
Perceived Risk and the Technology Acceptance Model: A Proposed
Study for e-Commerce Adoption
Winarto
*
and Maludin Panjaitan
Faculty of Economics, The Methodist University of Indonesia
Keywords: Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, intentions to use, TAM, IS adoption
Abstract: Electronic-commerce (e-commerce) nowadays has become an important platform for conducting business.
While researchers and market practitioners are trying to fully understand online consumer attitude and
behavior, one of the current issues in the management of information technologies is the difficulty of
recognizing significant factors that affect consumers to adopt, accept and continue to use the information
technologies. A model that commonly used by the researchers to examine behavior in the information system
field is the technology acceptance model (TAM), which consists of 3 variables; perceived usefulness (PU),
perceived ease of use (PEOU) and intentions to use. In this study, we propose the extension of the TAM for
its application in the e-commerce field. The original variables of technology acceptance model will be
modified, by adding a moderator variable, perceived risk, which is expected to strengthen or weaken the
relationship between perceived ease of use, perceived usefulness and behavioral intention.
1 INTRODUCTION
Your paper will be part of the conference proceedings
therefore we ask that authors follow the guidelines
explained in this example and in the file
«FormatContentsForAuthors.pdf» also on the zip file,
in order to achieve the highest quality possible
(Smith, 1998).
Electronic-commerce (e-commerce) nowadays
has become an important platform for conducting
business. Research shows that the commercial trade
development through the Internet has astonishingly
transformed the retail industry since 1990 (Chen &
Chang, 2003) due to the usage of the Internet in the
contemporary era as a means of transaction for
consumers in the global market (Delafrooz, Paim, &
Khatibi, 2011). While researchers and market
practitioners are trying to fully understand online
consumer attitude and behavior, one of the current
issues in the management of information technologies
is the difficulty of recognizing significant factors that
affect consumers to adopt, accept and continue to use
the information technologies. A model that
commonly used by the researchers to examine
behavior in the information system field is the
technology acceptance model (TAM), which consists
of 3 variables; perceived usefulness (PU), perceived
ease of use (PEOU) and intentions to use.
The technology acceptance model is based on the
Theory of Reasoned Action (TRA) and theory of
planned behavior that seeks to explain behavior
intention to use information system (Grandón, Nasco,
& Mykytyn Jr, 2011). This model has been widely
used by information system researchers because of its
understandability and simplicity (King & He, 2006),
although the model also has drawbacks. For instance,
Lim and Tang (2012) noted that findings of TAM
relationships are not borne out in all studies, and there
remains a wide variation of predicted effects in
various studies with different types of users and
systems. As a result, there are some modified or
extended models that have been developed to fully
understand the information system adoption, for
example the unified theory of acceptance and use of
technology (UTAUT) model (Venkatesh, Morris,
Davis, & David, 2003), the integration of risk and
trust on TAM model (Pavlou, 2003).
Over decades, information researchers have
closely examined factors that affect information
system adoption. However, little is known about the
acceptance of online shopping and the factors which
influence this behavior in the developing countries;
and what factors that can strengthen or weaken the
information system adoption. This study attempts to
478
Winarto, . and Panjaitan, M.
Perceived Risk and the Technology Acceptance Model: A Proposed Study for e-Commerce Adoption.
DOI: 10.5220/0010045104780482
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and Technology (ICEST 2018), pages 478-482
ISBN: 978-989-758-496-1
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

fill in this gap by providing insights on how
consumers form their online shopping intentions, and
the intentions are transformed in to actual use of e-
commerce. In addition, this study also will explore
the moderation effect of perceived risk; a factor that
possible can hinder the e-commerce adoption. The
original variables of technology acceptance model
will be modified, by adding a moderator variable,
perceived risk, which is expected to strengthen or
weaken the relationship between perceived ease of
use, perceived usefulness and intention to use. Based
on the study background that has been explained, we
formulate 3 research questions that will be answered
in this research. The research questions are:
1. Does perceived ease of use significantly influence
intention to shop online in an e-commerce
platform, and is the relationship moderated by
perceived risk?
2. Does perceived usefulness significantly influence
intention to shop online in a e-commerce
platform, and is the relationship moderated by
perceived risk?
The proposed research has several purposes to
achieve:
1. To examine the relationship between perceived
ease of use and intention to shop online in an e-
commerce platform. Further, the research also
investigates the moderation effect of perceived
risk on the relationship between between
perceived ease of use and intention to shop online
in an e-commerce platform.
2. To examine the relationship between perceived
usefulness and intention to shop online in an e-
commerce platform. Moreover, the research also
investigates the moderation effect of perceived
risk on the relationship between between
perceived usefulness and intention to shop online
in an e-commerce platform.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 e-Commerce Adoption
As the innovation of technology, e-commerce
develops rapidly in recent years. Fast spreading of the
Internet has made the e-commerce an indispensable
and effective tool to realize the commercial
transactions. E-commerce is described like to make
production, presentation, selling, insurance,
distribution and payment transactions of the goods
and services in the electronic domain (Çelik &
Yılmaz, 2011). The simplest meaning of the e-
commerce is described as buying and selling of the
goods via the Internet. For instance, consumers could
purchase clothes from online shop, they could order
football tickets through the internet order systems,
and they could buy anything from the online stores no
matter where they are now. Whereas e-commerce has
become an important issue with the growth of the
Internet, there are insufficient empirical studies to
explore consumer behavior in the e-commerce
platform, particularly the customer behavior to
accept, adopt and continue using e-commerce
platform.
In this study, we mainly focus on the B2C e-
commerce platform, where companies provide the
goods or services in the Internet directly and offer
sufficient information and convenient interface to
attract consumers to buy online in order to eliminate
channel intermediaries (Wawan, 2013). In Indonesia,
e-commerce is growing rapidly. Bhinneka.com
became the pioneer for –commerce platform in
Indonesia. Several e-commerce platforms followed,
such as Berniaga.com, TokoBagus.com (now it is
olx.com), Tokopedia.com, Bukalapak.com,
Blibli.com (Widjaja & Tedjawidjaja, 2012).
Although there are more and more e-commerce
platform, and other online shopping or ticketing sites,
there are not so a lot empirical studies to examine the
e-commerce adoption. This study is trying to fill in
the gap, specifically to get more insights on the e-
commerce adoption.
2.2 The Technology Acceptance Model
The Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) is very
popular modeling approach in information system
research. Originally, the Technology Acceptance
Model (TAM) was developed by Davis (1989), which
purposely explains the computer usage behavior in
order to predict technology acceptance. The TAM
suggests that beliefs in a technology are related to
users’ attitudes and their decision to adapt the
technology. Davis (1989) describes how people adopt
and accept new technology applications. In TAM, it
is hypothised that the perceived usefulness and
perceived ease of use predict intention to use
information technology which, in its turn, is believed
to affect the adoption of technology. Further, TAM
shows that perceived usefulness and perceived ease
of use improves the users adoption of the technology.
The general model of technology acceptance is
depicted below:
Perceived Risk and the Technology Acceptance Model: A Proposed Study for e-Commerce Adoption
479

Figure 1: The Technology Acceptance Model
Figure 1 shows the 2 variables; perceived
usefulness and perceived ease of use; which influence
the intention to use information technology.
Perceived usefulness is defined as the degree to which
a person believes that using a particular system would
enhance his or her job performance and perceived
ease of use is defined as the degree to which a person
believes that using a particular system would be free
of effort (Davis, 1989). Due to its understandability
and simplicity (King & He, 2006), the model has been
widely used by information system researchers to
examine the user adoption toward information
system. In fact, the model has limitations due to wide
variations of predicted effects, and this drives the
information system researchers to modify the original
model.
2.3 Perceived Risk
While the Internet offers online consumers with
additional way for searching information of products
and services, it still has some issues to be solved. For
example, when consumers do shopping on the
Internet, they cannot feel, watch, and touch the reality
of the products or services before they buy what they
need. They may worry about the safety and the
security of transmitting credit card information via
the internet when the payment should be made. It is a
problem that consumers perceive lack of security,
safety and privacy on the internet in the adoption of
electronic commerce. Internet users hope that the e-
commerce providers on the Internet could assure the
transaction security. Thus perceived risk is an
important factor should be taken into account on the
e-commerce adoption.
Previous research has examined the relationship
between the perceived risk of a new shopping channel
and the choice of purchasing using that channel
(Bhatnagar, Misra, & Rao, 2000). By definition, there
are 2 major components; the probability of a loss and
the subjective feeling of unfavorable consequences.
2.4 Hypotheses Development
The purpose of TAM is to explain and predict the
acceptance of information technology based on two
specific behavioral beliefs: perceived ease of use
(PEOU) and perceived usefulness (PU). Since TAM
has been applied to the transactions of electronic
commerce, it may help us to understand the context
of adopting electronic commerce.
Perceived usefulness is the individual’s
assessment of the utility offered by using new
information technology in a specific context.
Perceived usefulness in the TAM model reflects task-
related productivity, performance, and effectiveness.
Perceived ease of use refers to the degree to which the
user expects the target system to be free from effort
(Davis, 1989). The concepts of perceived usefulness
and perceived ease of use are individual subjective
judgments about the usefulness and ease toward
specific system.
The TAM posits users think that it is beneficial to
use the technology in completing his/her work; and
when users perceive the ease of using information
systems, there is likely that users will intent to use the
information system. However, due to the nature of e-
commerce platform, risk is one of the aspects that
may hinder the information system adoption.
Previous research use perceived risk as the factor that
influence user intention to use information system; on
this research, we use perceived risk as a moderator
variable which will strengthen or weaken the
relationship between perceived ease of use, perceived
usefulness and intention to use. Thus, we arrive at the
following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 1: Perceived ease of use is related to
customer intention to shop online in a e-commerce
platform. The relationship is moderated by perceived
risk; if perceived risk is high the relationship between
perceived ease of use and intention to shop online in
a e-commerce platform will be weaken.
Hypothesis 2: Perceived usefulness is related to
customer intention to shop online in a e-commerce
platform. The relationship is moderated by perceived
risk; if perceived risk is high the relationship between
perceived ease of use and intention to shop online in
a e-commerce platform will be weaken
Perceived
Usefulness
Perceived Ease
of Use
Intention to
use
ICEST 2018 - 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and
Technology
480
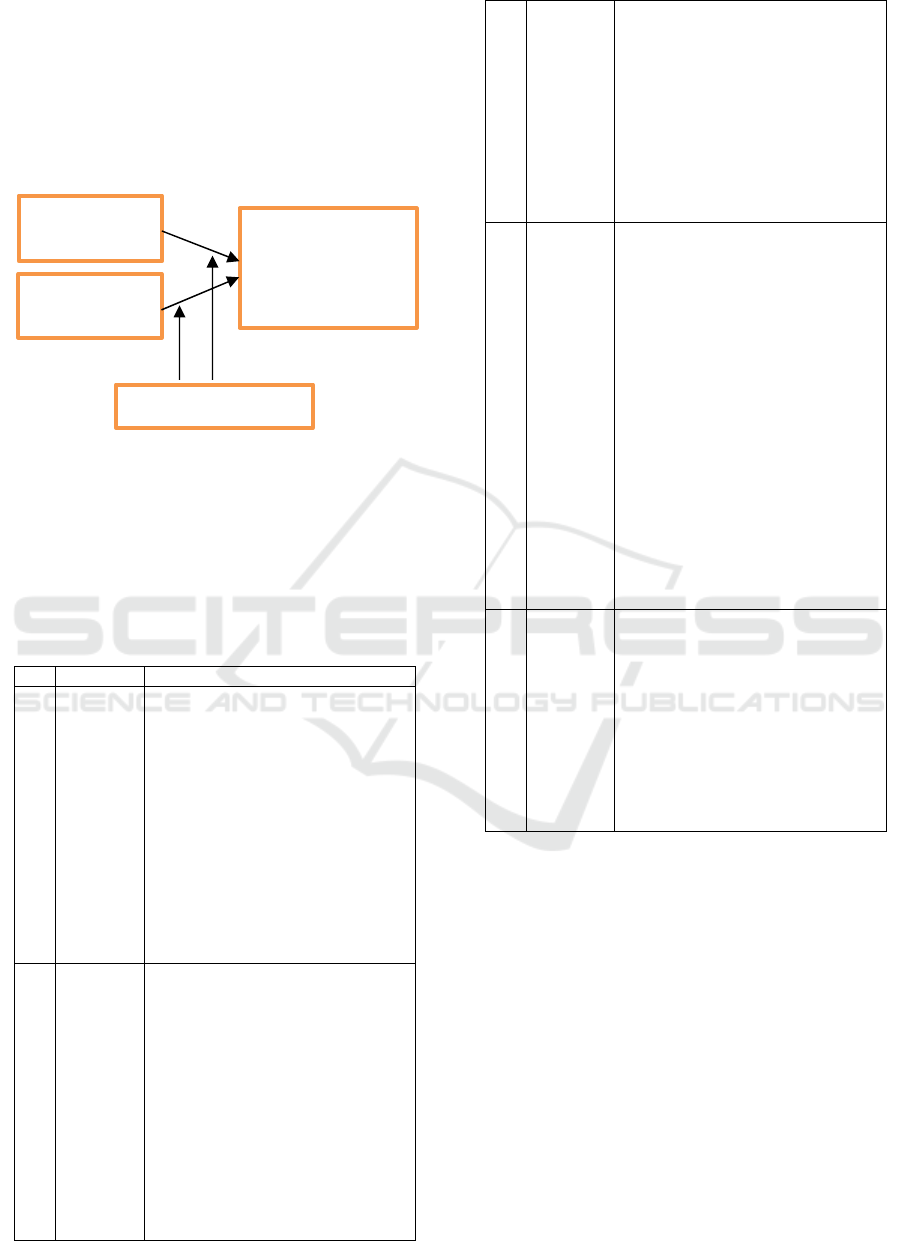
3 RESEARCH MODEL
Figure 2 depicts the research model which
summarizes the research questions. The first research
question consists of three independent variables and
one dependent variable. Finally, the gender difference
in satisfaction is examined.
Figure 2 the Technology Acceptance Model
4 MEASUREMENT
Table 1 shows the research indicators that will be
used in the research questionnaire.
Table 1: Research Indicator
No Variables Empirical indicators
1 Perceived
ease of
use
1. I find most online shopping sites
easy to use.
2. I find it easy learning to use most
online shopping sites.
3. I find it easy to use most online
shopping sites to find what I want
4. I find it easy to become skilful at
using most online shopping sites
5. I find it easier to compare
products when shopping at online
retailers.
6. I feel that most online shopping
sites are flexible to interact with.
7. I am able to browse online
shopping sites with ease.
2 Perceived
usefulness
1. I am able to accomplish my
shopping goals more quickly
when I shop online.
2. I am able to improve my
shopping performance when I
shop online (e.g. save time or
money).
3. I am able to increase my
shopping productivity when I
shop online (e.g. make purchase
decisions or find product
information within the shortest
time frame).
4. I am able to increase my
shopping effectiveness when I
shop online (e.g. get the best deal
or find the most information
about a product).
5. I find the website of online
retailers useful in aiding my
purchase decisions. Shopping
from online retailers improves
my purchase decisions.
6. Shopping from online retailers
makes it easier for me to satisfy
my needs.
3 Intention
to shop
online in
a e-
commerce
platform
1. It is likely that I will continue to
purchase products from online
retailers in the future.
2. I intend to continue purchase
products from the Internet in the
future.
3. I would likely visit an online
shopping site to shop for my
needs.
4. I plan to do more of my shopping
via online shopping sites.
5. When I need to buy a particular
product, I would search for an
online retailer which has the
product.
6. There is a substantial chance that
I would purchase the same
product from an online retailer.
7. There is a substantial chance that
I would purchase different
products from an online retaile
r
4 Perceived
risks
1. How would you characterize the
decision to transact with this Web
retailer? (Significant
risk/insignificant risk)
2. How would you characterize the
decision to transact with this Web
retailer? (Very negative
situation/Very positive situation)
3. How would you characterize the
decision to buy a product from
this Web retailer? (High potential
For loss/High potential for gain)
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This is a proposed research project that will be funded
by Lembaga Penelitian dan Pengabdian Masyarakat
Universitas Methodist Indonesia. We would
appreciate any comments or suggestions that will help
us to enhance and improve the research.
REFERENCES
Bhatnagar, A., Misra, S., & Rao, H. R. (2000). On risk,
convenience, and Internet shopping behavior.
Association for Computing Machinery.
Communications of the ACM, 43(11), 98-105.
Perceived
Ease of Use
Intention to shop
online in a
e-commerce
platform
Perceived
Usefulness
Perceived Risk
Perceived Risk and the Technology Acceptance Model: A Proposed Study for e-Commerce Adoption
481

Çelik, H. E., & Yılmaz, V. (2011). Extending the
Technology Acceptance Model for Adoption of E-
Shopping by Consumers in Turkey. Journal of
Electronic Commerce Research, 12(2), 152-164.
Chen, S.-J., & Chang, T.-Z. (2003). A descriptive model of
online shopping process: some empirical results.
International Journal of Service Industry Management,
14(5), 556-569.
Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived Usefulness, Perceived Ease
of Use, and User Acceptance of Information
Technology. MIS Quarterly, 13(3), 319-340.
Delafrooz, N., Paim, L. H., & Khatibi, A. (2011).
Understanding consumer’s internet purchase intention
in Malaysia. African Journal of Business Management,
5(3), 2837-2846.
Featherman, M. S., & Pavlou, P. A. (2003). Predicting e-
services adoption: a perceived risk facets perspective.
International Journal of Human-Computer Studies,
59(4), 451–474.
Grandón, E. E., Nasco, S. A., & Mykytyn Jr, P. P. (2011).
Comparing theories to explain e-commerce adoption.
Journal of Business Research, 64, 292–298.
King, W. R., & He, J. (2006). A meta-analysis of the
technology acceptance model. Information &
Management, 43(6), 740–755.
Li, Y.-H., & Huang, J.-W. (2009). Applying theory of
perceived risk and Technology Acceptance Model in
the online shopping channel. World Academy of
Science, Engineering and Technology, 29, 913-919.
Lim, W. M., & Ting, D. H. (2012). E-shopping: an Analysis
of the Technology Acceptance Model. Modern Applied
Science, 6(4), 49-62.
Moon, J.-W., & Kim, Y.-G. (2001). Extending the TAM for
a World-Wide-Web contex. Information &
Management, 38, 217-230.
Pavlou, P. A. (2003). Consumer acceptance of electronic
commerce: Integrating rrust and risk with the
Technology Acceptance Model. International Journal
of Electronic Commerce, 7(3), 69-103.
Venkatesh, V., Morris, M. G., Davis, G. B., & David, F. D.
(2003). User acceptance of information technology:
Toward a unified view. MIS Quarterly, 27(3), 425-478.
Wawan, M. (2013). Technology acceptance of e-commerce
in Indonesia. International Journal of Engineering
Innovation and Management, 3, 9-18.
Widjaja, D. N., & Tedjawidjaja, A. (2012). A Preliminary
Study of Merchants’ Intention to Adopt Online
Payment Gateway in Indonesia. International Journal
of Future Computer and Communication, 1(2), 155-
159.
ICEST 2018 - 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and
Technology
482
