta; Koran
Tempo, 26 April 2011).
Other information gathered from another
surveys showed that there were 63.8% students and
41.8% teachers are willing to be involved in force-
shutdown other religions’ house of worship.
Furthermore, there are participants of the surveys
whom considered that Pancasila (the Indonesian
National principles) is no longer relevant to be the
ideology of the nation; in which 25% were students
and 21% were teachers. Amongst 84.8% students and
76.2% teachers agreed with the implementation of
Islamic law in Indonesia. Of the numbers of survey
participants who stand for violent action in the name
of religion’s solidarity were hitting 52.3% students
and 14.2% teachers whom justifying bombing attack
(Tempo.co, 2011:
https://www.tempo.co/read/fokus/2011/04/26/1855/
Separuh-Pelajar-Setuju-Aksi-Radikal-%20Berlabel-
Agama).
These collections of surveys’ results should have
become some kind of awareness to the teachers,
essentially the teacher of Islamic education (PAI),
about the emerging moral dangers that is threatening
the students. Referring to the study by Research and
Development Agency of the Indonesian Ministry of
Religious Affairs, it revealed that reading materials
provided by both PAI’s public school and PAI’s
private school sylabus in Jakarta are majorly taken
from the internet sources than text books (Ministry of
Religious Affairs, 2016).
Such particular youths have similar attitudes
described by the collections of surveys’ results
discussed previously, which were affected from
anything they read, watch, and hear. In regards to this
matter, media has a strong influence on them,
especially the digital media.
In a collaborative research conducted by
Research and Development Agency of Department of
Religious Affairs and Paramadina University towards
six mass media between the year of 2008-2015, it
illustrated how these major mass media’s coverages
in Jakarta, West Java, and Banten had the tendency to
publish the news contained with violence that related
to various religious issues, regardless the media
company or the province. Of two out of the six
newspapers that were chosen to be the object of this
study, namely Kompas and Republika that based in
Jakarta, these two show the opposite patterns of
coveraging news. Whereas Kompas is very prompt in
publishing violence cases factually, Republika tends
to move slow and being reflective. In different takes
were surprisingly found in the other four newspapers
that is based outside Jakarta, for they show similar
patterns: the designated portions for local and
ceremonial news are bigger, for example like
coveraging terorism issues on the perpetrators arrest
highlight, more peace occasions covered than
violence incidents, and the newspapers are providing
the background of those violence incidents
(Department of Religious Affairs, Analisis Konten
Kekerasan Agama di Media 2008-2015, 2016).
Ibnu Hamad (Hamad, 2004) stated that due its
obligatory feature and fact that mass media editorial’s
tasks is to story tell the occurring events, so it does
not seem exaggerating if we found that the entire
content of a media are full of constructed reality. It
seems very natural if then the construction of reality
on each media is different from one to another, even
though they cover exactly the same reality. The way
these media constructing the reality of facts are
depends on the editorial policy, which very much
interrelated to the politic adapt by particular media.
Mass media, particularly those the Internet-based
mass media, are indeed giving bigger space for
individuals to show off their creativities, retrieving
infinite information about many things, as well as
mediating their self-actualization; however, it often
appears that the Internet are spreading false
Radicalism on Teens as the Effect of Digital Media Usage: Based on Survey towards High School Students in Depok City, West Java,
Indonesia
463

information (hoax) too, which in many case these
hoax are often believed to be the truth due to people’s
lack of knowledge and Internet literacy.
In Krathwohl’s opinion (1964:55)(Azjen, 1988)
the attitude and perspective that is being disclosed by
the youth based on the research discussed above, is a
form of agreement or acceptance to a value that
consists of five stages of behavior or affective. Those
five stages are (1) receiving, (2) responding, (3)
valuing, (4) organization, and (5) characterization by
a value or value complex.
In other words, is that when the youths are
independently accepting or approving the value of
violence or radicalism without proper supervisions or
the right guidance, this will cause the emergence of
violent personality in them, as a means to get what
they want or to achieve their goals. The targeted
youths for this research are the youths who live in
Depok city, West Java, Indonesia.
“BERIMBANG.COM, Depok – The threats of
Internet abuse are very prone in targeting the
students. The Service Departments of
Communications and Informatics (Diskominfo) of
Depok city is continuously spreading massive
awareness amongst the students, who naturally are
the digital native and the active Internet users.
The functional/public relations of Civil Service
Officer (ASN) of Diskominfo Depok city, Rita
Nurlita, explained that to provide a virtual world with
a clean and safe Internet for the smart, creative, and
productive community is one of the government
agendas. According Rita, the Internet is capable to be
a space for creativity and innovation for the user
whenever it got used correctly.
"The Internet has the benefit of which is to seek
information, data, pictures and knowledge as a means
of entertainment," he said during an Internet Safety
Seminar and Drug Abuse Prevention at SMAN 8
Cilodong, Depok city, on Friday (18/08/17).
(Diskominfo, 2017:
http://berimbang.com/diskominfo-depok-gencar-
kampanye-internet-sehat-di-kalangan-pelajar/)
Moreover, the mayor of Depok city has already
launched an Internet safety campaign to the Depok
city youth’s in particular. “Children are the leaders of
future generation. Therefore, it has been our duty to
always give them positive things, and one of them is
the accessible safe Internet,” said The Mayor of
Depok city, Idris Abdul Shomad, on Thursday (3/3).
Previously, Idris had made the announcement about
the launch of Internet Safety Program by the central
government through the agenda of the Ministry of
Communications and Information (Kemenkominfo).
The objective of this program is to socialize the safety
use of Internet through learning the ethics of safe
Internet usage involving the entire components of
society "The program will deliver through roadshows
and discussion forums," added Idris.
(Republika.co.id,
2017)http://www.republika.co.id/berita/koran/urbana
/16/03/04/o3iegk6-internet-sehat-agar-depok-lebih-
bersahabat).
Such positive campaign encouraged the youths of
Depok city to establish a circle to share positive
things, which consists of the students who are willing
to be the youth volunteers in campaigning the Internet
safety awareness to their peers.
The essence of Islamic Digital Media is to display
information about the activities being done by the
Muslims in Indonesia and abroad. For the adults who
read the broadcasted messages on the Islamic media,
would not be easily affected because adults can think
rationally. However, it is going to be a whole different
case if the broadcasted message on the Islamic media
is being read by the youth, which particularly
referring to the high school students in this research.
This logical connection and situation become the
motives for the researchers in conducting this
research. In accordance to the previously described
problems identification, the research question that is
going to be figured out in this study is: To what extent
does the content of the message broadcasted in
Digital Islamic Media? To what extent does the
attitude of radicalism able to emergence towards the
high school student? To what extent does the
probability of the content of messages in digital
media could affect the attitude of radicalism amongst
high school students?
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
As the development of technology gets advance, the
world has shifted from its old analog era into the
current digital era. Such technology advancement has
big influence in shaping the future of media, for it
consequently trigger the emergence of the new media.
Explained by Everett M. Rogers (Abrar, 2003) as
he broke down the development of media
communication into four eras. First, the era of written
communication; Second, the era of print
communications; Third, the telecommunications era;
and Fourth, the era of interactive communication.
The new media is the media that occurs in the era of
interactive communication.
New Media characterizes with its connection to
the Internet, it is a technology-based online media, its
flexible functions, has the potential for interactivity,
ICEST 2018 - 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and
Technology
464

and it allow the user to use it both privately and
publicly (Mondry, 2008). “Social Media has become
an integrated part of modern living. It is predicted,
that in the near future, a trend called 3S will appear:
Social, Shared, and Speed”. Social is how one is
connected with others people and undergo the habits
of sharing with people online. Shared is how one is
sharing their experience to other people through text,
photograph, video, and other means of
communicating the experience through media social.
According to the result of a study on how much
do the teenagers are spending their time using the
computers: Parents in the Annenberg survey report
that children (between 2 and 17 years) in homes with
computers spend approximately 1 h and 37 min a day
on computers, including video games (Stanger &
Gridina, 1999). In the HomeNet study, machine
records of weekly usage averaged across
approximately 2 years of data between 1995 and
1998 show that among the teens who had access to
the Internet at home, usage averaged about 3 h/week
during weeks when they used it, and over 10% used it
more than 16 h/week. Teens in the study were much
heavier users of the Internet and all its services than
were their parents.
The teens used the Internet for schoolwork, for
communication with both local and distant friends,
and to have fun, especially by finding information
related to their interests and hobbies. Teenagers were
more likely than adults to report using the Internet for
social purposes. For example, teens were more likely
to report using the Internet to communicate with
friends, meet new people, get personal help, and join
groups.
They were also more likely to use the Internet
to listen to music, play games, and download
software. In contrast, adults were more likely to use
the Internet for instrumental purposes such as getting
product information, purchasing products, or
supporting their employment. Teens also used the
Internet for instrumental purposes, such as doing
schoolwork and finding educational material.
(Subrahmanyam, Greenfield, Kraut, & Gross, 2001).
This particular study also remarks the mix
motives by the teenagers in using the computers: self-
entertaining, doing assignments, gathering
information about educational programs,
communicating with social circle, joining online
communities, as well as reading the news. The variety
of things that the teenagers could do with a computer
often causes them to ignore other activities that do not
require the use of computers.
Moreover, this study is figured out that the
teenagers who regularly use the computers at home
are receiving affects on their academic achievements,
as it explains on the following citations: One
program of note is that of Cole (Cole, 1996)
(Subrahmanyam, Greenfield, Kraut, & Gross, 2001),
who has been experimenting with the use of electronic
communication and games with children in both
classroom and after-school settings for nearly 15
years. The after-school programs are called ``The
Fifth Dimension,'' and include the typical uses of
home computers, such as educational software,
computer games, searching the Internet, and
multiuser dungeons (MUD) activities. Subject matter
includes social development, geography,
communications, reading, writing, math, social
studies, health, technology, language, and problem
solving (Blanton, Moorman, Hayes, & Warner,
1997). The electronic games and Internet activities
are based in a total social and cognitive environment
that includes a ladder of challenges. Program effects
include advances in reading and mathematics,
computer knowledge, following directions, grammar
and school achievement tests (Summary of cognitive
evaluation studies, n.d.). Although Cole's programs
are set in after-school settings, his results indicate
that well designed games and Internet activities for
home use can have a lasting impact on children's
academic performance.
The remaining result of the study highlights that
the teenagers who are using the computers or those
who are going online would eventually improve a
better quality of friendships and better relationships
with the family.
According to the annual report called 'we are
social' in 2017, the numbers of Internet users in
Indonesia reaching up to 132.7 million, with more
than 106 million users are active in social media
(https://digitalinasia.com/tag/we-are-social/). In
addition to this data, a collaborative survey conducted
by the Association of Internet Service Providers
Indonesia (APJII) together with the Center for Study
and Communication University of Indonesia
(Puskakom UI) in Indonesia pointed out that the
majority of Internet users in Indonesia is 49%
dominated by people in the age group between 18-25
years old. Hence, the largest age groups of the
Internet users in Indonesia are people who included
in the category of digital natives
. (Beritasatu.com,
2016: http://www.beritasatu.com/iptek/261297-
mayoritas-netizen-di-indonesia-berusia1825-
tahun.html)
The Internet becomes a preference channel for
communities to promote themselves or even to assault
other parties by purpose. Media and radicalism
constitute two central issues that attract public
attention because they share similar characteristic in
Radicalism on Teens as the Effect of Digital Media Usage: Based on Survey towards High School Students in Depok City, West Java,
Indonesia
465

several aspects. In reference to Sharma (Sharma,
2006), the intersection of the two issues lie in the
basic function of the mass media as a channel to
spread information, educating the public, and
entertaining the public through a certain packaging
that has been set up by radical groups for public
attention. Moreover, the common thread between
media and radicalism is their inseparability with the
aspect of commercial news. Another research about
digital media had also conducted by Wardhani,
Sabana and Adriati (Wardhani, Sabana, & Andriati,
2014), which examined the analysis of emotional
influence on different generations of Indonesia
women on magazine digitalization.
The collaborative survey by NGO Forum on
Indonesian Development (INFID) with the network
of pro-Gusdur (jaringan GUSDURian) in a study
themed “The Perception and Attitudes of Young
Generation towards Religious Radicalization and
Extremism”, were conducted with proportionate
stratified random sampling method to the 1.200
respondents spread out in six big cities: Bandung,
Makassar, Pontianak, Surabaya, Surakarta, and
Yogyakarta, in between August until October 2016.
Both organizations were observing the youth through
the most popular social media amongst the teenagers;
these social media are Twitter, Facebook, Instagram,
messenger applications (WhatsApp and Telegram),
and YouTube. Respondent sampling were taken from
the age group between 15-30 years old with gender
proportion of 50:50 of man and women (INFID,
2016)
Demant, Slootman, Buijs & Tillie (Demant,
Slootman, Buijs, & Tilie, 2008) describe
radicalization as a process of strengthening the
"delegitimization" of two things, namely the system
and the social situation. The occurring radicalization
that targeting individuals or groups is characterized
by a decline in confidence to the existing socio-
political order and as an attempt to withdraw oneself
from social relations of its own group. Due to the low
trust on the process change through the system and
not trusting the surrounding social environment, the
radicals tend to tolerate violence as an alternative way
out (Turmudi, 2005).
Within the Indonesian Political Constellation,
the issue of Islamic radicalism continues to escalate
in consequent to the significant numbers of
radicalism’s increasing mass of supporters. But
seemingly, these radicalism movements are gradually
splitting into groups that aiming at different
objectives and going through some altered movement
patterns. For example, some of the radical movement
groups fight only for the implementation of Islamic
Sharia’s yet ignoring the necessity of establishing an
"Islamic state"; other radical movement groups are
struggling for the establishment of Islamic state in
Indonesia. In addition to standing for the founding of
"Islamic Caliphate," the pattern of these Islamic
organizations are varied on the ideological moral
movements such as Majelis Mujahidin Indonesia and
Hizbut Tahrir Indonesia (HTI), or the one with
military styles takes like Laskar Jihad and FPI.
Peter G. Riddel divided the authoritarians power
of Islam in Indonesia post the era of Indonesian New
Order (Orde Baru) into four, which are; modernist,
traditionalist, neomodernist and Islamist. Broadly,
Riddel agreed towards the definitions of each
category as he ignored one of Woodward’s categories
on indigenized Islam. To him, each category has its
own characteristic in responding to crucial issues in
the early post-election period of the fall of the New
Order in 1999. These issues are regarded to the
Jakarta Charter, the Maluku crisis, establishment of
trade relation with Israel, the Indonesian federal state,
a place for minorities in the area of Indonesian state,
female president, and a lot of newly established
political parties after the New Order collapsed
(Riddel, 2002).
Mitchell V Charnley (Kusumaningrat &
Kusumaningrat, 2006) defines the news, as “¼
is
the
timely report of facts or opinion that hold interest and
importance, or both, for a considerable of people.”
The researcher understand that news is information
that will always been sought by the society because it
contains the things that considered to be either
interesting, or important, and maybe both. The news
also has the character of continuity, meaning, it is
always presented continuously at any time.
As for the structure of the news (Kusumaningrat
& Kusumaningrat, 2006) there is an inverted pyramid
pattern, in which: the news begins with a summary or
climax in the opening paragraph, then it flows into the
opening paragraphs, then continue to the subsequent
paragraphs which contain of details of the story
chronologically or it might as well be structured in
descending order. The following paragraphs that
included many details of the news are called news’
bodies and the opening sentences should always
contain a summary of the news, in which it termed as
news lead. When writing a story, a journalist will
summarize and sort out the climax point of the news
in the first paragraph, before it gets to be developed
further into details with a very important portion in
the news lead, follow with the news body with some
considerable importance portion. Thus, the entire
article eventually ends with a less significant
highlight of the news.
ICEST 2018 - 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and
Technology
466

As mentioned earlier, this study is facilitated by
the Reasoned Action Theory, which was first
introduced by Ajzen in 1980 (Azjen, 1988). This
theory is using the basic assumption about how
humans behave consciously and considering all
available information. In the Reasoned Action
Theory, Ajzen stated that a person's intention to
behave is determined by whether or not one is really
acting out such behavior. In addition to the intention
in performing certain behaviors, the action would
affected by two basic determinants, one is related to
attitude towards behavior, and the other is influenced
by subjective norms. The Reasoned Action Theory of
has also been used in many researches. One of them
is conducted by Sabar, Brillianto and Hapzi (Sabar,
Brillianto & Ali, 2017) with research theme about the
Intention to Watch television: Analysis of
advertising, social media and bandwagon effect
through brand equity.
In general, “the aim Of TRA to explain volitional
behavior. Its explanatory excludes with range of
behavior such as those spontaneous, impulsive,
habitual the result of craving, or simply scripted on
mindless” (Benter & Spekart, 1976)(Hale,
Householder, & Greene, 2002). This theory connects
beliefs, attitude, intention, and behavior. To know
what a person is going to do, the best way to predict
it is to know the person's intentions.
(1) Beliefs. According to Fishbein & Ajzen
(Azjen & Fishbein, Belief, Attitude, Intention and
Behavior : An Introduction to Theory and Research,
1975), Belief is “subjective probability of a relation
between the object of the belief and some other object,
value, concept or attribute”
(2) Attitude. “Attitude is a disposition to respond
favorably or unfavorably to an object person,
instution, or event” (Azjen, Attitudes, Personality,
and Behavior, 1988)
(3) Intention. “A behavioral intention,
therefore, refer to a person subjective probability that
he will perform some behavior” (Azjen & Fishbein,
Belief, Attitude, Intention and Behavior : An
Introduction to Theory and Research, 1975).
According to Ajzen (Azjen, Attitudes, Personality,
and Behavior, 1988) intention could be used to
predict the strength of a person to show one’s
behavior and how much one’s planning to deliver
such action or behavior.
(4) Subjective Norm. “...The person perception
of social pressure to perform or not perform the
behavior under consideration” (Azjen, Attitudes,
Personality, and Behavior, 1988). Azjen and
Fishbein (Azjen & Fishbein, Belief, Attitude,
Intention and Behavior : An Introduction to Theory
and Research, 1975) defined subjective norm as a
person's perception within the pressure to show or not
to show one’s behavior with certain considerations.
In the subjective norm, it also termed the second
determinant of the intention, which is often assumed
as a function of beliefs, but the kind of beliefs in
different forms. In this concern, the belief refers to a
person’s odd belief against or dissimilar with other
individual or group which causing to occur a
behavior. In an important note, individuals or groups
like this are also called referents. Referent is an
influential person or group for individuals, like
parents, spouses, close friends and other third
persons. The underlying belief is called normative
beliefs.
The TRA theory is used to measure the attitude of
youths in consuming media that affecting them with
the attitude of radicalism. The youths, in this context,
are mainly using media social to look for information
in a daily basis. In accordance to this matter, the
occurring hypotheses are the following:
Ho. There is no affect of the digital media use
towards the attitude of radicalism amongst high
school students
Ha. There are affects of the digital media use towards
the attitude of radicalism amongst high school
students
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
In order to trace the use of Islamic digital media that
might affected the attitude of radicalism towards high
school students, this research select the positivist
paradigm, with quantitative approach, and using the
explanative survey method.
The population in this study are highschool
students from 12 public schools in Depok city. The
study is using probability sampling technique, though
simple random sampling of 100 students who go to
public highschool in Depok city. This study uses
questionnaires and analysis techniques with Product
Moment Correlation and Linear Regression.
Reliability test result is 0.732 and the instrument’s
particles have a number above r table 0.4, which
means this instrument is reliable and valid to be used
for a research.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The research gathered more female respondents
(53%) than men respondents (47%), and exhibits a
Radicalism on Teens as the Effect of Digital Media Usage: Based on Survey towards High School Students in Depok City, West Java,
Indonesia
467
number of 56% highschool students are using social
media for 5 – 10 hours per day, and 71% are checking
the social media for more than 10 times a day.
The activities that these highschool student do on
social media; 96% are uploading their works to their
social media accounts or blogs or personal sites
(Creator); 85% checking their own personal account,
visiting someone else's account; 83% looking for
entertainment like music, movies, videos, games
(Joiners); 82% reading forums, blogs or friends’
status on social media (Spectator).
The necessities fulfilled by using social media are
vary; 95% are building relationships or making
friends, 92% are discussing and exchanging
information, and 82% are getting entertained. As for
the student’s necessities that fulfilled by the Internet;
98% are looking for data or information like text or
drawing as well as finding materials for class’
lecture, 95% are searching for homework or
assignment related materials, and lastly 82% are
keeping updated on the latest news. The result reflects
the category of social technographic ladder, created
by Forrester Research Inc. (Forrester,
2010:http://empowered.forrester.com/ladder2010/):
Creators make social content go. They write
blogs or upload video, music, or text
Critics respond to content from others. They
post reviews, comment on blogs, participate
in forums and edit wiki articles
Collectors organize content for themselves
or others using RSS feeds, tags, and voting
sites like Digg.com
Joiners connect in social networks like
Myspace and Facebook
Spectator, consumer social content
including blogs, user generated video,
podcasts, forum, or reviews
Inactive, neither create nor consumer social
content of any kind
According to these results, it is concluded that
high school students has a high rate of participation
in the virtual world, especially on the digital media
and social media.
As for the results on the attitude of radicalism
towards high school students in Depok city is
showing a high percentage by 47% and moderate by
36%. That is to say that the radicalism is not
significant towards the attitude of high school
students in Depok city, particullarly the students who
attend public highschool in Depok city and
participated this reaseach as the respondents.
Based on the regression analysis that examines the
affect of digital media usage towards the attitude of
radicalism, display the following results:
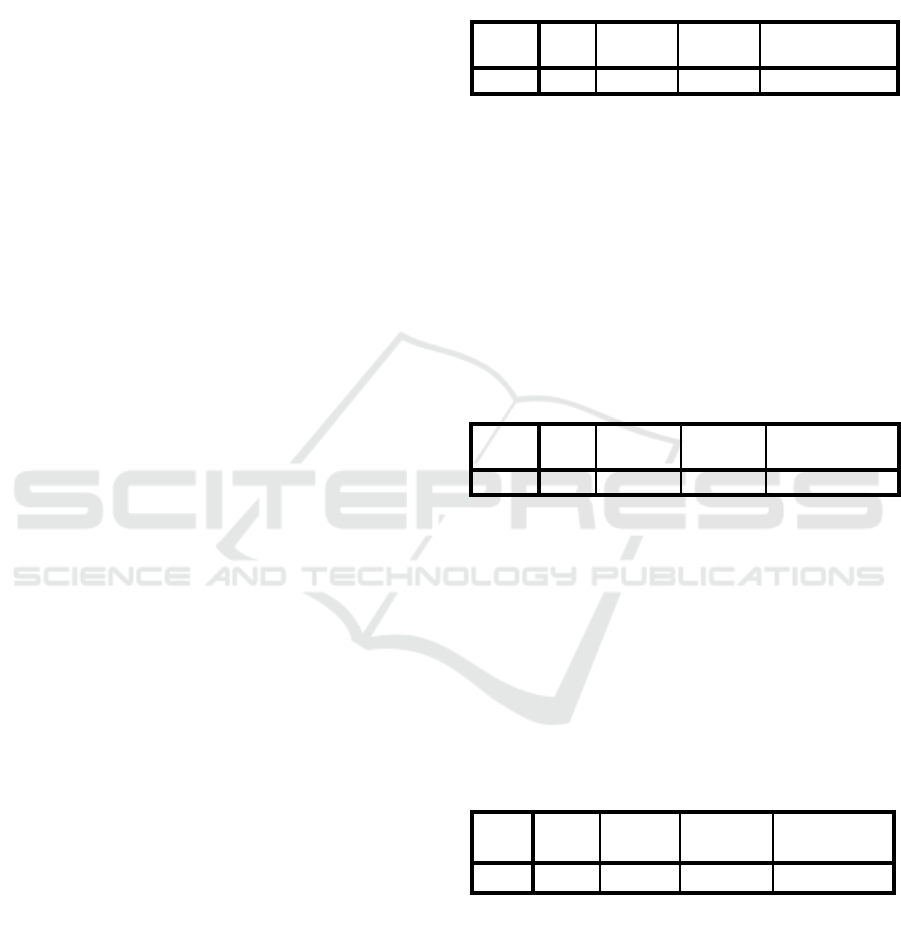
Table 1.1. Attitude of Radicalism
Model Summar
y
Model R R S
q
uare
Adjusted
R S
q
uare
Std. Error of the
Estimate
1
.171
a
.029 .019 .758
a. Predictors: (Constant), The Frequency of Social Media
Usage
Table 1.1. shows the affect of the frequency of
digital media usage amongst high school students is
contributing a rate of 2.9% towards the attitude of
radicalism. While the rest of 97.1% are being
influenced by other factors that are not examined by
this study. While the correlation between the
frequency of digital media usage towards the attitude
of radicalism is siginificantly weak at 0.171.
Table 1.2. Duration affects the Attitude of Radicalism
Model Summary
Model R R S
q
uare
Adjusted
R S
q
uare
Std. Error of the
Estimate
1 .135
a
.018 .008 .762
a. Predictors: (Constant), The Duration of Social Media
Usa
g
e
Table 1.2. shows the affect of the duration of
digital media usage only contributes a rate of 1.8%
towards the attitude of radicalism, while 8.2% are
being influenced by other factors that are not
examined by this study. The correlation between the
duration of digital media usage towards the attitude
of radicalism is siginificantly weak at 0.135.
Table 1.3. Duration and Frequency affects the Attitude of
Radicalism
Model Summary
Mode
l R
R
Square
Adjusted
R Square
Std. Error of
the Estimate
1
.193
a
.037 .017 .759
a. Predictors: (Constant), F The Frequency of Social
Media Usage, The Duration of Social Media Usage
Table 1.3. shows both the affects of the duration
and the requency of digital media usage
symoultenously contributes only a rate of 3.7%
towards the attitude of radicalism for high school
students in Depok city. The rest of 87.3% are being
influenced by other factors that are not examined by
this study. Thus, the correlation between the digital
ICEST 2018 - 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and
Technology
468

media usage towards the attitude of radicalism is
siginificantly weak at 0.193.
The result of this research is compatible with the
results of a survey conducted by the Institute of
Islamic Studies and Peace (LaKIP) in 2011, which
observing 59 private schools and 41 public schools in
Jakarta that shows the majority of students in Jakarta
tend to agree to use violence in solving religious
conflicts and moral issues. 48.9% said they are
willing to engage in violence act in the name of
religion and moral issues. Yet, it is by the utmost
surprised to find out that dozens of students are
supporting of the extreme act of suicide bombing.
(Cited from a writing by Prof., Dr., Bambang
Pranowo, a professor of Islamic sociology in the State
Islamic University (UIN) Jakarta; Koran Tempo, 26
April 2011).
The result of this reseach is also receiving
influences by digital media sites read by high school
students which appear to be dominated by the sites of
general news, including line today (20%), Detik.com
(15%), Kompas.com (10%), CNN Indonesia (5%),
and National Geographic. The rest of visited sites are
various Islamic media, like: VOA Islam, Dakwah
Media, Lampu Islam di Youtube, Al Manhaj, Yuvid
TV, Rumayso, UC News, Remaja Islami,
Muslim.or.id, Islam Post, Fiqih wanita, Hijabalia, OA
di Line, Islamic Theme Account on Instagram,
Muslimah berdakwah, Islamic broadcast on
Instagram, @indonesiabertauhidid @faktaagama
@hadistku @indonesiabertauhidofficial,
@tentangislam, Tanya ustaz.com tribun.com kabar
mekkah.com, eramuslim.com, pemuda hijrah, share
sunah, and Ammar TV.
The kind of web content that are being read by
high school students do not show significant
messages about radical doctrine or any message that
call for religious violence (radicalism).
Depok City is also affected by the existence of
internet safety campaign conducted by their peers
called the Sahabat Anak Internet Community (KISA):
In March 29, 2016, Sabahat Anak Internet
Community (KISA) is launching KISA youth, a group
of young volunteers that actively campaigning
Internet safety for students. This initiative is brought
up with the same background to foster the vision in
spreading the awareness to use the Internet safely
and positively by the teenagers. There are numerous
students of highs cool and vocational high school in
Depok city whom voluntarily joining the KISA
youth.” (komunita.id, 2016)
The activities showed by these high school
students in digital media are including; collecting
materials and data related to classroom’s lecture,
assignments, and homework. Other than that, there
are some additional activities spotted on the media
social such as uploading one’s work, checking self’s
account, looking around other’s people accounts, and
self-entertaining.
Ahmad Mulyana (Mulyana & Morissan, 2015)
also conducted a research on the Internet and social
media usage. The results shown that, ‘(1) The average
percentage news commentary assessed manners are
as much as 74 percent while the average percentage
of news comments judged to be polite is as much as
26.3 percent. (2) The amount of 74 per cent for
comments considered polite indicates that the new
media audience, especially visitors of portal news in
Indonesia has a relatively good level of politeness. (3)
Based on data obtained from the three coders in the
study, the average percentage of news comments
judged to be polite is as much as 26.3 percent. Thus,
the level of news portal visitor’s politeness in
Indonesia is categorized as a courtesy.
5 CONCLUSION AND
RECOMMENDATION
The research exhibits a high rate of radicalism shown
by highschool students in Depok city. The influence
of the frequency of digital media usage by these
highschool students only gives a little contribution
towards the attitude of radicalism. Whilst, the
corelation between the frequency of digital media
usage and the attitude of radicalism is significantly
weak.
Next, the research finds that the influence of the
duration of digital media usage only gives a little
contributeion the attitude of radicalism. While the
correlation between the duration of digital media
usage and the attitude of radicalism is also
significantly weak. The influences of both the
duration and the frequency symoulteously give little
contribution towards the attitude of radicalism to the
highschool students in Depok city. Moreover, the
correlation between the digital media usage with the
attitude of radicalism is significantly weak. In
conclusion, the radicalism is insignificantly attached
with the public highschool students in Depok city
who got involved as the respondents for this research.
Ultimately, the reseach recommends that the
digital media literacy awareness, especially the
internet safety literacy, should continously be
provided to highschool student in general and to the
teenagers within the range of age between 12 – 20
Radicalism on Teens as the Effect of Digital Media Usage: Based on Survey towards High School Students in Depok City, West Java,
Indonesia
469

years old, in order to halt the emergence of radical or
violence behaviour towards teenagers in the society.
REFERENCES
Abrar, A. N. (2003). Teknologi Komunikasi : Perspektif
Ilmu Komunikasi. Yogyakarta, DIY Yogyakarta,
Indonesia: LESFI.
Azjen, I. (1988). Attitudes, Personality, and Behavior.
England, Inggris: Open University Press & Chicago, IL
: Dorsey Press.
Azjen, I., & Fishbein, M. (1975). Belief, Attitude, Intention
and Behavior : An Introduction to Theory and
Research. NewYork, America: Addison-Wesley,
Reading MA.
Beritasatu. (2007). mayoritas netizen di Indonesia berusia
18-25 tahun. Retrieved Januari 20, 2016, from
www.beritasatu.com:
(http://www.beritasatu.com/iptek/261297-mayoritas-
netizen-di-indonesia-berusia-1825-tahun.html).
Beritasatu.com. (2016). mayoritas netizen di Indonesia
berusaia 18-25 tahun. Retrieved 1 15, 2017, from
www.beritasatu.com:
(http://www.beritasatu.com/iptek/261297-mayoritas-
netizen-di-indonesia-berusia 1825-tahun.html )
Demant, F., Slootman, M., Buijs, F., & Tilie, J. (2008).
Deradicalisation of Right-Wing Radicals and Islamic
Radicals. . (i. J. Rodrigues, Ed.) Amsterdam,
Nederland, Belanda: Achtste Rapportage : Anne Frank
Stichting.
Depag, B. (2016). Riset Penggunaan Referensi Guru-guru
PAI SMA di Jakarta. Balitbang Depag DKI Jakarta,
Balitbang DKI Jakarta. Jakarta: Balitbang DKI Jakarta.
Depag, B. (2016). Analisis Konten Kekerasan Agama di
Media 2008-2015. Balitbang Depag, Balitbang Depag
DKI Jakarta. Jakarta: Balitbang Depag DKI Jakarta.
Diskominfo. (2017, 8 18). diskominfo depok gencar
kampanye internet sehat di kalangan pelajar. Retrieved
10 23, 2017, from berimbang.com:
http://berimbang.com/diskominfo-depok-gencar-
kampanye-internet-sehat-di-kalangan-pelajar/ (akses
tanggal 23/10/2017)
Forrester, R. (2010). Kategori Sosial Technographic
Ladder@. Inc, Forrester Research, Inc, Forrester
Research. America: Inc, Forrester Research.
Hamad, I. (2004). Konstruksi Realitas Politik dalam Media
Massa : Sebuah Studi Critical Discourse Analysis
Terhadap Berita-Berita Politik. Jakarta, DKI Jakarta,
Indonesia: Granit.
Hale, J. L., Householder, B. J., & Greene, K. L. (2002).
Persuasion Handbook : Development in Theory and
Practice. NewYork, America: Sage Publications.
INFID. (2016). Survei Kaum Muda Menolak Kekerasan
Agama. Retrieved 2 2, 2017, from www.tempo.co:
https://nasional.tempo.co/read/827832/survei-kaum-
muda-menolak-kekerasan-atas-nama-agama
Komunita.id. (2016, 3 27). komunitas internet sehat anak
KISA resmikan KISA Muda kota Depok. Retrieved 10
23, 2017, from www.komunita.id:
https://komunita.id/2016/04/04/komunitas-internet-
sahabat-anak-kisa-resmikan-kisa-muda-kota-depok/
(akses tanggal 23/10/2017)
Kusumaningrat, H., & Kusumaningrat, P. (2006).
Jurnalistik : Teori dan Praktek. bandung, Jawa Barat,
Indonesia: PT. Remaja RosdaKarya.
Mondry. (2008). Pemahaman Teori dan Praktek
Jurnalistik.
Jakarta, DKI Jakarta, Indonesia: Ghalia
Indonesia.
Mulyana, A., & Morissan. (2015). Civility on Social Media
(The Tendency of Politeness Level of Internet Users on
Social Media. Jurnal Visi Komunikasi , 13 (1), 69-86.
Pranowo, B. (2011, April 26). Hasil Survey LaKIP. Koran
Tempo.
Republika.co.id. (2017, 3 3). Internet Sehat agar Depok
Lebih Bersahabat. Retrieved 10 23, 2017, from
republika.co.id:
http://www.republika.co.id/berita/koran/urbana/16/03/
04/o3iegk6-internet-sehat-agar-depok-lebih-bersahabat
(akses tanggal 23/10/2017)
Riddel, P. G. (2002). The Diverse Voices of Political Islam
in Post Suharto Indonesia. Journal Islam and Christian-
Muslim Relations , 13 (1), 65-84.
Sabar, M., Brillianto, A., & Ali, H. (2017). Intention to
Watch Television : Analysis of Advertising, Social
Media and Bandwagon Effect Through Brand equity.
International Journal of Development Research , 7 (1).
Sharma, S. K. (2006). Linkages of Democracy, Terorism
and Media. Journal of Political Science , II (1), 15.
Subrahmanyam, K., Greenfield, P., Kraut, R., & Gross, E.
(2001). Tke Impact of Computer Use on Children's and
adolescent Development. Applied Developmental
Psychology , 22, 7-30.
Tempo.co. (2011, April 26). Separuh Pelajar Setuju Aksi
Radikal Berlabel Agama. Tempo.co.
Turmudi, E. (2005). Islam dan Radikalieme di Indonesia.
Jakarta, DKI Jakarta, Indonesia: LIPI Press.
UNICEF. (2014). Children's Rights in the DIgital Age. 25
Convention on the rights of The Child, Australia
Applied Development Psychology. Australia: Yopung
and Well Australia.
Wardhani, A. K., Sabana, S., & Andriati, I. (2014).
Analysis of Emotional Influence on Different
Generation of Indonesian Women on Magazine
Digitalization. International Journal of Social Science
and Humanity , 4 (6), 439-442.
ICEST 2018 - 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and
Technology
470
